232
0
The prevalence of BPH among the male population over 40 years of age is quite high. Statistics say that by the age of 80, about 80% of men suffer from this disease. The disease begins with the formation of nodules in the periurethral zone of the prostate, after which the glandular tissue gradually grows, causing discomfort to the patient.
Today, the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia is carried out using different methods, which will be discussed further.
Prostatic hyperplasia: what is it? general information
The prostate is an unpaired tubular-alveolar gland in the male body.
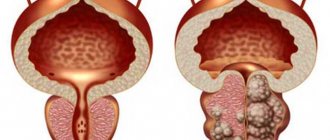
It is located around the initial part of the urethra and performs a number of important functions. Firstly, it is in the tissues of the prostate that a special secretion is produced, which ensures the liquefaction of sperm. Secondly, the organ blocks the flow of urine from the bladder during an erection, working like a valve. Many men face such a problem as prostate hyperplasia? What it is? The disease, which is also known as “adenoma,” is accompanied by pathological growth of prostate tissue, as a result of which the organ itself increases in size and changes structure.
Statistics show that this is a very common disease. The risk group includes men over 40 years of age. The older a person is, the higher the likelihood of developing hyperplasia. For example, approximately 70% of men over 70-80 years of age suffer from some form of the disease. Despite the fact that such processes in the prostate gland are benign, changes in the size and structure of the prostate bring a lot of discomfort and inconvenience to the patient’s life.
It is worth noting that the initial stages are almost asymptomatic. If any violations appear, they quickly go away on their own - the man simply does not pay attention to them. This is precisely where the danger lies, because patients seek help at a later stage, when therapy is fraught with difficulties.
As already mentioned, benign prostatic hyperplasia is accompanied by an increase in the size of the organ, as a result of which it compresses the urethra, reducing its lumen and disrupting the normal outflow of urine.
Patients complain of an increased urge to urinate - they often even wake up several times a night. In this case, the outflow of fluid is impaired, so the process of emptying the bladder itself is fraught with difficulties. A man needs to tense his abdominal muscles in order to complete urination. The urine stream becomes weak.
As the disease progresses, other symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia appear. What kind of violations are these? The process of urination is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, which, as the disease progresses, turn into severe, sharp pain. Sometimes, on the contrary, urinary incontinence develops and imperative urges arise (a man cannot restrain the urge to urinate).
Of course, such disorders also affect the functioning of the reproductive system. Many patients complain of problems with erection. Sometimes sexual intercourse, or more precisely, the process of ejaculation, is accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
The constant need to wake up at night and interrupt sleep several times affects the patient’s emotional state. Men tend to become more nervous and irritable.
Systemic symptoms include loss of appetite, weakness, drowsiness, and sudden loss of body weight.
In any case, if such violations occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. The sooner treatment for prostatic hyperplasia is started, the higher the chances of a quick and complete recovery. Under no circumstances should the signs be ignored.
Second stage
At the second stage of prostate hyperplasia, functional disruptions in the functioning of the bladder begin. It loses the ability to perform high-quality emptying; residual urine begins to accumulate in it, the volume of which reaches a significant amount as the disease progresses.
In addition, detrusor dystrophy develops - it stops actively expelling urine during contraction, as a result of which the size of the bladder increases significantly. Emptying the organ begins to be accompanied by straining, tension in the abdominal muscles and diaphragm during urination, which, in turn, leads to an increase in pressure inside the organ.
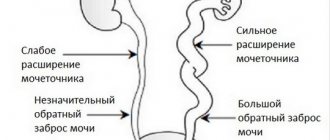
Urination is performed in waves, with breaks and periods of rest, the duration of which can be up to several minutes. An increase in pressure in the bladder, compression of the ureteric orifices by growing adenomatous nodes and bundles of stretched muscles, coupled with the loss of elastic properties of the muscles, lead to problems with the transportation of urine through the upper urinary tract, expansion of the latter and a decrease in kidney function. The decrease in renal function, which increases as the disease progresses, is accompanied by dryness, thirst, polyuria, and deterioration of the kidneys' ability to excrete nitrogen.
In the third stage, the man experiences a constant urge to urinate and pain in the lower abdomen
Prostatic hyperplasia: what is it? general information
Hyperplasia in men can take various forms. There are many classification schemes. For example, diffuse hyperplasia of the prostate gland is possible, which is accompanied by a uniform proliferation of organ tissue. Sometimes, against the background of the disease, the formation of nodes occurs - we are talking about the nodular form of adenoma. In most cases, cases of mixed, diffuse nodular hyperplasia are recorded.
The pathological process can involve the stroma of the organ - in such a situation, doctors talk about stromal prostatic hyperplasia. In addition, a glandular form of pathology is isolated.
Doctors also pay attention to the location of the tumor and the direction of its growth.
- Intravesical adenoma is characterized by tumor growth towards the bottom of the bladder. This form is considered the most dangerous, because an enlarged prostate leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra and disruption of the outflow of urine. If left untreated, the pathology can lead to the development of renal failure.
- Prevesical hyperplasia is accompanied by growth of the lateral lobes of the prostate gland. In this case, the organ does not put pressure on the bladder. This is a relatively mild form of the disease, which responds well to treatment and rarely leads to the development of any serious complications.
- If we are talking about subvesical hyperplasia, this means that the prostate tissue grows towards the rectum. Such adenoma does not directly affect the bladder, but affects the urinary tract and kidneys.
During diagnosis, it is very important to determine the form and type of benign prostatic hyperplasia (you already know what it is).
Classification of prostate adenoma
Based on their structure and location, there are 3 types of adenoma:
Type 1 – the tumor penetrates the bladder through the urethra, deforming the internal sphincter and interfering with its functions.
Type 2 - the tumor develops towards the rectum, the process of urination is disrupted - due to the loss of contractility of the prostatic part of the urethra, the bladder is not completely released.
Type 3 - there is a uniform compaction of the prostate under the pressure of the adenoma, no retention of urine in the bladder, no failure in the process of urination is observed. This type of adenoma is one of the most favorable.
Do you want to know the cost of cancer treatment abroad?
* Having received data about the patient’s disease, the clinic representative will be able to calculate the exact price for treatment.
Stages of development of hyperplasia. Features of the clinical picture
We have already reviewed information about why prostatic hyperplasia develops, what it is and what symptoms it is accompanied by. But it is worth understanding that the features of the clinical picture directly depend on the stage of development of the disease. In modern medicine, there are three stages, each of which is accompanied by a certain set of symptoms.
- The first stage, as a rule, proceeds hidden. But sometimes patients report problems with urination. The urge becomes more frequent, the intensity of urine outflow decreases. Often the urges become uncontrollable. From time to time the symptoms worsen and then disappear. Patients rarely seek help at this stage. The disease continues to progress.
- In the second stage the situation worsens. The outflow of urine is seriously impaired, fluid begins to accumulate, which is accompanied by corresponding symptoms. For example, men often complain of a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Urination becomes a problem—patients need to strain to pass urine. Stagnation of urine leads to overstretching of the walls of the bladder - their gradual atrophy begins. It is at this stage that, as a rule, the first kidney problems appear. The patients themselves become irritable, suffer from constant fatigue, increased thirst and dry mouth.
- The signs of the third stage are simply impossible to ignore. The urge to urinate becomes very frequent, and the process of urination itself is accompanied by severe pain. At this stage, as a rule, complications develop, in particular, infectious diseases of the excretory system and renal failure. There is constant weakness, irritability, dry mouth, headaches, nausea, loss of appetite. It is simply impossible to lead a normal life in such a state.
Treatment of prostate hyperplasia directly depends on the stage of development of the disease. The sooner therapy is started, the greater the chances of a complete recovery.
Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia in the initial stages can be carried out with the help of properly selected medications. Of course, the treatment regimen is drawn up individually, because everything depends on the patient’s age, the stage of development of the adenoma, the causes of pathological tissue proliferation, etc.
In most cases, the treatment regimen includes two types of drugs: 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Avodart, Finasteride) and alpha-blockers (Doxazosin, Alfuzosin, Terazosin). In the presence of an inflammatory process, anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Therapy can be supplemented with vitamin complexes.
It is worth understanding that drug treatment will not help get rid of hyperplasia. Nevertheless, properly selected drugs stop further tissue growth and help bring further pathological changes under control.
Depending on the stage of the disease, an individual treatment plan is developed for the patient. Diagnostics must be as accurate as possible; this affects the effectiveness of the process.
Stage II hyperplasia is characterized by a noticeable narrowing of the ureter
Table. Main stages of the disease.
| Disease stage | Clinical signs and pathologies |
| Compensated (light) | The mildest deviation in the condition of the prostate gland, pathological processes at the initial stage, in some cases it is possible to restore physiological standing through the use of medications. But this is rare; most often it is possible to slow down the process of pathological changes in tissues. The compensated stage is manifested by minor problems with urination, the rate of emptying the bladder decreases due to weak fluid structure, and urges appear during sleep. Most doctors consider one-time urination at night in men over sixty years of age to be normal. Situations when such desires appear two or more times should be alarming. The sooner a correct diagnosis is made, the greater the hope for successful treatment. This stage can cover a period of one to three years, later a second, more complex stage begins. |
| Subcompensated (average) | Pathological changes increase, pain symptoms appear, and the functions of the bladder change. The stream of liquid is very weak, immediately after urination there is an unpleasant feeling that the bladder still has liquid. Because of this, several urges occur in a row, but with each, only a few drops of urine are released. Urine may change color, darken, and indicate the presence of blood. |
| Decompensated (severe) | The prostate gland enlarges to such an extent that the process of urination is almost completely disrupted, the bladder is constantly full. The urethra is compressed, and there are clear signs of blood in the fluid. Against this background, inflammatory processes develop, over time they affect the kidneys, which can cause a very dangerous disease - renal failure. With such signs, immediate hospitalization of the patient is required. |
Epidemiology
Prostatic hyperplasia of the 1st degree does not bother the patient. But with the growth and development of the tumor, certain signs of pathology begin to appear. The presence of at least one of them should alert a man and become a reason to consult a doctor.
Patients experience the following symptoms:
- Weakness of the stream when emptying the bladder. Sometimes urine even drips.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Flow intermittency.
- Tension of the pelvic muscles during the urination process.
- Inability to completely empty the bladder.
- Congestion in the bladder, which often causes the development of infectious pathologies, the occurrence of stones in the urinary system, and impaired renal function.
If the indicated signs of nodular or other types of neoplasm in adults are present, it means that the tumor has large parameters or negatively affects the functioning of the urinary organs. Therefore, you should immediately be examined to determine the factor that caused such violations.
Treatment
There are clinical standards for the treatment of prostate adenoma, but in fact, doctors approach each patient individually. A set of therapeutic measures is developed taking into account the stage of the disease, the patient’s age, his consent to surgery, concomitant diseases, and the degree of urodynamic disturbance. Conservative treatment gives good results at the compensation stage. The second stage is the indications for surgical intervention. In case of decompensation, treatment is aimed at stabilizing renal function and relieving azotemic intoxication. After eliminating the consequences of renal failure, the issue of surgery is decided.
Drug treatment
Conservative treatment with medications is carried out to relieve symptoms and prevent tumor progression. For continuous use the following are prescribed:
- alpha-blockers that relieve spasms of the smooth muscles of the bladder neck and prostate muscle tissue (Retard, Setegis, Dalfaz, Tamsulosin);
- inhibitors of the enzyme 5-alphareductase, to prevent increased synthesis of the active form of testosterone and slow down the growth of the prostate gland (Alfinal, Finast, Dutasteride, Finasteride).
The most effective is considered to be the combined use of these drugs for several years. However, they have unpleasant side effects. The most significant for men are decreased libido, erectile dysfunction and decreased ejaculate.
Dietary supplements
The use of dietary supplements has not shown a clinically significant effect in the treatment of prostate adenoma, although a subjective assessment of the condition shows an improvement. Therefore, official medicine does not include herbal preparations in therapy. But nothing prevents the patient, in the absence of contraindications, from using dietary supplements containing lipidosterol extract of the Serenoa repens palm tree (Permixon, Prostagut, Prostamol Uno).
For adenoma, you can take dietary supplements containing lipidosterol extract of the palm Serenoa repens
They have virtually no side effects, are well tolerated and provide a positive effect at the initial stage of the disease. Some urologists prescribe them for the prevention of prostate adenoma.
Surgery
Surgery is the “gold standard” for treatment of the second stage of BPH. Several techniques are used. Adenectomy is an open operation to remove the affected prostate. Endoscopic methods:
- transurethral resection (used most often) involves excision of prostate tissue;
- transurethral electrovaporization - evaporation of prostate tissue using electric current;
- transurethral incision - dissection of the adenoma to free the urethra and increase its lumen.
Minimally invasive treatment methods are also used. This is embolization of the prostate arteries to deprive the tumor of nutrition, evaporation of gland tissue with a laser (laser vaporization), ultrasonic coagulation.
Video: a new method of treating prostate adenoma
Features of nutrition for prostate adenoma
Diet for prostate adenoma has therapeutic and preventive value. During treatment you will have to give up some foods and follow the following rules:
- eat small meals (5–6 meals per day);
- It is advisable to eat at the same time;
- include foods that have a laxative effect in your diet;
- give up sweet, spicy, fried and salty foods;
- boil or steam food.
Diet for prostate adenoma has medicinal value
Table: what you can and cannot eat with prostate adenoma
| Authorized products | Prohibited Products |
| Yogurt, kefir, yogurt | Fortified wines, beer, vodka |
| Green loose tea | Any spices (except dry herbs) |
| Poultry meat | Pork, beef, lamb |
| Salmon, herring, flounder | Canned food |
| Seafood | Marinades |
| Beef or pork liver | Any fish roe |
| Pumpkin | Strong tea and coffee |
| Tomatoes | Legumes |
| Porridge | Chocolate |
| Pistachios | Baking |
| Beet | Rich broths |
| Plums | Radish |
| Green pea | Radish |
| Zucchini | Sorrel |
| cucumbers | Animal fats |
| Dried fruits | Soda |
| Citrus | Factory-produced juices |
| Strawberry | Mushroom broth |
| Carrot | Garlic |
| Cauliflower | Cabbage |
| Dairy and vegetable soups | |
| Rye bread | |
| Greenery | |
| Low-fat cheeses | |
| Rose hip decoction | |
| A small amount of dry wine and cognac |
Allowed products contain large amounts of zinc and selenium, which slow down tumor growth and help reduce it.
Physiotherapeutic treatments
Physiotherapy has a pronounced therapeutic effect and is welcomed by most urologists. Expected Result:
- improving blood supply to the prostate gland;
- increased permeability of prostate cells and their greater accessibility to drugs;
- improvement of lymph outflow and removal of toxins and products of cellular metabolism from gland tissue;
- reduction of inflammation and pain;
- restoration of prostate function;
- stimulation of immunity.
Types of procedures are selected individually. Use:
- electrophoresis with drugs (an intracavitary technique is used with the introduction of electrodes through the urethra or rectum);
- ultrasound (percutaneous or intracavitary exposure through the rectum);
- magnetotherapy (Almag can be used);
- pulse therapy with the Akutest device (exclusively at the initial and second stages of the disease);
- ultraviolet treatment.
Another effective physiotherapy procedure is vibroacoustic stimulation. Microvibration of sound waves improves the outflow of lymph and the evacuation of dead cells and their decay products.
Microvibration improves blood circulation and lymph outflow
Prostate massage is prescribed at the initial stage and with slight tissue growth. It should only be done by a doctor. A gentle, non-invasive technique is used to stimulate the bladder muscles.
Massage for advanced prostate adenoma is contraindicated, as it stimulates tumor growth. It cannot be done at any stage if there are hemorrhoids or ulcerative lesions in the rectum.
Balneological methods are used as additional treatment. Radon baths have an immunostimulating, analgesic, and vasodilating effect. Zalmanov's turpentine bath has been used to treat adenoma for more than 100 years. It is called capillary therapy. During the intake process, blood circulation in the smallest blood vessels improves, metabolism increases, toxins are eliminated, and microcirculation in the pelvic organs improves. Hydrogen sulfide baths also work.
It is important that hydrotherapy is prescribed by the attending physician. With adenoma, as with any tumors, exposure to heat is contraindicated. This may cause an increase in hyperplasia.
Hirudotherapy
Hirudotherapy is a symptomatic treatment. It relieves congestion in the prostate gland and restores its function as a reproductive organ. At an early stage, leeches will help completely get rid of the pathology. What happens during treatment:
- mechanical irritation involves damage to the skin, which stimulates cell renewal processes;
- biological stimulation occurs under the influence of enzymes contained in the saliva of leeches - substances thin the blood and relieve pain;
- impact on biologically active points - leeches are placed in the reflex zones corresponding to the prostate gland.
Like any type of treatment, hirudotherapy is prescribed only by the attending physician.
Su-jok and yoga in the treatment of prostate adenoma
The most popular Eastern method of treating adenoma is yoga. The effectiveness of the special complex is achieved by correct breathing and fixation of positions. They are aimed at improving blood flow in the pelvic area. The set of exercises has no age restrictions and contraindications for people suffering from heart and vascular diseases.
The effectiveness of yoga lies in fixing positions and proper breathing.
Sujok therapy is based on a reflex effect on certain points - projections of the prostate gland. They are found on the feet and hands. Due to the effect on them, blood flow improves, hormonal balance is normalized and gland cell renewal is stimulated. The prostate point is located in the crease between the middle and ring fingers. You need to massage it three times a day for 10 minutes.
About the benefits of exercise for BPH and after removal of an adenoma
Lack of physical activity is one of the causes of prostate pathology. Therapeutic exercises are the prevention of the disease and its further development. Not all sports are useful for prostate adenoma; there are a number of restrictions:
- Strength exercises for the pelvic muscles are contraindicated;
- recommended sports activities - swimming, outdoor games, horse riding and cycling (during periods of remission);
- any physical exercise should be stopped if pain or discomfort occurs.
The set of exercises should include static, dynamic and general loads for the whole body. Static exercises stimulate blood circulation and nutrition of prostate cells, improve muscle tone of the bladder. Dynamic load includes running, swimming, and any physical activity. But it should be moderate. This is especially true for horse riding and cycling. The signal to stop exercising is lower back pain and blood in the urine. The complex for the whole body includes exercises for all muscle groups.
For prostate adenoma, exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles are necessary
Strelnikova’s breathing exercises showed good results in the treatment of adenoma. It is based on special ways of inhaling and exhaling. A few months of regular exercise - and the body becomes healthier, overall well-being improves, urination and metabolic processes in the pelvic organs are normalized. Dr. Kegel's exercises train the pubic muscle group. A man learns to control them. This is not physical exercise, but muscle tension and relaxation. The only exception is walking on your buttocks.
Why does pathology develop?
We have already sorted out information about which categories of men are most susceptible to prostate hyperplasia, what it is and what forms the pathology can take. It is worth noting that, unfortunately, it is not always possible to accurately determine the reasons for the development of pathology. However, doctors identify several main risk factors.
- The main reason for the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia is hormonal imbalance. A huge role in this situation is played by a change in the balance between the levels of male and female sex hormones. In most cases, pathological processes develop against the background of a decrease in the amount of testosterone. But there are known cases of the development of hyperplasia against the background of an increase in the level of estrogen in a man’s body.
- Risk factors include age. This is understandable, because as the male body ages, the amount of testosterone produced decreases.
- Hyperplasia often develops against the background of inflammatory processes.
- Since the work of the prostate is to one degree or another connected with the functioning of the organs of the excretory system, any infectious or inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract can lead to pathological changes in prostate tissue.
- Congestive processes in the pelvis are potentially dangerous. That is why men who lead a sedentary lifestyle are much more likely to become victims of this disease.
- There is also some genetic predisposition.
There are also so-called triggers that, if the prerequisites are present, can trigger the development of prostate hyperplasia. What are these factors? The onset of pathological changes is often associated with severe stress or nervous strain. Poor nutrition, as well as the presence of bad habits in a man, are also of certain importance. Irregular sex life, prolonged abstinence, and frequent, random changes of sexual partners are potentially dangerous.
Diagnostics
The first visit to the doctor involves filling out a questionnaire and a physical examination of the prostate gland. Before taking it, you must empty your rectum, but your bladder must be full, as you will need to have your urine analyzed. For accurate diagnosis, including differential diagnosis, the doctor collects anamnesis. BPH is differentiated from the following diseases:
- prostate carcinoma;
- bladder and urethral infections;
- stenosis (narrowing of the lumen) of the urethra as a result of injury, sexually transmitted diseases or prolonged use of a catheter;
- elevated sugar levels, causing a frequent urge to urinate;
- prostate infections;
- dysfunction of the bladder associated with the absence of nerve impulses (in diseases and injuries of the spine, stroke, multiple sclerosis).
To do this, a symptomatic scale is filled out, giving a complete clinical picture. Based on its data, a decision is made on conservative or surgical treatment. The assessment is made using a point system. The maximum number of points is 35. A score of up to 8 points allows you to leave the disease without medical intervention. The patient is given recommendations on nutrition and prevention of further development of adenoma. If the patient scores from 8 to 19 points, therapeutic treatment is carried out. A score of 20 or more is an indication for surgical intervention.
Physical examination includes rectal examination of the prostate
Physical examination includes visual examination of the skin, external palpation of the bladder and rectal palpation of the prostate gland. Painlessness, elasticity, smooth surface and uniform enlargement of the prostate indicate benign hyperplasia. In case of a malignant tumor, a lumpy surface with nodular formations is palpated. If there are doubts about the benignity of the adenoma, a biopsy is performed and a piece of tissue is sent for histological examination. To clarify the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound of the prostate through the rectum (allows you to detect adenoma at a very early stage);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- uroflowmetry - measurement of urinary flow rate;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder to determine the amount of urine remaining in it;
- urethrocystoscopy - an endoscopic examination that gives a visual picture of the internal state of the bladder and urethra;
- cystomanometry - shows the volume of the bladder and parameters of its functioning;
- CT scan.
Laboratory tests include a general urine test and kidney tests that determine important functional abnormalities in the kidneys. The level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a marker of prostate cancer, is determined in the blood. A comprehensive examination allows you to choose treatment tactics and determine surgical methods.
Obstructive symptoms
The cause of these symptoms is mechanical compression of the urethra and bladder neck. An enlarged prostate gland has a negative effect, which significantly complicates the outflow of urine and signals the presence of bladder outlet obstruction. As a result, the physiological activity of the detrusor decreases. What signs indicate the described problems:
- weak urine stream, increased duration of urination with decreased volume;
- urine output is difficult, it is necessary to strain the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- feeling of fullness, dripping after urination.
Obstructive symptoms of BPH
BPH. What it is? Statistics
As mentioned above, BPH is a benign neoplasm.
With it, small nodules form in the prostate (the abbreviated name for the prostate gland), which, as they grow, compress the urethra more and more. Because of this, a man develops urinary problems. This disease has a benign growth, and this is what distinguishes BPH from cancer.
BPH is one of the most common diseases in urology today. According to statistics, it appears in almost 80 percent of men in old age. In 20 percent of cases, instead of BPH, atrophy of the gland or its enlargement is observed.
BPH most often develops in men over 45 years of age.
More than half of men aged 40 to 50 consult a specialist with this disease, and only in rare cases can the disease overtake young people.
Irritative symptoms
They have a more complex and not fully understood reason. The functions of the sphincter change, and hyperactivity of the receptors in the bladder neck and urethra is observed. Symptoms may appear even at the stage of filling the bladder, which causes premature urge.
Nocturia is the most worrying symptom
These symptoms include:
- frequent urination, but the portions are very small;
- urinary incontinence at the first urge, the patient does not have time to reach the toilet;
- nocturnal pollakiuria more than twice;
- discomfort during urination.
BPH Clinic
Patient complaints
Reasons for the development of the disease
Diffuse prostate hyperplasia is the proliferation of the connective tissue of the organ, its intracellular changes with the formation of a benign tumor. This condition can be called precancerous, because the cells of the organ are already changing their structure, but they are not yet characterized by uncontrolled growth, as happens with oncology.
Doctors around the world recommend that men visit a urologist once a year, and if symptoms of any prostate disease are detected, twice a year.
In this way, it is possible to diagnose a serious illness in a timely manner, begin comprehensive treatment and prevent the transition of a benign neoplasm to a malignant one.
Prerequisites for the development of the disease:
- Age-related hormonal changes in the body - with age, testosterone production decreases, it is replaced by female hormones estrogens, which is why the cells of the connective tissue of the prostate gland mutate;
- Inflammatory processes - prostatitis leads to prostate adenoma, which develops into diffuse hyperplasia;
- Injuries to the groin area - mechanical damage to the groin area leads to the development of tumor processes;
- Diseases of the urinary system - the development of prostatic hyperplasia is interconnected with inflammatory processes of the bladder and ureters, but it is difficult to determine which disease is primary.
According to statistics, men over 55 years of age have a 50% chance of developing this disease, and in patients over 80 years of age, the disease develops in 90% of cases. If diagnosed in a timely manner, it will not lead to changes in your usual lifestyle.
Pathogenesis
In most cases, BPH appears in the center of the gland, and later the lateral lobes are affected. The stronger the growth of the paraurethral glands, the greater the volume, the more acute the clinical signs. The gland's own tissue shifts outward, and a dynamically changing capsule appears on the adenoma.
Pathogenesis of BPH
At the next stages of development of the pathology, the tissues shift towards the rectum and bladder. Depending on the type of growth, they can have several forms.
Mechanism of disease development
- Subvesical form. The displacement of the tumor is mainly observed towards the rectum, the main body is located under the bladder.
- Intravesical form. The tissues grow towards the bladder, discomfort increases quickly, and surgical intervention is required.
- Retrotrigonal form. The enlarged tissues are located in the triangle between the urethra and ureters. The most unpleasant location of the pathology causes double problems - the outflow of urine from the bladder and its passage through the mouth are hampered.
Changes in the prostate gland with its benign hyperplasia
Natural history of BPH
Causes of the disease
The mechanism of development of prostate pathology has not yet been fully studied. The connection of this pathology with chronic prostatitis has not been confirmed, as well as with the use of tobacco and alcohol.
There is no data confirming that the impetus for the development of the disease can be sexual activity, sexual orientation, or previous sexually transmitted and inflammatory diseases.
The reasons contributing to the formation of prostate adenoma include:
- patient's age. Doctors suggest that adenoma appears in men due to hormonal imbalances at the onset of male menopause (andropause);
- a man's lifestyle. Sedentary work has an impact, so it is important to have regular physical activity with a sedentary lifestyle.
There are also a number of other factors that increase the risk of adenoma. These include:
- heredity;
- overweight;
- atherosclerosis;
- ongoing inflammatory processes in the kidneys and urethra;
- poor nutrition;
- high blood pressure.
What complications can the disease lead to?
Treatment of prostatic hyperplasia should begin as early as possible. In the absence of timely treatment, very dangerous and sometimes irreversible complications can develop.
- Impaired urine outflow is accompanied by detrusor hypertrophy. Gradually, the bladder muscles begin to be replaced by connective tissue elements, which leads to the development of atony.
- Urine accumulates in the bladder, and if it is stretched too much, it stagnates in the renal collecting system. This, in the absence of timely treatment, can lead to the development of bilateral ureterohydronephrosis.
- It is possible to develop acute urinary retention, which is accompanied by severe pain. Hypothermia, unsatisfied sexual arousal, and dietary errors (consumption of spicy foods, alcohol) can provoke such a delay against the background of progressive hyperplasia.
- As has been mentioned more than once, urine is retained in the cavity of the bladder, which is accompanied by certain changes in its composition. Prostatic hyperplasia is often associated with the development of urolithiasis. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, fever, weakness, and acute urinary retention.
- Hematuria is another possible complication. In this case, the veins of the bladder neck become the sources of bleeding (against the background of prostate adenoma, they are often subject to varicose veins).
- Hydronephrosis may develop. The pathology is accompanied by expansion of the renal cup and pelvis, which is associated with progressive expansion of the ureters and fluid accumulation. Often, pyelonephritis and other inflammatory kidney diseases develop against the background of hydronephrosis.
- There is always a possibility of cancerous degeneration of cells.
Late diagnosis and lack of effective treatment of the gland cause very serious complications.
- Urolithiasis disease. Any stagnation of urine significantly increases the risk of stone deposition; the process can be triggered by the slightest catalysts and has no reverse mechanism. The presence of stones in the inflamed bladder causes severe pain and requires immediate medical intervention.
Possible complications - Acute urinary retention. It is provoked against the background of hypothermia, excessive intake of alcoholic beverages, unsatisfied sexual arousal and stress. The patient is not able to independently urinate; in some cases, it is necessary to go to a medical facility.
- Hematuria. Blood from tissues damaged by pathology enters the urine. The most common source is excessive vasodilation in the neck of the bladder.
Hematuria - Hydroureter. Due to incomplete exit of urine from the pelvis, fluid accumulates in the ureters. Subsequently, the pressure in the bladder increases, and the physiological outflow of fluid from the kidneys is disrupted. Inflammatory processes may begin, leading to very serious consequences. In the absence of adequate treatment and progression of ureteral dilatation, infectious diseases, hydronephrosis and other pathologies may appear.
Pyelonephritis
Possible complications
Adenoma leads to very serious health problems. One of the painful complications is acute urinary retention, when the bladder is full and it is impossible to empty it. In this case, resort to catheterization. The appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria) indicates possible bleeding from the dilated veins of the bladder. In some cases, when visible blood clots are present in the urine, the patient may require emergency surgery.
The most dangerous complication of adenoma is renal failure
A constant large residual volume of urine provokes the formation of stones. Congestion causes infection of the genitourinary system. But the worst, life-threatening consequence is the development of kidney failure.
Traditional medicine recipes
Taking pills and other medications can be supplemented with traditional medicine. There are actually a lot of recipes, and some of them are quite simple to prepare.
- Celandine is effective. Pour a tablespoon of dry herbs (it is better to collect and dry the raw materials yourself) with a glass of boiling water, cook for several minutes and strain after cooling. It is recommended to take a tablespoon before meals three times a day.
- The medicine can be prepared from ordinary onion peels. Wash a glass of husk thoroughly, add 500 ml of water, bring to a boil and cook over low heat for 5-7 minutes. The product is infused for 40 minutes, after which it is filtered. You need to dissolve three tablespoons of honey in the broth. Healers recommend taking half a glass 2-3 times a day (preferably before meals).
- Pumpkin is a very useful product. Traditional healers recommend drinking three tablespoons of fresh pumpkin juice or eating a handful of seeds every day. This helps remove toxins from the body, improve blood circulation and tissue trophism.
- In your daily diet, you must definitely include fresh onions, parsley and other herbs, as well as walnuts and carrots - this has a positive effect on the functioning of the entire body, in particular the prostate gland.
It must be remembered that inept use of certain means can only cause even more harm. Before starting to use any medicine (even those prepared at home), you should always consult with your doctor.
Surgical intervention
Unfortunately, sometimes drug treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia does not produce the desired results. In such cases, patients require surgical intervention.
The essence of the procedure is simple: you need to excise the pathologically altered tissue of the prostate gland. The operation can be performed in different ways. For example, sometimes the prostate procedure is performed directly, through an incision into the abdominal wall.
Transurethral resection is considered much more preferable - in this case, instruments are inserted through the urethra, and the removed prostate tissue is washed into the bladder and leaves the body naturally. In most cases, the patient is prescribed this particular procedure, because it is less traumatic, safer and does not require such a long rehabilitation period.
In modern medicine, lasers are increasingly used to remove pathologically altered prostate tissue. This procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis. The laser beam not only removes tissue, but immediately cauterizes damaged blood vessels, thereby speeding up the recovery process and preventing tissue infection.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Etiological factors for the development of disorders:
- Hormonal changes in the body.
- An increase in the level of female sex hormones and a decrease in male hormones occurs with age. As a result of this imbalance, which occurs in most men after age 50, the prostate gland increases in size. As a result, the posterior portion of the urethra is compressed by the enlarged gonad. Spasms of the muscles surrounding the urethra are observed.
- Complicated family history.
- A sedentary lifestyle when a man does not exercise. The pelvic area has many muscles and ligaments that must constantly work like a pump.
- High testosterone levels.