Psoriasis (squamosal lichen) manifests itself as red, scaly spots and the appearance of silvery scales on the surface of the skin.
These scales constantly itch and cause a person very noticeable discomfort. As a rule, the disease affects skin areas on the head, elbow and knee joints, and in the lower back. Psoriasis of the nails, external genitalia and joints is also known, however, these forms are much less common compared to skin lesions.
Considering that 2-7% of the working population is diagnosed with psoriasis, the treatment of this disease represents a very pressing medical problem. The main difficulty with this is that the reasons for the rapid death of cells have not yet been studied. Some researchers associate this process with disorders of the immune system, others with poor heredity. There are also theories that explain the appearance of plaques due to poor nutrition, climatic conditions and stress. Most likely, there is a coincidence of all these factors, which triggers the mechanism of the disease.
Causes
Since psoriasis is treated according to medical indications, the disease appears to be serious and difficult to treat. The reasons why the disease manifests itself have not yet been precisely established. Research conducted by doctors has shown that plaques are usually inherited from older to younger generations. At the same time, the disease is absolutely safe for others, since it is not transmitted even through close communication and tactile contact.
Some experts believe that psoriasis occurs as a response to a weakened immune system of the body. When its protective functions are weakened, psoriasis occurs on the head or body. By the way, it can appear anywhere, but the elbows, knees, inguinal folds and the area between the buttocks are considered more preferable for the occurrence of the disease. The disease prefers to be localized in areas of increased friction of the skin.
Sometimes a completely healthy person who has not encountered such manifestations before wonders what psoriasis is. Doctors say that psoriasis may require treatment if it occurs after extreme stress. The disease can also appear after a burn or injury that disrupts the integrity of the skin. Sometimes, before wondering how to cure psoriasis, patients note that it goes away on its own. This happens especially often in children during the transition to puberty (adolescence).
Predisposing and provoking factors
The key pathological manifestation of psoriasis is the excessive proliferation of defective epidermal cells. Therefore, the fundamental point in elucidating the mechanism of development of the disease and deciding how to treat psoriasis is to establish trigger factors. The main ones:
- Psychosomatics - the influence of short-term severe stress, as well as unexpressed, but long-term or frequently repeated negative psychological effects, moral dissatisfaction, sleep disturbances, depressive states.
- Metabolic disorders in the body, dysfunction of the digestive organs, especially the liver and exocrine function of the pancreas.
- Disease or dysfunction of the endocrine glands (hypothalamus, thyroid, parathyroid and thymus glands, endocrine activity of the pancreas).
- Immune system disorders (allergic reactions and immune diseases).
- The presence of chronic foci of infection in the body (tonsillitis, rhinosinusitis, otitis, etc.). Pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, especially Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci and yeast-like fungi, their toxins, skin cells damaged by these microorganisms, are powerful antigens that can provoke the immune system to aggression against them, altered and healthy cells of the body.
- Mechanical and chemical damage to the skin, long-term use of antibiotics or glucocorticoids for any disease, hyperinsolation, smoking and alcohol abuse, acute infectious diseases (respiratory viral infection, influenza, sore throat, etc.).
Psoriasis can also be provoked by completely third-party factors. True, they act exclusively on persons predisposed to the disease. Cold, heat, dry wind and other weather phenomena act as provocateurs of the disease.
Causes of psoriasis
To date, medicine has not identified the exact causes of the development of psoriasis. Medicine cannot say exactly where the disease comes from. But it has been proven that the chronic disease is not contagious and is not transmitted through contact from patients.
In medicine, the following causes of the disease are identified:
- psoriasis in children and adult patients occurs at the genetic level;
- dysfunction and weakened immunity provokes accelerated division of epidermal cells. The old layer of skin does not have time to come off, but new layers are already breaking through. As a result, psoriatic erythroderma develops, affecting various surfaces of the body. This is the main factor explaining where the disease comes from;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- The causes of the disease are various infections caused by viruses;
- the occurrence of a skin disease can be triggered by a psycho-emotional factor;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- the presence of chronic pathology of internal organs;
- insufficient amounts of microelements and vitamins in the body.
Psoriasis is an incurable, autoimmune disease. Regardless of where the disease comes from, it is impossible to completely cure psoriatic rashes in adults or children.
Classification
There are a large number of classifications of psoriasis, which are based on the severity of the condition, the nature of the rash, the location of the lesion, etc. The most common types of disease are:
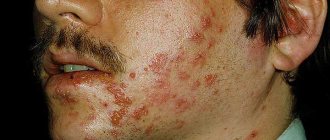
- Non-pustular psoriasis. The non-pustular form includes plaque psoriasis of the skin, which is the most common form of the disease in people with the disease. Plaque psoriasis appears as dense spots that rise above the skin. The top layer of spots is covered with scales, which, when peeled off, cause blood and cracks in the skin. Scaly islands are capable of enlarging and connecting with neighboring spots, forming scaly plates on the skin.
- Psoriatic erythrodemia. The form of the disease is an exacerbation of plaque-type psoriasis and is accompanied by lesions of large areas of the skin, causing exfoliation of scales, inflammation of the skin, intense itching, swelling of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, these processes are characterized by painful sensations and have a negative effect on the performance of the body, which loses the ability to perform protective and barrier functions of the body. Psoriatic erythroderma can become the initial form of the disease, transforming into other forms of psoriasis;
- Pustular psoriasis. The pustular type of psoriasis is expressed in the appearance of vesicles and blisters on the epidermis. The type of psoriasis includes several subtypes of the disease: guttate form of psoriasis, chronic persistent acrodermatitis, seborrheic psoriasis, psoriatic onychodystrophy, psoriatic arthritis, exudative skin psoriasis;
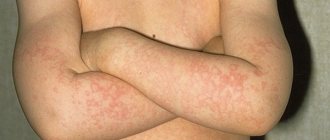
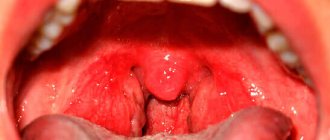
- Guttate psoriasis is expressed in a large number of small, dry, purple or red raised areas throughout the patient’s body. The spots appear in the form of small balls mainly on the head, thighs, neck, legs or shoulders. The disease is most often provoked by streptococcal infections, for example, streptococcal sore throat, pharyngitis;
- Seborrheic psoriasis affects the scalp, nasolabial folds, areas between the shoulder blades and ears with small psoriasis blisters. The rash is accompanied by severe itching, which can lead to purulent wounds and complicate the course of the disease;
- Chronic persistent acrodermatitis - plantar psoriasis and pustulosis of the palms, affecting the inner surface of the hand and foot, forming small spots and blisters, subject to constant friction, which complicates the course of the disease;
- Psoriatic arthritis is a disease that affects the joints and connective tissue. The most vulnerable places for the development of the disease are the phalanges of the fingers and toes. The affected fingers become enlarged, swollen, and swollen. Affecting the joints of the knees, pelvis, shoulder blades, shoulders, spine can lead to disability, limitation of physical abilities, and sometimes to the inability to move and fatal consequences;
- Psoriatic onychodystrophy or nail psoriasis affects the nail plate, changing it and forming spots underneath that show discoloration and the appearance of colored speckles on the nails. The disease causes thickening of the skin under the nail, separation and transformation of nails, and loss of nails;
- Exudative psoriasis is the most severe form of the disease, which is accompanied by raised, convex blisters and capsules filled with liquid - pustules. The pustules are surrounded by inflamed, reddened skin, causing pain and sometimes itching. Peeling of pustules can lead to re-infection of the skin, which will give rise to a purulent process in the blisters. A severe and advanced form of exudative psoriasis contributes to an increase in the number of pustules, which can appear on all areas of the skin and merge into larger, painful capsules.
What is psoriasis
This disease is expressed in the appearance of red spots on the skin that constantly bother, the areas of the rashes itch, which interferes with a full life. With complications, arthritic pain in the joints may appear.
The quality of life of people who have such problems decreases. And although the general condition often does not deteriorate much, the usual way of life changes. This serious, unsightly skin disease brings a lot of inconvenience, for example, the inability to wear revealing clothes or go to saunas or beaches.
In some cases, psoriasis causes suffering comparable to such serious diseases as heart failure, acute forms of hypertension or post-heart attack. The danger is increased itching, since wounds that are difficult to heal appear on scratched areas.
The difficulty of this disease is that it is practically incurable. Everything that is offered by the pharmaceutical industry at present gives temporary results. And measures such as psychotherapy, vitamin complexes and diets can only improve the condition slightly.
Symptoms of psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis are so characteristic that they allow an accurate and quick diagnosis. The main manifestation of the disease is red, scaly spots (plaques) on the surface of the skin, consisting of papules. Patients are concerned about severe itching and signs of inflammation in the area of the spots. One of the characteristic features of psoriasis is the spread of plaques where there are skin lesions - microtraumas, scratches, cracks.
The favorite localization of rashes is on the head under the hair, on the extensor surfaces of the joints, on the lower back and sacrum, in all natural skin folds. Sometimes the disease affects the nail plate, which can become thinner or, on the contrary, thicken, become covered with spots, grooves and grooves.
Psoriasis has an undulating course, in which periods of exacerbation are spontaneously replaced by remission. Many patients note that they cannot connect any event in their lives with the onset of an exacerbation. During this period, the symptoms of psoriasis manifest themselves most clearly - peeling intensifies, the redness of the spots becomes clearly bright, and as a result of peeling of skin flakes and infection, suppuration of plaques is possible.
Depending on the time at which the disease worsens, its forms are distinguished - winter, summer, and independent of seasons. Most patients suffer from the winter form, the symptoms of which subside under the influence of summer sunbathing. In the summer form of the disease, its course, on the contrary, worsens due to natural ultraviolet radiation.
Symptoms and first signs of psoriasis
Psoriasis can be identified by how the disease begins. The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of a psoriatic triad of symptoms.
Steaorine stain
These are such manifestations on the skin:
- A stearin stain is an accumulation of scales, essentially a focus of a rash. If you try to remove these scales, after a while there will be many more of them. This is the first and most characteristic symptom.
- Terminal film. After removing the scales, a thin red film is visible, which can be easily damaged. If it is damaged, a bleeding wound is formed.
- Bloody dew. After removing the scales, small droplets of blood appear.
Other symptoms appear: redness of the skin, dryness and itching, fever, irritability and constant fatigue. The onset of the disease often goes unnoticed: the patient mistakes the symptoms of psoriasis for an allergy or other skin reaction.
Gradation of psoriasis by severity
Psoriasis is usually classified by severity as mild (involving less than 3 percent of the skin surface), moderate (involving 3 to 10 percent of the skin surface), and severe (involving more than 10 percent of the skin surface). Psoriatic joint damage is regarded as a severe form of psoriasis, regardless of the area of skin damage. There are several scales for assessing the severity of psoriasis.
Assessment of the severity of the disease as a whole is based on an assessment of the following factors: the area of the lesion (percentage of the body surface involved in the process), the degree of disease activity (the degree of redness, swelling, hyperemia of psoriatic plaques or pustules, the severity of skin itching, the degree of skin thickening, the degree of peeling , the presence of bleeding or exudation, secondary infection of plaques, the degree of swelling and tenderness of the joints), the presence of general symptoms of process activity (such as increased fatigue, increased ESR, increased uric acid levels in blood tests, etc.), the patient’s response to previous attempts at treatment, the impact of the disease on the general condition and daily life of the patient, on his social functioning.
The Psoriasis Severity Index (PASI) is the most commonly used tool to measure the severity and activity of the psoriatic process. The PASI index combines an assessment of the severity of lesions (redness, itching, thickening of the skin, swelling, hyperemia, peeling) with an assessment of the area of the lesion into a simple linear scale from 0 (no skin manifestations of the disease) to 72 (maximum severe skin manifestations). However, PASI is quite difficult to use in routine clinical practice, outside of clinical trials of drugs and treatments. This has led to numerous attempts to simplify the PASI score to make it more suitable for use in clinical practice and for patients to self-monitor changes in their condition.
Psoriasis and pregnancy
A connection between a woman’s hormonal changes during pregnancy and the course of psoriasis has not been identified. Although, many scientists have studied this issue more than once. It is known that most often the disease first appears during puberty, when hormonal surges are no less than during pregnancy; no clear connection with psoriasis has been found. Most women note that pregnancy makes dermatosis easier. Menopause, on the contrary, makes the situation worse.
Psoriasis is not an infectious disease, which means it does not pose a threat to the development of the fetus. However, you should be careful not to injure psoriatic plaques, so as not to introduce third-party infection into the cracks.
Treatment of psoriasis in women in an interesting situation can be difficult if the disease previously had an advanced form. Most drugs for systemic use can lead to disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus. You also need to be careful with ointments for external use, as they can be absorbed into the blood through the skin. Therefore, before conceiving, it would not hurt a woman to undergo a course of treatment and improve the condition of her skin.
After delivery, the disease returns in a more severe form. Despite this, there is no need to fear that the child may develop dermatosis, since the disease is not contagious. A woman can calmly hold her baby in her arms and breastfeed him if therapy allows this.
What psoriasis looks like: photo
Most often, with the development of psoriasis, spots appear on the surface of the skin, covered with grayish or white scales, which are easily separated when touched. It is with this symptom that another name for the disease is associated - scaly lichen.
The size of the rashes may vary. The primary elements are considered to be small papules of bright red or burgundy color. Over time, their size increases significantly, and they also tend to merge.
Photo of psoriasis.
What does psoriasis look like (photo)
How psoriasis begins (photo)
Psoriasis at an early stage (photo)
Papule in a child (photo)
Complications
It is a mistake to think that psoriasis on the legs, arms or head is dangerous only because of the plaques that appear. Its disadvantage lies not only in its unaesthetic appearance. The worst thing is the risk of complications. To prevent them, it is recommended to carry out prevention and consult a doctor on time.
What diseases are at risk? Among them:
- Failure in the functioning of the liver and kidneys;
- Metabolic and metabolic disorders;
- Development of heart muscle diseases;
- Damage to the lymphatic system;
- Joint dysfunction;
- Erythroderma.
If you do not promptly contact a specialist who will prescribe medicine for psoriasis on the head and other places, the disease will quickly spread throughout the entire base of the skin. As a result, the dermis will not be able to breathe and carry out air exchange processes, which will negatively affect the functioning of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Over time, this will lead to inflammation of the skin and can cause blood poisoning, which can be fatal.
For men, advanced psoriasis has a terrible effect on potency. Erectile dysfunction can become a constant companion for a previously healthy man. This is caused by disorders in the vascular system. By depriving the intimate area of the proper amount of blood flow, psoriasis reduces sexual activity, sometimes making it a completely unattainable dream.
Reasons for the development of psoriasis
Many years of research by specialists in this field have not made it possible to establish the exact and only cause of the development of the disease. It is believed that several systems and factors are responsible for the development of psoriasis.
The main versions of why dermatitis occurs include:
- genetic predisposition;
- endocrine disorders.
It is believed that psoriasis develops in those whose parents suffered from this disease. However, medical practice knows cases when such a diagnosis was simultaneously made to all family members. Although genetics has an influence, this is not a guarantee of the development of this pathology.
Note! Even if the father or mother has psoriasis, there is no guarantee that this pathology will develop in the child.
A significant number of researchers have proven the connection between the occurrence of psoriasis and diseases of the endocrine system. Hormonal imbalances have a powerful effect on the body. This leads to problems such as diabetes, adrenal dysfunction, and brain disorders. All this weakens the body as a whole and makes it more susceptible to pathologies.
Psoriasis is neither viral, nor infectious, nor fungal in nature. Therefore, you should not be afraid of contracting some kind of infection from a person suffering from psoriasis.
Treatment of psoriasis
Treatment of the disease must be carried out by a qualified doctor and individually for each patient.
Treatment of psoriasis depends on the patient’s age, general health, profession (the influence of occupational factors), gender and personal characteristics of the patient. The nature of the course of the disease and its stage are established, and provoking factors are eliminated (drinking alcohol, drug intolerance, allergic diseases).
Attention is paid to the general condition of the patient (psychological and physical). Normalization of the environment, rest, short hospitalization or change in work schedule can make changes in the course of the disease. If signs of psoriasis are detected, it is recommended to immediately seek medical help. It is the doctor who prescribes various drugs and other therapeutic methods.
The treatment regimen for psoriasis can be presented in the form of a table:
| Systemic therapy (indicated in severe cases or lack of effect from local treatment) | Local treatment (indicated in all cases of psoriasis alone or in combination with other methods) | Instrumental methods (Assigned differentiated and individually) |
|
|
|
Physiotherapeutic procedures such as paraffin baths and UV irradiation are indicated for various forms of psoriasis. In the progressive stage of psoriasis, anti-inflammatory ointments are used; if there is an infectious process, then antibiotic ointments are used. Laser treatment of psoriasis and phototherapy are effective. When psoriasis enters the stationary stage, keratolytic ointments and creams are indicated, for example salicylic, retinoic and Bensalitin. Cryotherapy is performed for psoriatic plaques.
If psoriasis affects the scalp, then low-percentage sulfur-salicyol ointments are used, since with an increase in the content of salicylic acid, the ointment has a pronounced keratolytic effect.
Treatment methods
If a patient is diagnosed with psoriasis, treatment will take a long time. You need to understand that you won’t be able to get rid of an autoimmune disease completely. Treatment cannot be achieved with drug therapy alone.
Treatment is usually complex and should accomplish the following tasks:
- reduce the manifestations of psoriasis;
- improve overall well-being;
- prolong the period of remission.
Timely, comprehensive treatment methods give good results and prevent the development of side effects.
Psoriasis is treated in the following ways:
- Drug therapy. Special preparations are used for external use. In severe forms of the disease, hormonal medications are prescribed for oral administration.
- They use traditional medicine recipes. They can only be used after consulting a doctor. Home therapy refers to a special diet and lifestyle adjustments.
- Physiotherapy sessions are prescribed.
The use of several treatment methods makes it possible to achieve long-term remission from treatment. First, doctors prescribe light, gentle medications, and adjust the prescriptions during the treatment process.
Next, we will analyze each treatment method in more detail.
Medications
Treatment for psoriasis is prescribed based on symptoms and diagnostic testing.
Doctors prescribe local treatment with ointments and creams, combining therapy with external agents with medications for internal use.
The following medications are indicated for treatment:
- with a sedative effect. This is a tincture of valerian and motherwort, the drug Persen, Novo-Passit;
- antihistamines: Suprastin, Fenistil, Claritin;
- medications with anti-inflammatory effects: Ibuprofen, Naproxen.
Psoriasis can be effectively treated with external remedies. These are gels, creams, ointments, lotions. Skin treatments can be hormone-based or hormone-free. Hormonal ointments are prescribed for severe cases, and in cases where other drugs have not had the expected effect.
The following types of ointments are used to combat psoriatic plaques:
- salicylic ointment;
- tar;
- naftalan
For psoriasis, hormonal ointments such as Nazacort, Kenalog, Triacort are effective.
Cygnoderm psoriasis ointment is very helpful. Eliminates symptoms with ointment from China Skin King.
The following medicinal creams are used:
- Akriderm. The cream relieves swelling and inflammation, soothes affected areas of the skin, and prevents allergies.
- Calcipotriol. Vitamin D cream is used to treat affected skin areas on the body, arms and legs.
- Kremgen. A universal drug against psoriasis, which has a tonic, soothing and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Wax cream Zdorov, consisting of natural ingredients, helps restore the skin.
You can fight psoriatic rashes with the following gels:
- Nano Gel. The product is more often used to treat affected skin on the legs;
- Xamiol gel. When applying the product, the epidermis is covered with a protective film.
To eliminate rashes on the scalp, it is recommended to use special medicated shampoos. These are shampoos based on zinc and tar.
What drug treatment will be prescribed depends on the stage of development of psoriasis, the location of the rash, and the individual characteristics of the body.
Folk remedies
Treatment of psoriasis with the help of folk remedies performs the same tasks as drug therapy. Traditional methods can reduce symptomatic manifestations and prolong the period of remission. For treatment, effective recipes are used that have been used in folk medicine for several years.
You can fight psoriatic plaques using the following folk recipes:
- Baths with sea salt and the addition of string. First, a decoction is prepared. A series (2 tbsp) is poured with a liter of boiling water. Let the broth brew for 15 minutes, then strain. Prepare a bath with 4 tbsp. l. sea salt. Add a decoction of string to the bath. The duration of the soothing procedure is half an hour.
- Lotions from medicinal herbs. Take 2 tbsp. l. calendula, string, motherwort and chamomile, add 4 tbsp to the herbal mixture. l. celandine. Pour the collection with a liter of boiling water and leave in a water bath for 20 minutes. Apply lotions 2-3 times a day, applying gauze soaked in solution to the affected areas.
- To cleanse the body and remove toxins, drink tea made from medicinal herbs. Dandelion roots, St. John's wort and nettle leaves are mixed in equal proportions.
- Herbal decoction. Take 1 teaspoon each of licorice, string, nettle, burdock root. Pour 0.5 liters of water, boil, and let it brew. Wipe areas affected by psoriasis several times a day.
- Ointment. A home remedy is prepared from fish oil, aloe juice, olive oil, birch tar and pine resin. All components are taken in equal proportions and mixed. The infused solution is applied to problem areas every day. The ointment promotes skin healing, relieves itching, and has a calming effect.
- Birch tar can be used in its pure form. The natural product is applied to elbows and ears affected by psoriasis.
You can buy monastery tea produced by monasteries.
Therapy
A feature of the treatment of psoriasis is the simultaneous use of several methods. Treatment includes medication and home treatment.
External skin treatments and oral medications are used to help quickly eliminate toxic substances. The use of more than one method in treatment can increase the duration of the remission period.
To enhance the effect of complex treatment, doctors prescribe physiotherapy sessions. The following types of physiotherapy sessions are shown:
- laser and magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- light treatment;
- cryogenic sessions;
- selective phototherapy. Psoriatic plaques are exposed to UV rays;
- PUVA therapy. During the session, simultaneous exposure to herbs and ultraviolet radiation occurs on the skin affected by psoriasis;
- sessions of thermal exposure, irradiation with quartz.
Complex therapy can be supplemented with exercise therapy.
When choosing a treatment method, the doctor takes into account the general condition of the patient and the severity of the development of psoriasis. Only complex therapy that can reduce the symptomatic manifestations of psoriasis will help improve well-being and prolong remission.
Ointments for the treatment of psoriasis
The ointment can be hormonal or not; the product is often used for psoriasis on the arms, legs, and body:
- Ointments Nazacort, Triacort, Kenalog, Berlicort - hormonal agents containing triamcinolone have a quick and effective effect on psoriasis, eliminating irritation, itching, redness and other symptoms of the disease. The drug can be prescribed for psoriasis on the face.
- Ointments Lokasolen, Sinalar, Flucort, Flucinar contain the main components flumethasone, fludcortonol and are hormonal agents. Ointments for psoriasis with hormones quickly eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
- Mometasone is one of the most effective drugs for the treatment of psoriasis, which is part of the following hormonal ointments: Momat, Uniderm, Skin Light.
- Salicylic ointment for psoriasis is a popular non-hormonal remedy to combat the disease, used in combination with other drugs. Salicylic ointment has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected areas.
- Dayfobet ointment is a non-hormonal drug containing calcipotriol and betamethasone, which have a positive effect on diseased skin, soothing the epidermis and eliminating rashes.
Non-hormonal ointments for psoriasis have a slower effect, while hormonal drugs have a much more effective and stronger effect. But hormonal ointments have a number of disadvantages in the form of contraindications and adverse reactions, as well as negative effects on internal organs: kidneys, heart, blood vessels. Before using such products, you should consult a dermatologist.
Is psoriasis contagious?
The skin of a person suffering from psoriasis looks repulsive. Many people fear that the disease is contagious. This is a misconception, and psoriasis is not transmitted through:
- towels, dishes, bed linen;
- sweat and saliva;
- during sexual intercourse;
- while caring for the patient;
- You can't get infected through blood.
Psoriasis can be transmitted at the genetic level, but not through everyday life. The disease is dangerous not for others, but for the person himself. At an advanced stage, joints may be affected, the nervous system and internal organs may suffer.
Creams for psoriasis
What creams are most popular in the treatment of psoriasis?
Containing synthetic hormones. They are good because they quickly and effectively relieve itching and inflammation, and help reduce the size of psoriatic plaques. Depending on which hormone is used, there are:
- psoriasis creams that contain hydrocortisone. They are prescribed at the very beginning of the disease, when the skin lesions are not yet extensive, or during a mild course of the disease.
- Moderate creams containing prednisolone, fluocortolone and prednicarbate. Used for long-term chronic disease.
- potent creams containing dexamethasone, budesonide, mometasone and other strong hormones. They are used in severe cases of extensive skin rashes when other remedies have had no effect.
Hormonal creams have many side effects and should be used strictly as directed and under the supervision of a physician. The most effective means used in treatment are fourth-generation hormones, which have a minimum of harmful side effects on the body.
But even they can cause harm if you prescribe them to yourself and apply these creams to your skin for a long time. Side effects can affect the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system, and cause hypertension. Another disadvantage of hormonal medications is that the skin quickly “gets used” to them, and other medications become less effective. It is necessary to discontinue a cream containing hormones not abruptly, but gradually, reducing the dosage every day.
Non-hormonal creams have the same effect as hormonal ones, but it takes much longer to occur, after prolonged use. Therefore, they are not used as an ambulance. But, unlike hormones, such creams are not addictive, and they have almost no side effects. They usually have a multicomponent composition, each substance of which is aimed in its own way at eliminating the symptoms of psoriasis. The most popular hormone-free products are Psorilom, Picladol, Losterin, Antipsoriasis, etc.
What is the best way to treat psoriasis on the body?
Prescriptions include antihistamines, various ointments and lotions. The disease tends to return, so the use of certain medications is possible during remission.
To restore the nervous system, use motherwort tincture. To improve sleep, drink valerian tincture, medications with a sedative effect. If there is an infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
Relief is brought by Naproxen and Ibuprofen ointments, which relieve swelling and itching. The composition of ointments should include sulfur and salicylic acid. Let's use Diprosalik and Fluorocort.
Calcium gluconate is used for injection. The course of the disease is accompanied by dry skin, which is removed with moisturizers. Plaques are removed using sulfur ointments. Having achieved stabilization, use ichthyol ointment and tar.
Taking vitamins and minerals reduces recovery time. If joints are affected, paraffin wraps are necessary.
Patients with this disease should lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well, and not drink alcohol. Spicy, fatty and smoked foods must be removed from the diet.
Spa treatment
If we compare the effectiveness of treatment methods, solidol-containing ointments come in first place - 37% of success, in second place is diet with 33% improvement in well-being. In 26% of cases, a change of place of residence or a summer vacation in a different climate zone gives results.
Among the most popular resort areas where psoriasis of the head and other parts of the body is treated, experts note:
- Sulfide mineral waters of Yeisk, Pyatigorsk, Goryachy Klyuch, Sochi.
- Water with radon in Zhitomir, Tskhaltubo, Pyatigorsk.
- Sodium chloride mineral waters of Angara, Ust-Kut, Sosnovski.
- Rape springs in Evpatoria, Saki, Berdyansk.
- The healing muds of lakes Uchum and Elton, the cities of Yeisk, Sochi, Anapa, and Evpatoria have proven themselves well.
Salt baths help to get rid of psoriasis, softening the symptoms of itching and flaking in 19% of cases. If you don’t have the means to go to the sea and rinse your body in the salty waves, doctors recommend buying high-quality sea salt at the pharmacy so that you can take baths with it at home. In combination with these methods, you should apply sports, going to baths, saunas and swimming pools, and therapeutic fasting.
In 10% of patients, symptoms are reduced by herbal medicine with lotions, internal administration of infusions and decoctions. The beneficial effects of burdock, oregano, valerian, nettle, birch and celandine are known. To cure psoriasis on the legs, you should do foot baths.
Treatment at home
In addition to following dietary nutrition at home, a person with a disease must follow the following rules:
- Careful skin care. She needs additional protection; damage to the skin must not be allowed, since any abrasion or crack can become inflamed. With this disease, secondary inflammation often occurs, which can lead to suppuration;
- During the treatment period, you should stop using cosmetics; it is better to cut your nails short; with psoriasis, they also suffer, become brittle, and peel;
- Do not be in direct sunlight. You can sunbathe, but for a short period. Prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause aggravation and damage the skin;
- It is necessary to exclude exposure to stress factors and direct efforts to improve immunity. It is recommended to take vitamin complexes, exercise, and exercise.
When treating psoriasis at home, you can use the following folk remedies:
- If the elbows and hands are affected, cold herbal baths are taken; the composition must include celandine, chicory, and valerian. You can lubricate the areas of inflammation with fresh celandine juice, but this must be done very carefully so as not to burn the skin. Chicory decoction helps well; compresses are made on its basis.
- Treatment of psoriasis on the legs is similar, you can also use the following recipes. Baths with apple cider vinegar or sea salt have worked well. The feet are kept in warm water for several minutes, after which the damaged areas are carefully cleaned of scales.
- Lesions on the head are the most unpleasant type of disease and are very difficult to treat. It is recommended to rub salicylic or tar ointment into the scalp. Home recipes include a mixture of mustard and warm water, rub the inflammation areas with the mixture, and cover the head with a towel. You can apply a mixture of grated onion to the affected areas.
- Nail psoriasis is treated with solutions of vitamins A and E. At home, you can make baths based on yarrow infusion. You should definitely stop using cosmetics.
Psoriasis during pregnancy requires increased attention from women to their health, strict adherence to diet, and strict adherence to recommendations to increase immunity. Although the disease is not transmitted in utero and does not affect the course of pregnancy, its development due to the restructuring of the body is difficult to predict.
Physiotherapy
The procedures are aimed at achieving various therapeutic effects:
- The main type of physiotherapy is phototherapy (or photochemotherapy). Treatment consists of treating the skin surface with ultraviolet irradiation of different wavelengths. To make phototherapy more effective, patients may be prescribed drugs to increase sensitivity to ultraviolet light - this treatment is called photochemotherapy. The procedures allow you to clear the skin of psoriatic plaques and achieve remission (lasting improvement). Phototherapy and photochemotherapy are contraindicated in the erythrodermic form of psoriasis and during exacerbation of the disease.
- Ultrasound has an anti-inflammatory, calming and analgesic effect. How to treat psoriasis with ultrasound? Small areas of the body are processed by the sensor in continuous or pulse mode. A type of treatment is ultraphonophoresis, when medicine is injected into the lesions simultaneously with the influence of ultrasonic waves. Waves promote better penetration of the drug into the thickness of the skin.
- X-ray methods – treatment of the skin surface with soft x-rays. The procedure allows you to reduce itching and inflammation, promotes the healing of plaques.
- Cryotherapy – treatment of the skin surface with nitrogen to accelerate regeneration, relieve inflammation and itching. The procedure is carried out in special baths or barrels, or sprayers are used for topical use.
- Electrosleep is the introduction of a patient into a state of sleep using electrical influence on the brain. The procedure does not treat skin rashes, but helps reduce excitability and manifestations of neurosis, and due to this, the general condition of patients improves.
- Magnetic therapy is used when psoriasis is complicated by arthritis. It relieves skin itching and inflammation, promotes regeneration of the upper layer of skin, and inhibits excitation processes in the central nervous system.
- Laser therapy is used primarily to treat plaque. Thanks to her, the rashes quickly regress.
Physiotherapy is a remedy for psoriasis, actively used in official medicine.
Psoriasis in children
Scaly lichen can occur not only in adults, but also in children of preschool and primary school age. There are frequent cases of psoriasis developing in infants. At the first suspicion of dermatosis, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. Only a dermatologist with special qualifications has the right to prescribe treatment at such an early age. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a pediatrician.
The types of psoriasis in children are the same as in adult patients. The reasons are also largely similar. Most often, psoriasis in children is associated with the appearance of a red rash with islands of whitish scales. Scaly plaques often crack, causing minor bleeding. This leads to infection and the development of secondary skin diseases. The situation is complicated by the fact that all this is accompanied by pain and severe itching. In infants, the disease manifests itself as constant diaper rash and eczema.
Treatment of psoriasis in children will be similar to treatment for adult patients. Many medications and ointments can be suitable for even the youngest patients. In addition, ultraviolet lamps, sea air and water are excellent in the fight against dermatosis in children. The calm state of the child also plays a big role in treatment. A special hypoallergenic diet is simply necessary in this case. Parents must take all this into account. Many hospitals in our country and foreign clinics are ready to accept small patients.
Psoriasis may have a genetic predisposition. Studies have shown that if one of the parents is sick with dermatosis, then the risk of developing the disease in children is about 15%, if both parents are sick, then the risk will be over 60%.
Diet for psoriasis
Patients with psoriasis simply must follow a diet and adhere to the basic principles of proper nutrition. The main task of the diet is to maintain a normal acid-base balance. But it is important to note that the alkaline background of the body should slightly prevail over the acidic one.
Naturally, the balance of the body depends on the foods that psoriasis patients consume daily. It is important for every person suffering from this disease to know that 70% of the daily diet should come from foods that form alkali in the body. For acid-forming substances – no more than 30%. It’s easier to say this: alkali-producing foods must be consumed 4 times more than acid-forming ones.
List of products that form alkali in the body:
- Any vegetables except rhubarb, pumpkin and Brussels sprouts. It is important to remember that potatoes, peppers, eggplants and tomatoes are strictly prohibited.
- Don't exclude fruits. The main thing is not to eat prunes, cranberries, currants and blueberries. It is worth noting that bananas, melon and apples should not be consumed at the same time as other foods.
- Be sure to drink fresh vegetable juices from carrots, beets, parsley, celery and spinach.
- You can consume fruit juices of grapes, pineapple, pear, orange, papaya and grapefruit, mango, lemon and apricot daily. It is important to add lecithin and lemon juice to your food.
List of foods that people with psoriasis should not eat (they form acid):
- The consumption of foods containing starch, fats, sugar and oils should be eliminated completely or reduced to a minimum. Typically, these include the following products: potatoes, beans, cream, cheese, grains, meat, dried peas. Unbalanced daily consumption of these products inevitably leads to the initiation of acid reactions in the blood. The result is a deterioration in health.
- It is important to properly balance food. There are a number of products whose consumption at the same time is prohibited. For example, meat products with products that contain a large amount of sugars, and you should not combine sweets and starch.
- It is important to limit your sugar intake. Preservatives, vinegar, dyes and various food additives should be included in the diet as little as possible.
- The main point is that it is necessary to completely eliminate the consumption of alcohol and alcohol-containing drinks.
Every psoriasis patient should remember that eating right is an important condition in the treatment of this disease. It is imperative to replace frying with stewing or boiling. It is necessary to consume foods that are subject to gentle processing. You should forget about fried and fatty foods.
Treatment
At the moment, there is no single pill for the treatment of psoriasis. There are a number of ointments and medications that help fight the disease, but they cannot cure it forever. When choosing a particular therapy, the dermatologist takes into account many factors:
- age;
- patient's gender;
- standard of living;
- chronic diseases;
- state of the nervous system.
The choice of treatment is directly dependent on the type of psoriasis, its location and the severity of the disease. Each patient requires individual treatment, which may not be suitable for another.
At the very beginning of the disease, a dermatologist may prescribe topical ointments to soften excessively dry skin and phototherapy (irradiation of the affected areas with ultraviolet light). At the second stage of treatment, phototherapy is combined with chemical photosensitizers. This approach can be very effective. In the most severe cases, special tablets or injections for psoriasis are added to everything described above.
It should be remembered that the development and course of the disease largely depends on the state of the nervous system. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations. If this is not possible, you should consult your doctor, who will prescribe a suitable antidepressant.
Following a strict diet is simply necessary. As a rule, patients with psoriasis often have food allergies, which will aggravate the course of the disease. Eating hypoallergenic foods will help with treatment.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, there are many recipes for remedies, both for local use and for oral use. You can prepare an ointment and apply it over the plaques. The following recipes are the most popular:
- Mix celandine and lard (1:5) to create an effective remedy.
- Grind the meadowsweet flowers and mix them with petroleum jelly (1:1). After this, heat to 900C and cool. The ointment does not last long, so it is better to prepare it in small portions.
- Combine lard, pine resin and beeswax, heat it over fire, stirring constantly. After this, add vitamin A from the pharmacy.
- Regular birch tar (25 g), petroleum jelly (10 g), boric acid (5 g), honey (15 g), egg white, fish oil (5 g) mix very well and place in a dark container. This cream should be applied only once a day.
- Elecampane ointment helps with exacerbation of the disease.
Traditional medicine for oral administration is usually aimed at maintaining immunity and reducing inflammation and itching:
- Oat kvass is prepared from 700 g of grain, three liters of water and five large spoons of sugar. All this should be insisted for two days.
- An infusion of bay leaves is taken orally in 100 ml doses.
- To prepare a tincture of Sophora buds, you need to take 500 ml of vodka and 50 g of dry raw materials, and then place it in a dark place for a month. Take a teaspoon.
- A decoction of dill seeds helps eliminate acute symptoms and also has a slight hypnotic and sedative effect.
Baths with the addition of copper sulfate are also used to treat psoriasis.
Types, first signs and treatment of the disease
How to recognize the signs of an insidious disease in yourself and prevent it from spreading? The course of psoriasis is cyclical: periods of exacerbations are followed by periods of remission. The disease has several forms, each of them has its own distinctive features, but there are common symptoms, the totality of which clearly indicates that the patient has psoriasis. This is the so-called psoriatic triad:
- The phenomenon of stearic drop. If you scrape the surface of a psoriatic plaque with your fingernail, keratinized skin flakes, similar to droplets of frozen stearin, will separate from it.
- Under the separated layer of keratinized particles, a red shiny thin film is found.
- "Bloody Dew" If you scrape this film with your fingernail, small drops of blood will appear. The fact is that underneath there are capillaries with thin walls, and the slightest physical impact causes multiple pinpoint hemorrhages.
All these symptoms are accompanied by itching in the affected area. Most often, the first psoriatic plaques appear in places such as the knees, elbows, groin area, scalp, and armpits. At first, the rashes are single, but as the disease progresses, their number increases, and the plaques can merge with each other, affecting an increasingly larger surface of the body.
Koebner syndrome also occurs - the appearance of new rashes in areas of skin irritation.
One of the most common forms of the disease - psoriasis vulgaris is diagnosed in 80% of psoriasis patients. The most characteristic sign is the appearance on the body of reddish papules - nodules that have a rounded shape, clearly defined boundaries and slightly rise above the skin.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Allergic skin rash: causes, types, treatment
The spots are covered with a grayish coating of separated dead scales. Rashes can affect both individual parts of the body and spread throughout the entire skin, mainly localized in skin folds, joint surfaces, places of frequent contact and friction of the skin with clothing.
With this form of the disease, the part of the head covered with hair is mainly affected, but as the disease progresses, the plaques can spread to the face, ears and neck area. Since it is quite difficult to see what is happening on the head on your own, often at the initial stage, hair psoriasis is confused with ordinary dandruff and they do not attach much importance to the symptoms.
What signs should alert you:
- Dry scalp;
- Severe itching;
- Pain and burning in the affected area;
- The appearance of flaking, similar to dandruff;
- Hair loss.
Nail psoriasis
Psoriatic onychodystrophy, or nail psoriasis, can manifest itself as an independent disease or as a complication of regular psoriasis. External signs of the disease are very similar to a fungal infection. The nail plate thickens, its color changes - it can vary from yellowish to gray. Traces of subungual hemorrhages are visible to the naked eye - red or purple spots.
Oil stain syndrome is observed - a yellowish spot under the nail plate. The nail itself flattens, becomes rough to the touch, and depressed marks appear in the center. Small pits also appear - as if pricked by a needle, the surface begins to resemble a thimble. Under the nail bed, the process of accumulation of dead cells begins, which can later lead to nail detachment and loss. All the nails on the fingers of both hands can be affected, or just a few.
Pustular psoriasis
It differs from the usual one in that the lesion is characterized by the appearance of redness and pustules - blisters with purulent contents. With further development of the disease, the blisters begin to peel off, exposing the erosive surface. Pustular psoriasis has a more severe course and can be complicated by the addition of a secondary infection, intoxication of the body, even death.
Guttate psoriasis
A fairly rare form of the disease. It is characterized by the appearance of small drop-shaped plaques up to 1 centimeter in diameter. Favorite places: limbs and torso. The appearance of rashes is accompanied by severe itching, often preceded by a previous streptococcal infection.
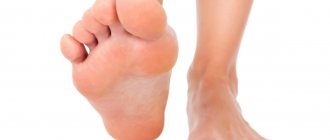
Diagnosed in 15% of all patients with psoriasis. This form is characterized by the appearance of papules on the palms and soles of the feet. The affected areas become extremely itchy and hot, and the skin often cracks and bleeds. Patients experience severe difficulty walking and the inability to perform any manual actions. The pustular type of palmoplantar psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of redness and blisters with liquid contents on the skin.
This type of disease is characterized by the formation of weeping plaques with uneven edges, covered with numerous layers of grayish crusts. Such crusts are formed from the impregnation of keratinized particles with exudate; when trying to remove them, the plaque becomes reddish in color and may begin to bleed.
Characterized by a combination of symptoms of psoriasis and arthritis. Patients experience joint pain, limited mobility, fingers become very swollen, and the skin around them becomes bluish. In addition, the disease can affect the spine and sacral area. In addition to the joints, tendons and articular cartilage are also affected.
Psoriasis can occur in different forms, the main types of course are combined into pustular and non-pustular. No form of the disease can be transmitted to another person.
With psoriatic arthritis, inflammation of the joints and connective tissue occurs, which leads to deformation of the hands or feet. Psoriatic onychodystrophy is accompanied by damage to the nails. The most severe form of the disease is erythroderma. Blisters form; when the affected area is large, the body cannot maintain a constant normal body temperature.
The onset of psoriasis can be triggered by stress, exacerbation of a chronic disease and other circumstances. A malfunction occurs in the body’s immune system, which leads to increased division of skin cells and the appearance of characteristic plaques.
The first signs of the disease:
- the appearance of local areas of skin with changes;
- pathological formations are very dry;
- white or red areas rise above healthy skin;
- the plaques that appear begin to peel off.
Any form of psoriasis requires treatment. There is local and general therapy. The affected areas must be smeared with rich creams and ointments to soften and moisturize the skin. In severe cases, hormonal medications are prescribed in the form of topical medications or injections that affect the entire body.
Immunostimulants and immunosuppressants are often used, which alter autoimmune reactions. Thanks to the latest generation of drugs from these groups, the life of patients with psoriasis has become much easier. After a properly selected course of treatment, the majority experience long-term remission.
Following a diet excluding spices, foods that burden the liver and pancreas, and a ban on alcoholic beverages allow patients to live in stable remission. Health promotion in sanatorium-resort areas helps reduce the manifestations of psoriasis.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is mandatory to undergo examination at a medical institution. Characteristic symptoms of psoriasis are:
- Scarlet spots with defined edges, especially in places where the skin is damaged.
- Formation of peeling in the center of papules.
- Severe itching in areas of the rash (occurs in people with weak immune systems).
Skin pathology is characterized by gradual growth of the rash. Usually small plaques appear, which after a few days begin to multiply on the body, becoming covered with gray scales. The initial stage lasts no more than 2 - 3 weeks, and then the spots increase in size and unite, their number increases significantly.
The rash can be localized anywhere: on the elbows, arms, legs, head, nails, face. The disease appears even in children (including infants) and the elderly.
From ancient times to the present day, psoriasis has been one of the most common skin diseases. People with this disease can be found everywhere, so the question is relevant in society: is psoriasis contagious or not, and how is it transmitted? Knowledge about such skin lesions is necessary for everyone, because a friend, colleague, or loved one can have psoriasis.
- It is the lack of information about the disease that sows panic among healthy people, since the external signs of such a disease are not very aesthetic: the skin has inflamed and flaky spots and plaques of varying numbers and sizes.
- Fictions that psoriasis can be contracted through a handshake, household items, sexual contact, or through the air confuse and constrain not only those around us, but also those who suffer from this disease.
- To overcome discomfort and misconceptions about this skin disease, it is necessary to have an understanding of its characteristics and causes of its occurrence.
Peculiarities
Psoriasis, or scaly lichen, is a chronic disease that sometimes worsens in the autumn and winter. If the disease is not treated, it progresses, affecting healthy areas of the skin.
The disease shortens the lifespan of cells located in the pathological zone from 35 to 5 days. The dying cells appear as white plaque and scales, which when peeled off the skin lead to severe itching.
Squamous lichen is characterized by disturbances in the functioning of body systems, which is confirmed by the inability to renew skin cells. Cases where several people in one family have psoriasis at once speak only of the hereditary characteristics of this disease.
Lichen squamosus generally has no preference: it affects men and women equally. Most often in adults, the disease manifests itself by the age of 30. Children are also affected by this disease if they are prone to it. According to statistics, girls are more likely to get sick in childhood.
Manifestations
Prevention of exacerbation of psoriasis
Those who have latent psoriasis also need to prevent exacerbations. Everything here is very similar to the previous recommendations:
- Wear the right clothes. When choosing a wardrobe, you should give preference to a loose cut and natural materials. Clothes should not create strong friction, press, or be too tight. Particular attention should be paid to underwear; it should be made of soft natural fabric.
- Avoid stress. This is the main requirement against exacerbations; you need to try to maintain a positive attitude as much as possible. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can take additional medications to support the nervous system.
- Follow your diet. It is recommended to minimize fried, too fatty, sweet and smoked foods. Also, for prevention, it is better to avoid or minimize allergenic foods (citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts, honey).
- Replace the blanket and pillow. It is better to replace feather pillows and duvets with analogues with hypoallergenic filling.
- Do not self-medicate. This applies not only to psoriasis, but also to any other diseases. Even seemingly harmless diseases, such as acute respiratory viral infections or colds, should be treated under the supervision of a doctor and chronic forms should be avoided.
The main recommendation for the prevention of scaly lichen is to change your lifestyle. People with a tendency to this disease are advised to play sports, be sure to relax in the fresh air, and lead an active lifestyle. This will help solve several problems at once: increase stress resistance, improve health and improve appearance. The latter, scientists say, is a particularly important factor for those who have already experienced an outbreak of the disease.
Dyshidrotic eczema - what is it and how to treat it? Neurodermatitis: treatment with ointments, creams and medications Neurodermatitis: symptoms and treatment at home
Symptoms of the disease
Psoriasis has its own characteristic symptoms - the presence of psoriatic plaques. The spots can be bright pink, and sometimes red, with loose white scales.
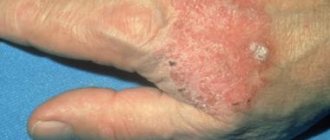
In the affected areas, the skin will rise slightly and thicken. The scales are located over areas of healthy skin. Many people compare the appearance of psoriatic plaques to hardened paraffin or wax due to their grayish-white color and shape. If the plaque is removed, healthy, shiny, red skin can be seen underneath. Most often, plaques are single and not connected to each other, although there are exceptions (advanced cases that have not previously been treated).
One of the main symptoms of psoriasis is that it initially occurs in areas of friction on the skin and body. These could be elbows, knees, buttocks. Unfortunately, dermatosis is an insidious disease. It is not limited to just these areas and sometimes occurs in more sensitive places: palms, soles, genitals. There are frequent cases of psoriasis on the nails and scalp, in the armpits.
It is necessary to distinguish scaly lichen from eczema. It, unlike it, can be located not only on the inner side of the folds, but also on the outer extensor part of the joints. Symptoms may go away almost completely with the arrival of summer. Studies have shown that psoriasis goes away when exposed to sunlight in the summer. Remission sets in. Sea air and salt water can prolong it.
The symptoms of the disease also depend on the stage of psoriasis. In remission, the plaque may appear as a shiny ring with light, wrinkled skin. During the stationary stage, you can easily determine the boundaries of the psoriatic spot by touch, which distinguishes it from seborrhea. With your eyes closed, it is not possible to determine the boundaries of skin damage caused by plaques. As psoriasis progresses, the symptoms will become more pronounced. A red rim around the entire perimeter of the plaque, not covered with scales, and the appearance of new papules at the site of a recent injury may suggest psoriasis.
Psoriasis is not a contagious disease - this is considered a proven fact
Psoriasis is a chronic disease in which changes in the skin of various areas of the body are observed, in some cases damage to the nail plates and joints occurs. The resulting red plaques with white areas of dead epidermis are often called lichen planus.
This name makes most people associate it with an infectious process and raises suspicions about whether psoriasis is contagious or not. But, the development of psoriasis occurs against the background of psycho-emotional overload, disorders in the functioning of the endocrine and immune systems, and not due to infectious lesions.
The possibility of transmission of skin psoriasis from an infected person to a healthy person is an acute issue. The disease can pose serious threats to health and is currently classified as an incurable disease.
- Lichen squamosus, the second name for skin psoriasis, is a common disease.
- Despite this, psoriasis is not an infectious disease, but has only external similarities with lichen.
A patient with psoriasis does not pose a danger to society; frequent contact with him and living in the same house cannot cause the development of psoriasis. The disease can occur in a person only if there is an existing predisposition and the pathology is activated against the background of any shock to the body.
Communication with a person with psoriasis can be a source of purely aesthetic discomfort. The danger of psoriasis to others is a myth that arose against the background of insufficient awareness of people about the nature of the disease.
This is the basis for widespread erroneous assumptions about the nature of psoriasis.
Society assigns the following etiology to psoriasis:
- fungal;
- viral;
- bacterial.
Based on the supposed nature of the disease, the most common myths about the risks of infection are:
- airborne droplets;
- domestic;
- infection through sexual intercourse;
- infection through contact with blood.
Confirmation of contagiousness is indicated by the fact that several people in one family can have it at once. Also, with close communication with an affected person, after some time psoriasis reveals itself in someone else from his environment.
Some people are inclined to believe that lichen planus is a disease that can be transmitted through airborne droplets and be a consequence of various infectious diseases.
The theory is widespread, but there is not a single medical confirmation of it.
Research in laboratories has confirmed that it is virtually impossible to contract psoriasis in this way and it is not a viral disease.
However, the name “squamosal” was given to psoriasis due to some visual similarity of the affected areas.
Psoriasis is not an infectious disease and cannot be transmitted to a healthy person through everyday contact - by touching a flaky part of the skin with your hand.
Sexual contact with a person who has red, scaly areas on the skin that resemble lichen is unacceptable for many due to their lack of awareness about psoriasis.
Lichen squamosus is not a sexually transmitted disease and does not pose a threat to a partner in the event of intimate contact.
At the same time, the pleasure received during sex increases the intensity of endorphin synthesis, this has a positive effect on the general condition of a person and improves the functioning of the nervous system.
A permanent partner is an important step in the adaptation of a sick person to normal life. In 50% of cases, sexual satisfaction influences the success of adaptation to a new lifestyle dictated by the disease.
Socialization of people with lichen planus is an important task, since the emotional and mental stiffness characteristic of patients can lead to complex psycho-emotional disorders.
The contact method of transmission is characteristic of many types of skin diseases that are provoked by pathogenic microorganisms. Bacteria, fungi and viruses can be transmitted through bedding and contact with it.
When a patient with psoriatic rashes touches various objects, exfoliated scales may end up on things, but contact with them does not pose a threat to the health of other people. The disease occurs due to disorders of the rate of cell division and does not have an infectious etiology.
In the process of caring for a person who is infected with psoriasis, it is impossible to get sick, provided there is no hereditary predisposition to this disease.
The pathology cannot be contracted by touching plaques on the skin, since lichen planus is not transmitted through household or airborne transmission. The patient does not pose a threat to others, and even with close bodily contact with him, you cannot get the disease.
Psoriasis is an immune pathology with a chronic course.
The disease reduces the quality of life, and there are no ways to achieve complete recovery, but with adequate treatment there are opportunities to achieve long-term remission, the duration of which is calculated in years.
When psoriasis is accompanied by a staphylococcal or fungal infection, pathogens remain on household items. When healthy people come into contact with them, only pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted, but not psoriasis.
It is possible to become infected with such diseases through blood transfusions, the use of unsterile medical instruments, needles in tattoo parlors, insect bites and in the prenatal period - transmission occurs from mother to fetus.
When studying the factors that provoke the disease, it is possible to determine that psoriasis is not transmitted through the blood, since it is not provoked by an infection, but by a genetic code in 9 loci and disorders of cell division of the epidermis.
Doctors have confirmed that psoriasis cannot be transmitted to a healthy person who lives with someone suffering from psoriasis, regardless of the intensity of contact.
- Also, each patient has his own “own” psoriasis, since there are many varieties of the disease, which differ in the characteristics of their course and therapy.
- In the presence of a predisposition at the gene level, the body reacts to the factors that trigger the disease differently.
- Psoriatic disease also has different manifestations in women, men and children.
The transmission of the “psoriasis gene” from parents to a child is a scientifically proven fact - about 50% of children whose parents have psoriasis also have a predisposition to it. If one of the parents is ill, psoriatic pathology is diagnosed in 10-25% of children. The disease may not make itself felt until the age of 30-35, and develop only in adulthood or old age - when immune mechanisms weaken and metabolic processes in the body become less intense.
The predisposition is already present in the genetic code of the fetus - it already contains some “defective” genes that form it in the child’s body to this pathology. Genetics have not yet discovered a way to stop this transmission of “psoriatic genes” from older generations to subsequent ones.
At the moment, doctors suggest that psoriatic disease is a specific reaction of the body to environmental irritants, which results in the formation of plaques and general erosion of the skin. According to scientists, scaly lichen can be triggered by the following unfavorable factors and effects on the body:
- The genetic predisposition of a child, which arose due to the presence of “psoriatic genes” in one of the blood relatives.
- Infectious diseases.
- Unfavorable, often cold, climate in the region of residence.
- Disorders of the body's metabolic processes.
- Abuse of alcohol-containing products, prolonged smoking, taking narcotic drugs, toxic substances.
- Immunodeficiency, which can be observed not only as an independent phenomenon, but also occur during gestation, puberty, and menopause.
- Prolonged contact with aggressive chemical compounds, including chemotherapy, burns.
Often, psoriatic disease does not manifest itself in people with high levels of health and a strong body, at least - so far doctors have not recorded such clinical cases. However, doctors point out that there are factors that can potentially trigger the disease even in a healthy person.
Such factors include the following adverse effects and conditions:
- thin and excessively dry skin;
- constant stressful situations;
- immeasurable hygiene, which inhibits the natural protection of the skin;
- addictions – tobacco, drugs and the like;
- prolonged use of pharmacological drugs;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- frequent serious injuries.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: A child has a fever, vomiting and a rash on the body
In most cases, an unreasonable exacerbation of the course of the disease and its manifestation in a healthy person is impossible. Often, psoriatic manifestations are caused by a combination of several negative effects on the body, which triggers the onset of the disease or its relapse.
The disease manifests itself regardless of age, but there is a pattern - the earlier psoriatic disease makes itself felt, the more consequences and complications a person will have.
It is not possible to completely eliminate the disease even with the most expensive and intensive treatment. In most cases, psoriatic manifestations reappear after a long period of remission.
Nevertheless, treating psoriasis and maintaining a state of remission for several years at home is possible, as is getting rid of acute symptoms and cleansing the skin of papules and plaques.
The key principle of home treatment is to monitor the progress of the disease and prevent complications of psoriasis.
It is possible to treat pathology at home using the following means:
- ointments, creams;
- lotion;
- shampoo - in case of damage to the scalp;
- baths with infusions;
- decoctions;
- powders
However, before using any products, including those based on natural ingredients, you should consult with your doctor.
- Psoriasis is not transmitted through contact with a patient, neither through a handshake, nor through touching, hugging, etc.
- When caring for a patient, psoriasis is not contagious.
- You can use common household items: towels, dishes, etc., without fear of becoming infected, since psoriasis is not transmitted from person to person through contact and household contact.
- Also, psoriasis is not sexually transmitted.
- Psoriasis is not caused by pathogenic microorganisms, therefore, a person with psoriasis is not contagious to people around him, since there is no potential source of infection.
- In cases where in one family one family member gets sick, and then others, many see this as psoriasis being contagious. However, this does not indicate a physical reason for the transmission of the disease through contact with a patient, but is explained by a hereditary disposition.
Genetics of psoriasis
Predisposition to psoriasis runs in families, so doctors usually ask patients about their family history of the disease. If one of the monozygotic twins suffers from psoriasis, then the second twin has about a 70% risk of developing the disease. But in the case of dizygotic twins, this risk is significantly lower - only 15–20% [6]. If you have a brother or sister with psoriasis, your chance of developing the disease is close to 6%. If one parent is sick, the risk increases to almost 20%, and if both parents are sick, it increases to 65%.
More than 40 regions on chromosomes are known to be associated with the risk of developing psoriasis, which are collectively called PSORS (psoriasis susceptibility loci) - psoriasis susceptibility loci. The strongest connection has a locus on chromosome 6, called PSORS1: it contains one of the genes of the major histocompatibility complex - HLA-C [7]. This gene encodes a receptor protein on the cell membrane, which is “read” by T lymphocytes to recognize “self” and “non-self” in the human body. The HLA-C receptor variant, HLA-Cw6, is found in all familial cases of psoriasis and is a marker of early onset psoriasis. Based on the presence of this antigen, cases of psoriasis are divided into two large groups. HLA-Cw6-positive psoriasis is a disease with a family history and early onset (before 40 years of age). HLA-Cw6-negative psoriasis is a late-onset psoriasis. Apparently, in the second case, the primary pathology of the immune response occurs over time, due to the influence of exogenous factors.
The HLA-C gene also plays an important role in the epigenetics of psoriasis: there is a relationship between the early onset of the disease and the level of methylation of this gene [8]. Today, scientists have not yet been able to understand whether this relationship plays any functional role in the development of the disease. Because methylation is a way of fine-tuning gene expression, it is likely that increased levels of methylation result in altered expression that may contribute to disease development. Is this so? Research in the coming years should tell us.
Symptoms
Since psoriasis is a systemic disease, it affects not only the skin, but also the joints, spine, tendons, immune, endocrine and nervous systems. In most cases, the thyroid gland, liver and kidneys are affected.
Psoriasis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe weakness;
- chronic fatigue;
- depression;
- pink-red homogeneous rash;
- deterioration in the appearance of nails;
- pronounced inflammatory process;
- unpleasant odor from cracks;
- subungual hemorrhages;
- swelling;
- stiffness of movements;
- joint pain;
- joint deformation;
- shortening the fingers.
Important! 10-15% of patients with psoriasis are diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis.
Psoriatic arthritis may cause swelling in the fingers and toes, causing pain and making it difficult to find comfortable shoes. In this case, you should seek help from an orthopedist. He will select special shoes.
Psoriasis – photo of the initial stage on the hands
Psoriasis on the hands first appears as small spots, then the spots become covered with scales.
Initially, smooth, round, small spots appear on the hands. They have clear boundaries. After a few days, the spots begin to become covered with scales, which peel off and fall off. Then the pathology progresses, the rashes increase and spread to other areas of the skin. In addition, patients notice swelling of the joints, inflammation and redness of the skin around the nails. If you damage the papule, drops of blood will appear on it.
Classification of psoriasis according to ICD-10
Psoriasis can manifest itself in many forms. Variants of psoriasis include vulgar (simple, ordinary) or, otherwise, plaque psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris, plaque psoriasis), pustular psoriasis (pustular psoriasis), guttate psoriasis, and flexural psoriasis.
This section provides a brief description of each type of psoriasis along with its ICD-10 code. .
Plaque psoriasis, or ordinary psoriasis, vulgar psoriasis, simple psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris) (L40.0) is the most common form of psoriasis.
It is observed in 80% - 90% of all patients with psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis vulgaris most often manifests itself in the form of typical areas of inflamed, red, hot skin raised above the surface of healthy skin, covered with gray or silvery-white, easily flaking, scaly, dry and thickened skin.
Red skin under an easily removable gray or silver layer is easily injured and bleeds, as it contains a large number of small vessels. These areas of typical psoriatic lesions are called psoriatic plaques.
Psoriatic plaques tend to increase in size and merge with neighboring plaques, forming entire plates of plaques (“paraffin lakes”). .
Most often, this form of psoriasis affects the folds in the external genital area, in the groin, on the inner thighs, armpits, folds under an enlarged abdomen due to obesity (psoriatic pannus), and in the folds of skin under the mammary glands in women.
This form of psoriasis is particularly susceptible to worsening by friction, skin trauma and sweat, and is often accompanied or complicated by secondary fungal infection or streptococcal pyoderma.
Guttate psoriasis (guttate psoriasis) (L40. 4) is characterized by the presence of a large number of small, raised above the surface of healthy skin, dry, red or purple (even violet), similar in shape to drops, tears or small dots, circles of lesions.
These psoriatic elements usually cover large surfaces of the skin, most often the thighs, but can also be observed on the legs, forearms, shoulders, scalp, back, and neck.
Guttate psoriasis often first develops or worsens after a streptococcal infection, in typical cases after streptococcal sore throat or streptococcal pharyngitis.
Pustular psoriasis (L40. 1-3, L40.82) or exudative psoriasis is the most severe of the skin forms of psoriasis and looks like vesicles or blisters raised above the surface of healthy skin, filled with uninfected, transparent inflammatory exudate (pustules).
The skin under and above the surface of the pustules and around them is red, hot, swollen, inflamed and thickened, and peels off easily. Secondary infection of pustules may occur, in which case the exudate becomes purulent.
Pustular psoriasis can be limited, localized, with its most common localization being the distal ends of the limbs (arms and legs), that is, the lower legs and forearms, this is called palmoplantar pustulosis.
In other, more severe cases, pustular psoriasis can be generalized, with a wide distribution of pustules over the entire surface of the body and a tendency for them to merge into larger pustules.
Pathophysiology of psoriasis, pathogenesis
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease, therefore, it develops as a result of an abnormal immune response of the body to certain environmental factors.
In addition, cytokines stimulate cells of the stratum corneum of the epidermis to more actively reproduce, as a result of which the number of rows of cells increases, and immature cells are observed in the surface layers.
Immature epidermocytes, unlike mature horny scales, ready for exfoliation naturally, have not yet lost their desmosomal connection with surrounding cells and form a characteristic macroscopic picture of hyperkeratotic scales.
To eliminate them, keratolytic agents are used, which destroy desmosomes (protein contacts between the cells of the stratum corneum) and promote more physiological exfoliation.
1.Adapted from: Nickoloff BJ, Nestle FO. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:1664-75.
Classification of psoriasis according to ICD-10
Psoriasis is a chronic, relapsing skin disease. All forms of psoriasis can be most broadly classified into non-pustular and pustular:
- Non-pustular psoriasis Ordinary, or vulgar, simple psoriasis (chronic stable psoriasis, plaque psoriasis);
- Psoriatic erythroderma (Erythrodermic psoriasis);
- Generalized pustular psoriasis (von Zumbusch pustular psoriasis);
Additional forms or types of psoriasis identified by a number of authors include:
- Drug-induced psoriasis;
- Psoriasis of the flexural surfaces and skin folds, or “reverse psoriasis”;
- Napkin psoriasis;
- Seborrheic-like (seborrheic) psoriasis.
The modern classification of psoriasis distinguishes 3 degrees of severity: mild, moderate and severe. To objectify the criteria for determining the severity of the disease, various scales and indices are used. 3 indices have become most widespread in clinical practice:
- The affected area index (BSA, Body Surface Area) expresses the area of skin with psoriasis as a percentage of the total skin surface. To determine it, you can use the rule of nines, or assume that the area of the patient’s palm is approximately 1% of the total skin area.
- PASI index (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index) The index allows you to take into account not only the prevalence of psoriasis, but also the severity of the three main symptoms (erythema, infiltration, peeling) in different anatomical areas. To determine the index, a special table is filled in or programs are used.
- The Dermatological Life Quality Index - DLQI (Dermatological Life Quality Index), is calculated based on the patient's completion of a questionnaire developed by Professor Andrew Finlay from Cardiff Medical University. The questionnaire consists of 10 questions, depending on the answers you can score from 0 to 30 points. The more points, the stronger the impact of the skin disease on the patient’s quality of life.
In addition to the indices themselves, their dynamics during the treatment process is very important, this allows us to determine the effectiveness of the latter.
Immunology of psoriasis
The main pathological processes that lead to the formation of psoriatic plaques are:
- inflammatory reaction in the dermis (deep layer of skin);
- an abnormal increase in the number of epidermal cells (which leads to the proliferation of the epidermis and the appearance of a plaque raised above the skin)…
- ...coupled with a violation of their differentiation (on the one hand, keratinocytes divide more actively and do not enter the terminal stage of differentiation in time, due to which a normal stratum corneum of the epidermis is not formed, on the other hand, dead epidermal cells accumulate on the surface of the skin, which form a flaky layer on the surface of the plaque).
Pathological cell division may be a reaction to skin damage and in this case is considered as an altered epithelial repair process.
At first glance, it is completely unclear where this strange tendency towards epithelial hyperplasia comes from. If we consider the pathological processes in the skin in detail, it becomes clear that some inflammatory changes in the dermis are observed even when there is no epidermal hyperplasia. Therefore, one hypothesis suggests that it is the inflammatory reaction in the dermis that triggers the cascade of epidermal hyperplasia.
Currently, the main role in the “pro-inflammatory” component of psoriasis is assigned to T-lymphocytes and dendritic cells, as well as to the signaling substances produced by these cells - cytokines (primarily various interleukins and tumor necrosis factor, TNF-α). The fraction of CD4+ lymphocytes is found predominantly in the deep, dermal layer of the skin even at the stage of plaque formation [5]. Due to the deregulation of immune cells (primarily dendritic cells, regulatory and effector T cells), a pro-inflammatory immune response is activated, provoking epidermal hyperplasia and the formation of a psoriatic plaque.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
As in the treatment of any other disease, the main thing is to recognize the enemy by sight and begin comprehensive treatment as early as possible. The first thing to do if you suspect you have psoriasis is to consult a dermatologist.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination, scrape the affected area and prescribe tests:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Analysis of stool for worm eggs.
Blood test Urine analysis Stool analysis We invite you to familiarize yourself with Baziron: how to use, contraindications, types
Sometimes these measures may not be enough to make an accurate diagnosis, since the symptoms of psoriasis may be blurred. In this case, to distinguish psoriasis from other similar skin diseases, a biopsy is prescribed - separation of a piece of tissue and subsequent histological examination in the laboratory.
Additionally, the doctor collects information about the patient’s clinical manifestations, complaints, as well as his lifestyle, bad habits and hereditary predisposition to the disease.