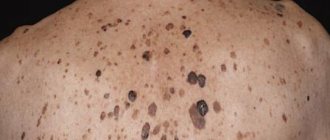
For many years, scientists and doctors around the world have emphasized the unsafety of prolonged exposure to the sun without appropriate protective measures.
One of the reasons for the negative attitude towards excess ultraviolet radiation is the possibility of the formation of keratomas on human skin.
Keratoma occurs as a result of uncontrolled growth of the epidermis. During this growth and its later keratinization, a growth is formed on the body, the average size of which varies between one and two centimeters. The tumor visually resembles a raisin.
It is this benign formation that is called a keratoma.
What it is
Keratoma is a benign neoplasm on human skin. In appearance, the keratome is shaped like an oval of brown or dark brown color. The formation may be rough to the touch and have a crust. The disease is most often asymptomatic, but there have been cases where keratomas were itchy and painful.
People often confuse papilloma and keratoma, thinking that they are the same thing. Externally, the neoplasms are a little similar, but have completely different symptoms and causes.
Types of actinic keratosis
Depending on the histological structure of the tumor, different authors distinguish different types of keratomas. Foreign doctors distinguish 6 histological types of tumor:
- acantholytic type - with pronounced destruction of the spinous layer of the skin;
- adenoid or reticular type - with enlargement of skin glands;
- hyperkeratotic, or papillomatous type - with increased exfoliation of the upper layers of the skin;
- clonal type - with the formation of many new cells of the basal layer of the skin;
- inflamed type – with pronounced symptoms of inflammation;
- irritated type – formation of easily traumatic keratomas.
In addition to those listed, 2 more rare types of keratomas have recently been identified: adamantoid, which are characterized by the accumulation of mucin in the intercellular spaces, and keratomas of the pseudorosette type, when the cells of the basal layer of the skin are arranged in a certain order.
Article on the topic: Another name for the disease is Senile Keratoma
Why does it appear
With age, the skin becomes insensitive to external factors, and epidermal cells begin to transform into keratinized tissue, rising above the skin.
Experts identify several main factors that contribute to the appearance of keratomas:
- age-related skin changes;
- disruptions in the immune system;
- diseases associated with the endocrine system;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal imbalance;
- insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body;
- uncontrolled and prolonged use of antibiotics;
- exposure to skin chemicals;
- wearing tight synthetic clothing;
- prolonged exposure to sunlight;
- hereditary predisposition (usually in the male line).
Treatment with conservative methods
Methods that allow you to influence the growth dynamics of an existing keratoma and reduce the risk of new formations include the available methods, which include:
- taking shock doses of ascorbic acid - this allows you to stop the pathological process of keratinization of the upper layer of the epidermis, improve the general condition of the affected skin and stop inflammatory processes in the skin;
- the use of external hormonal ointments that improve the condition of the upper surface of the keratoma by increasing blood supply and slowing down the inflammatory process in the skin;
- use of special sunscreens before each trip outside , which can significantly reduce the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin;
- making changes to nutrition and diet - your doctor may recommend replacing all types of animal fats with vegetable fats;
- stabilization of the psychological atmosphere - this can apply to both the home microclimate and the state at work, and, if necessary, changing the place of work.
As a conservative method, curettage of the cavity of the follicle of the hair follicle is used in the development of follicular keratoma. For seborrheic and senile forms of the disease, applications of hormonal ointments can be prescribed - they can reduce the degree of inflammation on the surface of the skin and improve the overall condition of the skin.
The listed methods do not require surgical intervention, however, they are quite effective and can bring significant benefits to the general condition and reduce the manifestations of any skin neoplasms.
What is the danger
Keratoma (not every person knows what it is and how dangerous it is) is a serious disease, primarily because it can degenerate into a cancerous tumor. To prevent this, it is necessary to consult a qualified medical specialist with subsequent monitoring of the development of the tumor.
Of all the varieties of this neoplasm, types such as solar and horny are characterized by the greatest likelihood of transition to oncology.
There are several factors that can provoke the transition of keratoma into an oncological form:
- radioactive and ultraviolet radiation;
- careless infliction of injury, including constant friction with clothing;
- incorrectly prescribed treatment.
If the keratome is damaged, the healing process will be long. The neoplasm should not be allowed to bleed; in this case, conditions will be created for infection to enter.
Where can aging warts appear?
The disease is dangerous because it affects almost any area of epithelial tissue, even those that the patient may not notice before the development of a dangerous stage. However, the most common localization areas are the following:
- in the head and face area,
- on the neck and collarbone,
- area from neck to chest,
- hands and fingers,
- legs and fingers.
Helpful information!
You should not avoid a person who has age-related keratomas, because it is not at all contagious. This disease is non-viral in nature and can only be transmitted from older generations to younger ones.
How does it affect the patient’s well-being?
A neoplasm in the form of a keratoma in most cases does not cause any discomfort to a person if it is not located in open areas of the body.
According to statistics, the main complaints are:
- itching;
- burning;
- tingling;
- cosmetic defect;
- uncomfortable wearing clothes.
Important! Not all types of keratomas can manifest themselves; some of them are invisible to humans, especially if the location is not visible to the eye.
What does a keratoma look like at the initial stage?
Once a skin keratoma begins to form, regardless of its type, the main signs and symptoms will be the same:
- Keratoma (photo - the initial stage proceeds almost unnoticed - shown in the article) implies the appearance of a small spot of a pale yellow hue.
- The spot then becomes darker in color.
- At the next stage, the neoplasm begins to rise above the skin and resemble a wart-like appendage.
- The last stage is characterized by the growth of the neoplasm in width and height with noticeable peeling and darkening.
Important! Keratoma cannot be scratched or removed on your own; this may lead to infection and development into an oncological form.
Symptoms and manifestations of seborrheic keratosis
As such, there are no tendencies to form in specific areas of the body with keratoma. The tumor can appear anywhere.
Initially, the patient notices a smooth spot on the body, the color of which varies from light yellow to dark brown. The neoplasm does not protrude above the skin and does not show a specific structure. Keratoma is characterized by slow growth, so new lesions will appear spontaneously and unnoticeably. After 50 years, the lesions tend to unite.
Over time, the spots transform into papules and nodules. They have clear boundaries and rise above the level of the dermis.
Then the papules become keratinized and become seborrheic in nature. The tumor is convex. The color becomes dark. The shape is round with a rough surface, resembling a wart. The size of the formed keratome does not exceed 3 cm.
The new growth is greasy and rough to the touch. The scales are easily separated, exposing the inside of the node. If the keratoma is accidentally caught, pain is felt and bleeding is observed. The tumor can become inflamed, which can lead to infections and fungi. Trauma occurs frequently, since the nodes are voluminous.
The clinical picture of seborrheic keratosis is represented by several stages of the disease.
1)Stage 1. Spot.
On the skin of older people, you can often see areas with dark yellow-brown spots that do not rise above the skin and do not have roughness. With age, their number gradually increases.
Spot stage
This stage usually begins around age 50 or 60, but may begin earlier in some people. This is especially true for people who like to sunbathe in the sun. At this stage there is no wart yet.
2) Stage 2. Papular form.
Small nodules and papules begin to appear on the skin. These are limited raised areas of skin just in the area of brown spots. But at this stage there is no peeling yet, and horny scales do not yet appear on the surface of the wart.
Nodules and papules appear
3) Stage 3. Keratotic.
At this stage, a keratoma appears in place of the nodule on the skin. This is a classic-looking senile wart - a brown or gray-black round or oval formation on the skin, rising several millimeters above its surface.
When scales are scraped off the surface of a wart, a bleeding surface appears.
A keratoma appears
4) Stage 4. Cutaneous horn.
This stage is characterized by excessive growth and keratinization of the seborrheic keratoma.
Keratotic keratoma
Above is a classification of the stages of the disease, which is generally accepted in medicine today. But some dermatologists believe that senile wart and seborrheic keratosis are different types of diseases.
In any case, until fundamental medicine finds the true cause of the appearance of seborrheic keratosis and senile warts, such disagreements in the interpretation of diagnoses and classifications will continue to occur for a very long time.
Senile (seborrheic, senile) keratoma - photo
Seborrheic keratoma, according to statistics, occurs mainly in old age, after fifty years. The causes of the disease have not been clarified, but experts confidently claim that it is a non-infectious pathology.
If the size of the neoplasm reaches more than 3 mm, then you need to constantly monitor the development process together with a medical specialist. Only he will be able to determine the severity of the pathology and prescribe effective treatment.
The main symptoms of seborrheic type keratomas include the following:
- Seborrheic type keratomas can be located on all parts of the body, with the exception of the feet and palms.
- New growths may be accompanied by itching or burning.
The disease develops slowly, so it is not always possible to immediately understand that it is a keratoma.
Important! If rapid growth of the tumor is noticed, you should contact a qualified oncologist for a detailed examination. These changes may indicate that the keratoma is entering the oncological stage.
Seborrheic type keratomas are determined visually at an appointment with a dermatologist. To determine the susceptibility to oncology, cells are collected, namely, a histological analysis is carried out.
Skin keratoma (photos, symptoms and treatment in adults are reflected in the article) of the seborrheic type is determined at several stages:
- Primary stage - This is the formation of unusual spots on areas of the skin. At this stage, small spots are formed, smooth to the touch or with a slight roughness. As tumors develop, they can become covered with keratinized cells and acquire a rougher surface.
- In the second stage, papules appear. The neoplasm becomes convex, resembling a wart in appearance.
- The third stage is keratotic. The formations become more pronounced, darker and denser to the touch. When the upper scales are removed from the surface, wounds are formed that bleed.
- The last fourth stage is distinguished by the fact that the keratome acquires a more rigid surface. At this stage, the neoplasm is susceptible to injury, which is fraught with infection.
Treatment of senile keratoma cannot be ignored, because in case of injury, it can develop into a malignant tumor. It is this type, compared to others, that most often turns into oncology.
Classification
Benign hyperkeratotic skin neoplasms in dermatology are classified according to clinical manifestations and the degree of risk of malignancy.
There are senile, seborrheic, horny, follicular, solar keratoma and angiokeratoma.
Seborrheic keratoma
Seborrheic keratoma appears approximately as often as senile keratoma. Its characteristics are unhurried growth with the formation of multilayer crusts.
The characteristics are as follows:
- by type - spots;
- by color - yellow;
- in size - no more than 3 cm in diameter;
- by location - most often on the chest, shoulders, back, scalp.
At the same time, there is a disruption in the functioning of the sebaceous glands - because of this, the spots in the lesion are covered with loose scales, which are easily separated.
With the development of seborrheic keratoma, the spots rarely remain separate from each other - they are grouped and can sometimes merge into a single whole. Also, such spots tend to grow along the edges. Crusts grow along with them - at the same time they begin to peel off and become covered with cracks. The thickness of such crusts in advanced cases can reach 1 cm. The keratoma becomes brown and sensitive to mechanical stress - even slight damage to it causes bleeding and pain.
Seborrheic keratoma is not prone to spontaneous disappearance or malignant degeneration.
The first sign of the disease is the appearance of a light yellow or brown spot, which looks like a small hyperpigmented area of skin. As the spot develops, it acquires a darker color (burgundy, brown, gray), while increasing in size.
The growth of the neoplasm is combined with a change in its structure: it becomes loose, soft to the touch, while including keratinized cysts in the tissues of the base, which appear when the hair follicles are blocked. Infiltration, as well as accelerated growth of individual areas, leads to the formation of a lumpy surface with alternating protrusions and depressions, layers, veins, dark spots, etc. Later, the keratoma becomes rough; the layer of cells covering it flakes off, exfoliating in the form of small grayish scales.
Senile keratoma can range in size from 0.5 to 6 cm, most often 1-2 cm in diameter. Some keratomas may lighten over time, becoming pale brown or grayish. Often, age-related keratomas have a multiple distribution pattern, localized on the arms and lower extremities, face, neck, and occasionally on the body. If damaged, the tumor is prone to bleeding and inflammation, and can cause pain.
Senile keratomas, which can be treated in several ways, are often carried out in several stages, since the disease often recurs. Among the most effective methods of treating senile keratomas are:
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave method;
- cryodestruction;
- solcoderm;
- surgical excision.
If the keratoma is multiple in nature, the patient may be additionally prescribed a course of therapy with aromatic retinoids.
In addition to age-related and seborrheic nodes, experts identify the following types of pathology:
- Follicular keratoma. This type of disease occurs near the hair follicles. The most common locations are the face, lips, and scalp. The appearance of small, colorless nodules on the body with a rough surface and a cone-shaped depression in the center is a sign of such a disease. As the papules grow, multiple clogged hair follicles (horny cysts) appear. Such a tumor is prone to recurrence even after removal.
- Solar keratoma (actinic keratosis). The main group that is susceptible to developing this form of the disease is men with fair skin. This precancerous disease is dangerous because the process of malignancy occurs hidden. At the initial stage, the patient may notice small multiple pink nodules on the body (most often on the face). As they grow, the sun seals become brown or brown in color and are covered with dense scales that come off easily.
- Angiokeratoma. This compaction does not have clear boundaries, often occurs in the scrotum area, and does not resolve on its own. Externally, it looks like a skin hemangioma. It may contain blood vessels, which is why the color of the neoplasm is blue or even black (depending on the number of capillaries). Nodes can be either single or multiple.
Large tumors covered with a thick crust can be damaged and torn off by clothing. These lumps often bleed and hurt.
Other types of keratomas with photos
There are several other types of keratomas, among them are:
- actinic;
- follicular;
- horny.
Keratoma (see photo below) of the actinic type is a disease that manifests itself after forty years. People with dry and light skin are most susceptible to this pathology. The neoplasms have an irregular rounded shape and a brown color.
There may be a slight tingling or itching sensation in the area where the keratoma has formed. This type of keratoma is localized on open areas of the skin. Follicular keratoma is a common disease that can occur in both children and adults. This type of keratoma also has names such as lichen ruber, goose bumps, and dyskeratosis.
The most common places of localization are:
- hips,
- buttocks,
- elbows,
- knees,
- head,
- hands.
Initially, symptoms such as small blood nodules, a desire to scratch the tumor, and keratinization of the skin may occur.
Horny keratoma is an overgrown tissue of the epidermis. People after forty years of age are at risk, because... It is after this age that the skin begins to react to the sun and external influences differently. This type can develop from a seborrheic (senile) type of keratoma.
The following can provoke formation:
- viral infections;
- injury to the skin surface;
- lupus (red or tuberculous);
- long exposure to direct sunlight.
Brief characteristics of skin keratomas and their localization
Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation from the sun's rays, the upper layer of the epidermis of the skin may begin to thicken, the upper part of the formation acquires pronounced pigmentation, and the density of the skin may be characterized by the formation of the stratum corneum.
The benign nature of such a formation is determined using laboratory methods, but you should not delay a visit to the doctor - the continuation of the process of keratinization and further growth of the tumor may indicate a deepening of the process of skin changes and a change in the nature of such formation is possible.
If the process continues, the keratoma can develop into squamous cell skin cancer, which is characterized by an aggressive course and the possibility of metastasis.
Most often, keratomas are located in places that are most accessible to the sun's rays - often this is the area of the face, neck, and arms . Often, after an active growth process, the keratome can be torn off on its own without requiring any intervention.
Advice from the author: since the formation in question is located mainly on the skin of the face, the occurrence of keratoma can be considered as a problem of a cosmetic nature. For this reason, if any obvious formation on the skin occurs, you should consult a doctor to establish its nature and make a diagnosis - this is what will allow you to quickly get rid of the unnecessary formation and not experience psychological discomfort.
This formation can have several of the most common types and forms, which differ in external manifestations and methods of influencing them. Let's look at them in more detail.
Which doctor should I contact?
Keratoma (what it is, how to treat it must be clarified in consultation with a doctor) is diagnosed by a dermatologist. If necessary, he will refer you for a consultation with an oncologist. But there is no reason to panic, because... this tumor can be removed.
The main thing you should not hesitate to do is visit a qualified medical specialist, otherwise you may miss the transition of the disease to an oncological form.
Details of the treatment of senile warts
Age-related keratomas must be treated so that the formations stop growing and invade new areas of epithelial tissue. You can choose one of the following methods:
- drug therapy - you will need to take pills, or smear creams and gels, give injections,
- the use of devices and tools for removal - a doctor or employee of a cosmetology center will perform the procedure for directly removing growths,
- alternative medicine - it is possible to use infusions, creams, baths, and some pharmaceuticals.
Whatever method you prefer, you should definitely consult with your doctor in advance to determine that in your case this therapy will be appropriate (even if it is treatment with folk remedies).
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a correct diagnosis, the following studies may be prescribed:
- obtaining anamnesis through physical examination;
- examining the tumor through a dermatoscope;
- carrying out histology of keratoma;
- taking a biopsy;
- conducting an ultrasound examination of the patient’s internal organs;
- taking blood to study hormonal levels;
- checking your immune status.
Treatment is prescribed only by the attending physician after studies have been carried out. To exclude the risk of malignancy, a biopsy is taken and histological examination is performed.
Removal methods
There are several methods for removing keratoma.
These include:
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- removal by radio waves;
- cauterization;
- using liquid nitrogen;
- surgical method of removal.
Removal of keratoma using a laser is considered the most common and best option for the patient. This method allows you to remove the tumor so that there are no scars or scars left. This procedure has contraindications, so first of all the patient undergoes a consultation with a dermatologist and surgeon.
Before removal begins, the area where the keratoma has formed is lubricated with a special pain-blocking gel. The laser beam acts on the tumor in a targeted manner, evaporating damaged cells and not touching healthy skin. The procedure takes no more than 30 minutes.
After removing the main formation, an additional laser beam is applied, which seals the vessels and disinfects the surface so that infection does not penetrate. A wound remains at the site of the keratoma, which heals within seven days.
Contraindications to laser removal:
- poor blood clotting;
- oncological diseases;
- pregnancy period;
- pathological processes in the respiratory organs;
- temperature;
- impairment of kidney and liver function;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis disease.
You can get rid of keratoma using electrocoagulation. This method involves applying electric current to the tumor. With its help, the affected area is literally cut out. After removal, a crust remains at the site of exposure, under which final tissue healing occurs.
You should not touch the scab during the rehabilitation period; it will fall off on its own after 14 days. This method is most suitable for treating keratomas that have not reached a large size. Keratomas are not removed using this method in visible areas of the body, so as not to leave an unsightly scar or scar.
Electrocoagulation is contraindicated for angina pectoris, arrhythmia and problems with blood pressure.
Removal of keratomas by radio wave method is most often practiced on open areas of the body, for example on the face. This procedure is carried out without contact with the skin. The skin is exposed to high temperatures, evaporating the neoplasm. A crust remains at the site of exposure, which comes off on its own without scars on the seventh day after the procedure.
Cauterization of the tumor is performed using chemicals, namely acids, alkalis and mineral salts. Today, this procedure is not relevant, as it has many contraindications and undesirable consequences.
According to statistics, people use this method at home, which is fraught with irreversible consequences. Due to an incorrect procedure, a keratoma can turn into oncology.
Getting rid of keratoma using liquid nitrogen is also a popular procedure in medical practice. The procedure takes no more than two minutes. The specialist who performs the removal dips a wooden applicator with cotton wool at the end in liquid nitrogen and presses it firmly against the keratome for 30 seconds.
Such applications are carried out until redness appears around the neoplasm. You should not be afraid of such a procedure, since the sensations during exposure to nitrogen on the problem area are compared to a slight tingling or burning sensation.
After the procedure, a crust remains, which comes off after a couple of days, and the wound heals after 14 days. There is no need to treat the area where the keratoma was after the procedure.
The photo shows the skin healing process after keratoma removal.
Surgical removal of keratoma is the standard method. The tumor is eliminated using a scalpel, after applying anesthesia. After removing the keratoma, sutures are applied, which must be removed after seven days. The removal is carried out by the doctor, assessing the quality of the operation performed.
Causes
Reasons that provoke the appearance of warts with age:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- improper diet (excess of animal fats in the diet, hypo- and avitaminosis, especially vitamins E, A, PP);
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- elderly age;
- genetic predisposition;
- concomitant diseases (oily seborrhea, leukoplakia, skin tuberculosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, etc.);
- floor. Dyskeratoses develop in both sexes, but some of their forms are more common in males (cutaneous horn);
- mechanical and chemical damage.
A peculiarity of the appearance of warts with age is that one pathological neoplasm can cause another (the skin horn can develop due to other keratoses).
What drugs are used for cauterization
Keratomas are cauterized with drugs containing active substances such as:
- glycolic acid,
- fluoruacil,
- podophyllin,
- trichloroacetic acid.
The procedure must be performed only in a specialized clinic. Self-administration of such drugs can lead to chemical burns. As a result, an irreversible process of transition of the keratoma into a malignant formation may occur.
Folk remedies
Skin keratoma in some cases is treated using folk remedies.
The most common folk recipes for the treatment of keratoma:
- Take 2 juniper leaves, 10 laurel leaves, 10 g fir oil, 100 g butter, crushed into powder. Mix everything well so that you end up with a homogeneous mass. This composition must be used to treat the tumor daily, without skipping days.
- You need to cook several potatoes, rinse them well and grate them on a very fine-toothed grater. The resulting pulp is applied to the neoplasm and fixed with a cloth or film. The holding time is at least 40 minutes. Residues are washed off with warm running water.
- Take a little castor oil and heat it in a water bath, and use a cotton pad or swab to treat the keratoma daily.
- The onion is cut in half and applied with the cut to the neoplasm. You can secure it with a bandage or cotton cloth. Such manipulations are performed before bedtime. Their duration depends on the speed of disappearance of symptoms.
- Another effective decoction is made from celandine leaves. To use, dry celandine leaves need to be brewed and wiped with the new growth composition.
- You can wipe the keratoma with an infusion of walnuts and vegetable oil. To do this, you need to bring the vegetable oil to 90 degrees and add a few walnuts to it. It is important that the nuts are unripe. It is necessary to create thermal conditions for the resulting mass, so you should place it in a specialized thermos. You need to infuse the composition for 12 hours. Before using, the liquid is allowed to cool and filtered to get rid of any small particles. The course of treatment is 14 days. The liquid is used to wipe the new growths daily.
- Internal treatment of keratosis using agrimony root. For this procedure you need to brew tea. To prepare it, take 4 tbsp. l. agrimony root and 2 tbsp. boiling water Then let it sit in the thermos for at least 4 hours. The infusion should be consumed daily before meals, ½ cup. The main thing is that the tea is warm. You should not sweeten the infusion with sugar; if you need to improve its taste, it is recommended to add 1 tsp. honey
Any use of folk remedies at home must be coordinated with a qualified specialist. It will help adjust the dosage. For greater effectiveness, procedures should be performed daily.
Preventive measures and forecasts
Preference should be given to loose, light-colored clothing made from natural fabric. A wide-brimmed hat or cap is suitable to protect your face. Glass sunglasses will keep your eye skin healthy.
Keratoma rarely affects the body of people with strong immunity. After 30 years, it is important to be physically active, perform breathing exercises, and maintain a sleep and work schedule.
Special attention is paid to the quality of food. It is recommended to include fresh vegetables or fruits in every meal. To replenish vitamin A deficiency, boiled or baked pumpkin, liver dishes, carrots, apricots and dandelion leaf salads are suitable.
If the keratoma has developed into cancer, survival rate is reduced due to the spread of atypical cells throughout the organs and systems of the human body. Fortunately, senile pathology rarely malignizes and a person lives to a ripe old age. If unknown changes appear on the body, you should consult a dermatologist to exclude malignant pathology and preserve a full life.
The prognosis for timely diagnosis of keratoma and its subsequent treatment is favorable. Regular monitoring by a dermato-oncologist is indicated.
How to avoid the appearance of new keratomas
To prevent new keratomas from arising:
- It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and regularly take vitamin complexes. This is especially true for vitamin P. It is found in buckwheat, beans, burdock, greens, and citrus fruits.
- In addition, there is no need to overexpose yourself to the sun on hot summer days. The skin can react in an unpredictable way and trigger the formation of keratomas.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing, especially synthetic ones.
- It is necessary to carry out hygienic procedures in a timely manner and treat skin folds, cleansing them of contaminants.
- If it is not possible to hide from the sun in summer, then you must definitely use sun protection creams. It is important to pay attention to the composition: titanium dioxide must be present among the components. It protects especially effectively from the sun.
This neoplasm is benign, but you need to know that there is a risk of it degenerating into malignant. At the same time, skin keratoma (photos, symptoms and treatment in adults are described in this article) is not a death sentence, because you can remove it without a trace.
Prevention
Prevention of keratosis involves avoiding the causes and factors leading to its occurrence.
Since senile changes in the epidermis cannot be avoided, a person must protect his skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation all his life, consume enough vitamins with food, try not to get nervous, and eat right.
1) Don't sunbathe
2) Take vitamins
3) A varied diet with plenty of greens, fruits and vegetables
4) Juices
5) Healthy lifestyle
6) Get more rest, less stress at work and at home
Avoiding solariums, reducing time spent in direct sunlight, and regular preventive examinations with doctors will help you protect yourself from skin keratosis shown in the photo, including rare follicular keratosis.