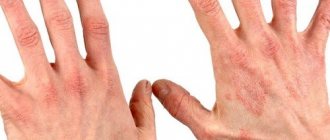
During the warm season, many people develop itchy small blisters in the thickness of the skin on their palms and fingers. The disease is called dyshidrosis of the hands, and in order not to panic and know how to treat it, it is worth studying its “passport data”.
The disease makes no exception for either children or adults; it affects both men and women equally. It should be noted that dyshidrosis is not contagious and cannot be transmitted through direct contact. Men usually get sick after the age of 40. Women - up to 25 years old. Restructuring the body in connection with pregnancy can permanently eliminate the disease. Children under three years of age suffering from diathesis are also potential victims of dyshidrosis.
Why does it appear
Medicine defines this disease as polyetiological, that is, the causes of its occurrence are diverse. Like many skin diseases, it signals trouble within the body. Doctors believe that the main culprits in the appearance of dyshidrosis are malfunctions in the endocrine, nervous and digestive systems. Heredity matters. The following factors provoke dyshidrosis:
- metabolic disease;
- exposure to allergens;
- stress;
- increased sweating;
- decreased immunity;
- chronic infections;
- long-term medication use;
- alcohol abuse;
- fungal skin diseases;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Causes of the disease
Reliably confirmed causes of the disease have not been established. There is a complex of factors that play a role in the occurrence of dyshidrosis. Most often, the disease manifests itself in the spring and summer, less often in the fall.
Possible causative factors are:
- Contact with toxic substances, which may be industrial and household chemicals, dyes, medications, pesticides, etc.
- Mycoses (fungal infections of the skin of the hands and feet), such as trichophytosis.
- Stressful situations (nervous shocks, overwork, chronic lack of sleep).
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Failures of the immune system (increased readiness of the immune system to respond to an irritant or, conversely, its decreased activity).
- Increased body sweating (hyperhidrosis).
Kinds
It is important to distinguish between the forms of the disease:
- True dyshidrosis. It is characterized by the appearance of blisters and their development until the skin peels off and the episode ends.
- Dyshidrotic eczema. It is characterized by additional rashes during periods of nervous stress, and has a chronic course with exacerbations.
Sometimes, instead of small blisters, the skin reacts to the disease with active peeling and flakes off in plates. This type is called dry lamellar dyshidrosis.
How it manifests itself
In its development, the disease goes through several stages.
- There is a feeling of itching and tingling in some areas on the palms and fingers. The skin in these areas may become warmer, but there is no change in color.
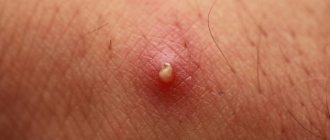
- The itching intensifies, and small bubbles with clear liquid appear in the thickness of the skin. The size is usually smaller than the head of a pin.
- The bubbles may merge, the liquid in them becomes somewhat cloudy and yellowish. The palms and fingers are somewhat swollen.
- The opening of liquid formations occurs spontaneously or as a result of scratching. If there are a lot of burst bubbles, painful sensations appear.
- The skin of the palms peels off, separates into plates, and becomes rough.
At the stage of opening of the blisters, cracks form on the skin, which easily become infected, especially when scratching. As a result, depending on the strength of the immune system, local suppuration, phlegmon, and inflammation of the lymphatic vessels appear. In severe cases, the axillary lymph nodes are involved.
Dyshidrosis of the hands photo:
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine can significantly ease the course of the pathology, especially when the disease has already entered the chronic stage:
- to reduce itching and peeling, slightly warmed sea buckthorn oil is used, which is used to treat the affected areas several times a day;
- will relieve inflammation and soothe the skin with a mixture of the juice of one lemon with the white of a chicken egg, one teaspoon of glycerin and 2 tablespoons of cologne: with this liquid it is necessary to wipe the affected areas;
- eucalyptus tincture (buy at a pharmacy) with water in a 1:1 ratio, moisten a bandage in this liquid and apply to the affected areas for 5-10 minutes;
- After the crusts have formed, you can lubricate the skin with 100 ml ointment. tar, 50 ml cream, 4 egg yolks;
- prepare an ointment with the following composition: 200 grams of vegetable oil, 100 grams of aloe, 50 grams of laundry soap, 50 grams of rosin, 50 grams of beeswax. Grind the solid ingredients, mix, bring to a boil, cook for 10-15 minutes. Lubricate painful areas several times a day;
- An ointment with the following composition is also popular: grind black currant leaves (the number of leaves per serving is about two branches of the plant) in a mortar, add 1 stick of butter, boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. Treat affected skin areas with cooled ointment. This remedy relieves itching and inflammation well;
- wash the affected areas with an infusion of crushed blackberry leaves (50 grams of leaves per 1 liter of boiling water);
- baths made from a decoction of birch buds, crushed willow bark are useful; warm baths with a decoction of string, celandine, chamomile, sage or yarrow also have a healing effect;
- Grind celery leaves or root, pour 20 grams of raw material into 150 ml of boiling water, leave in a water bath for 4 hours. Soak natural fabric in the infusion and make compresses;
- Lubricate the affected areas with grease, cover the top with waterproof paper and wrap with a bandage. At first the itching will intensify, but then it will go away. Keep the compress for one hour, rinse the skin with cool water. Carry out the procedure until the stage of remission;
- pour a glass of sea salt into a basin and add two liters of hot water. Cool slightly, then steam the affected areas until the water cools. After completing the procedure, pat your hands or feet with a dry towel and apply baby cream.
- It is recommended to drink three times a day, a third of a glass of decoction of willow bark (a tablespoon of bark in 2 incomplete glasses of boiling water), infusions of St. John's wort (1 spoon of herb per glass of boiling water), calendula flowers, yarrow, (1 teaspoon per 200 ml of boiling water), leaves sage (2 tablespoons per glass of boiling water). Consuming these herbs will help heal wounds and increase the body's resistance.
Dyshidrotic eczema of the hands
In the development of this type of dyshidrosis, all of the listed reasons are important, to which can be added prolonged exposure to the skin
- industrial hazardous substances;
- solar radiation
- local hypothermia;
- traumatization.
Doctors make a diagnosis of dyshidrotic eczema if the disease does not end with a single eruption of blisters, but their number increases with nervous stress, and an infection occurs. The patient's general condition worsens. Appear
- weakness;
- fever;
- headache;
- soreness of the skin of the palms, fingers, along the lymphatic vessels.
Clinical manifestations of eczema may be more striking than true dyshidrosis.
- Bubbles with liquid are large in size, merge and open with the formation of weeping erosion.
- The skin of the hands is swollen and there is a change in its color.
- Bubbles can appear not only on the palm, but also on the back of the hands.
Dyshidrotic eczema on the fingers photo:
For proper treatment, dyshidrotic eczema should be differentiated from other types of hand skin diseases:
- fungal infection;
- contact dermatitis;
- psoriasis
- Andrews pustular bacterid;
- chronic form of acrodermatitis Allopo.
The role of ointments in recovery
Treatment of dyshidrosis with ointments is very effective when combined with systemic therapy.
Ointments moisturize the skin and have an antipruritic effect, which allows you to avoid damaging the affected areas with constant scabies.
Some of the drugs also have an antibacterial effect, which is very important for preventing bacterial infection.
Ointments can be bought at a pharmacy, or you can prepare them yourself using traditional medicine recipes.
Dermatologists often prescribe the following ointments:
If a fungal infection has occurred, the affected areas are lubricated with Fukortsin before applying the ointment.
Only a doctor can combine drugs; you should not do this yourself to avoid the formation of unknown compounds.
Ointments can be prepared at home using butter as a base and adding sage, celandine, chamomile and others to it.
Diagnostics
Since there may be several causes of the disease, when seeking medical help you will need to be examined by several specialists:
- neurologist;
- endocrinologist;
- dermatologist;
- gastroenterologist.
During consultations, it is possible that a number of factors provoking the disease will be identified, the elimination of which will help to quickly recover or reduce the severity of manifestations.
In addition to examination and conversation, to clarify the diagnosis, doctors send for laboratory testing:
- contents of the bubbles,
- scraping the skin of the palms.
Dyshidrosis of the hands: treatment
Treatment of a disease that has several causes is carried out comprehensively. Do not neglect any of the components of therapy:
- General treatment with medications.
- Local impact
- Physiotherapy.
- Diet.
- Avoiding contact with the irritant.
It is important to remember that treatment should be carried out only as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor. Self-prescriptions can lead to the disease becoming chronic and worsening the condition.
General treatment
- Antihistamines. Used to eliminate itching and reduce the body's reaction to allergens.
- Sedative medications. They normalize nervous excitability, which provokes exacerbation.
- Immunocorrection.
- Vitamins. Normalize skin condition and support immunity.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. Non-steroidal drugs such as Indomethacin are used.
- Diuretics.
- General strengthening preparations containing calcium, magnesium and potassium.
Local impact
Treatment is carried out in accordance with the identified dominant cause of the disease.
- In case of excessive sweating and the presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the palms are lubricated with a solution of atropine 0.1-0.25% concentration. In this case, 0.5% novocaine is taken orally.
- If there is a clear connection between the exacerbation of dyshidrosis and a fungal infection, the mycosis is first treated with ointments and, if necessary, general medications.
- Then drying and anti-inflammatory ointments, baths and lotions are used. Use zinc ointment, salicylic acid, potassium permanganate, boric acid, Furacilin, Burov's solution.
- Folk remedies include lubrication with celandine juice, aloe, baths with sage, chamomile, string, and oak bark.
Physiotherapy
It is prescribed when acute manifestations of the disease subside. The goal is to normalize metabolic processes in the skin, improve blood circulation, eliminate itching and harmonize the nervous system. Considered the most effective
- magnetic therapy,
- electrophoresis,
- mud and seaweed wraps,
- acupuncture,
- paraffin applications,
- cold exposure,
- laser therapy,
- ultraphonophoresis,
- ozone therapy
- acupuncture.
Diet for dyshidrosis
Changing your diet will help relieve allergy in the body, improve digestion, eliminate adverse effects on the nervous system, and maintain a healthy heart.
Should not be consumed
- citrus,
- red fruits,
- nuts,
- chicken,
- chocolate,
- honey,
- coffee,
- tea,
- natural milk,
- canned food,
- alcohol,
- products containing gluten.
- spicy, salty, fatty.
Recommended
- fresh vegetables and fruits,
- dairy products,
- buckwheat, rice porridge,
- legumes,
- corn,
- butter and vegetable oil
- dietary meat (beef, turkey, rabbit).
Cooking method: preferably boil or steam or bake.
Drinking regime: you should drink at least 2 liters of water during the day, including juices or green tea.
Diet Basics
In the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema, the organization of proper nutrition plays an important role.
During an exacerbation, all foods with a high allergenic ability should be excluded from the diet, which helps to significantly reduce the severity of itching. These products include: exotic fruits, citrus fruits, berries (especially red ones - strawberries, strawberries, raspberries), melon, tomatoes, honey, chicken eggs, fresh milk, fish, chicken, cocoa and chocolate, coffee, canned food, pickles and marinades, smoked meats You should significantly limit, or better yet exclude, foods rich in light carbohydrates (including cakes, sweets, jam, and baked goods).
You should give preference to boiled or stewed dishes, as well as steamed ones.
| Basic diet: |
|
| Sample menu for the day: |
|
For dyshidrotic eczema of the hands, housework (washing dishes, laundry, cleaning) should only be done with protective gloves.