General information
In the first trimester of pregnancy, until about the 8th week, the process of development of the maxillofacial organs begins. If during this period the mother is diagnosed with a viral disease, a genetic failure is quite possible, as a result of which cheiloschisis, or cleft lip, develops. This is an anomaly in which the upper lip is divided into two parts by a cleft. Interestingly, this cleft can also pass through the upper palate, and can also be one of several malformations that are diagnosed in a baby.
Note! The pathology occurs in one child out of 1000. As a rule, boys are susceptible to it. According to available statistics, the cleft usually appears on the left. Moreover, the defect is detected in Asians 2 times more often than in light-skinned people.
It is known that the anomaly was first diagnosed in Ancient Egypt. At the same time, local healers began to make attempts to cure patients through surgery, as evidenced today by the remains of mummies. At that time, animal tendons were used for suturing. Later, the correction procedure was described in more detail in China.
At different times, attitudes towards people with cleft lips were different. Some considered them to be punished by the gods for their atrocities, others called them special, endowed with supernatural powers.
Today, patients with this diagnosis are recommended to consult dentists and surgeons. The anomaly complicates their lives from an early age, but is successfully corrected with the help of plastic surgery.
Diagnosis ↑
Nowadays, the existence of such a pathology in the fetus is easily determined using ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
If a cleft lip is discovered, then this is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy, because the development of the fetus is not impaired, and the child after birth will not suffer from mental retardation (unless, of course, cheiloschisis is not part of congenital pathological syndromes). Children born with a cleft lip do not differ in any way in mental and mental development from other babies.
After the birth of the baby, the doctor must fully examine the child, after which he can accurately diagnose the disease and establish the fact that cleft lip is in no way connected with mental illnesses, and that it is an independent disease.
Cleft lip: causes of development
The main reason for the development of pathology is mutations at the gene level. The TBX22 gene is involved in them, which provokes the development of cleft lip. This happens in cases where:
the mother has severe toxicosis;- she is subject to frequent stress;
- there is an infectious or radiation exposure;
- the child’s parents abuse alcohol, smoke, and use drugs;
- the family lives in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation;
- the mother has been diagnosed with chronic diseases or toxoplasmosis, herpes, rubella, smallpox, measles, cytomegalovirus, sexually transmitted diseases in the first trimester;
- Diseases are treated with antibiotics;
- vitamin deficiency is present - the mother lacks folic acid, vitamins B12, B6, , ;
- late pregnancy occurs - after 35 - 40 years;
- a uterine tumor was diagnosed;
- the mother had a history of abortions;
- the woman attempted to terminate the pregnancy;
- mechanical damage occurred as a result of falls from a height.
Heredity plays a huge role in the formation of cleft lip. That is why parents of children with this diagnosis are advised to seek medical and genetic consultation before a new pregnancy.
What complications does cleft palate cause?
The consequences of the disease can be expressed on the mental and physical level of the patient. Quite often, cleft palate is a cause of disability. It lasts until all operations necessary to eliminate all negative symptoms are completed. Another consequence of a cleft palate is the fact that the patient may have a child with a similar defect.
The most common complications of the pathology include:
- infectious diseases of the hearing organs;
- sinusitis;
- frequent colds;
- dental problems;
- disorders of the digestive system;
- dysfunction of the speech apparatus.
Symptoms
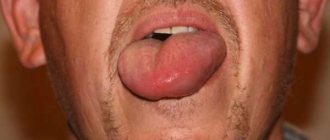
You can verify the presence of an unfused lip during the first examination of the baby. He will be found to have a unilateral or bilateral cleft on his upper or lower lip. The pathology itself affects the child’s self-esteem in the future, and therefore requires immediate correction.
Important! The situation is aggravated by the presence of a cleft palate, an anomaly that accompanies a cleft lip. Depending on the depth and size of the cleft, the doctor may prescribe feeding the baby through a nasal tube, if it is impossible to do otherwise.
The developmental defect leads to tooth deformation and malocclusion. In children with this diagnosis, some teeth may be missing in the dentition or, conversely, additional teeth may be present. They also have an incorrect angle of tooth growth, and they themselves are prone to developing caries.
Because of such problems, patients have difficulty chewing food and pronouncing sounds. They develop a nasal tone and consonants “disappear” from their speech. In some children, due to the presence of a cleft palate, the position of the ear canals may be disrupted, which increases the risk of pathogenic bacteria entering them.
Prevention
To prevent your child from developing a cleft lip and cleft palate, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- While pregnant, eat a balanced diet, including fresh fruits and vegetables.
- To strengthen the immune system, take vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Minimize the risk of contracting infectious diseases during pregnancy.
- Do not self-medicate or take any medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- Avoid the negative impact of adverse environmental factors.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy.
- Avoid medical examinations that expose the fetus to radiation.
- Do not contact people who have infectious diseases, for example, chicken pox.
To protect their child from the possibility of genetic mutation, expectant mothers are advised to be attentive to issues of their health and the future baby
Classification
Most often, a cleft appears on the upper lip on one side of the middle . Meanwhile, medicine also knows cases where the anomaly appeared on both sides of the middle or affected the lower lip.
A cleft lip may have:
- full form - when a deep crack stretches from the lip to the nose on one or both sides, resulting from non-fusion of the nasal process with the maxillary;
- partial form - when a slight depression appears on the lip as a result of nonunion.
The depth and extent of the cleft varies from patient to patient. At best, it affects the soft tissues of the lip, at worst, the palatine bone and the bone of the upper jaw.
Important! In rare cases, the anomaly occurs in isolation, but often it appears along with other anatomical pathologies, such as nasal deformities, cleft palate.
Diagnostics
The best way to see a cleft lip is immediately after the birth of the child, meanwhile, during an ultrasound during pregnancy, a specialist may notice the defect in the later stages, in the third trimester, or less often at 16–20 weeks.
Such an early diagnosis allows parents to mentally prepare for correction. Due to possible disturbances in swallowing, chewing food, speech, and breathing, this correction must be carried out at an early age.
How dangerous is the disease?
The defect, in addition to aesthetic problems, is accompanied by such phenomena as:
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Dental disorders . If the problem is not eliminated before the baby's first teeth begin to emerge, this may lead to the absence of some teeth, or, conversely, to the appearance of extra ones.
- Speech impairment . The child cannot pronounce certain sounds correctly, and his voice becomes nasal.
- Hearing impairment, possible otitis media.
- Difficulties in adaptation . The child experiences psychological problems related to his appearance.
Over time, the child’s bite becomes disturbed, and this is fraught with problems such as impaired digestion of food (since the child cannot chew it well), tooth sensitivity, and a tendency to form caries.
Cleft lip: surgery, about and after photos
The only treatment option for the pathology is surgery. A specialist performs plastic surgery, usually in several stages. If necessary, the patient is given a consultation with a phoniatrist or orthodontist.
Doctors recommend performing the operation from the second to the twelfth birthday of the child, as well as from the sixth to the eighth months . Early surgical intervention can reduce the risk of developing pathologies of the nose and upper lip. Meanwhile, newborns have a hard time coping with the blood loss they provoke. The situation is aggravated by the small size of the upper lip. At the age of 6–8 months, the risk of complications decreases due to the stabilization of the rate of bone tissue development.
Note! If there is a bilateral cleft, surgical intervention is postponed until the child reaches six months. Repeated operations are performed no earlier than after several months. Bone and cartilaginous structures are corrected at the age of 4–6 years, and correction is completed after 16 years, when the process of development of facial bones stops.
If the pathology cannot be corrected by the age of three, when speech development occurs, the doctor prescribes speech therapy treatment. If desired, plastic surgery is performed to remove the scar.
Correction methods
In order to rid the patient of pathology, the doctor carries out:
- Cheiloplasty is the simplest method that allows you to eliminate a cleft lip. During its implementation, the functional and anatomical usefulness of the problem area is restored. The procedure can be performed in several stages, depending on the severity of the situation. The incision is made linearly, when only one scar remains after the operation, or using the triangular flap method. In this case, a triangular flap is used to create a symmetrical lip shape. The quadrangular flap method involves the use of the latter for the correction of severe pathologies.
- Rhinocheiloplasty – involves correction of the upper lip and nasal septum. It can be primary (when the surgeon changes the position of the cartilage tissue for the first time) and secondary (when other pathologies begin to develop after the first operation).
- Rhinocheilognatoplasty is a complex operation that corrects the deformation of the anterior jaw, improves the shape of the lip, and corrects pathologies of the nose. The procedure is indicated for patients with cleft palate. During its implementation, the mucous membrane is peeled off on both sides in order to correct the nasal opening. The integrity of the jaw is restored through the use of a periosteum graft taken from the anterior surface of the lower leg. Then flaps are cut from the upper lip in order to stitch the wound. As a rule, after rhinocheilognatoplasty, patients are recommended to undergo dental treatment.
Important! The type of operation is selected not only based on the nature of the cleft, but also on the basis of the child’s age, weight, individual developmental characteristics, and the risk of complications.
Preparation and contraindications
Before the operation, examinations and tests are prescribed to identify contraindications to it. Two weeks before the scheduled date, patients are prohibited from taking acetylsalicylic acid and anticoagulants.
Contraindications:
underweight;- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- problems with the respiratory system;
- congenital defects of vital organs - nervous system, digestive, endocrine;
- birth injuries;
- physiological jaundice;
- anemia.
Features and rehabilitation
The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. In the first case, patients with shallow clefts are operated on, in the second - with deep clefts or bilateral ones. General anesthesia may also be given to children who are uneasy during surgery.
The duration of rehabilitation depends not only on the complexity of the procedure, but also on the general condition of the child and his reaction to anesthesia. After local anesthesia, feeding the newborn is allowed within a few hours. After the general meal, the doctor determines the meal time.
Note! Sutures are removed 7–10 days after surgery. Then, for another 3 months, a tube is inserted into the nose, which prevents deformation of its cavity and wings. In rare cases, a special headgear is recommended to prevent lip stretching and suture dehiscence. The baby's hands are fixed with splints.
Rehabilitation lasts for a year. At this stage, the patient receives consultation from a speech therapist, orthodontist, or ENT specialist, who can rule out the presence of developmental pathologies, make sure that the dentition is correctly formed and that there are no problems with speech.
Complications
The most common complication after surgery is suture dehiscence. It can occur either as a result of a violation of the technique of performing the operation, or as a result of injury, or the development of inflammation.
In rare cases, scars are possible in the area of the vestibule of the mouth, which can cause deformation of the jaw. Also possible:
- narrowing of the nasal passage;
- facial deformation;
- speech disorders.
If problems with the respiratory or digestive system are identified after the operation, a disability is assigned, meanwhile, in order to receive compensation, the child is prescribed an examination.
results
Objective results are obtained one year after the operation. Most often it ends successfully. In this case, patients develop a barely noticeable scar in the area of the nasolabial triangle, which, if desired, can be removed with a laser.
Cleft lip is a rare pathology that leads to the development of an inferiority complex in children, as well as problems with breathing, speech, and eating in the absence of medical care. Despite the fact that modern medicine offers several options for eliminating it, the easiest way is to try to prevent its development. To do this, you need to monitor your health, avoid stress, as well as crowds of people during the period of exacerbation of viral diseases.
Chumachenko Olga, medical observer
17, total, today
( 169 votes, average: 4.63 out of 5)
How to treat hair at home
The benefits and harms of solariums, rules for visiting a solarium
Related Posts
Manifestations and dangers of the defect
A cleft palate is not only a cosmetic defect; its appearance puts the baby in danger immediately after birth, when amniotic fluid can enter the baby’s respiratory tract, causing suffocation.
In addition, the defect disrupts natural processes:
- Problems with sucking and swallowing. A child with a cleft palate is unable to latch onto his mother's breast and chokes when bottle-fed. As a result, the child does not receive adequate nutrition, which affects his general condition.
- Respiratory system disorders. Already from birth, the baby’s breathing is difficult, and oxygen starvation develops. If the defect is not eliminated, the child will develop shallow, shallow breathing, which leads to respiratory failure. The brain suffers from a lack of oxygen and, accordingly, intellectual abilities decrease. The air entering the lungs is not sufficiently warmed and humidified, which leads to the appearance of inflammatory processes.
- Chewing disorders. If the split is wide and extends to the teeth line, it can create an incorrect taste. And disturbances in the process of chewing food will create an excessive load on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Speech disorders. Anomalies in the soft tissue of the palate lead to dysfunction of voice production (nasal voice, incorrect production of sounds).
A cleft palate seriously affects a person’s social adaptation. Because of their appearance, children avoid their peers, become withdrawn and shy. Low self-esteem interferes with a child’s development in society, reducing the adolescent’s quality of life.
Cleft palate in children can be successfully eliminated, although this will require the efforts of doctors and parents, because The success of treatment largely depends on the patience, perseverance and perseverance of the child’s loved ones.
The presence of cleft palate pathology causes difficulties and troubles for the baby from the moment of birth, since during childbirth there is a possibility of amniotic fluid entering the respiratory tract