- Drug treatment
Hyperhidrosis - what is it? Hyperhidrosis is a pathological condition characterized by excessive sweat production. It can occur as a consequence of certain diseases or be an individual congenital feature.
A characteristic sign of pathology is excessive sweating
Excessive sweating is a fairly common occurrence; according to statistics, approximately 2% of people experience its manifestations. However, they rarely go to the doctor with such a problem, so it is believed that the real number of patients is much higher.
Forms of pathology
There are two forms of the disease:
| Form | Description |
| Local hyperhidrosis | In this case, the whole body sweats |
| Local hyperhidrosis | Increased sweating occurs in certain areas of the body: palms, feet, armpits |
In most patients, idiopathic hyperhidrosis occurs from time to time, in response to certain stimuli (hormonal changes, stress, alcohol consumption). But in a small percentage of people, symptoms of the disease are constantly present.
According to etiology, the disease is divided into two types:
| View | Description |
| Primary | Excessive sweating occurs in the absence of any pathologies |
| Secondary | Excessive sweating indicates the presence of certain diseases |
Diagnostics
To find out how to get rid of increased sweating, a patient should definitely consult a doctor. Any self-medication can provoke the appearance of an enhanced symptom and the progression of the pathology. When turning to a doctor for help, the therapist must determine the cause of the symptom. To identify factors that provoke increased sweating at night or during the day, the patient is examined. When collecting anamnesis, the doctor should clarify the following points:
- intensity of manifestation and how long the symptom appears;
- additional symptoms - rapid heartbeat, poor appetite, weight loss, disturbed emotional state;
- are there any other diseases;
- Are there any allergies?
- frequency of stressful situations;
- whether any drugs were used.
In addition to a general practitioner, you can consult a cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, somnologist, allergist, or oncologist with a certain disease
The patient also needs to take a blood test to check for hormones and glucose. After determining the presumptive diagnosis, the patient is referred for a more accurate diagnosis using instrumental methods in order to accurately determine the source of the unpleasant symptom.
Sweat and sweat glands
Sweat is an aqueous solution that contains salts of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, uric and lactic acid and ammonia. It is secreted by sweat glands, of which there are more than 2.5 million on the human body. At normal ambient temperatures, from 400 ml to 1 liter of sweat is released.
Sweat glands are responsible for secreting sweat
In hot weather or during physical activity, the human body can secrete more than two liters of sweat , which is also normal. At the exit from the sweat glands, this liquid is transparent and odorless. Bacteria that live on the skin give it a specific aroma and a yellowish tint.
The sweat glands on the human body are divided as follows:
- apocrine . They are located in the groin and axillary region and secrete a whitish secretion containing fatty acids, cholesterol and other substances. It has a specific odor because it is a breeding ground for many bacteria. It is believed that the sweat secreted by the apocrine glands contains pheromones (substances that attract members of the opposite sex);
- Eccrine . They are located on the face, chest, back, feet and palms. They produce a clear, odorless liquid containing a large amount of salts and acids.
Through sweating, the body regulates body temperature, preventing overheating .
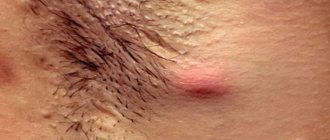
Also, sweat from the eccrine glands has an antibacterial effect, which creates an obstacle to the proliferation of bacteria on the skin and prevents the development of inflammatory processes.
Causes of hyperhidrosis
The following factors influence the process of sweating:
- increase in air temperature;
- stress;
- nervous tension;
- vigorous physical activity;
- eating spicy or hot foods.
Primary hyperhidrosis
Causes of primary hyperhidrosis include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- increased sensitivity of the body to the hormones norepinephrine and adrenaline;
- features of the functioning of the nervous system, when a large number of nerve impulses are synthesized in the cortical centers and ganglia;
- high levels of sex hormones.
Secondary hyperhidrosis
Infectious diseases
The cause of increased sweating can be both acute and chronic forms of infectious diseases:
- flu;
- tonsillitis;
- malaria;
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis.
Neurological diseases
The centers of the autonomic nervous system, which are located in the spinal cord and brain, as well as the sympathetic nerve nodes located along the spine, are responsible for the regulation of sweating. If there is a failure in any area, it can cause hyperhidrosis.
Causes of sweating can be:
- concussion;
- spinal injuries;
- inflammatory processes in soft tissues;
- Parkinson's disease;
- stroke;
- epilepsy;
- diencephalic syndrome in newborns.
Autoimmune diseases
There are diseases in which the body’s own immune cells attack the body, causing problems in the functioning of internal organs. Excessive sweating can be caused by:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- Raynaud's disease;
- systemic lupus erythematosus.
Use of certain medications
Some medications affect the functioning of the nervous system, thereby causing increased sweating. These medications include:
- antiviral agents: Gerpevir, Acyclovir, Valavir;
- antibiotics: Ciprofloxacin, Erythromycin;
- antiemetic drugs: Metoclopramide, Cerucal, Ondansetron;
- psychotropic drugs: Amitriptyline, Phenazepam, Azaleptin;
- drugs against glaucoma: Pilocarpine, Lanotan;
- hormonal agents: Prednisolone.
Psychogenic factors
In some cases, increased sweating can be caused by psychogenic factors:
- acute psychological trauma;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- neuroses;
- asthenia;
- psychological trauma;
- neurocircular dysfunction;
- severe pain.
Increased sweating may occur due to psychoemotional stress
Treatment
To diagnose and treat the disease, you must consult an endocrinologist or therapist. The doctor will conduct a survey, determining when symptoms of hyperhidrosis first appeared, and if other family members have such symptoms. The specialist also clarifies in what situations sweating increases and how much it interferes with everyday life.
To identify the causes of the disease and prescribe treatment, you must contact a therapist or endocrinologist.
Your doctor may order certain tests:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- analysis for hepatitis, HIV;
- fluorography;
- blood sugar test;
- blood test for thyroid hormones.
For diagnostic purposes, the Minor test (iodine-starch test) is performed. It allows you to identify areas of increased sweating. Before it is carried out, the skin is dried, treated with an aqueous solution of iodine and sprinkled with starch. Areas where the sweat glands are overactive turn blue. They are marked and photographed in order to carry out medical procedures.
Treatment for the disease depends on how much discomfort a person experiences. If it is not possible to cope with the problem with the help of medical antiperspirants, other methods are used.
Drug treatment
You can reduce sweating by taking drugs from the group of anticholinergics. They block the transmission of impulses to the sweat glands, thereby reducing sweating. Atropine, Scopolamine, Deprim Forte, Bellaspon, Bellataminal are used to treat hyperhidrosis.
In most cases, the effect of using such drugs occurs 10–14 days after starting treatment. The course of therapy usually lasts from 4 to 6 weeks.
The disadvantage of this treatment method is that the drugs have a large number of contraindications. Treatment of excessive sweating requires fairly high doses of medications, which increases the likelihood of side effects.
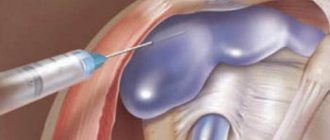
Sympathectomy
This is a medical procedure in which, using current, laser, chemicals or surgical endoscopic equipment, the nerve fibers that transmit impulses to the sweat glands are destroyed.
The disadvantage of this method is that scars or hematomas may form at the site of punctures or incisions. After surgery, half of the patients develop compensatory hyperhidrosis, in which excessive sweating occurs in the groin folds, legs or torso.
Most often, sympathectomy is performed for secondary hyperhidrosis, if it cannot be cured by other methods.
Curettage
This treatment method is used to eliminate excess sweating in the armpits. A surgical spoon (curette) is inserted through a small puncture, and with its help the sweat gland or part of the fatty tissue is removed.
The disadvantage of this method is the formation of scars, hematomas or the growth of scar tissue. This method of therapy also has contraindications.
Traditional medicine
For people suffering from excessive sweating, traditional medicine has accumulated many different recipes based on natural substances. Here are some of them.
Chamomile baths
Take 7 tbsp. l. crushed chamomile flowers and pour 2 liters. boiling water After an hour, you can take a foot or hand bath. Usually the procedure is done before bedtime, once a day.
Nettle and sage tea
One tablespoon of nettle and sage leaves is brewed into 0.5 liters. water. The resulting decoction should be drunk every other day for a month.
Horsetail compress
Horsetail leaves, alcohol and vodka are taken in a ratio of 1:5:10. A mixture is prepared and infused for several weeks. The resulting extract is used to lubricate problem areas of the skin.
In addition, oak and willow bark, ordinary table salt and vinegar are widely used as a means to reduce sweating. And, although it is not always possible to cure hyperhidrosis only with folk remedies, before resorting to drastic surgical measures, it is worth trying natural remedies.
Currently reading: Tea tree oil for excessive sweating
Consequences of hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis significantly affects a person's life and provokes social problems . The patient feels awkward in society, since the unpleasant smell of sweat causes hostility from others. In severe cases of the disease, the patient becomes withdrawn and rarely leaves the house.
Excessive sweating can seriously impair quality of life
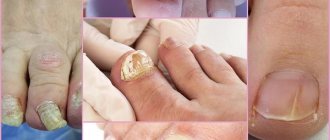
Increased sweating is characterized by an increased risk of developing mycoses, since favorable conditions are created for the functioning of the fungus.
Constant skin moisture leads to the appearance of various rashes caused by a bacterial infection. Inflammation of the sweat glands in the armpit area is often observed.
If excessive sweating causes inconvenience and you cannot cope with it on your own, you should consult a doctor.
Reviews
Patients with hyperhidrosis use various medications and folk remedies, which in itself is an indicator of their body’s attitude to such treatment, so their reviews vary significantly.
Alyona
I use Dry Dry antiperspirant deodorant, it fully lives up to its name. Friends recommended Persen, they say it helps them.
Maksim
During the day at work I run so hard that I twist my socks. I recently bought a drionic, my friends started shaking my hand and not shying away when I appeared.
Patients with excessive sweating should be reminded that before starting self-treatment, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist, therapist and neurologist. Doctors will help discover the cause of the pathology, which will lead to faster healing.