- Symptoms and brief description
- Ointment or cream?
- General recommendations for the use of non-hormonal ointments
- Children's ointments for dermatitis without hormones
- Dermatitis on the face
- Non-hormonal dermatitis creams
- When are hormonal ointments prescribed?
- Contraindications to the use of ointments with hormones
Dermatitis is inflamed redness of the skin caused by contact with allergens. This disease is typical not only for adults, but also for children even in infancy - it can be caused by a host of symptoms.
Bepanten ointment can be used even for children
Symptoms and brief description
Symptoms of dermatitis are a phenomenon that a person may not immediately notice. They can occur all at once, or several of them:
- itching;
- hyperemia;
- rash;
- peeling;
- inflammation with discharge (in acute form).
Types of dermatitis:
- photodermatitis is when rashes appear after exposure to sunlight on the skin;
- atopic dermatosis caused by a food allergen or from the external environment;
- contact type is formed by direct contact with an irritant, friction against tissue;
- Seborrheic causes excessive sebum production and the proliferation of skin fungi.
Dermatitis occurs at any age. The choice of topical agents in the treatment of dermatitis is based on a transition from weaker, hormone-free drugs to stronger drugs. Depending on the stage and course of the disease, hormonal ointments are selected for dermatitis, or vice versa. If the disease manifests itself in an acute form, then strong drugs (hormonal) are prescribed at the very beginning of therapy. In other cases, you can get by with non-hormonal ointments and creams.
Photodermatitis is caused by sun exposure
Types of dermatitis
Due to the many factors in the formation of dermatitis, several types of the disease are distinguished. The most common are allergic and contact, often found in adults; in children, atopic is mainly observed. In addition, a person may have actinic, solar or eczematous dermatitis on the hands. Each type is caused by its own negative factors, which must be identified for subsequent successful treatment.
Contact
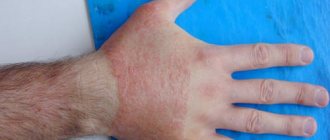
Dermatitis forms when hands come into contact with an irritating factor. It can be simple and allergic. The first is caused by chemicals, temperature changes, and mechanical influences. Symptoms appear exclusively on the contact area.
It is important to know! Dermatitis is localized on the hands due to frequent use of detergents and chemicals.
Signs of the disease depend specifically on the irritant:
- with mechanical, rashes or blisters and mild itching are noted;
- chemical - blisters, sometimes quite voluminous, create a crust after bursting;
- the effect of cold is burning, intense itching in the pathological area, inflamed foci of a bluish color, the skin peels.
| Manifestations of contact dermatitis on the hands |
Allergic contact type is caused by a response to external pathogens that the hands come into contact with. Inflammation occurs after contact with animal hair, nettles or other plants. The symptoms are always the same:
- redness and swelling of the affected area;
- blisters filled with clear liquid;
- after their breakthrough, the wound becomes covered with a crust, then peeling is noticeable.
The peculiarity of the contact type is that when the influence of the negative stimulus ceases, the inflammation gradually subsides and recovery occurs.
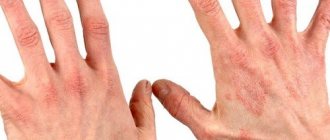
Atopic
It often has a chronic form, since it is difficult to establish its cause. The main factor in the development of atopic dermatitis is a hereditary predisposition to allergies. It is observed mainly in children. The disease is caused by:
- metabolic disorders;
- infectious pathologies;
- negative environmental environment;
- frequent stress.
| Photos of atopic dermatitis on the skin of the hands |
In this type, the inflammatory process of the skin is formed on the fingers in the area of the joints, and on the back of the palms. In the acute form, severe itching, red rashes and spots, and swelling are noted. Chronic is characterized by rough and dry skin that itches and flakes. The resulting blisters turn into pathological wounds, and then scars become noticeable.
Attention! If you consult a doctor in time for help and follow all the recommendations, use modern means for treatment, the dermatitis will gradually disappear and not a trace will remain on the skin.
Allergic
Appears in people prone to allergies. This is due to a weakened function of the immune system, as well as the presence of asthmatic bronchitis or bronchial asthma in a person.
An allergic form of skin disease is the body’s reaction to certain substances that enter through breathing or ingestion. The problem is caused by:
- food products (chocolate, eggs);
- pollen from plants, for example, maple, poplar;
- medications (sulfonamides, antibacterial drugs);
- esters released by plants;
- dust.
| Allergic form |
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis do not appear immediately after exposure to the irritant, but after some time. The skin becomes red, inflamed and swollen. Intense itching, rashes, and blisters occur. Both the hands and other parts of the body are affected. Along with this, the patient suffers from a runny nose and difficulty breathing. The consequence of the allergic form is urticaria.
Solar
A serious form of the disease, localized due to the influence of sunlight on the dermis. A distinctive feature is redness of the skin, the formation of a small rash, and this is associated with a painful sensation. Signs of dermatitis appear almost immediately after prolonged exposure to direct sun.
| Solar dermatosis |
Actinic
Develops as a result of exposure to ultraviolet light or radiation. The main difference from other types is that it does not occur immediately, but after several hours, or even days, depending on the duration of contact. Actinic dermatitis is often observed in welders and farmers. The manifestation of symptoms is directly determined by the amount of radiation exposure.
| Actinic form of dermatitis |
Eczematous
The consequence of the allergic form of the disease in adult patients is the transformation of the pathology into an eczematous form. Basically, human contact with chemical compounds or metal is enough for this.
| Eczematous dermatitis on the skin |
Signs of dermatitis appear after a couple of weeks. There is peeling of the skin, redness of the pathological area, itching, burning. If the disease is not treated, eczema will appear on the hands, and due to a feeling of discomfort, a disorder of the nervous system will appear.
Ointment or cream?
Ointments are used mainly for flaky lesions; they have a transparent color and greasy texture, with slow absorption. The cream has a light texture and is quickly absorbed, but after drying, peeling may appear. The duration of the effect is ensured by the use of local therapeutic drugs. The result depends on antihistamines and sedatives that have an antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effect.
In modern medical practice, there is a huge variety of all kinds of creams, gels, and ointments to eliminate such an unpleasant problem that both adults and children face today.
However, we should not forget that treating the external manifestations of the disease is not a panacea. The rash may reappear if the true cause is not identified and appropriate therapeutic measures are taken. What to do:
- Absorbing enough water will help get rid of dermatitis faster;
- sorbents such as white carbon, atoxil or activated carbon will not be superfluous;
- take an antihistamine;
- elimination of contacts with pathogens is mandatory;
- hypoallergenic diet.
The differences between hormonal and non-hormonal ointments are an important aspect to pay attention to.
- Non-hormonal ointment for dermatitis. The main advantage of the application is that it can be used for a long time, both by adults and children, without harm to health. They do not affect the hormonal balance of the body. The downside is that with very long use they can cause allergies, and the effect will be completely absent.
- Hormonal ointment. Prescribed for acute manifestations of dermatitis, when treatment with a non-hormonal agent does not produce results. They are divided according to the type of action into four types: from weak to maximally strong. When treating the first two types, the process is quite slow, but the risk of side effects is very low. The effect is short-term, although quick, as the body becomes accustomed to the drug. They have a negative effect on all organ systems. And there is the so-called withdrawal syndrome. The drug cannot be stopped abruptly.
Naftaderm - ointment without hormones
Antihistamines
In the pathogenesis of many dermatitis, histamine, which is normally in an inactive state in mast cells, plays a decisive role. Under the influence of external or internal factors (triggering an allergic reaction), the substance becomes active. This occurs when antigen-antibody immune complexes become attached to the mast cell membrane. Active histamine acts on special H1 receptors located on the surface of cells.
Basic pharmacological properties of antihistamines:
- antipruritic;
- antispastic;
- decongestant;
- antiserotonin;
- sedative;
- local anesthetic.
1st generation products
First generation antihistamines (Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen, Suprastin, Fenkarol) dissolve in lipids, pass the blood-brain barrier, block central serotonin and m-cholinergic receptors, acetylcholine receptors. Due to this mechanism, the sedative effect of the drugs is ensured. They act for a short time, so to achieve results they require frequent use - up to 3 times a day.
Drugs in this group quickly become addictive, so with long-term use they must be alternated.
Due to the sedative effect and slowing of psychomotor reactions, these drugs cannot be used for work that requires increased attention (driving a car, hazardous industries).
Side effect:
- fluid retention in the body;
- from the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, lethargy;
- irritant effect on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
2nd generation products
Second generation antihistamines have a weaker effect on allergic reactions. These include: Zyrtec, Zodac, Cetirizine.
Positive properties:
- High selectivity for H1 receptors.
- Well absorbed - peak concentration in blood serum after 2-3 hours.
- They do not have a depressant effect on the central nervous system.
The main disadvantage of group II antihistamines is their cardiotoxicity due to blocking potassium cardiac channels.
The therapeutic effect is carried out thanks to the main active substance - cetirizine.
It cannot be used simultaneously with antifungal agents (Ketoconazole, Itraconazole) and antibiotics (Erythromycin, Clarithromycin) due to the accumulation of metabolic products in the body and a negative effect on the myocardium.
3rd generation products
III generation antihistamines: Erius, Claritin, Telfast. They do not suppress the activity of the central nervous system and do not cause drowsiness, but the antiallergic effect is comparable to drugs of the first group.
Contraindications:
- period of pregnancy and lactation in women;
- children under 6 years of age;
- renal failure;
- lactase enzyme deficiency;
- genetically determined galactose intolerance;
- elderly age;
- heart diseases.
The side effect is expressed in a negative effect on the central nervous system and sensory organs. There are symptoms of depression (drowsiness) or excitement (nervousness, increased emotionality), impaired cognitive functions - decreased memory, attention, intelligence.
The drugs are well absorbed when taken orally. They are partially metabolized in the liver, the main part is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The half-life in adults is 10 hours.
- Zyrtec is the active substance cetirizine dihydrochloride. Acts at the first stage of an allergic reaction. By reducing the permeability of the capillary wall, the liquid part of the blood does not sweat into the tissue, which relieves swelling. After oral administration, it begins to work within 20 minutes, the maximum therapeutic effect is observed after an hour. The medicine remains in the body for 24 hours.
- Chloropyramine is a metabolite of ethylenediamine. Refers to histamine H1 receptor blockers. Reduces itching, reduces the activity of the allergic reaction. Has a sedative effect.
- Loratadine - relieves itching and swelling of tissues well. The maximum concentration in the blood is reached after 1.5-2.5 hours. Food slows down the absorption of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract. It should be used with caution in the elderly: due to an increased tendency to accumulate medication due to insufficient metabolism in the liver.
General recommendations for the use of non-hormonal ointments
Non-hormonal cream for dermatitis, like tablet drugs, is a medicine, the use of which without the consent of a doctor may not only not have an effect, but also complicate the situation.
- They begin to be treated with the weakest means, as needed, gradually moving on to aggressive drugs.
- The ointments are applied in a light layer to a clean, dry skin two to three times a day.
- Ointments are not rubbed into the skin, but wait until completely absorbed.
- If the lesions are on the scalp, it would be advisable to use lotions or liniment with a similar composition.
- If suddenly dermatitis begins to progress, then you need to stop the remedy and consult a doctor.
Hormonal ointments all contain glucocorticosteroids - hormones produced by the adrenal glands. The effectiveness of these drugs is achieved due to their effect on the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates. They are prescribed when the body does not produce enough of the hormone cortisone, which provokes an inability to cope with the inflammatory process.
Radevit is a non-hormonal mild ointment
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is basic in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults. It includes a wide range of medications.
Groups of drugs used for atopic dermatitis:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- antihistamines;
- immunosuppressants of the macrolide class;
- moisturizers of various groups.
Antihistamines
These drugs have an antiallergic effect. By blocking the release of histamine, they eliminate redness, relieve swelling, and reduce itching. They are mainly prescribed in tablet form, but can also be given as injections. This group of drugs includes medications such as chloropyramine (suprastin), clemastine, loratadine.
Glucocorticosteroids
This group of drugs is traditional in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. They are prescribed both locally (in the form of ointments) and systemically (orally in the form of tablets). Drugs in this group vary in degree of activity - weak (hydrocortisone), medium (Elocom) and strong (Dermovate). However, recently, the effectiveness of these drugs has been questioned, since very often their prescription is complicated by secondary infection
Moisturizers of various groups
This group of drugs includes various lanolin-based products, as well as those based on thermal waters. Basically, they moisturize the skin. These drugs are prescribed during the period of remission, that is, in the chronic and subacute period of the disease.
This group also includes drugs that accelerate the epithelization process. They are prescribed when patients have wounds or cracks. Like skin moisturizers, these drugs are prescribed during the chronic period of atopic dermatitis.
Immunosuppressants of the macrolide class
These drugs, like steroids, have an immunosuppressive effect. These include pimecrolimus (Elidel) and tacrolimus. The first drug was developed as a means of local therapy and is available in the form of an ointment, the second - in the form of capsules.
Children's ointments for dermatitis without hormones
The causes of childhood dermatitis are as follows:
- food allergens;
- untimely replacement of diapers, inappropriate hygiene of children's skin;
- synthetic fabrics of clothing, bed linen, inappropriate children's cosmetics;
- medicines;
- air pollution;
- infectious diseases;
- tight swaddling.
For the treatment of childhood dermatitis, ointments and powders without hormones are suitable. In the choice of drugs, preference is given to antihistamine antiseptics. Here are some of them:
- Bepanten and its analogues. It can be used from birth.
- Skin cap and Radevit.
- Naftaderm.
- Desitin does not treat infected skin areas.
- Thymogen cream or Sudocrem.
- Zinc ointment.
- Gistan is an ointment based on natural herbs. Has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Exoderil is prescribed for secondary infection.
- Epidel should be used with extreme caution. During its use, avoid exposure to ultraviolet radiation. One of the components of the medicine can cause the development of a cancerous tumor.
- Wundehil is another drug based on natural extracts. Hemostatic, wound healing, bactericidal drug.
Exoderil helps with secondary infections
Ointments and creams with corticosteroids for children are dangerous because, penetrating through the skin into the blood, they can cause adrenal insufficiency or the development of Cushing's syndrome over time.
Hormonal ointments are used in rare cases when dermatitis is in advanced form. It is especially rare to prescribe drugs with corticosteroids for children, and for adults for facial skin, since there is a high risk of thinning of the skin. You can also make a non-hormonal cream for dermatitis yourself. Sometimes, when the use of medications is not possible for some reason, you can use folk remedies by consulting a dermatologist ahead of time.
- To treat dermatitis on the hands, the following remedy is suitable: a few drops of retinol acetate in an oil solution (can be purchased at a pharmacy) mixed with baby cream.
- Mix St. John's wort flowers, whole celandine (top and root), calendula with propolis and vegetable oil. Grind the mixture thoroughly until smooth. Store in a dark, dry, cool place.
- Mix celandine powder with Vaseline. Use at intervals of four days.
Drugs approved for children
For children with severe forms of atopic and allergic dermatitis, first-generation antihistamines are used to reduce itching. These drugs have an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system and cause a hypnotic effect . Schoolchildren may experience deterioration in academic performance due to decreased attention and ability to concentrate.
Usually prescribed:
- Antihistamines of the first generation. Diphenhydramine - from 1 year, Diazolin - from 2 years, Tavegil tablets - from 6 years. Suprastin - for newborns and infants as prescribed by a doctor. Over the age of one year, tablets are allowed.
- Antihistamines of the second generation. Loratadine - from 2 years old, Zyrtec tablets - from 6 years old.
- Antihistamines of the third generation. Claritin - from 4 years old, Telfast - from 12 years old, Erius - from 12 years old in tablets. Prescribed in syrup from one year onwards.
Side effects:
- dry mouth;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- increased activity of liver enzymes (ALT, AST);
- in infants - diarrhea, chills, poor sleep, agitation.
Glucocorticoids
Hormones should be prescribed to a child with extreme caution, since complications in the form of immunosuppression can develop without obvious signs. Large doses of glucocorticoids destroy lymphoid tissue and reduce the production of antibodies.
A serious complication of hormone therapy in children is Cushing's syndrome with characteristic symptoms: obesity, stretch marks on the skin, facial acne, swelling, steroid diabetes.
To prevent such complications, a short course lasting 3-5 days is chosen for children, taking the medicine every other day. If necessary, the course is repeated after 4 days.
Drugs: Prednisolone acetate, Dexamethasone.
Tablets for dermatitis are rarely prescribed in isolation. The combination of tablet medications together with external agents significantly enhances the therapeutic effect and reduces the possibility of complications.
Dermatitis on the face
Dermatitis is an inflamed skin rash accompanied by itching and peeling. The locations on the body are different. But the most unpleasant place for its justification is the face. The first thing, of course, is to get rid of it as quickly as possible. Non-hormonal ointments for dermatitis on the face are ideal, by the way. They are used in a system with other drugs aimed at overall health of the body. Presents the following ointments:
- skin cap;
- radevit;
- isida;
- wevideam
- sun protection cream.
Skin cap - preparations for dermatitis on the face
Tablets for the treatment of atopic dermatitis
Antihistamines, membrane-stabilizing and sedatives are prescribed in tablet form.
- Sedatives. Constant, sometimes painful itching is the cause of psycho-emotional disorders. In turn, stress and tension act as provoking factors in the development of atopic dermatitis. Therefore, it is very important to normalize the patient’s emotional background in order to prevent exacerbation of atopic dermatitis. For the purpose of calming, both herbal remedies and tranquilizers are used. The first include tinctures of motherwort and passionflower, the second - alprazoles, tofisopam.
- Membrane stabilizing drugs. These drugs are prescribed in the acute period of the disease together with antihistamines. They prevent the release of allergic reaction mediators, such as histamine and serotonin. Representatives of this group of drugs are sodium cromoglycate and ketotifen.
- Drugs that normalize intestinal function. These drugs are integral in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, since pathologies of the intestinal tract can be not only provoking factors, but also the main cause of atopic dermatitis. First of all, such drugs include agents that absorb toxins from the intestines or sorbents (smectite, lignin). They are prescribed during the acute period of the disease, lasting 7–10 days. After a course of treatment with sorbents, drugs are recommended that normalize the flora and restore the protective properties of the intestines. These drugs include eubiotics (bifidumbacterin) and prebiotics (hilak forte).
In addition to the above medications, hyposensitizing drugs are used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. They are prescribed in the acute period of the disease and most often in the form of injections.
Non-hormonal dermatitis creams
The list of creams and ointments that do not contain hormones is simply huge - below you can familiarize yourself with the most popular of them and choose something suitable for your specific case.
Skin cap. Designed to eliminate unpleasant symptoms of skin diseases, including dermatitis. A broad-spectrum medicine. The release form is not only in cream, but also in aerosol and shampoo. Produced in Spain.
Actovegin is a white odorless cream. Helps accelerate the regeneration process, activating metabolic processes in the integumentary tissues, and enhances blood circulation.
Zinocap is an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drug with local action.
Desitin is a dermatoprotective ointment used for skin inflammation and irritation. Prevents the formation of diaper rash.
Eplan has a wound-healing, bactericidal effect. Creates a so-called protective film that lasts for eight hours.
Bepanten is intended to treat dermatitis in infants, as well as to heal wounds on the nipples in nursing mothers.
Naftaderm is an anti-inflammatory and itching remedy.
Histan protects skin from bacteria
Gistan is a topical antihistamine. Creates a film on the skin that allows air to pass through and prevents the penetration of bacteria and allergens.
Aisida is a new generation cosmetic product that affects the immune system and is also an antiseptic.
Radevit increases the protective functioning of the skin and eliminates keratinization.
Fenistil is indicated for itchy dermatoses of various types and burns.
La-Cri is a cosmetic product that restores the skin, created for use at any age.
Pantalfamarin is indicated for atopic dermatitis, quickly relieves itching and swelling.
Thymogen is an immunostimulant cream with anti-inflammatory action. Indicated for the treatment of a variety of dermal rashes.
Zinc ointment for dermatitis is the most versatile and safe remedy. Due to the absence of toxic additives, side effects are kept to a minimum. Broad spectrum ointment.
Solcoseryl is a nutritional stimulant. The drug is based on an extract from the blood of young calves. It does not have a disinfectant effect, therefore it is applied after pre-treatment with an antiseptic.
Videstim contains retinol, which accelerates healing and regeneration. Indicated to accelerate and heal skin rashes accompanied by dryness, peeling, and inflammation.
Losterin is a drug for daily use for dermatitis that causes dry skin. Can be used in combination with external hormonal agents.
Protopic is a selective inhibitor of inflammatory mediator compounds. Zorka stimulates tissue regeneration, nourishes and moisturizes.
Losterine can be used every day
Ointments for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults
The choice of dosage form of the drug, be it ointment, cream or emulsion, depends on the form of atopic dermatitis and the stage of its development. So in the acute phase, which is accompanied by weeping and the formation of crusts, emulsions, tinctures and aerosols are recommended. For example, chamomile tincture (which has antiseptic properties) or Burov's liquid is prescribed. If the acute phase is not accompanied by maceration (wet softening of the skin), then creams and pastes can be used. For chronic atopic dermatitis, ointments are prescribed.
Ointments and creams that accelerate the healing process:
- Solcoseryl. Thanks to its composition, it promotes tissue healing and enhances restoration processes in the area of inflammation. The gel or ointment is applied directly to the wound surface, which is previously cleaned. Apply 1 – 2 times a day, and if necessary, cover the wound with a bandage.
- Methyluracil ointment. Has an anti-inflammatory effect, stimulates and accelerates healing. Apply a thin layer of ointment to the previously cleaned damaged surface. After application, fix with a bandage.
Emollient creams:
- Atoderm. Moisturizes the skin and eliminates its hypersensitivity. The cream is applied to slightly damp but cleansed skin twice a day.
- Topicrem. Restores the lipid barrier of the skin, eliminating the feeling of tightness. Apply to dry areas of skin twice a day.
- Trixera. Reduces skin hypersensitivity, moisturizes and restores the lipid layer. Apply the cream to previously cleansed skin once or twice a day.
Antihistamine group:
Fenistil gel. Blocks H1 receptors, thereby preventing the release of histamine. The gel is applied to the itchy surface for 3 to 5 days.
Macrolide group:
- Elidel. Blocks the release of inflammatory mediators, thereby providing an antiallergic effect. The product is applied in a thin layer and gently rubbed into the affected surface. The procedure is performed twice a day for 6 – 8 weeks.
Group of glucocorticosteroids:
- Elokom. Relieves swelling and has an antipruritic effect. It is recommended to use ointment in case of severe peeling of the skin and cream if inflammatory infiltration predominates.
- Hydrocortisone. Inhibits allergic reactions and the development of edema in the lesion. Reduces redness. Apply a 1 mm layer onto the affected areas of the skin twice a day.
- Dermovate. Has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Apply a thin layer once or twice a day. The duration of treatment should not exceed 4 weeks.
Ointments and creams from various groups:
- Isis cream. Has an antiseptic effect, increases metabolic processes in the skin. Deeply moisturizes the skin and restores the lipid layer. Apply the cream with light circular movements morning and evening to damaged areas of the body.
- Ichthyol ointment. The ointment prevents excessive keratinization of the skin. It also has an antiseptic effect, thus preventing secondary infection of atopic dermatitis. The ointment is applied once or twice a day to areas of rough skin.
- Silver sulfathiazole. Promotes wound healing and prevents the development of secondary infection. A thin layer of 1 - 2 mm of ointment is applied with a tampon to the affected surface twice a day.
Any pharmaceutical drug intended for the treatment of atopic dermatitis is available in several forms. For example, solcoseryl is available in both ointment and gel form. [adsense3]
When are hormonal ointments prescribed?
Hormonal ointments for atopic and seborrheic dermatitis are prescribed without fail. They are used in a specific sequence and in combination with other medications in the system. Their long-term use leads to a stable dilation of blood vessels. Such medications give a relatively quick effect in acute manifestations of the rash, relieving the most painful symptoms. Based on the severity of dermatitis, corticosteroids may be used:
- topical;
- combined (in addition to hormones, the composition includes antibiotics)
The second type is gentle, with less hormone content. List of hormonal drugs:
- Mometasone is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid. Has antihistamine, antipruritic, anti-inflammatory effects.
- Dermovate. By reducing the formation of collagen in the skin, it has a non-specific antibacterial and antiallergic effect.
- Triderm is a corticosteroid with a local antibiotic. Shows antibacterial, antifungal effect, relieves swelling.
- Pimafukort. Indicated for dermatoses complicated by a secondary or fungal infection, Vipsogal is intended for the treatment of psoriasis and has a general therapeutic effect on the skin.
- Aurobin. Indicated for disorders of the mucous membranes of the anorectal zone and the skin of the entire body - an antipruritic, anesthetic, anti-inflammatory agent, Lorindel is prescribed for allergic dermatoses with keratinized crust.
- Celestoderm. Prescribed to eliminate signs of skin dermatitis sensitive to corticosteroids, fucicort is indicated for inflammatory dermatitis caused by bacteria sensitive to fusidic acid.
- Lokoid, lipocrem. It retains a positive result for quite a long time after stopping use. Fluorocort is a vasoconstrictor with anti-inflammatory, antihistamine action - according to patients, it is quite well tolerated.
- Betamethasone valerate. A decongestant, antipruritic drug, has low absorption into the skin, which reduces the risk of side effects; pulcortolone reduces capillary permeability, relieves swelling, itching, and inflammation.
- Diflucortolone. Reduces the number of lymphocytes and eosinophils - in children it is used under strict medical supervision, for no more than five days.
- Diprosalik. Indicated for the treatment of dermatitis on the scalp and other parts of the body, it disinfects and keratolytizes.
Hormonal ointments should, in strict order, be prescribed for use only by a doctor. Hormonal ointments for the treatment of dermatitis on the face are indicated for a short course, with sequential withdrawal. The advantage is high efficiency, the disadvantage is possible hyperpigmentation, stretching of the skin, as well as its death. May also cause acne.
However, new generation hormonal ointments are designed with minimal risk of side effects and are intended for long-term use.
Aurobin relieves irritation in the rectal area
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
The appearance of seborrhea in children is caused by the proliferation of a fungal infection that affects the delicate skin of babies. In severe cases, antifungal drugs may be prescribed. Mild seborrheic dermatitis is treated with topical agents:
- Baby or olive oil. It is applied to problem areas where crusts form and softens them. Removal is carried out using a baby comb with frequent small teeth.
- Special cosmetics for seborrheic dermatitis. These can be gels, shampoos, bathing foam. Foam shampoo Mustela Bebe and Fliderm have proven themselves well.
- Bathing a child in decoctions of celandine, string, nettle and chamomile has an anti-inflammatory and drying effect (more details in the article: celandine and other herbs for bathing newborns).
- To care for the scalp and face of newborns and older children, Bioderma Serbio or Saforel are prescribed. For the oily form of seborrheic dermatitis, products containing zinc are used (we recommend reading: how and how is seborrheic dermatitis treated in children?).
Contraindications to the use of ointments with hormones
If the ointment with the hormonal composition is selected correctly and the correct dosage is chosen, then the treatment is successful and without complications, quickly achieving the goal. However, there are a number of diseases for which this type of medication should absolutely not be used:
- acne;
- mycoses;
- herpes, chickenpox, shingles;
- scabies;
- venereal diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- diaper dermatitis in infants.
The most important thing is not to forget that only by eliminating the main problem can you forget about dermatitis once and for all.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis for adults
The treatment regimen for atopic dermatitis in adults will depend on the location of inflammation, the age of the patient, and the presence of secondary diseases.
Therapy should be comprehensive and consist of several stages: elimination of the causative factor;
- drug symptomatic treatment;
- relapse prevention,
- lifestyle correction.
It is often difficult to immediately identify the cause of dermatitis. Before allergy testing, the patient needs to review his diet. Completely exclude products with a high allergenicity index. The diet should include porridge, fermented milk products, and green vegetables. Avoid skin contact with aggressive detergents, powders, varnishes, and paints. [adsense2]
Types of dermatitis are classified by doctors depending on the triggering causes.
- Itchy dermatitis
is a “product” of the body’s reaction to contact between the nerve endings of the skin of the hands and an irritant, including those of allergic origin. Diabetes mellitus, liver and kidney pathologies are also the reasons for its development. In addition, the disease can be caused by mechanical stress: friction or pressure. - Infectious dermatitis
is caused by diseases such as smallpox, scarlet fever, etc. The rash is part of the complex of their symptoms. It can also be triggered by surgical complications of an infectious nature (streptococci, staphylococci, etc.). - Dermatomycosis
(or fungal dermatitis) manifests itself in the form of mycids (rashes characteristic only of this species). Favorable conditions for the development of fungal infections are created when immunity decreases.Forms and treatment of dermatomycosis
- Cold
(dry) dermatitis provokes exposure to low temperatures, causing spasm of peripheral capillaries. Under the influence of cold, additional dryness of the skin occurs or compounds of skin proteins are formed, causing inflammatory processes. As a result of the disease, spots of red, burgundy and bluish color (2–5 cm) appear on the integument with burning and itching. - Ear dermatitis
appears only in the specified location. The cause is scratching of the auricle or the skin around it, a fungal infection in the ear canal, or mechanical or chemical damage to the skin. - Red dermatitis
is a chronic form in which papules (nodular rash of red-pink color) form. The rash may be located on the genitals, oral mucosa, sides of the torso, or the inner surface of the joints of the hands. - Food dermatitis
(an allergic reaction to food, typical for children in the first year of life, but may appear later). Signs: seborrheic scales on the head, redness of the integument, diaper rash.
The occurrence of atopic dermatitis
Typically, dermatitis that “chooses” the hands is of an allergic nature. This form cannot be cured, you can only alleviate the symptoms. If the disease is provoked by an adverse physical effect or due to internal causes, therapy is most often successful.
The following preventive measures are recognized as effective: adherence to personal hygiene rules (especially during contact with aggressive substances), use of personal protective equipment.
Video - Dermatitis: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
What is atopic dermatitis and how do you know if you have it? Guide to the problem
How to distinguish just dry skin from atopic skin, and what products will help cope with dryness and itching?
Let's say thanks to the sub-zero temperature outside and the dry air indoors: winter is a time of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis. Although all this is not a cause, but a consequence. The cause of atopy is a disorder in DNA.
Together with experts from four dermatology brands, we decided to look into this problem. Our questions were answered:
- Tatyana Shchankina, dermatologist, valeologist, training manager of Uriage dermatological laboratories
- Elena Pasternak, dermatologist, cosmetologist, trichologist, practicing specialist in the field of aesthetic and anti-aging medicine, head of the medical department of the official representative office of Sesderma in Russia
- Alexander Prokofiev, practicing dermatovenerologist, medical expert of the La Roche-Posay brand
- Pascal Piedimonte, international trainer of the Bioderma brand
What is atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is one of the most common skin diseases. American scientists introduced the concept of “atopy” in 1923, and the term “atopic dermatitis” began to be used in 1933.
This disease is chronic (that is, it will stay with you for life, the only question is how long the remissions will be), non-contagious, inflammatory. “The main symptom of atopic dermatitis is itching,” says Uriage dermatologist Tatyana Shchankina. “This is an allergic disease that is genetically determined.”
“If you are unsure whether you have atopic dermatitis or just dry skin, think about your family members,” advises Bioderma international trainer Pascal Piedimonte. — Did any of your parents or siblings suffer from the same problem? Did they have allergic rhinitis? Asthma? Dry and itchy skin, allergic rhinitis and asthma are three manifestations of the same disease.”
“The presence of atopic hypersensitivity (rhinitis, dermatitis, asthma) in parents or close relatives determines the likelihood of AD in a child in 50% of cases,” agrees Sesderma dermatologist Elena Pasternak. “If both parents have atopy, the chances that the child will develop it are about 80%.”
Neurodermatitis and diathesis—are these separate diagnoses?
“Neurodermatitis and exudative diathesis are synonyms for atopic dermatitis,” explains dermatologist, La Roche-Posay expert Alexander Prokofiev. — Diathesis is often called infant weeping rashes on the cheeks, and neurodermatitis is dry infiltrative rashes in adults. However, these terms are becoming outdated. Currently, it is customary to call it “atopic dermatitis.”
When does atopic dermatitis first appear? Can it occur in adulthood?
Atopic dermatitis occurs in people of both sexes, different ages, living in all countries. In metropolitan areas, the incidence is higher than in rural areas. Women get sick more often - up to 65%.
There are three forms of the clinical course of AD: infant (up to two years), childhood and adolescent-adult. According to statistics, most of the first manifestations occur before the age of 5 years (90% of all cases of the disease), and in 60% of these children - already in infancy.
“It’s rare, but it happens that the diagnosis is made in adulthood,” says Pascal Piedimonte. “True, it could also mean that you simply weren’t diagnosed correctly as a child.” “At the age of 25-40, atopic dermatitis manifests itself in only 4% of cases,” says Alexander Prokofiev. “But this is also possible.”
However, in most patients by the age of 30, incomplete remission is observed (dry skin, increased sensitivity to irritants remain, and moderate seasonal exacerbations are possible). And after 40 years, a cure can occur.
What is the cause of atopic dermatitis?
First of all, the body’s hyperreactivity in response to interaction with various substances. Essentially, this is an allergy, and its “activation” is embedded in the DNA.
Allergies can occur to food products, household factors (house dust, pillow feathers, etc.), epidermal factors - pet hair and dander, bird feathers, fish food, etc. And the trigger can be psycho-emotional overload, changes in climatic zones, ecology, and diet violations.
Sometimes the cause can be found, and then it is possible to isolate the patient from the allergen. But sometimes it is impossible to determine the allergen, or contact with it is inevitable (as in the case of dust).
What exactly happens to the skin with atopic dermatitis? What is the mechanism of this disease?
Alexander Prokofiev: “It is based on a mutation with loss of function of filaggrin. Filaggrin is a special protein that is involved in the differentiation of epidermal cells. It is necessary to maintain the barrier function of the skin - it ensures adhesion and interaction between corneocytes.
If there are disturbances in the structure of filaggrin, the connections between corneocytes are weakened, and transepidermal loss of moisture increases. In addition, in the upper layers of the skin, filaggrin breaks down into organic acids (urocanic and pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic), and they are natural moisturizing factors and help maintain normal pH. If there is not enough fillagrin, the hydrolipid mantle is disrupted.
All these changes lead to the development of atopic dermatitis. The subcutaneous fat layer, which is a moisture depot, becomes thinner, the functioning of the sebaceous glands and the process of cell division are disrupted. As a result, dryness appears, inflammatory redness, cracks, and itching occur, which leads to scratching. (The complete absence of filaggrin leads to the development of another disease - ichthyosis.)
To help you understand these scientific terms, you can compare the skin to a brick wall, where the cells are the bricks and the cement is the lipid layer. With atopic dermatitis, lipid loss occurs (the composition of the “cement” is disrupted), the brick cells are poorly retained, and the wall becomes unreliable. In other words, the skin becomes fragile and vulnerable to irritants.”
What are the reasons for the spread of atopic dermatitis in the world?
According to statistics, the incidence of atopic dermatitis is increasing. An exact answer to the question “why?” scientists don't. Popular versions include unfavorable ecology and an increase in the number of allergens. As well as excessive use of aggressive detergents - shampoos, shower gels, soaps - with a high pH value.
“Living in a modern metropolis with air full of polluted particles seems to be one of the main factors,” says Pascal Piedimonte. — The skin reacts to them, inflammation occurs as a response to contact with pollution. We want to cleanse it of all this and are too carried away with products with harsh surfactants. We constantly shower with soap... In fact, this is not necessary - often just water is enough. Whether you have atopy or not, cleansing should be as gentle as possible.”
Besides dry skin, how does atopic dermatitis manifest?
“In acute cases, severe itching, red spots and papules, weeping, and swelling appear. Crusts form,” says Tatyana Shchankina. — Papules are located mainly on the face, in the area of skin folds, on the elbows and under the knees, as well as behind the ears. The skin becomes very dry and peeling appears. Outside of exacerbations, the skin remains noticeably dry and may crack, especially on the back surfaces of the hands and fingers.”
“Dry skin is just one of the symptoms,” says Alexander Prokofiev. — The presence of characteristic rashes and itching helps to make a diagnosis. Chronic inflammation is characterized by lichenification (thickening and infiltration of the skin with increased skin pattern), peeling, and scratching. These scratches not only cause discomfort, but can also provoke complications: after all, the skin is injured, and the risk of a secondary infection increases.”
“When making a diagnosis, the localization of the rash is important,” notes Elena Pasternak. “This could be the cheeks, forehead, scalp, elbows and knees - where the limbs bend.”
To make a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, you need to visit a dermatologist who will examine the skin, listen to complaints and collect anamnesis. Peeling and itching do not always indicate that it is atopy. The diagnosis is always made by a doctor, prescribing a comprehensive examination. During examination, you can also determine dermographism of the skin: you need to rub it with a blunt object, for example, a spatula. During an exacerbation, the stripe will be white; during remission, it may turn pink - this is a good sign.
What treatment can a dermatologist prescribe?
The basis of treatment is always, regardless of the severity, prevalence and severity of the process, daily basic skin care products.
If the course of the disease is mild or moderate, and skin lesions are limited, then during exacerbations, predominantly external therapy can be prescribed: glucocorticosteroid drugs and calcineurin inhibitors.
Alexander Prokofiev: “In severe cases, systemic therapy is prescribed - it can be hormonal and cytostatic. But the main thing is always the regular use of emollients (fats and fat-like substances that can be fixed in the stratum corneum of the skin and soften it - Ed.). If we remember what changes occur in the skin, it becomes clear that patients’ protective function suffers due to impaired production of lipids (fats).”
“Dermatological cosmetics significantly reduce the frequency of exacerbations, increasing the period of remission,” says Tatyana Shchankina. — This care is aimed at increasing the barrier function of the skin. If dryness is not eliminated, it will not be possible to get rid of scratches and cracks that lead to infection.”
What should be included in cosmetics for atopic dermatitis?
Tatyana Shchankina, Uriage: “Moisturizing ingredients - urea, mucopolysaccharides, hyaluronic acid, glycerol. Emollients - shea butter, panthenol. Emollients are lipids that can be fixed in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. And, of course, complexes of components that soothe itching, restore the skin barrier, reduce inflammation, and stimulate the production of antimicrobial peptides are important. Uriage has products from the Bariederm and Xemose lines.”
Cerate lipid-restoring cream against irritations Xemose, Uriage
Restoring cica cream with Cu-Zn Bariederm, Uriage
Restoring drying cica spray with Cu-Zn Bariederm, Uriage
Elena Pasternak, Sesderma: “Moisturizing and anti-inflammatory. These are ceramides, polyunsaturated fatty acids, humectants and anti-inflammatory components (tranexamic acid, niacinamide, glycyrrhetinic acid, boswellic acids, red grape extract, milk proteins, etc.). To make the ingredients work better, liposome forms or lamellar emulsions are used.”
Body milk for dry, reactive, atopic-prone skin with liposome ingredients Atopises, Sesderma
Moisturizing oil for sensitive and atopy-prone skin Atopises Oil, Sesderma
Alexander Prokofiev, La Roche-Posay: “Moisturizing agents - glycerin, oils (shea butter, macadamia butter), vitamin E, urea, hyaluronic acid. Soothing, restorative and anti-inflammatory ingredients. These include components of natural sebum: ceramides, triglycerides and phospholipids. Panthenol and niacinamide restore the skin, relieve inflammation and accelerate healing. There are also components that help restore the skin microbiome - La Roche-Posay has, for example, Aqua Posae Filiformis.”
Lipid-restoring balm for face and body Lipikar Baume AP+, La Roche-Posay
Stick for skin prone to irritation and itching, Lipikar AP+ Stick, La Roche-Posay
Pascal Piedimonte, Bioderma: “The most basic ingredients of emollients for atopy are those that moisturize (for example, glycerin) and those that create a film on damaged skin that it cannot create on its own (this prevents moisture loss). They already bring relief to atopic patients. All additional ingredients are designed to extend the effect of the cream, which, for example, only works for you for 10 hours out of 24, for a longer period. This is possible by stimulating the skin with various ingredients to produce its own proteins and lipids. That's why we added vitamin PP to the Atoderm line in 2000 - studies have shown that it stimulates the production of natural lipids. And in 2007, a special plant extract was added that affects inflammation-causing staphylococci in the skin microflora.”
Remedy for quick relief of itching SOS Spray, Atoderm, Bioderma
Softening ultra-nourishing balm with anti-itch effect Atoderm PP Baume, Bioderma
Balm Atoderm Baume Intensive, Bioderma
Do I need to use cosmetics for atopic dermatitis constantly or only during exacerbations?
All experts agreed that cosmetic care is required constantly. “It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it,” says Tatyana Shchankina. Alexander Prokofiev agrees with her: “You need to use competent care even outside of exacerbations. You can choose lighter milk or emulsion textures at this time. In children, even during the inter-relapse period, the skin should be shiny from creams. All this will reduce the risk of such a formidable complication as the “atopic march” - the development of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma.”
My atopic dermatitis cream only helps for half a day - by lunchtime I start to itch. What to do?
“It is better to select products for basic use in atopy with a specialist,” says Elena Pasternak. — In addition to cream, cleansing products (never soap!) and “intensive care” products are important. The most pronounced effect will be if you use all this constantly. In winter, it is preferable to switch to denser textures. The cream should be applied either 15 minutes before or 15 minutes after using the anti-inflammatory drug. It is important that the volume is sufficient: an adult consumes up to 600 grams per week, a child consumes up to 250 grams per week. If used consistently and correctly, the use of corticosteroids can be avoided or limited.”
Alexander Prokofiev: “You have to choose the right emollient by trial and error. You need to moisturize your skin as needed, this can be 5 times a day or more often. In winter, when there is frost outside and dry air in heated rooms, more frequent use of emollients may be required. At work, they can be applied locally in the most sensitive areas; for this, there are more compact formats, for example, sticks to relieve itching and moisturize the skin (like Lipikar AP+).”
What should and should not be done if you have atopic dermatitis?
Not recommended:
- Take long showers and baths. “Prolonged contact with water destroys the protective hydrolipid layer,” says Alexander Prokofiev. “Try to keep water treatments no longer than 10 minutes, and then you need to moisturize the skin.”
- Wash in hot water. It provokes itching.
- When wearing clothes made of synthetics and wool, it is better to have a layer of cotton fabric between the skin and these fabrics.
- Sunbathe. Sun rays also lead to a decrease in local skin immunity and disruption of the barrier layer.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol. “Smoking and alcohol add damage, and atopic skin is already damaged,” reminds Pascal Piedimonte. Avoid even passive inhalation of tobacco smoke.
- Comb and rub the skin.
- Use hard washcloths.
- Use alcohol-containing products, such as lotions.
Recommended:
- Maintain a temperature at home of 20-22C.
- Install a humidifier, this is especially important during the heating season.
- Avoid stress.
- Avoid intense physical activity that leads to increased sweating.
- If a food allergen is identified, follow a diet. “A third of patients may experience exacerbation of dermatitis as a result of food allergies,” advises Alexander Prokofiev. “But if a food allergy is not diagnosed by a doctor, then there is no need to torture yourself with hypoallergenic diets; on the contrary, food diversity will only strengthen the body.”
- Avoid fragrances and fragrances, as they can be allergenic and lead to exacerbations.
- If you wear perfume, apply it not to your skin, but to your clothes to reduce the likelihood of contact with allergens.
- Avoid using irritating cleansers. Alexander Prokofiev: “You absolutely cannot use soap! Ordinary bar soap has a sharply alkaline pH and degreases the already fragile protective hydrolipidic mantle of the skin.” Use specialized products - they often have the words Syndet in their names (syndet is a synthetic detergent, a soap-free mild detergent), “soap-free” or soap free.
- When working with paints, varnishes, and solvents, wear gloves and a mask.
- If the water in your house is very hard, it is better to wash your face with boiled water or install a filter.
“And the main advice,” insists Pascal Piedimonte, “is to use creams constantly. Experience shows that people, unfortunately, do not do this. Often the reason is that they don't like the product - it's boring, no fragrance, no interesting textures. Using this cream makes you remember that you are sick with something, and this is unpleasant. Those who suffer from atopic dermatitis want the same beautiful and pleasant products that others use. We know about this and are working in this direction - for example, we are looking for hypoallergenic fragrances.”
What else can you do to help an atopic?
- The doctor may recommend that you take B vitamins. “They increase the effectiveness of treatment,” says Elena Pasternak, “and accelerate skin restoration processes. The stability of cell membranes increases, lipid oxidation is regulated, and the immune system is stimulated.”
- Your doctor may also recommend taking polyunsaturated fatty acid complexes (PUFAs). They participate in the restoration of lipid metabolism and increase the protective functions of the skin.
- Vitamin C may be useful (it is responsible for the production of interferon, the deficiency of which results in insufficient stabilization of lysosomes) and vitamin A (with its deficiency, macrophages are poorly regulated, cellular reactions become non-standard).
Photo: © Yuichi Ikehata
How to treat dermatitis on the body in an adult
If the disease is detected at an early stage, the use of antihistamines internally and externally is quite sufficient treatment. In complicated clinical pictures with the appearance of purulent wounds and exudative rashes, oral antibiotics in the form of tablets and the use of external corticosteroids are necessary. If signs of dermatitis are preceded by increased activity of a fungal infection, treatment should include antifungal agents.
Drug treatment
The attending physician decides whether to take hormones or antibiotics, based on the characteristics of the clinical picture. If there are no complications, the adult patient is prescribed antihistamines orally. These are tablets Claritin, Loratadine, Cetrin, Suprastin, Fenistil, L-Cet, Tavegil and others. The course of intensive therapy varies between 7-14 days and is adjusted by the doctor on an individual basis. If one allergy medicine is not suitable, it must be replaced, taking into account the body's compatibility with the active components.
Additionally, pay attention to representatives of the following pharmacological groups:
- sorbents: Enterosgel, activated carbon;
- probiotics: Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Hilak Forte;
- antibiotics: Rovamycin, Doxycycline, Sumamed, Zitrolide, Erythromycin;
- antiviral drugs: Acyclovir, Famvir, Valtrex, Alpizarin;
- multivitamin complexes for dermatitis.
Local treatment
Dermatitis appears not only on the face; the presence of a characteristic rash is possible on the back, buttocks and other parts of the body. If taking pills kills a pathogenic infection from the inside, then the external use of creams and ointments helps to effectively eliminate a cosmetic defect, reduce the intensity of unpleasant sensations, and completely eliminate discomfort from your daily life. Here are the medications doctors prescribe for the treatment of dermatitis in adults:
- anti-inflammatory drugs: Elokom, Diprosalik or Akriderm;
- local products for skin regeneration: Solcoseryl, D-panthenol, Bepanten;
- corticosteroid drugs: Elokom, Afloderm, Lokoid, Advantan.
- antifungal agents: Triderm, Pimafucort;
- local antibiotics: erythromycin ointment;
- antimicrobial compounds: Fukortsin;
- local antiseptics.