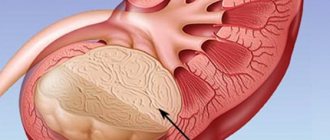
Sarcoma is diagnosed in children and adults. This is a common cancer. It is not tied to a specific organ and affects connective, muscle and bone tissues. In the first stages of growth, the appearance of swelling and nodes is noted, after which spasms appear. Symptoms depend on the specific type of pathology. Treatment is carried out by an oncologist.
Reasons for appearance
Sarcoma is a complex of cancer diseases that develop in the soft and bone tissues of the body.
The exact origin of the tumor cannot be determined. Occurs due to exposure to ionized radiation on the body. A person can receive such radiation at work and during the treatment of other pathologies. Radiation affects human DNA, which leads to mutations. Oncology spreads after contact with chemicals (benzene, asbestos), which also negatively affect the state of DNA and RNA.
Oncopathology develops from benign neoplasms (fibroadenomas, etc.). A person is at risk if he has the hepatitis virus, immunodeficiency virus or herpes. The disease also appears as a result of injury. This occurs because cells in the body begin to regenerate and divide rapidly. Therefore, the body cannot timely identify immature cells that form a tumor.
Genetic pathologies are common causes of sarcoma. These include:
- Gardner's syndrome;
- Wermer's syndrome;
- neurofibromatosis;
- retinoblastoma.
Bad habits, such as smoking, are a predisposition to the development of cancer.
In addition, cancer develops in the following cases:
- hormonal imbalance and accelerated growth in young men;
- diseases in the lymph nodes;
- nicotine abuse;
- genetic predisposition.
Why does a bone tumor develop?
Osteogenic bone sarcoma is more common in children during the period of bone growth or in the elderly. In adolescents, Ewing's sarcoma of the ilium or other areas of the musculoskeletal region is often diagnosed. The neoplasm is characterized by rapid progression and an aggressive course. The pathology develops independently and is dangerous due to the spread of metastases to other organs. The main causes of the tumor have not been established by doctors, but predisposing factors are as follows:
- frequent bruises or fractures;
- bacterial damage to bone tissue, for example, with osteomyelitis;
- professional activities associated with contact with pesticides and their subsequent accumulation in the body;
- living in areas with high levels of radioactivity;
- genetic predisposition;
- malignant formations in surrounding tissues, for example, sarcoma of the humerus develops due to tumor metastases in the neck, upper spine, and skull bones.
Types of oncology
Primary and secondary sarcoma are distinguished. The first type indicates that the tumor is the initial focus of pathology. In the second case of oncology, these are metastases. Oncology is divided into pathology of soft and bone tissues. There are approximately 70 species. Their division occurs according to the principle of localization of the tumor in the tissues of the body. If the disease is difficult to classify using histology, then it is an undifferentiated sarcoma. The most common types are sarcoma of the bones, uterus, mammary glands, skin, gastrointestinal tract, neck and head. The treatment method for the patient depends on the type of disease. There are such varieties, which are detailed in the table:
| Name | Structure and description |
| Osteosarcoma | Formed from the cellular parts of bone tissue |
| Reticulosarcoma | Distributed in the bone marrow |
| Chondrosarcoma | Represented by cartilage tissue |
| Paraostral | Based in the periosteum |
| Ewing's sarcoma | A subtype of osteosarcoma that affects the ends of bones |
| Fibrosarcoma | Consists of a variety of connective tissues |
| Kaposi's sarcoma | Affects the vascular system and lymph nodes |
| Liposarcoma | Localized in adipose tissue |
| Lymphosarcoma | Affects the lymphatic system |
| Neurofibrosarcoma | Grows from nerve sheaths |
Types of sarcoma depending on height:
- poorly differentiated;
- moderately differentiated;
- highly differentiated.
What is sarcoma and its types
Sarcoma forms in soft tissue structures containing fatty tissue, layers of connective tissue, tendons, and striated muscles.
Soft tissue sarcoma is an oncological disease with a high mortality rate; it has a tendency to rapidly metastasize and form secondary lesions in the lung, liver and other tissues. Sarcoma can occur on any part of the human body where there is soft tissue - on the buttocks, fingers, back, forearms, legs, feet, etc. Most often, soft tissue tumors (STT) are located on the lower extremities, on the hips, less often they can be found on the arms, neck, and head.
Soft tissue sarcoma can be dense, soft or jelly-like to the touch, without a capsule, and usually forms as a single tumor, but multiple formations can also occur. For example, fibrosarcoma is a dense tumor to the touch, liposarcoma or angiosarcoma is soft, myxoma is jelly-like.
Localization
A malignant neoplasm occurs in soft tissues, and it is not tied to a specific organ.
The pathology is not tied to a specific organ. Cancer and sarcoma differ in location. The difference is that the latter disease occurs in bone, connective, muscle and fatty tissues. Secondary foci of the disease are the results of metastases. They do not contain the cells of the tissue in which they are located. For example, angiosarcoma spreads to the bones, but is composed of blood and lymph vessel cells.
Causes of bone sarcoma formation
People of all ages are at risk for developing the disease. A defect in cellular DNA is the clear and primary cause of the disease. The main predisposing factors for this pathology are:
- benign neoplasms;
- viral diseases not treated in time;
- injuries of varying severity;
- environmental conditions;
- irradiation in the form of x-rays, radiation exposure;
- congenital pathologies in the body;
- hereditary factor of morbidity.
With reduced immunity, the likelihood of disease increases several times. Due to physical stress on the body, the immune system weakens; smoking and alcohol also negatively affect the development and course of the disease.
Symptoms of disorders
The differences in the signs of the disease depend on its location. But the main symptom is spasms that cannot be relieved with antispasmodics or analgesics. With the development of disorders, it manifests itself as spots on the skin, expansion of the venous network, and an increase in local temperature. Fatigue and inactivity appear. Often accompanied by deformation and swelling of body parts. Sarcoma differs from cancer in its delicate pink surface color. The tumor looks less lumpy. The difference is that this type of oncology spreads faster to neighboring healthy organs.
The following symptoms of sarcoma are characteristic of the pathology of the lymph nodes:
- rashes and swelling on the skin;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- sudden weight loss;
- dyspnea;
- bluish color of lips;
- voice changes;
- pallor;
- high sweating;
- heat.
Signs of soft tissue sarcoma:
- the appearance of swelling;
- spasms when touching a swollen area;
- temperature;
- itching
Prognosis and prevention
Any form of malignant disease, and bone sarcoma is no exception, is insidious in that relapses often occur after treatment. To exclude the possibility of a recurrence of this terrible disease, you need to regularly visit an oncologist to identify unwanted symptoms. The frequency of visits depends on the severity of the disease.
It is advisable to eat foods that cleanse the blood lymph of toxins and block the spread and formation of new metastases:
- sea fish with high fat content: herring, trout, salmon, saury, mackerel;
- garlic in any form;
- vegetables that are green and yellow in color: peas, zucchini, cucumbers, asparagus, cabbage, bell peppers, carrots, pumpkin;
- cold (first) pressed olive oil;
- a large amount of liquids, including juices, mineral water.
The prognosis for osteosarcoma depends on certain factors both before and after treatment. Factors influencing the prognosis before treatment for osteosarcoma:
- Size and location of the tumor.
- Stage of osteosarcoma (localized tumor, presence of metastases in other organs).
- Age and general health of the patient.
After treatment, the prognosis is determined by the effectiveness of chemotherapy and the outcome of surgery. A more optimistic prognosis is with a significant reduction in the site of stasis and the primary lesion after chemotherapy, as well as with complete removal of the tumor.
In the past, osteosarcoma was one of the malignant tumors with the most unfavorable prognosis. Even though severe mutilating operations were performed during treatment - amputation and disarticulation of limbs, the five-year survival rate did not exceed 5-10%. Currently, due to the emergence of new treatment methods and the use of effective organ-preserving operations, the chances of patients for a successful outcome have increased significantly even in the presence of metastases in the lungs.
Diagnostic methods
To identify the location of the tumor and its size, magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
To begin therapy, it is necessary to examine the patient to determine the location of the tumor, growth rate, stage of development and depth of the lesion. They take a general blood test and do a biopsy to find out what tissue the tumor consists of. A biopsy is performed with histological, cytochemical and cytological examination of tissues. Ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance and computed tomography (MRI and CT) are done to see the location and outline of the disease.
In addition, diagnostic procedures such as:
- radiography;
- neurovascular diagnostics;
- radionuclide research;
- Dopplerography;
- angiography.
Diagnostics
As symptoms increase, a person consults a specialist. Signs such as pain, bleeding, dark-colored formation, metastases confirm the presence of a tumor process. First of all, after examining the patient, a doctor prescribes a diagnosis to determine the type and nature of the tumor.
Diagnostics consists of the following procedures:
- Biopsy;
- Histology;
- Immunological research;
- Blood tests.
A mandatory test is a biopsy. It is prescribed for taking biomaterial from the lesion for the purpose of histological examination.
Histology will determine the type of sarcoma and the degree of malignancy.
Immunological examination reveals malfunctions of the immune system. Based on the results obtained, it is determined whether there is a need to restore immunity and prescribe therapy.
A blood test helps determine the presence of anemia and the number of white blood cells. The blood is tested for HIV, since this infection is a common cause of the tumor process.
If necessary, additional CT, MRI and tumor marker tests are prescribed. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging will help determine how affected the skin is and whether metastases are present.
Tumor treatment
He is being treated in the oncology department. The detected tumor must be excised. Excision is carried out together with nearby healthy tissues in which cancer cells can develop. If a malignant tumor affects bone and muscle tissue, then the limb has to be amputated. After this, chemotherapy is carried out to stop the development of the cancer process. Using a drip, potent chemicals are administered intravenously, which slow down the development of pathology. Radiation therapy is also used for treatment. This method uses ionizing radiation that affects the tumor and metastases.
Therapy for different stages of sarcoma is treated differently, more details about this in the table:
| Stage | Treatment |
| First | They use surgical methods to remove pathology and lymph node dissection, after which chemotherapy or radiation therapy is used |
| Second | |
| Third | Combined method of all treatment methods |
| Fourth | The pathology is often incurable |
| Removed only if the tumor does not affect vital organs |
Preventive recommendations
Giving up bad habits and proper nutrition will help prevent the onset of the disease.
The best prevention is a healthy lifestyle. Doctors strongly recommend getting rid of bad habits, avoiding stress and overwork. The daily diet should be complete. Meals may include fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, nuts, and fresh berries. It is recommended to devote more time to sports. Some people live a long time and do not pay attention to changes in their body. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a systematic check with doctors in order to identify violations in time.
Treatment measures
After an accurate diagnosis is made, complex treatment is prescribed, which involves surgery to remove the tumor, a course of chemotherapy and radiation. Considering that the bones in the hands are thin, gentle surgical intervention with the removal of only the tumor formation and part of the healthy tissue is ineffective and often leads to relapse.
To increase the chances of a full recovery, doctors most often recommend amputation of a limb. In addition, regional lymph nodes are removed. Radiation may be prescribed as an adjunct to surgery. Radiation therapy reduces the risk of tumor recurrence. When treating hand sarcoma, the following chemotherapy drugs are often used:
- Adriamycin.
- Cyclophosphamide.
- Dacarbazine.
- Doxorubicin.
- Vincristine.
- Epirubicin.
Radiation and chemotherapy have a negative effect not only on tumor cells, but also on healthy tissue. Such treatment regimens are selected for patients individually in order to reduce the adverse effects of these methods of therapy on the patient’s body.
Patients are required to be prescribed medications to eliminate symptomatic manifestations. Medicines are often used to relieve intense pain and signs of dysfunction of internal organs.
If sarcoma was detected in the late stages of the pathological process, palliative treatment is prescribed to improve the patient’s quality of life.
To increase immunity and improve the general condition of the patient, a gentle diet may be recommended. Food should be taken in small portions. Food needs to be steamed, stewed or boiled. It is recommended to include in the diet:
- dairy products;
- vegetables and fruits;
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- vegetable oils;
- cereals;
- cereals;
- honey;
- herbal teas.
The patient needs to actively fight depression. After completing a course of treatment, to reduce the risk of relapse, patients need to normalize their wakefulness and sleep patterns. Stress and physical overexertion should be avoided. After stabilization of the patient’s condition, it is recommended to spend time in the fresh air as often as possible and perform a complex of exercise therapy.
Prognosis for sarcoma
The survival rate depends on the type of cancer and progression. Thus, gastric sarcoma begins to metastasize early and quickly, which makes therapy difficult. Retroperitoneal is dangerous because it is difficult to identify and diagnose. In this case, treatment for sarcoma may begin too late. On average, the 5-year survival prognosis for stages 1 and 2 with a comprehensive therapy program is 75%. At 3 tbsp. the percentage drops sharply to 30%. 16 percent of people experience local tumor recurrence. At stage 4, sarcoma can rarely be cured completely.
Life prognosis for osteosarcoma in children
For osteogenic sarcoma in children, the prognosis depends on several factors:
- tumor size and presence of metastases;
- histological type of sarcoma;
- its location;
- volume of formation removal;
- reaction to chemotherapy.
The prognosis for people with cancer of the bones of the arms or legs is slightly higher than for those with cancer located in the torso and head.
High life expectancy for osteosarcoma in children who underwent radical surgery, and the response to chemotherapy showed good results. Statistics show that a poor response to chemotherapy reduces the chances of survival by almost 2 times. Recurrence of osteosarcoma also significantly worsens the prognosis.
In general, a 5-year life expectancy is observed in 60-70% of young patients who have undergone complex treatment. A young body recovers faster; the main thing is to notice the signs of the disease in time and start therapy in a timely manner.