Detected nail fungus during pregnancy causes anxiety in women. The infection can manifest itself not only on the legs, but also penetrate inside the body. And this can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus in the womb. After the birth of a child, the risks of transmission of infection are also high. The infant's imperfect immunity reacts negatively to exposure to nail fungus. Constant contact with a sick parent is a favorable condition for repeated infections, so it is important to treat onychomycosis before the baby is born, and not postpone solving the problem until later.
Causes of onychomycosis
The appearance of fungus on the nails and feet during pregnancy is provoked by endogenous (internal) factors. These include:
- Deficiency of minerals and vitamins entering the body with food;
- Hormonal changes;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases of internal organs;
- Hyperhidrosis of the feet;
- Anomalies in the development of the feet (flat feet, narrow spaces between the toes, deformation of the fingers and toes);
- Tendency to dermatitis, which is accompanied by the formation of ulcers and wounds on the skin of the feet;
- Edema of the lower extremities;
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus);
- Presence of endocrine diseases;
- Somatic problems;
- Excess body weight.
Causes of onychomycosis
Important!
The vitality of fungal flora outside a living organism is extremely stable. Favorable conditions for its reproduction are moisture, dust, and warmth. Favorite places for fungus to accumulate:
- Public transport handrails;
- Chairs, benches, deck chairs;
- Bathroom partitions;
- Wet floor;
- Rugs, towels.
Therefore, during pregnancy, exogenous (external) factors of infection with nail fungus should be taken into account:
- Use of common things, shoes;
- Visiting public saunas, baths, showers, locker rooms;
- Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules when visiting public places;
- Professional affiliation.
The trigger for onychomycosis can be wearing tight shoes made of synthetic materials that do not allow air to pass through. Foods high in sugars and carbohydrates accelerate the development of fungus. Salon pedicure procedures are undesirable during pregnancy; the infection can be transmitted through poorly treated accessories of the master. The source of infection of a woman with nail fungus during pregnancy can be relatives or pets.
Prevention of fungus in pregnant women
To prevent a woman with a child at heart from encountering this problem, she must follow several important rules:
- You cannot walk barefoot in pools and beaches; you must have personal slippers;
- Do not wear rubber shoes for a long time;
- Shoes should not be too small;
- It is better to refrain from using other people's slippers, socks and other clothing;
- Bedding and linen should be changed promptly;
- You need to eat well to prevent a weakened immune system.
Doctors also advise pregnant women to eat dairy products, which will help maintain the correct microflora in the body.
important In any case, a pregnant woman should remember that at the first manifestations of fungus, she should consult a specialist. It is not worth using folk remedies alone and delaying professional treatment, because it is easier to get rid of the disease in the initial stages, when you can get by with the use of local remedies. This will help maintain the health of the unborn child.
Risks during pregnancy
Onychomycosis is dangerous for both the expectant mother and her child. In cases where due attention is not paid to the treatment of the fungus during pregnancy, the following is noted:
- infection is a factor in the exacerbation of congenital diseases;
- as a strong allergen, the fungus enhances the symptoms of allergic diseases (rhinitis, bronchitis, asthma);
- onychomycosis further undermines the weakened immune reserves of the female body;
- the infection in adults and children becomes chronic, affects internal organs, and as a result disrupts their functions;
- the fungus suppresses the immunity of children, reduces its resistance to infections of bacterial and viral origin.
Development of complications with onychomycosis
Important!
Ignoring nail and foot diseases on the part of a pregnant woman in the first trimester is a risk of miscarriage. The Candida fungus is insidious in this regard.
Diagnostics
If an expectant mother notices suspicious spots on her fingernails or toenails, she should consult a dermatologist. Laboratory tests are performed to diagnose onychomycosis. To conduct the study, take a piece of the nail (in the distal form) or make a scraping from the nail plate.
The analysis allows you to determine the type of pathogen, as well as select the most effective remedy for nail fungus.
Types of pathogens and symptoms of onychomycosis
Regardless of the genus and species, the foot fungus actively multiplies during pregnancy, forming new foci of infection outside the nail plates. The most vulnerable is the cracked, dry skin of the feet.
The causative agents of onychomycosis are:
- yeast fungi (unicellular organisms - Candida);
- mold fungi (mold – Scopulariopsis, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis);
- dermatomycetes (parasites, keratinophilic organisms - Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitale).
The fungus brings discomfort into the life of a pregnant woman:
- itching of the periungual fold, between the fingers, feet;
- burning in the area of greatest accumulation of infection;
- pain in the lower extremities due to the formation of deeper cracks and ulcers.
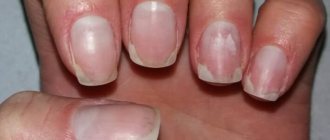
Unpleasant sensations in many cases are complemented by an aesthetic problem - a change in the appearance of the toenails. Under the influence of the fungus, they become brittle, change their healthy color to a yellow or brown tint, and peel off from the base.
Itching, burning and pain due to foot fungus
Description of the disease
In medicine, fungal nail diseases are called onychomycosis. This infection is extremely common, but many sufferers ignore it until the nail begins to break down.
Advice! In the early stages, the disease seems to be purely a cosmetic problem, but if the disease is not treated, then after some time physical discomfort will appear.
The development of onychomycosis can be triggered by different types of pathogenic microorganisms, in particular, it can be fungi:
- filamentous;
- moldy;
- yeast-like.
Spots on nails are essentially accumulations of pathogenic microorganisms. Fungi not only destroy the nail, but also have a negative effect on the entire body. In particular, the immune system suffers, as a result of which a patient with a fungus may begin to experience allergic reactions.
Forms
Depending on where the nail is affected, three forms of the disease are distinguished. This:
- Subungual distal. The most common option. At the first stage, a yellowish spot appears in the corner of the tip of the nail. If left untreated, the spot increases in area, gradually covering the entire plate. In later stages, the nail begins to deteriorate.
- Subungual proximal. With this form, the first signs of nail damage can be seen at the inner edge. The lesion then spreads over the entire area of the plate. This form is relatively rare.
- Superficial. With this form, white spots appear on diseased nails; they can be located in the center or along the edges. The infection is located on the upper part of the plate, so the nail itself begins to deteriorate only if the infection is not treated for a long time.
Advice! The superficial form is noted only when the toenails are affected. This form is the easiest to cure, since the infection is located on the surface of the plate, and not under it, as in the case of other forms of the disease.
It is possible that other forms of nail damage may develop, so you should definitely get diagnosed by contacting a specialist.
Stages
The fungal disease develops gradually. The rate of development of the disease is determined by the type of fungus.
Advice! Onychomycosis caused by yeast-like fungi progresses most quickly.
Depending on the stage of the lesion, three main stages are distinguished:
- Initial. At this stage, only minor changes are noticeable - the appearance of spots on the nail, loss of shine.
- Progressive. The spots occupy more than half the area of the nail plate, and the nail may begin to thicken, become deformed, or become thinner.
- Launched. The nail is destroyed and peels off from the nail bed.
Ideally, treatment should be started at a very early stage of the disease; in this case, you can get by using only external agents or even folk methods.
Principles of drug therapy for nail fungus
For onychomycosis, pregnant women are prescribed antifungal drugs, despite the fact that many antifungal drugs are not recommended for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is possible to cure nail fungus through topical application, while the use of oral medications is strictly contraindicated.
Important!
Self-medication of nail fungus during pregnancy and lactation is unacceptable! Specific antimycotics are prescribed only by the attending physician based on the results of laboratory tests!
Fungicidal ointments, creams, varnishes, used during pregnancy, help suppress the fungus in the first stages of development. These drugs inhibit pathogenic microflora and promote the restoration of damaged nail plates, the healing of the periungual epidermis, and the skin of the feet. Medicines for nail fungus for external use are intended to eliminate superficial onychomycosis. They do not penetrate into the general bloodstream, so they cannot negatively affect the baby in the womb.
Local anti-fungal preparations are applied to the affected nails after preliminary preparation, which includes:
- foot baths with the addition of sea salt or soda;
- cutting down the destroyed nail plate, which is the site of the greatest accumulation of fungus;
- treating extremities with antiseptic wipes or solutions.
The list of effective drugs approved for use in the treatment of nail fungus during pregnancy includes:
- Ointment, spray, solution, cream, gel Lamisil (terbinafine) Novartis Consumer Health (Switzerland);
- Spray, gel Totaldez (terbinafine, herbal extracts) Domix Green Professional (Russia);
- Ointment, varnish, serum Mikozan (rye enzyme) Serrix Consumer Health (Netherlands);
- Tinedol ointment (essential oils, lanolin, vitamin E) INAT-Pharma LLC (Russia);
- Ointment, solution, spray Mikoseptin (zinc salt of undecylenic acid) Zentiva / Lechiva (Czech Republic);
- Ointment, solution Mycospor (bifonazole, urea) Bayer AG (CIS);
- Cream, solution Exoderil (naftifine hydrochloride) Sandoz GmbH (Austria);
- Cream Travogen (isoconazole nitrate) Schering AG (Germany);
- Cream, ointment, solution Clotrimazole (clotrimazole) Glaxo-Wellcome Poznan (Poland);
- Cream Fundizol (zinc oxide, salicylic acid, vegetable oils, celandine extract) LLC Infarma 2000 (Russia);
- Lac Loceryl (amorolfine hydrochloride) Laboratoires Galderma (France);
- Varnish, cream Batrafen (ciclopirox olamine) Aventis, Roussel Laboratoires (France);
- Gel Mycogel (miconazole nitrate) Arterium (Russia);
- Ciprosept drops for external use (grapefruit extract, vitamin C, bioflavonoids) Chintomani LLC (Russia);
- Solution, spray Miramistin (Miramistin) FC Infomed (Russia).
Effective and approved drugs during pregnancy
Local antiseptics are effective and harmless in the fight against nail fungus. During pregnancy it is recommended:
- Hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide) Yuzh-Pharm LLC (RF);
- 5% alcohol solution Iodine (iodine, potassium iodide) AGM LLC (RF);
- Tablets Hydroperit (urea peroxide) OJSC Tatkhimfarmpreparaty (RF);
- Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) CJSC Obnovlenye (RF);
- Boric petroleum jelly (boric acid) JSC Rassvet (RF);
- 1% solution Salicylic acid (salicylic acid) Bayer JSC (RF);
- Chlorhexidine solution (chlorhexidine) Rosbio LLC (RF);
- Taimurov paste (boric acid, salicylic acid, zinc oxide, lead acetate) Muromsky Industrial Plant (RF);
- Sulfur ointment (sulfur) Murom Instrument-Making Plant (RF);
- Balm Star (essential oils) Danafa Pharmaceutical Joint (Vietnam).
Treatment with traditional recipes
If a woman in an “interesting” position notices the manifestation of this disease, you can also use traditional methods of treatment:
- Golden mustache. The leaves of this plant need to be crushed and the resulting juice taken. It must be rubbed into the diseased nail plate, and then wrapped in cellophane and a bandage. This allows the affected area to be softened and removed easily. After each removal of part of the nail covering, the area is covered with tar purchased at the pharmacy. This technique will help fight the infection in the initial stages.
- Propolis with alcohol. To prepare the tincture, you need to take 100 grams of alcoholic liquid and 10 grams of the plant. Before applying the product, wipe the nail plate with potassium permanganate. Afterwards, the sore spot is generously covered with tincture and bandaged.
- Egg and dimethyl phthalate. You need to take 1 egg, 1 tablespoon of medicinal product and 1 teaspoon of oil, mix it all and apply it to your fingers. They need to be kept warm. Treatment is used for 4 days before bedtime.
important Traditional methods may not be effective for a pregnant woman. She shouldn't rely on self-medication. The best solution would be to consult a doctor so that he can prescribe the correct treatment.
Antifungal diet during pregnancy
It is not always possible in practice to stop the negative effects of an active infection only with the help of antifungal ointments and antiseptics. A combination of drug therapy and diet improves the results of treatment of toenail fungus during pregnancy.
Dietary nutrition is aimed at stimulating the immune system. The daily diet of a pregnant woman does not include foods that promote the proliferation of fungal flora:
- Smoking, pickling;
- Alcoholic, carbonated sweet drinks;
- Yeast baked goods;
- Fatty meats and fish;
- Sweets (sweets, jam, ice cream, chocolate, sweet fruits, cakes);
- Delicacies with mold;
- Semolina and rice cereal.
Despite the exclusion of tasty foods, a pregnant woman’s diet remains healthy if it includes:
- Whole wheat bread;
- Dairy products;
- Low-fat broths;
- Vegetable soups;
- Lean meats (rabbit, turkey, chicken);
- Seafood;
- Mousses and compotes from unsweetened fruits and berries without added sugar;
- Fresh vegetables and herbs;
- Vegetable oils (sunflower, olive);
- Nuts;
- Buckwheat, oatmeal, wheat, pearl barley;
- Mint, lemon balm, chamomile tea.
Allowed foods for an antifungal diet
What is the danger?
The disease is not dangerous for the child, but it brings quite unpleasant sensations to the woman during pregnancy. An expectant mother should not use many remedies for the treatment of onychomycosis, as a result of which problems arise in eliminating the symptoms of fungus on the nails.
The disease can be transmitted from mother to newborn, and it will be more difficult to cure the disease, since the symptoms may spread to the deeper layers of the nail plate - antibiotics will be required.
Clinical picture
Athlete's foot and trichophytosis are often combined under one term - “mycoses of the feet”, which is directly related to the similarity of their course. They have four main forms: squamous, dyshidrotic, intertriginous and onychomycosis. Candidiasis is separate. The following table will help you understand in detail the symptoms and manifestations of each form of infection.
| A form of fungal infection | Symptoms and clinical manifestations |
| Squamous | Initially, the fungus affects only one foot, gradually moving to the second. At the site of the skin lesion there is an area of redness, which subsequently begins to peel off. Areas of peeling and redness may vary in size. Another symptom is itching, which may not be experienced by everyone. Often the clinical picture can be so blurred that the patient does not notice any signs of the disease. This contributes to the spread of infection. If it persists for a long time, it can turn into a dyshidrotic form. |
| Dyshidrotic | On the arch of the foot (most often one) one or several bubbles with a diameter of 2 to 8 mm form. The smallest of them begin to gradually merge, forming larger ones, which open over time, leading to the occurrence of erosions and areas of diaper rash. Soreness and a feeling of itching in the affected area are characteristic. After the erosions dry out and heal, peeling begins, which indicates the transition of the process to a squamous form. It tends to have a long course with frequent relapses. In some cases, a bacterial infection may occur, which is accompanied by the appearance of intense pain at the site of the lesion and an increase in body temperature. The contents of the blisters gradually become cloudy and turn into pus. The skin becomes very red and swollen. |
| Intertriginous | The most common form. It can occur against the background of the squamous form or independently. The beginning of the infectious process is noted on the skin between the IV and V toes on the foot, less often - III and IV. It is characterized by cracks in the skin with a whitish rim of exfoliating epidermis around it. Weeping, a strong feeling of burning and itching appears in the area between the fingers. Erosions may occur at the site of cracks, accompanied by intense pain. It often has a chronic course with exacerbations in the summer. This form is dangerous due to the development of streptococcal infection with the appearance of pustules on the skin, which will be accompanied by severe pain, swelling, redness of the skin and increased body temperature. |
| Onychomycosis | The fungus affects the toenails. Characteristic is the onset of pathological changes from the free edge of the nail plate and the appearance of yellow stripes and spots. Most often it affects the third and fourth toes. It has three main varieties: With damage to mold fungi: most often develops against the background of other infectious diseases of the nails. The color of the nail can vary, ranging from green and yellow tones to brown and black. Atrophic: the fungus leads to thinning and destruction of the nail plate, under which there is keratinized skin. Hypertrophic: characterized by yellowness and thickening of the nail, which eventually begins to crumble. Beneath it, thickened, flaky skin is exposed. |
| Candidiasis | The fungus mainly affects the third and fourth or fourth and fifth toes. The surrounding skin swells and turns red. Around the lesion there is a rim of exfoliated epidermis. In some cases, small blisters or pustules may appear. |
Important! To accurately determine the form of the fungus, you should consult a doctor, who will conduct a thorough examination of the lesion and prescribe additional research methods to make the correct diagnosis.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the site of manifestation and type of infection. In the initial stage, the disease has an aesthetic defect, which negatively affects the psycho-emotional background of the pregnant woman.
The skin around the nail is affected by fungus and becomes inflamed, itchy, flaky and hyperemic. The color of the plate changes, becoming dull, pale yellow or white. As the disease progresses and there is no therapy, a bacterial infection may occur and the general condition of the expectant mother may change.
Treatment with medications
Dermatologists recommend using the following pharmaceutical products:
- Citrosept is a natural drug that does not cause side effects. It contains grapefruit pulp extract. It is enough to rub Citrosept into areas affected by pathogenic microorganisms 2 times a day. This will help get rid of the fungus.
- Clotrimazole is available as an ointment. It can be used from the second trimester of pregnancy under medical supervision.
- Fundazol is intended to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The active ingredient of the drug is miconazole. The product has a strong antifungal effect. Before use, it is best to trim off the defective areas and apply the medicine.
Most drugs intended to treat fungal infections are not suitable for pregnant women. They contain substances that pose a danger to the health of the mother and unborn child.
The choice of treatment method depends on the individual characteristics of the body. For small lesions, traditional methods are used. To treat fungal infections in pregnant women, you need to choose drugs that cannot affect the development of the baby.
Types of fungus
In medicine, all diseases caused by one or another pathogenic type of fungus are usually called in one word - “mycoses”. When the fungus affects the skin, we should talk about dermatomycosis. If nails are involved in the pathological process, it will already be onychomycosis. A combination of them is also possible. The prevalence of mycoses is extremely wide. They occupy second place after pyoderma (pustular lesions) in the field of skin diseases.
Science knows a large number of different types of fungus, but not all of them are able to grow and multiply on the human body.
Among the fungi that affect the feet are the following:
- Athlete's foot. The fungus invades the nails and skin of the feet, as well as other parts of the body. Infection often occurs in gyms, saunas or baths. The fungus is transmitted through shared towels, linen, sports equipment and a number of other items. Increased sweating of the feet contributes to the penetration of the pathogen.
- Trichophytosis. The main causative agent is various types of trichophyton fungi. The infection is highly contagious and is transmitted through bath accessories, shoes and common objects.
- Candidiasis. It is somewhat less common than the first two types of fungus. It is opportunistic and is normally present in the human body. The fungus causes the development of the disease due to a decrease in the functioning of the immune system. This is the type that most often occurs during pregnancy. The Candida fungus can get onto the surface of the skin from absolutely any common item or food.
The penetration of any type of fungus is greatly facilitated by microtraumas and cracks on the surface of the feet and nails.