Types of abscess
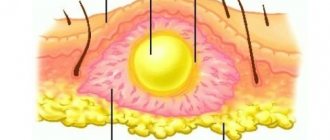
example of abscess formation in the photo
When an abscess occurs, the tissues adjacent to the source of inflammation create a protective barrier in the form of a membrane wall, which limits the penetration of pus beyond its boundaries. In medicine, there are several types of these dangerous abscesses:
- Pulmonary.
- Brain abscess.
- Peritonsillar.
- Spinal, epidural.
- Subdiaphragmatic.
- Soft tissue abscess.
- Post-injection.
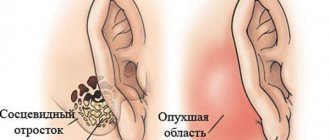
- Bezoldo.
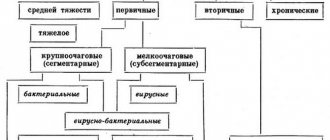
They are also classified by duration: acute and chronic. Any of them causes severe discomfort and is accompanied by pain. An abscess can occur on its own or after an injury or illness such as tonsillitis or pneumonia. This disease cannot be treated independently; the help of a specialist is mandatory.
Prevention of abscess formation and prognosis
Measures to prevent the formation of hip abscesses consist of the sanitation of chronic infectious foci, the treatment of immune and humoral diseases. If it is necessary to perform procedures that damage the skin, antiseptic treatment is required to prevent pathogenic microflora from entering the soft tissues of the body. General recommendations for the prevention of abscesses include a balanced, nutritious diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The prognosis of abscess formation depends on the location of the abscess, the size of the cavity, and the type of pathogen. Spontaneous opening is considered a favorable outcome for superficial ulcers. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, deep abscesses can break into the body, causing serious complications: blood poisoning and the formation of purulent leaks.
If hip abscesses occur, it is important to consult a doctor for medical help at the first signs of the disease. If the purulent formation is not sanitized in time, there is a risk of destruction of the membrane limiting the source of inflammation and the spread of the infectious process through the bloodstream throughout the body.
Signs of the disease
An abscess can occur not only on a person’s skin, but also on his internal organs and tissues.
The first sign of the disease is redness, swelling and the formation of a hard node; after a few days, a purulent formation appears in this area.
The course of the disease is similar to the symptoms of any purulent inflammation. With this disease, there is general weakness, pain in the area of pus formation, increased body temperature, headache, and impaired functioning of the part of the body where it develops.
In the final phase of the disease, a rupture of the skin may occur, which will lead to the natural release of pus. In the external form of the disease, after the pus is released, the abscess loses its shape and volume when completely cleansed. Next, scar formation occurs.
In the internal form of an abscess, when ruptured, pus can enter the body cavity and lead to inflammatory processes in other organs. It is very important to prevent this from happening, since the consequences can be meningitis, arthritis, peritonitis, pleurisy, pericarditis and other purulent processes.
While skin abscesses are easy to diagnose, deep internal forms of the disease are more difficult to identify. This requires a blood test, in which an increased number of leukocytes will indicate an inflammatory process. In some cases, a specialist will prescribe an ultrasound or x-ray or puncture.
Characteristic symptoms of ulcers
Superficially located abscesses occur with signs of local tissue inflammation. There is redness around the abscess, swelling, and pain. There may be a ripple effect (fluctuation) when, upon palpation of a tubercle with an encapsulated formation, waves from rising liquid are felt. If the membrane wall is thick, this symptom is absent.
The appearance of pronounced symptoms indicates the further spread of the infectious process, in which there is a threat of developing sepsis.
With deep hip abscesses, symptoms of inflammation and swelling may be absent. The body's reaction is due to its intoxication with tissue breakdown products and bacterial toxins. The signs are less pronounced. Chills, weakness, insomnia, headaches, loss of appetite are observed. Laboratory tests show changes in blood parameters.
What is abscess formation
Cases of complications during the treatment of abscesses are quite rare, and with timely surgical care they are minimal. The process of abscess formation can occur with advanced abscesses, then the progression of purulent inflammation, an increase in the affected area, and its transition to a chronic form and to other organs and tissues of the human body are possible.
Other complications may include disruption of the functioning of vital organs, entry of bacteria into the blood, arrosive bleeding, and exhaustion of the body due to tissue breakdown.
An abscess is classified as a surgical disease, so you should not try to cure it yourself at home, you need to consult a specialist.
Consequences of suppuration and possible complications
If hip abscesses are not treated in a timely manner, the risk of developing phlegmon, pleural empyema, peritonitis, and meningitis increases. When the infection spreads to the nerve endings, neuritis develops, and to the bone tissue - osteomyelitis.
Involvement of blood vessels in the inflammatory process threatens the formation of bleeding. An increase in pressure in the abscess cavity leads to damage to the membrane, which contributes to the generalization of the infectious process with the development of sepsis and purulent leaks.
Causes of the disease
One of the causes of an abscess can be a bacterial infection, usually staphylococcus. This type of pathogenic microorganisms helps weaken the body's immunity, which helps fight the disease. The bacteria can get under the skin through minor scratches and abrasions.
Another cause of an abscess may be any medical procedure associated with injections, performed in a medical facility without observing the rules of asepsis. Or the spread of another inflammatory purulent process, such as a boil, to neighboring tissues and organs, that is, abscess formation of the main focus.
In addition to the above reasons, the development of the disease can also occur when substances containing chemicals are injected under the skin, hemorrhages suppurate, or hematomas develop. The size of the abscess can be completely different, ranging from very small ones, the size of a grain, to wounds in which the amount of pus can reach one liter.
Causes of abscess formation and risk factors
Purulent abscesses develop when microbes penetrate the body tissues through the wound surface or hematogenously. During bacteriological examination of the contents of the capsule, monocultures or associations of bacteria of various groups are identified. More often, the following types of microorganisms are found in purulent exudate:
- Proteus;
- staphylococci (hemolytic, aureus);
- streptococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Klebsiella;
- coli;
- legionella;
- bacteroids.
The lack of microflora growth when inoculating the abscess contents on nutrient media is explained by the fact that the thigh abscess is caused by pathogens that cannot be detected by known microbiological methods.
The penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the body is facilitated by the following factors associated with damage to the skin:
- frostbite;
- burns;
- bedsores;
- injuries;
- abrasions, scratches;
- open fractures;
- hematomas.
A high incidence of post-injection abscess formation is observed after intramuscular injections of anabolic steroids.
The causes of hip abscess are due to the presence of chronic diseases that occur with hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders, blood circulation, as well as a decrease in the body's defenses. Such diseases include:
- phlebitis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- hypothyroidism;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disorders.
The likelihood of the formation of encapsulated suppurations is high when pathogenic pathogens spread from chronic purulent foci through the bloodstream through various tissues.
Postoperative scar abscess
No one is immune from complications after surgery. The development of an abscess can occur after almost any type of surgery; even taking antibiotics is not always able to stop the inflammatory process.
The most common causes of a postoperative scar abscess may be the following:
- the wound could become infected;
- During the operation, the subcutaneous fatty tissue was damaged, which caused a hematoma;
- high tissue reactivity of suture material;
- improper postoperative drainage.
In this case, an abscess can also be triggered by weakened immunity, chronic diseases and infections, and allergies.
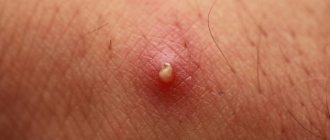
abscess symptoms in the photo
The disease does not appear immediately after the operation, but after a week or more, sometimes the time frame is reduced. The main signs of a postoperative scar abscess are: increased body temperature, which cannot be brought down by antipyretics, redness and swelling in the suture area, pain when pressed.
Diagnosing an abscess in this case is not difficult; the specialist asks about the symptoms, examines and palpates the sore spot. In some cases, an ultrasound is performed and a biopsy is performed in order to create the most effective treatment regimen.
For this disease, treatment usually includes a course of antibiotics, artificial reduction of body temperature, bed rest, physiotherapy, and symptomatic therapy. If the treatment is ineffective, the seam is opened again, cleaned and sutured.
Diagnostics
Identifying superficial abscesses does not cause difficulties, while deeply located infiltrative capsules require ultrasound and/or puncture. The exudate obtained as a result of puncture of the pyogenic membrane is sent for bacteriological examination, during which the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics are determined.
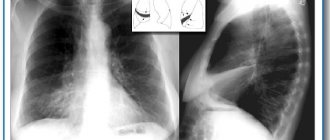
Oropharyngeal lesions are detected during an otolaryngological examination. At any location of the abscess, a blood test reveals signs of an acute inflammatory process in the form of an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in ESR, and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. Diagnosis of abscesses of the brain, lungs, and abdominal cavity is carried out using:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- magnetic resonance, computed tomography;
- radiography.
Abscess treatment methods
Having diagnosed the disease, the specialist, regardless of the location of the abscess, opens it and cleanses it of pus. Often the abscess requires major surgery, so the patient is hospitalized. Treatment can be provided on an outpatient basis only in case of minor external inflammation.
For abscesses of internal organs, such as the liver or lungs, the surgeon performs a puncture to remove pus and then inject antibiotics into the vacated cavity.
In case of a chronic course of the disease, a specialist surgeon may suggest removing part of the organ affected by the abscess.
After the pus is removed from the wound, the patient is given the same treatment as for ordinary purulent wounds. The patient should eat well, get plenty of rest and take medications prescribed by the doctor. Special therapy may be required for people with diabetes.