Causes of multiple myeloma
The exact cause of the disease is unknown.
However, the disease begins with a single abnormal plasma cell that multiplies rapidly in the bone marrow. The resulting myeloma cancer cells do not have a normal life cycle. Instead of reproducing and dying, they continue to divide endlessly. This destroys the body and impairs the production of healthy cells. Most patients have a genetic predisposition to the disease.
Here's what triggers the development of multiple myeloma:
- genetic predisposition;
- chemical and radiation radiation;
- constant antigenic stimulation;
- obesity due to metabolic disorders;
- male gender, the development of the disease occurs with a decrease in the amount of male sex hormones;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- surgical interventions.
- Stage I. The amount of hemoglobin is more than one hundred, the level of calcium in the blood is within normal limits, there is no bone destruction. Immunoglobulin J is less than 50 g/l, immunoglobulin A is less than 30 g/l. Bence-Johnska protein in urine is less than 4 grams per day.
- Stage II. The amount of hemoglobin is from 85 g/l to 120 g/l. Moderate bone destruction. Immunoglobulin J 50 – 70 g/l, immunoglobulin A 30 – 50 g/l. Bence Jones protein 4 – 12 grams per day.
- Stage III. The amount of hemoglobin is less than 85 g/l. The level of calcium in the blood exceeds normal levels. Noticeable bone destruction. Immunoglobulin G is above 70 g/l, immunoglobulin A is more than 50 g/l. Bence Jones protein in urine is more than 12 grams per day.
By degree of progression:
- smoldering – the disease does not progress over many months and years;
- slowly progressive;
- rapidly progressing;
- aggressive.
You can prevent Rustitsky-Kahler disease by following these tips:
- avoid contact with infectious patients;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- include more fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet;
- maintaining immunity: hardening, sports, try not to get too cold;
- carefully study the composition of food products.
Myeloma: causes, signs, stages, life expectancy, therapy
Myeloma is a type of hemoblastosis in which bone marrow is replaced by tumor plasmatic myeloma cells. Myeloma infiltrates grow more often in flat bones and the spine. Cavities form in places where they grow. Bone destruction is associated with proliferation of the tumor clone. Myeloma cells secrete osteoclast-activating factor, which activates osteoclasts, which are responsible for removing bone tissue, dissolving the mineral component and destroying collagen. The cause of the disease is not fully known. But ionizing radiation and genetic predisposition play a certain role.
Diet and folk remedies. For multiple myeloma, there is no special diet that would satisfy each form and stage of the disease, so the doctor.
With a normal leukocyte count
The diet must include protein foods, in particular fish, poultry, and eggs. Fermented milk products are a source of calcium, so kefir, cottage cheese and yogurt should be on the menu daily.
Vegetables are best boiled. It is recommended to choose potatoes, cabbage, carrots, beets, and sweet peppers.
Fresh fruits - apples, bananas, pears, can also be replaced with dried fruits.
In between meals you need to drink water, preferably 2 - 3 liters per day. This can be not only ordinary clean water, but also mineral water, but only without gas, tea, compote, jelly.
Dairy products must only be pasteurized. You should not eat soft and sharp cheeses, as well as cheeses that contain herbs.
The meat must be well cooked. Ideal for choice - beef, pork, beef. Eggs are only fully boiled. Undercooked and raw eggs are completely excluded from the diet.
Soups should not be consumed without boiling. Okroshka and soups with fruit are excluded. Homemade soup is only homemade and only fresh.
Only fresh fruits include oranges, bananas, grapefruits, tangerines and melons. You cannot drink kvass and homemade juices prepared without pasteurization.
Potatoes, rice, pasta are allowed. You cannot eat French fries or any fresh vegetables.
Cookies – only packaged. Bread is only packaged.
How is multiple myeloma treated in Israel?
To undergo diagnostics, you need to spend 3-4 days in Israel.
The examination costs $5,226.
- 1st day. The patient receives an appointment with diagnostician Dr. I. Molchanov. The doctor examines him, takes a medical history in Hebrew and issues referrals for research. If the patient has performed a bone marrow biopsy at home, tissue samples are sent for revision. The results will be ready in 6-10 days.
- 2nd day. In the morning, the patient undergoes blood tests and a urine test, which detects Bence Jones protein, which can signal kidney damage. This is followed by a PET-CT scan. During research, translation is performed by a medical coordinator who constantly accompanies the patient.
- 3rd day. The patient is seen by an oncohemetologist - prof. E. Naparstek or Dr. O. Gur. A specialist doctor informs the patient of the final diagnosis and prescribes a cancer treatment plan in Israel
. You can receive treatment according to the program compiled by our specialists both in Israel and at home.
Contact the Top Ichilov clinic
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs are prescribed to patients in the form of droppers or tablets. Chemotherapy drugs Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), Vincristine, Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) and Liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil), etc. are used. New drugs for multiple myeloma are currently being tested in Israel, which increase survival rate for this disease by 10 years or more.
Targeted therapy
Targeted (targeted therapy treatment in Israel) therapy is treatment with drugs that affect tumor cells at the molecular level. In Israel, the drug Bortezomib (Velcade) is used for tergetary therapy of multiple myeloma.
A stem cell transplant allows you to use higher doses of chemotherapy, which destroy not only tumor cells, but also healthy bone marrow cells. In Israel, both autologous transplantation is performed, when the patient is transplanted with his own cells, and transplantation of donor stem cells. Healthy stem cells are injected into a large vein of the patient. After some time, normal blood cells are formed from them.
Symptoms of multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma has a long course. It takes 10-20 years from the first symptoms of the disease to clear clinical signs.
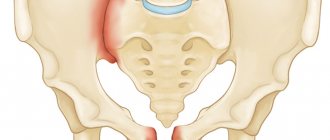
- Bone marrow syndrome is manifested by bone lysis. Mainly the spine, flat bones, and proximal parts of the tubular bones are affected. Distal parts are affected extremely rarely. Patients complain of bone pain and frequent fractures. On percussion there is pain in the limbs.
- Kahler's triad (osteoporosis with spontaneous fractures, pain, tumors) is pathognomonic for these patients.
- Characteristic disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system up to the development of paraplegia (complete immobility in the limbs), weakness, and fatigue. Due to the deposition of amyloid in the bones of the skull, disturbances in the functioning of the cranial nerves are possible. Characteristic is damage to the peripheral nerves of the extremities and sensory disturbances of the “gloves and socks” type. Lack of sensation in the distal limbs.
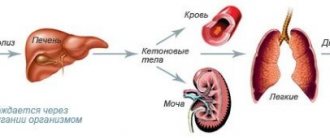
- Kidney failure can be caused by high levels of M protein in the body.
- Immunoglobulinopathy syndrome. Amyloid protein begins to be synthesized. During urine formation, it is actively reabsorbed by the kidneys, damaging them. Proteinuria (Bence Jones protein) increases in the urine. The concentration and filtration function of the kidneys gradually decreases, swelling appears, and a positive symptom of effleurage (pain in the lower back when hitting this area with a fist) appears.
- Immunodeficiency syndrome. Normal protein begins to be replaced by pathological one. The synthesis of antibodies and immune components is disrupted. As a result, the defect in humoral immunity gradually increases. Patients become unprotected from bacterial and viral infections. The appearance of opportunistic infections is characteristic. Any contact with an infectious agent leads to the development of the disease
- High viscosity syndrome: increased bleeding, Raynaud's syndrome (impaired microcirculation in the distal segments of the extremities), retinal hemorrhages, decreased blood supply to the brain, possible development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
- Hypercalcemia. As a result of increased activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bones), large amounts of calcium are released into the blood. Symptoms of hypercalcemia - nausea, vomiting, convulsions. Cardiac conduction disturbances are characteristic: the QRS and T intervals increase, AV conduction decreases, up to AV block. Formation of kidney stones. This is due to calcium deposition and decreased filtration and reabsorption. The kidney shrinks.
- Damage to internal organs: splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, gastric ulcer. Amyloid is deposited in various organs and tissues, which leads to disruption of their functioning. Characters of pain in the heart, expansion of the boundaries of cardiac dullness, dullness of tones. Muscle pain can be permanent.
- Anemic syndrome. Over time, tumor cells displace the normal lineage of hematopoiesis. The amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells decreases. The skin becomes covered with bloody spots and turns pale (see 2 photos above), and there is a constant feeling of weakness. Hair and nails become brittle.
Conclusions and recommendations for patients with myeloma
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely recover from this disease, but the prospect of long-term remission exists even at the 3rd stage of development. The patient should not forget that the diagnosis requires constant monitoring and treatment, especially if the disease is progressive. Therapy should be aimed at stopping the development of malignant cells and improving the patient’s quality of life. Today, there are several methods used to treat myeloma:
Chemotherapy. Radiation therapy. Symptomatic treatment. Bone marrow transplantation.
Chemotherapy
It is the main method of therapy. In order for the effect of myeloma treatment to be positive, chemotherapy courses are carried out for quite a long time. If the patient’s disease stops progressing, then after 6-9 courses, treatment is stopped until a relapse occurs. The procedure has many side effects, because the drugs act on both healthy and malignant cells.
Radiation therapy
Destroys tumor cells using ionizing radiation. The method is suitable for patients with a single plasmacytoma. More often it is prescribed for compression of the bone marrow, with the threat of bone fractures due to tumor growth.
Symptomatic treatment
It is used when the patient exhibits dangerous signs of the disease, such as hypercalcemia, dehydration, and compression of the spine. In this case, treatment should be aimed at correcting the local lesion or metabolic disorder. If anemia, painful bone lesions or inflammatory processes are observed, doctors prescribe palliative therapy, antibiotics, etc.
Bone marrow transplantation
Characterized by high risk and side effects. However, in clinical practice there are quite a lot of successful operations using transplantation even at the 3rd stage of the disease.
Under no circumstances should discomfort and pain in the bones be ignored, as myeloma may begin to progress in the body. The life expectancy of patients with this disease depends on timely treatment, so it is necessary to consult a doctor on time!
Myeloma belongs to the group of paraproteinemic hemoblastoses, in which malignant transformation of plasma cells is accompanied by their overproduction of abnormal immunoglobulin proteins. The disease is relatively rare; on average, 4 people per 100 thousand people become ill. It is believed that men and women are equally susceptible to the tumor, but, according to some data, women still get the disease more often. In addition, there are indications of a greater risk of myeloma among black populations in Africa and the United States.
The average age of patients ranges between 50 and 70 years, that is, the majority of patients are elderly people who, in addition to myeloma, have other pathologies of internal organs, which significantly worsens the prognosis and limits the use of aggressive methods of therapy.
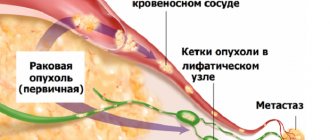
Myeloma is a malignant tumor, but it is a mistake to call it “cancer”, because it does not originate from the epithelium, but from hematopoietic tissue. The tumor grows in the bone marrow, and its basis is made up of plasma cells. Normally, these cells are responsible for immunity and the formation of immunoglobulins necessary to fight various infectious agents. Plasmocytes are derived from B lymphocytes. When cell maturation is disrupted, a tumor clone appears, which gives rise to myeloma.
Under the influence of unfavorable factors in the bone marrow, there is an increased proliferation of plasmablasts and plasmacytes, which acquire the ability to synthesize abnormal proteins - paraproteins. These proteins are considered immunoglobulins, but they are not capable of performing their direct protective functions, and their increased quantity leads to thickening of the blood and damage to internal organs.
The role of various biologically active substances has been proven, in particular interleukin-6, which is elevated in patients. Bone marrow stromal cells, which perform a supporting and nutritional function (fibroblasts, macrophages), secrete interleukin-6 in large quantities, as a result of which tumor cells actively multiply, their natural death (apoptosis) is inhibited, and the tumor actively grows.
Other interleukins can activate osteoclasts, cells that destroy bone tissue, which is why bone lesions are so characteristic of myeloma. Being under the influence of interleukins, myeloma cells acquire an advantage over healthy ones, displacing them and other hematopoietic germs, leading to anemia, immunity disorders, and bleeding.
The course of the disease is conventionally divided into chronic and acute stages.
In the chronic stage, myeloma cells do not tend to multiply quickly, and the tumor does not leave the bone, patients feel satisfactory, and sometimes are not aware of the onset of tumor growth. As myeloma progresses, additional mutations of tumor cells occur, resulting in the emergence of new groups of plasma cells capable of rapid and active division; the tumor extends beyond the bone and begins its active spread throughout the body. Damage to internal organs and inhibition of hematopoietic germs lead to severe symptoms of intoxication, anemia, and immunodeficiency, which make the acute stage of the disease terminal, which can lead to the death of the patient.
The main disorders in myeloma are bone pathology, immunodeficiency and changes associated with the synthesis of a large number of abnormal immunoglobulins. The tumor affects the pelvic bones, ribs, and spine, where tissue destruction occurs. Involvement of the kidneys can lead to chronic kidney failure, which is quite common in patients suffering from myeloma.
During remission
During the period of remission, a varied and nutritious diet is required. There are no special restrictions or prohibitions during this period. Therefore, a diet for multiple myeloma is, as a rule, not needed here.
But it is still recommended to avoid semi-finished products and products that have to be stored for a long time, as well as those containing large amounts of preservatives or dyes. Preference should be given to liver - any beef, pork or chicken will do. You should also regularly eat veal and lamb, fresh dairy and fermented milk products, especially if you have osteoporosis.
To replenish iron, you need to include oysters, mussels and shrimp in your diet. The best vegetables and fruits to eat are those that grow in the region where the patient lives.
Of course, we must not forget about products that have antitumor effects. These include:
- Sprouted grains.
- Soy.
- Carrot.
- Tomatoes.
- Tangerines.
- Oranges.
- Olive oil.
- Linseed oil.
- Beet.
- Blackberry.
- Blueberry.
- Cherry.
- Cabbage.
- Radish.
- Pineapples.
- Garlic.
- Corn.
- Eggs.
- Beans.
- Broccoli.
- Green tea.
These foods should be included in every person's diet.
Life expectancy with myeloma
Depending on the form of the disease and its course, and the stage at which treatment began, prognoses for the patient’s life expectancy vary from a few months to ten years. This is also due to the disease’s response to treatment, the presence of other pathologies, and the age of the patients. In addition, with myeloma, severe complications develop that lead to death: renal failure, sepsis, bleeding, damage to internal organs using cytostatics.
With stage IA, life expectancy is on average about five years, with stage IIIB - less than 15 months.
Diagnostics
Doctors often detect multiple myeloma before any symptoms appear. If there is a suspicion of illness, doctors will do the following:
- collecting an anamnesis of the disease (the doctor finds out what, in the patient’s opinion, the disease is associated with, when the complaints appeared);
- general examination (examination can reveal hemorrhages on the skin, pallor, and bone pain on percussion);
- general blood test (all forms are characterized by normocytic anemia, in more than half of the cases an increase in ESR; there may be no changes in white blood, but neutrophilia with a shift to the left is often observed);
- bone marrow puncture (megakaryocytes are isolated in the bone marrow);
- general urinalysis (a morning sample of urine is used for analysis. It must be delivered to the laboratory within a few hours. In the urine there is an increased level of relative density due to the presence of protein molecules, proteinuria. Bence-Jones protein is a pathognomic sign of multiple myeloma);
- biochemical blood test (total protein, ALT, AST, bilirubin, creatinine level, uric acid);
- radiography of all bones of the skeleton except the distal parts (pictures are taken from the middle of the shoulder to the hand and from the middle of the thigh to the foot);
- computed tomography can detect foci of bone tissue destruction and spinal cord compression;
- sternal puncture is the main diagnostic method (a puncture is made with a special needle in the sternum or ilium. Cells are removed and a smear is made. A bone marrow tumor, a large number of plasma cells, and immature blood cells are found in the smear);
- urine test according to Zimnitsky (allows you to evaluate the concentrating ability of the kidneys. To perform this analysis, a person collects urine every three hours during the day, a total of eight servings are obtained. The total amount of urine, density, night and daytime diuresis are assessed).
Forms
Based on the clinical and anatomical classification, several forms of multiple myeloma are distinguished:
- Diffuse.
- Diffuse-focal.
- Multifocal.
- Sclerosing.
- Mainly visceral.
The basis for this classification is the results of an X-ray examination of the skeleton, as well as analysis of punctures and biopsies of the patient’s bone tissue.
Depending on the activity of the disease, there are 2 forms of multiple myeloma:
- “Smoldering” (asymptomatic) – does not manifest itself with typical symptoms, there are no osteolytic foci and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Serum M gradient greater than 30 g/L and/or bone marrow level of clonal plasma cells ≥10%.
- Active – there is a process of osteodestruction, an increase in the mass of tumor cells, the development of infectious complications, increased blood viscosity syndrome and other signs of disease activity.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7 (495) 151-14-53
What to give up
First of all, you need to give up shelf-stable products that contain a huge amount of dyes, preservatives and stabilizers. It is necessary to exclude canned food and factory-made sauces, smoked meats and sausages from the diet.
Rich fatty broths, both meat and fish, should also be excluded from the diet. You need to limit animal fats, butter with streaks of fat, margarine, and all fats that are used in confectionery products. You should also avoid mayonnaise and fried foods.
Simple carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet, namely sugar, baked goods, pastries, cakes, pastries, and candies. All this stimulates the growth of cancer cells. You can replace such foods with dried fruits and nuts.
But fermented milk products of natural origin can be eaten without any restrictions throughout your life.
Common symptoms of myeloma that may be confused with other diseases
Often, some symptoms of multiple myeloma are very similar to other diseases of various human organs and systems:
- The first symptoms of myeloma are painful sensations in the bones. At night or after changing body position, these sensations migrate throughout the body, causing discomfort. The pain can also be located in the chest. Such symptoms usually indicate the presence of amyloidosis.
- A certain stage of the disease is characterized by signs of anemia, accompanied by weakness and fatigue, pallor of the skin and heart failure.
- Symptoms such as weight loss and fever, which often appear in advanced stages of myeloma and the addition of infectious diseases to it, can be confused with anorexia and other dangerous diseases.
- The early stage of the disease can manifest itself with symptoms characteristic of kidney failure: nausea, vomiting, increased fatigue and weakness in the body.
In order not to confuse myeloma with other diseases, it is necessary not to self-medicate, but to trust the specialists! Doctors will be able to conduct a full examination of your body, identify a tumor in time and provide the necessary treatment.
Myeloma (Rustitsky-Kahler disease, plasmacytoma, multiple myeloma) is a disease from the group of chronic myeloblastic leukemia with damage to the lymphoplasmacytic series of hematopoiesis, leading to the accumulation of abnormal immunoglobulins of the same type in the blood, impaired humoral immunity and destruction of bone tissue. Multiple myeloma is characterized by a low proliferative potential of tumor cells that primarily affect the bone marrow and bones, and less commonly, lymph nodes and lymphoid tissue of the intestine, spleen, kidneys and other organs.
Multiple myeloma accounts for up to 10% of cases of hemoblastosis. The incidence of multiple myeloma averages 2-4 cases per 100 thousand population and increases with age. As a rule, patients over 40 years of age are affected; children – in extremely rare cases. Representatives of the Negroid race and males are more susceptible to myeloma.
Myeloma
Treatment of multiple myeloma
Treatment methods include:
- local irradiation of a bone marrow tumor;
- inpatient chemotherapy;
- high-dose chemotherapy with bone marrow transplantation.
The initial tactics for managing the patient are determined by his age, the presence or absence of severe concomitant diseases.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QEO8vCB-O5s
If the patient is under 65 years of age and there are no severe pathologies, high-dose chemotherapy with bone marrow transplantation is used. Local irradiation of myeloma is mainly used as a palliative treatment, especially for severe pain in the skeletal region.
Chemotherapy is the most popular treatment for multiple myeloma. Drugs can only be prescribed by a chemotherapy doctor.
During therapy, it is necessary to constantly monitor the patient’s condition and blood picture.
The following approaches to chemotherapy are distinguished:
- monochemotherapy – treatment with one drug;
- polychemotherapy – the use of more than two drugs.
Alkeran (Melphalan) – antitumor, cytostatic agent
Side effects:
- dyspeptic symptoms: nausea, vomiting;
- skin itching;
- allergic reactions;
- pneumofibrosis;
- decreased ovarian function.
Prednisolone is a hormonal drug. Has an immunosuppressive effect. Reduces protein synthesis in blood plasma, increases protein catabolism in muscles. Prescribed to prevent side effects of chemotherapy.
Cyclophosphamide is an antitumor agent.
Vincristine is an antitumor drug of plant origin. It blocks substances necessary for the synthesis of plasma cells. Vincristine is administered continuously intravenously throughout the day.
Side effects:
- convulsions;
- nausea, vomiting;
- hives;
- dysuria, urinary retention.
Adriablastin is an antibiotic that has antitumor activity. Reduces the growth and activity of neoplastic cells. Under the influence of adriablastin, free radicals are formed that affect the cell membrane.
Side effects:
- phlebitis;
- dermatitis;
- cardiac conduction disturbance;
- allergic reactions
- pain in the heart area.
After a course of chemotherapy, patients are prescribed Interferon to maintain immunity. If anemia occurs, red blood cell transfusion is necessary.
Bortezomibum is a new drug in the treatment of the disease. Its mechanism of action is stimulation of apoptosis. Administered intravenously in a hospital setting.
Drug combination regimens:
- VAD diagram. It includes three drugs: vincristine, dexamethasone, doxorubicin;
- VBMCP scheme. It includes 5 drugs: prednisolone, melphalan, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, carmustine.
Signs of therapy effectiveness:
- healing of fractures;
- increase in red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood;
- reduction in tumor size;
- decrease in the number of plasma cells in the blood.
Local radiation therapy is indicated for patients at high risk of fracture. Especially in the supporting parts of the skeleton: spine, pelvic bones.
Unfortunately, even after effective therapy and achieving complete remission, the risk of relapse is high. This is due to the fact that the tumor contains a variety of cells, which begin to divide again after chemotherapy is stopped.
Analgesic therapy is carried out in several stages. To eliminate mild pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used:
- Spasmalgon;
- Ibuprofen;
- Indomethacin.
For severe pain and ineffectiveness of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), opioid analgesics are prescribed:
- Codeine;
- Tramadol;
- Prosidol.
Long-term use can cause drug addiction, so they must be used with caution. For unbearable pain, strong opioids are prescribed:
- Morphine;
- Naloxone;
- Buprenorphine.
Magnetoturbotron is the effect of a low frequency magnetic field. It reduces the side effects of chemotherapy, reduces pain, and disrupts the division of plasma cells. The course is conducted 2 times a year.
Electrosleep is the effect on brain structures of low frequency currents. Currents reduce pain and have a calming effect.
Antibacterial and antiviral therapy is used to treat infectious complications. Since the immunity of all patients is reduced, the development of infection is a common occurrence. For treatment, mainly third and fourth generation cephalosporins and protected penicillins (ampicillin) are used.
Treatment of fractures should not differ from therapy in healthy people. Surgical treatment and immobilizing bandages are used. In the postoperative period, bed rest and wearing orthopedic structures are indicated.
Osteoporosis is treated with bisphosphonates (zoledronate). They suppress the activity of osteoclasts.
In multiple myeloma, paraproteins (pathogenic proteins of the immunoglobulin class) are deposited in the kidneys, which leads to disruption of their function. To avoid this, it is important to stop the progression of plasmacytoma growth.
Special medications are used to maintain kidney function.
- Hofitol helps cleanse the blood and removes urea.
- Retabolil is an anabolic drug that promotes muscle growth. Under its influence, nitrogen is used for protein synthesis.
- Sodium citrate is used for acid-base metabolism disorders, reduces the amount of calcium in the blood
- Prazosin dilates peripheral blood vessels and lowers blood pressure. Increases renal blood flow.
- Captopril is an ACE inhibitor. Dilates peripheral vessels, reduces resistance in them, promotes the excretion of calcium. Improves renal filtration
- In case of serious impairment of the filtration function of the kidneys, plasmapheresis is performed.
For hypercalcemia, glucocorticosteroids and chemotherapy are used
Surgery
For multiple myeloma, bone marrow transplantation is used as a surgical treatment. This can be either autotransplantation (transplantation of one's own bone marrow) or allotransplantation (transplantation of a donor's bone marrow).
Autotransplantation (or autologous transplantation) allows you to increase the dose of cytostatics (a group of antitumor drugs), improve the outcome of treatment, and increase the period of remission.
Allotransplantation has good results, but is used only in young patients. Since it has a high percentage of deaths.
Nutrition for myeloma
For any cancer, it is important to follow a diet. Smoked, fried, flour, and canned foods should be excluded from the menu.
The diet should be varied and contain as many vegetables and fruits as possible. Limit protein intake to reduce paraproteinemia and the toxic effect of nitrogen, which is formed during the destruction of protein, on the kidneys.
The drinking regime is three liters. About two and a half liters should be excreted in urine per day. If there is swelling, then you need to limit your salt intake.
Treatment
The patient's life expectancy largely depends on the correct diagnosis and choice of the right treatment methods. When determining treatment tactics for myeloma, one should take into account the patient’s age, stage and form of the disease, as well as the presence or absence of concomitant pathology. For patients under 65 years of age without serious somatic pathologies, high doses of chemotherapy and transplantation of their own stem cells are recommended. For patients over 65 years of age, as well as patients with concomitant pathologies, new drugs without high doses of chemotherapy are used, also in combination with stem cell transplantation.
Signs of the disease
At the initial stage, the disease develops covertly – there is no obvious clinical manifestation. With cancer, cells gradually spread throughout the body, affecting the internal cavities of flat bones - the area of the shoulder blades, vertebrae and skull, as well as tubular bones.
In medical practice, there are examples of diagnosing myelosarcoma, an oncological process formed by white blood cells. With further development, oval-shaped growths with a soft elastic consistency appear on the surface of the bones, which leads to the destruction of the bone structure.
Destruction of bone structure by myeloma
The main symptoms of myeloma are:
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- body temperature is constantly changing - it can rise to thermal readings and immediately decrease;
- muscle weakness due to rapid fatigue;
- indicators of basic blood elements characterize signs of anemia;
- frequent infectious diseases are observed;
- pain syndromes in the soft tissue area with a feeling of discomfort;
- frequent heart rate - 100-120 beats per minute;
- there is a feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium area;
- severe pain in the head;
- vertebral hypercalcemia leads to internal changes in structure;
- myelomalacia develops when a differentiated tumor compresses neighboring tissues;
- nephropathy develops when kidney cells are damaged.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination of the body to determine the type of pathology. Treatment at the initial stage of formation guarantees a positive effect and rapid recovery.
The initial period of oncology is asymptomatic, without causing any subjective sensations in the cancer patient. As the disease progresses, the disease may manifest itself as follows:
- periodic attacks of pain in bone tissue;
- anemia, which manifests itself as fatigue and chronic malaise;
- rapid loss of body weight;
- disruption of the higher nervous system, constant thirst. These symptoms often indicate that calcium levels are exceeded;
- chronic kidney pathologies;
- regular infectious processes.
Often, myeloma develops without attracting much attention, manifesting itself as pain in the bones. As a result of development, the disease spreads to the internal parts of flat bones (scapulae, sternum, vertebrae, skull) or epiphyses of tubular bones. There are frequent cases of detection of myelosarcoma - malignant elements, mainly consisting of white blood cells.
Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, blurred vision, unstable body temperature, general weakness, anemia, and private infectious diseases are detected: from the common flu to leukoplakia of the vulva or cervix. As a result of damage to internal organs, discomfort and pain, palpitations, and a feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium appear.
Forecast
If the patient is not treated, he may die from myeloma within 2 years, with daily quality of life regularly declining. If you systematically undergo courses of chemotherapy with the participation of cytostatics, the life expectancy of a clinical patient increases to 5 years, in rare cases - up to 10 years. Representatives of this pharmacological group provoke acute leukemia in the patient in 5% of clinical pictures. Doctors do not rule out sudden death if the following progresses:
- stroke or myocardial infarction;
- malignant tumor;
- blood poisoning;
- renal failure.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Laboratory research methods are used to diagnose myeloma. The most characteristic changes can be identified on the basis of a general analysis of blood and urine, paying attention to the following indicators: an elevated calcium content in the urine or blood serum, at the same time a high level of protein in the urine and a low number of red blood cells, platelets and hemoglobin, increased to 80 mm/h. and higher ESR. High levels of total protein in the blood against the background of low albumin levels.
A more accurate diagnosis is obtained by determining monoclonal paraproteins and testing urine for Bence-Jones protein. A positive test indicates the presence of light chains of paraproteins passing through the kidney tubules. In addition, a number of other studies are carried out: radiography, bone tomography, bone marrow trephine biopsy, cytogenetic studies, and quantitative indicators of immunoglobulin in the blood are determined.
In most cases, the diagnosis of myeloma is based on the results of a biochemical blood test, which was prescribed for a completely different reason. The following changes in the parameters of the circulatory system can cause the doctor to be oncological alert:
- Hypercalcemia due to anemia.
- Increased createnine concentration, which is a sign of chronic renal failure.
- Increased protein content in blood and urine. In this case, there is a deficiency of albumin.
In addition to laboratory analysis, oncological diagnosis of myeloma lesions includes x-ray examination. The presence of a malignant focus of bone tissue can be determined even on a traditional x-ray.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is recommended to undergo laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of the body. A smoldering disease in the spinal cord can be asymptomatic for a long time. If myeloma is detected early, you can be cured faster and completely.
The doctor uses laboratory and x-ray methods to examine the patient:
- a general examination is carried out, a medical history and a complete anamnesis are collected;
- a general blood test for myeloma reveals a high level of ESR with low hemoglobin, thrombocytosis, red blood cells and albumin;
- urine analysis shows elevated levels of calcium and protein;
- X-rays are prescribed to study structural changes in bones;
- computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide detailed pathological information;
- A bone marrow trepanobiopsy procedure is prescribed, followed by a cytological examination.
Particular attention is paid to the quantitative level of immunoglobulin in the blood. A CT scan can determine the extent of damage to other organs. The symptoms of the disease often look like blood cancer, so doctors examine the patient’s body more carefully to rule out possible pathologies.
Treatment of patients
This technique is based on high-frequency effects on the brain to correct self-awareness. In some cases, such treatment can briefly improve the condition of a cancer patient.
Surgical intervention very often significantly extends the patient's life expectancy.
Antitumor drugs are a less effective means of anticancer therapy than transplantation and induction. Intravenous administration of chemotherapy drugs is associated with a high likelihood of complications. In this regard, this treatment of blood myeloma has a number of contraindications, which limits its use.
Systemic administration of corticosteroids, as a rule, acts as an addition to chemotherapy, which reduces the risk of side effects of cytostatics.
The use of radiation therapy is determined individually depending on the sensitivity of tumor tissues to highly active radioactive radiation. For some patients, radiotherapy is the only way to relieve pain and briefly stabilize the growth of malignant tumors.
Bruises on the body characteristic of blood myeloma