Any infectious disease is serious for a child and dangerous due to its complications. Scarlet fever is no exception. Therefore, if you have a child, then you need to know how it manifests itself and how to treat scarlet fever in children. Scarlet fever is an acute infectious disease that affects the tonsils. In fact, scarlet fever is a whole group of diseases (there are about 80 types in total), which is a form of streptococcal infection. Scarlet fever is translated as “purple fever.”
Pathogen
Before treating scarlet fever in children, you need to know that its causative agent is group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. In addition to scarlet fever, it also causes another disease of the tonsils - sore throat. Coccus is quite stable in the external environment, but does not have high volatility. This type of streptococcus is capable of producing an exotoxin, which causes sensitization of the body, which in turn causes allergies. In addition, it has the following properties:
- pyrogenicity – causes an increase in temperature;
- cytotoxicity – causes cell death.
Treatment of scarlet fever, drugs and methods
Treatment of scarlet fever in children in most cases is carried out at home. Inpatient treatment in a separate room in the infectious diseases department is required only for newborns and children with a complicated course of the disease.
Therapeutic measures for scarlet fever:
- Bed rest for 1 week until the temperature normalizes.
- Gargling with a decoction of chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula or furatsilin will soften the throat and relieve pain.
- Antibiotic therapy - Augmentin, Duramox, Femolux in tablet forms or as a suspension for the treatment of uncomplicated scarlet fever.
- In severe cases, penicillin antibiotics are administered intramuscularly. In case of sensitization to penicillins, cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Cefuroxime) or macrolides (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin) are used. The duration of the course is at least 10 days.
- Antihistamines (Zyrtec, Suprastin) - reduce sensitization to endotoxin.
- Probiotics (Acipol, Probifor) will prevent the development of dysbacteriosis when taking antibacterial agents.
- Multivitamin complexes - to strengthen the body.
- Detoxification - drinking plenty of fluids will help relieve severe symptoms of intoxication. In severe cases, intravenous infusions are advisable.
Forecast
Usually, scarlet fever can be successfully cured provided that antibacterial treatment is started in a timely manner and all medical recommendations are followed.
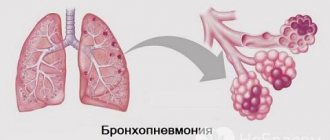
Complications in the form of arthritis, glomerulonephritis, pneumonia, myocarditis are diagnosed in weakened children or in the septic form of scarlet fever.
Recovery is accompanied by the formation of stable immunity, but sometimes scarlet fever infection occurs up to 3 times upon contact with different serotypes of the pathogen.
Risk groups and routes of transmission
This disease affects children aged 1 to 7 years. After 15 years, cases of the disease also occur, but quite rarely. This is due to two points:
- A child is often weaned at about one year of age. Breast milk contains antibodies that protect the baby from this type of infection.
- At this age, children begin to attend kindergarten, that is, they become susceptible to various unfavorable factors.
There are 4 groups of people who can become a source of infectious infection:
- patients with scarlet fever;
- patients with sore throat;
- carriers of streptococcus;
- recovering from any streptococcal infection.
After the baby recovers, he develops immunity, which is usually persistent. But! Only to the strain of streptococcus that he suffered from. So there is an opportunity to get sick again, only with a different type of disease.
Possible routes of transmission of hemolytic streptococcus:
- airborne;
- contact-household (much less common than the above);
- nutritional (food) – milk, ice cream, confectionery.
In spring and summer, infection occurs most often, especially through the airborne and nutritional routes.
Causes of scarlet fever
The causative agent of scarlet fever is a bacterium of the genus β-hemolytic streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes. The infection is transmitted from a sick person or carrier through airborne droplets, less commonly through household or contact contact. The disease develops only when antimicrobial and antitoxic immunity is absent. Factors that contribute to the occurrence of this disease are:
- Cold season
- Dryness and insufficient hydration of mucous membranes
- Any chronic pathologies, especially diseases of the nasopharynx
- Presence of wounds and other damage to the skin
- Frequent transmission of acute viral infections
- Reduced or emerging immune system
Varieties of scarlet fever
In addition to the classic clinical picture of scarlet fever, when hemolytic streptococcus settles on the tonsils, the following forms are possible:
- wound (burn) scarlet fever - when streptococcus enters the body through the skin or mucous membrane, the integrity of which has been damaged due to injury or other exposure;
- pulmonary - when the pathogen does not linger on the tonsils, but passes into the lungs. With this form, lung tissue is necessarily damaged;
- postpartum – the pathogen enters the body through the mucous membrane of the uterus.
Purple fever is characterized by the following symptoms:
- general malaise: chills, headache, nausea;
- increased body temperature above normal;
- tonsillitis (tonsillitis);
- skin rashes;
- prone to complications.
Good to know: Is it possible to get scarlet fever again?
Bright picture
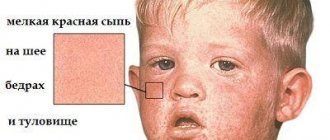
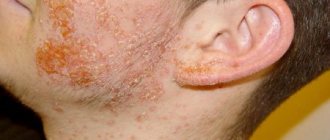
Streptococcus releases poison into the blood - erythrotoxin. Because of this, all the clinical symptoms of the disease appear: high body temperature (38–40 °C), weakness, enlarged tonsils, terrible sore throat when swallowing. These symptoms are identical to sore throat. But in contrast, by the end of the first day of illness, a profuse, pinpoint purple rash appears on the neck and upper body, which quickly spreads throughout the body. Most of it is on the elbows and under the armpits. The rash also covers the face, leaving only the space between the nose and lips untouched - the so-called nasolabial triangle, which remains pale. The tongue, under the influence of toxins, also changes color to bright red, with enlarged papillae (“crimson” tongue). The throat is red, with ulcers. The high fever and rash last for about 3 days, then gradually disappear, but peeling of the skin occurs on the body, face, hands and feet, which lasts 2-3 weeks.
Such a vivid clinical picture, it would seem, makes it impossible to make a mistake with the diagnosis, but in practice, scarlet fever is often confused with ordinary sore throat, rubella, measles, or even prickly heat, allergies and dermatitis. Indeed, in many children, especially those with reduced immunity, scarlet fever occurs in an erased form - almost without a rash, with a slight fever and unexpressed sore throat. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to take a throat swab to determine streptococcus A.
Clinical manifestations of scarlet fever
From the moment of infection until the appearance of the first clinical signs, an average of 2 to 7 days can pass; the incubation period can last 1-12 days. It is important to consider that the sick person is contagious from the very beginning.
Scarlet fever begins suddenly: a child, seemingly completely healthy, suddenly has a fever, a sore throat, and enlarged lymph nodes. He weakens, there is general weakness, headache, nausea and even vomiting.
When examining the throat, pronounced redness is detected, the so-called “flaming pharynx”.
A constant symptom of scarlet fever is sore throat. Beta-hemolytic streptococcus can cause various types of inflammation, depending on which the type of sore throat is determined:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- necrotic;
- pseudofibrinous.
Necrosis of the tonsils occurs on days 2-3 and disappears after 7-10 days.
Just a few hours after the onset of the disease, a rash begins to appear on the skin. It spreads quite quickly throughout the child’s body in the following order: face–neck–torso–limbs. The rash appears as small red dots that appear against the background of reddened skin. Most of all, it concentrates on the lateral surfaces of the torso, lower abdomen, on the flexor surfaces of the limbs and especially in the natural folds of the skin. The points can be located separately from each other, or they can merge together.
The rash lasts up to a week. After which it begins to fade, then lamellar peeling occurs (which is characteristic only of scarlet fever) in the form of a symptom of “gloves” on the hands and “socks” on the feet. After peeling, the child’s skin becomes very dry, which is due to the cytotoxic effect of beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Don't be afraid of this, this is a common manifestation of scarlet fever. The main thing is to remember in what order all this should happen.
Scarlet fever is characterized by the so-called white dermographism: if you run your fingers over a child’s skin, a white mark remains.
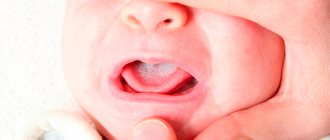
It is imperative to regularly examine the child’s oral cavity, because the action of the pathogen is also displayed on the tongue. In the first days of the disease, i.e. after the first signs of scarlet fever appear, the tongue is covered with a white coating. From 3-4 days, it is cleared of plaque, starting from the tip of the tongue, and acquires a bright crimson color. The papillae on the tongue swell and become raspberry-like. Hence the name of the trait – “raspberry tongue”.
The submandibular lymph nodes are palpated: they are significantly enlarged, dense and painful.
There are 3 forms of scarlet fever based on severity
- Mild form – general malaise, body temperature within 38oC.
- Medium form – severe malaise, body aches, nausea, temperature 38-39oC.
- Severe form – temperature 39-40°C, severe headache, nausea, repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief. Sometimes - delirium, hallucinations.
There are two forms along the flow:
- complicated;
- uncomplicated.
The complicated form is the most dangerous for the child’s health. Complications are divided into nonspecific and specific. In turn, specific ones are divided into:
- septic (myocarditis, lymphadenitis, mastoiditis, brain abscess, otitis, nephritis, sinusitis);
- allergic – autoimmune diseases (rheumatic carditis, rheumatism, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, glomerulonephritis, infectious-toxic shock).
Good to know: Manifestations of dangerous complications after scarlet fever
Symptoms and signs
Typical signs of scarlet fever in children and adults include:
- headache;
- severe weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- prolonged low-grade or febrile fever;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the submandibular region and neck;
- a pinpoint rash (sometimes petechial or vesicular), without a tendency to spread and the appearance of new elements, appears on the face (leaving the nasolabial triangle clean), body and limbs in the first days of the disease;
- hyperemia and swelling of the arches, tonsils and uvula in the pharynx, the appearance of follicles, lacunae or necrosis on its surface;
- change in the normal color of skin folds, their redness (Pastia's symptom);
- tourniquet symptom (Rumpel-Leed and Konchalovsky), the appearance of hemorrhages on the skin due to mechanical impact on it;
- hypertrophy of the lingual papillae (“crimson tongue”), appears due to its cleared from the initial yellow or gray coating on the first day of the disease, usually observed from 3-4 days from the onset of infection to 2 weeks;
Photo of the rash and surface of the tongue in children with scarlet fever - spasm of peripheral vessels due to a violation of vegetative functions in the body, externally manifested as white “dermatographism” of the skin;
- expansion of cardiac boundaries, systolic murmurs and changes in rhythm (bradycardia), this condition is called “scarlet heart”.
Symptoms in adults are mild, the rash goes away quickly, the temperature lasts from several hours to several days, recovery occurs faster and the risk of complications is not high. This is due to the fact that mature people have encountered streptococcal infection more than once in their lives and their body is already able to recognize it and “turn on” defense mechanisms in time.
Children are helpless against this pathogen and therefore their disease is more aggressive.
Video:
Diagnosis of the disease
Scarlet fever is diagnosed based on:
- epidemiological indicators: the incidence of scarlet fever and tonsillitis among the child’s environment is determined - in a group, at home, among neighboring children;
- clinics: a thorough examination of the child is carried out (oral cavity, throat, skin, especially natural folds of the skin);
- laboratory tests: general and clinical blood test (ESR, number of leukocytes, neutrophils and eosinophils increases).
Prevention of scarlet fever
To prevent scarlet fever, it is recommended to isolate the patient, take measures aimed at strengthening the human immune system, carry out wet cleaning of the room, and ventilate the rooms more often. It is important to eat properly, nutritiously, follow basic hygiene rules, and devote time to proper sleep. It is necessary to promptly and correctly treat any diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. If a sick child attended a children's group, a week-long quarantine is imposed.
Therapeutic measures
If a child is diagnosed with scarlet fever, then first of all he needs to be isolated from others. The patient is placed in a separate room, personal belongings and dishes are separated. Patients with mild and moderate forms are treated at home. If the course of scarlet fever is complicated, then it is advisable to transport the child to the infectious diseases department, where the treatment will be completely handled by the attending physician and nurse.
If the child is being treated at home, then parents must be familiar with how scarlet fever is treated in children. The child must observe strict bed rest for 5-6 days, regardless of the severity. You definitely need to keep an eye on this.
During fever, measures should be taken to reduce body temperature.
Important! Temperature reduction should be carried out gradually, as acute vascular insufficiency may develop.
Events
- physical cooling methods are the safest method of reducing temperature, used at 37-38°C. Apply: airing, wrapping, using an ice pack on the forehead and large blood vessels, wiping the body with water or vinegar and water;
- medicinal – at a temperature of 38°C and above. Used: paracetamol, aspirin, Panadol, etc.
- lytic mixtures - they are used if the temperature is above 38.5 ° C and does not decrease or even increases. If such a situation occurs, parents should call an ambulance, which will administer the lytic mixture. It is not available for free sale. It contains: analgin, diphenhydramine, papaverine.
The basis of treatment for scarlet fever is the use of antibiotics. Scarlet fever cannot be cured without their use. The course of treatment is 5-7 days. Drugs from the penicillin group are used, and one is selected:
- benzylpenicillin 2 times a day (intramuscular). Calculation of 100,000 units per kg of the child’s body;
- If the use of benzylpenicillin causes an allergic reaction in a child, then roxithromycin or Co-trimoxazole are used. Be sure to use antiallergic drugs;
- Bicillin-3 once (intramuscularly). Dose – 20,000 units per kg of weight;
- phenoxymethylpenicillin (orally). The daily dose is increased by 2 times. Frequency – 3-4 times a day.
Antihistamines are used together with any of the above remedies. They fight inflammation and suppress the sensitizing effect of streptococcus.
Symptomatic treatment
- food is served warm and ground. You should not eat cold or hot foods or drinks, as they injure the pharyngeal mucosa;
- the use of warm drinks and fortifying drinks (fruit drinks, decoctions, teas with herbs and berries) to improve immunity;
- vitamins of groups B, C;
- immunomodulators;
- It is mandatory (after the temperature drops) to gargle with one of the antiseptic solutions: chlorophyllipt, furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide up to 5-6 times a day. For one glass of water use 1 tsp. chlorophyllipt, furatsilin in a ratio of 1:5000 or hydrogen peroxide 1 tbsp.
Good to know: Building immunity to scarlet fever
In addition to antibacterial treatment, parents are required to care for their sick child.
Basic hygiene requirements that must be observed when treating a child:
- regular wet cleaning of the patient’s room;
- ventilation of the room;
- wearing seven masks by other members (masks must be changed every 2 hours; used masks can be thrown away or boiled and used again);
- use of oxolinic ointment by other family members;
- regular change of underwear and bed linen for the sick person.
Since the child is weak and cannot take care of himself, parents do it for him.
Child's toilet
- Rinse eyes using cotton pads and boiled water.
- Washing your face using cotton balls, boiled water and a soft towel.
- Cleansing the nasal passages using cotton swabs and petroleum jelly.
- Cleansing the ear canals using cotton swabs soaked in hydrogen peroxide.
- Wiping natural folds and then drying.
Diagnosis of the disease
What tests to take
Despite the abundance of obvious external manifestations of scarlet fever, in rare cases, the results of some laboratory tests may be needed to make a diagnosis. If a patient is suspected of having scarlet fever, the doctor will refer him for a general blood test, the results of which will show changes characteristic of a bacterial infection - an increase in white blood cells and ESR. It is also often necessary to carry out bacteriological culture from the nasopharynx and pharynx to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to a particular antibiotic and identify streptococcus. An additional throat swab helps determine streptococcal antigens. The presence of streptococcal infection can also be indicated by the result of a blood test for antistreptolysin-O. Carrying out all of the above laboratory tests helps to detect the presence of infection even before the first symptoms develop.
Differential diagnosis
As already noted, scarlet fever is often diagnosed during a routine medical examination, since it has specific symptoms. Information about contacts with people with infection and the history of pathology in childhood will help confirm this assumption. However, the presence of some related symptoms with measles, rubella, pseudotuberculosis and diphtheria requires differential diagnosis.
A specific symptom of scarlet fever is a burning pharynx with a clear limitation of the transition of the mucous membrane to the area of the hard palate. Also, only with this infection do changes in the tongue appear - it becomes bright crimson in color, and the papillae on its surface significantly hypertrophy. The rash with scarlet fever is pinpoint, it usually thickens in the joint flexures. The only place on the patient’s body free from rashes is the pale nasolabial triangle. When you press on the skin with a rash, the rash disappears for a while. When the rash completely disappears, the patient’s skin peels off very much, and in the area of the feet and palms it can peel off in huge layers.
The moment of development of all the main symptoms of scarlet fever is always accompanied by hyperthermia, which can vary from 38.5 degrees in a mild form of the disease to 41 degrees in a severe form.
Treatment with folk remedies
- Break a fresh egg and add 1 glass of warm water. Gargle 5-6 times a day.
- I take 1 tsp of fresh onion juice. 3-4 times a day.
- Use a thick decoction of blueberries. 100 g of dried berries are poured into 500 ml of water, boiled until 300 ml of water remains.
- Mix 1 glass of yarrow and 1 liter of hot beer. Drink 1 tbsp. 3 times a day, dressed warmly.
- Cut off the top of the black radish, make a hole, fill it with honey and cover with the cut top. They insist for 3 days. Take 1 tbsp. l. 5-6 times a day.
- Add 1 glass of fresh carrot juice 2-3 times a day for 2-3 days.
Do not replace folk methods with traditional treatment. It is better to use it in conjunction with antibacterial treatment. Traditional methods are used more to increase immunity than for primary treatment.
How does infection occur?
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets: coughing and sneezing, as well as through dishes, toys, and clothing. The child is a source of infection a day before the first symptoms appear and in the next 2-3 weeks. Babies 6-7 months old rarely get sick because they are protected by maternal immunity through breast milk. More often, scarlet fever occurs in children under 10 years of age who actively communicate with each other in kindergarten and school, and walk on playgrounds.
Many parents are interested in whether an adult can become infected from a child. This risk exists if a person did not get sick in childhood and his immunity is weakened. They get sick again in exceptional cases.
Prevention
Isolation of a sick child is carried out within 10 days from the moment the disease is detected. The child is sent to an educational institution only 22 days after the onset of the illness. This is due to the fact that the exact duration of the infectious period is not clearly understood. Contact children are quarantined for 7 days.
When treating a child suffering from scarlet fever, it is important not to get lost or panic. You must remember that the child needs your help. Of course, the incidence of complications after this disease is high, but a lot depends on your care. Knowing how to properly treat scarlet fever in children, you will save yourself from unnecessary worries, and your baby from unnecessary suffering.
Scarlet fever in children - what to do?
As soon as the first signs of scarlet fever appear in a child, it is necessary to call a doctor at home. Only after examination by a specialist and diagnosis of scarlet fever in children can treatment begin. This is an infectious disease that provokes numerous complications, so therapy must begin almost immediately after the disease is detected.
Otherwise, there is a high risk of such negative consequences as:
- myocarditis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pneumonia;
- rheumatism.
Is it possible to treat scarlet fever at home?
If a child falls ill with scarlet fever, the decision about the need for hospitalization is made by the doctor. In most cases, the patient is prescribed a home regimen. The child is allocated a separate room, limiting his contact with other family members, especially children aged 2–9 years. Home quarantine lasts about two weeks. Hospitalization is carried out only in severe cases of the disease, which are accompanied by a high risk of complications.
Is it possible to cure scarlet fever without antibiotics?
Fearing the effects of medication components on the child’s body, mothers often ask the doctor whether it is possible to treat scarlet fever without antibiotics. Due to the fact that the disease is provoked by a bacterium, taking antibiotics is simply necessary to neutralize and completely destroy it. However, according to the doctor’s decision, for mild forms of scarlet fever in children, treatment can be carried out without antibiotics.
In this case, mandatory maintenance therapy includes:
- antihistamines (Parlazin);
- anti-inflammatory (Ibufen);
- antipyretic (Paracetamol).
Classification
Doctors distinguish two main groups of scarlet fever.
In the first variant, the disease proceeds typically, affecting the upper respiratory tract and accompanied by general symptoms. This form of scarlet fever does not present any difficulties during diagnosis. Atypical scarlet fever may have different symptoms that differ from the classic course of the disease. With this form, there is no damage to the upper respiratory tract, rash or other usual symptoms. Atypical cases of scarlet fever also include extremely severe or erased types of the disease.
Among the typical cases of scarlet fever, doctors identify:
- mild form - symptoms disappear after 4-5 days;
- medium form - characterized by a more pronounced course, symptoms disappear after 5-7 days from the onset of the disease;
- severe form - characterized by the appearance of severe symptoms and damage to other organs, most often found in adults.
There is also a classification according to the course of the disease - uncomplicated and complicated forms of scarlet fever. The first option occurs without damage to other organs, all symptoms are limited to local manifestations and general intoxication. Complications of scarlet fever are divided into early and late.