Laryngopharyngitis is a complex disease that affects the upper respiratory tract, tonsils, pharynx and vocal cords. The pathological process consists of two diseases - laryngitis, during which the larynx and vocal cords become inflamed, and pharyngitis (the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and tonsils become inflamed). Often they occur simultaneously.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
The disease occurs in a person who often strains the vocal cords or in the absence of treatment for laryngitis or pharyngitis.
Etiology
The pathological condition can be triggered by a number of factors:
- viral diseases;
- regular exposure to stressful situations;
- bacteria;
- lack of treatment for colds;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- active or passive smoking;
- tension of the vocal cords for a long time.
These factors influence the development of the disease in both adults and children.
Halotherapy
If a child often and for a long time suffers from colds, then the prevention of laryngitis may also involve visiting salt rooms. Such rooms are analogues of natural salt caves, the air of which is beneficial for human health.
The salt rooms maintain optimal temperature and humidity; the air in such rooms is saturated with potassium, which has a beneficial effect on people's health. To increase efficiency, salt rooms are equipped with special ionizers.
The benefits of halotherapy for children who often suffer from respiratory diseases have already been proven. The beneficial properties of salt caves and rooms can be described as follows:
- normalize the functioning of the respiratory organs;
- help cleanse the respiratory tract of mucus and pathogenic bacteria;
- help strengthen the immune system;
- reduce inflammation and swelling.
Such procedures are an excellent prevention of laryngitis, but it is worth considering that visiting salt rooms is necessary in courses. The duration of treatment should be at least 2 weeks. Modern salt rooms for children include toys, comfortable chairs and a TV showing cartoons . The procedures for inhaling healing air for a baby are very interesting.
Not every family can afford to visit a salt cave. But the cost of visiting the salt rooms is quite affordable.
Classification
Doctors classify the disease into the following types:
- acute laryngopharyngitis;
- chronic laryngopharyngitis.
An acute type of laryngopharyngitis can provoke rhinitis or be accompanied by complications in the form of the development of an inflammatory process in the bronchi and trachea.
There are cases of the development of fungal laryngopharyngitis in a child, when the causative agent is a fungal infection. It is not always differentiated: there is a possibility that instead of mycotic agents, antibacterial drugs will be prescribed that are not able to cope with the fungus.
The chronic form of the disease often occurs in adults and occurs:
- chronic catarrhal;
- chronic atrophic;
- hypertrophic chronic course.
Determination of the form of the disease is carried out diagnostically.
Results
- Laryngitis is predominantly a childhood disease that requires treatment under the supervision of a physician.
- The main difference between laryngitis and ordinary ARVI is hoarseness and barking cough.
- Taking special medications is a mandatory aspect of laryngitis treatment.
- An attack of false croup can be stopped using inhalations with special drugs.
- All preventive methods come down to maintaining a correct lifestyle, on which the state of the immune system largely depends, and, therefore, the ability to resist infections. We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with Clenbuterol cough syrup in this material.
Symptoms
The acute form of laryngopharyngitis is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- sudden sore throat, sore throat;
- dry cough;
- rhinitis, nasal congestion;
- slight increase in temperature;
- hoarse, barely audible voice;
- separation of sputum in the throat when the cough becomes wet.
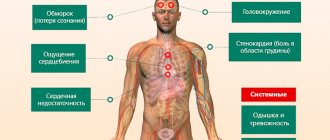
Symptoms characteristic of intoxication of the body may occur in parallel with an increase in body temperature.
In children, the acute form may proceed differently. The following symptoms will be characteristic:
- dyspnea;
- moodiness and tearfulness;
- coughing;
- bluish tint of the nasolabial triangle.
Chronic laryngopharyngitis occurs differently, depending on the form of the disease. Catarrhal disease is different:
- changes in the color of the throat mucosa: initially a red, then a gray tint appears;
- restless state (in case of illness of the child);
- changing from dry to wet cough.
Hypertrophic laryngopharyngitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- feeling of dryness in the throat;
- tissue growth in the palate and larynx;
- the back wall of the throat becomes covered with growths;
- continuous progressive cough.
The atrophic form develops after the hypertrophic one and has the following symptoms:
- thinning of throat tissues;
- prolonged crying, which can provoke coughing and vomiting in the child;
- pronounced dryness in the throat;
- increased intensity of tickling and coughing;
- loss of voice.
Due to the thickening of the mucous crusts, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Symptoms of acute and chronic laryngopharyngitis
What not to do
- Children aged 3 years cannot be treated with conventional steam inhalations, since the baby may get burned during the procedure.
- Use mustard plasters or other warming agents and methods during the period of acute laryngitis.
- Use expectorants for stenosing laryngitis, since the accumulation of mucus in the throat and the inability to cough it up due to severe swelling can worsen the already difficult breathing of a 3-year-old child.
- Treatment should not be carried out using hot drinks, which can irritate a sore throat and increase swelling.
Diagnostics
To correctly diagnose a pathological condition, a specialist must:
- examine the patient;
- inquire about complaints that bother the patient;
- study medical history.
After the examination, the doctor will prescribe the following laboratory tests:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- bacterial culture of a throat swab.
Bacteriological culture of a throat smear is needed to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed, such as x-ray examination of the chest area and laryngoscopy.
Forecast and preventive measures
If you take timely care of your health, this disease will end safely within a week. However, if left untreated, it can become chronic or cause serious complications such as an abscess.
To ensure that the disease no longer bothers you, you need to avoid hypothermia, not contact with sick people, and not overstrain your vocal cords. It is advisable not to talk loudly for more than an hour and a half. If the disease was of allergic origin, contact with the allergen should be stopped.
Treatment
Treatment of laryngopharyngitis is carried out exclusively in a complex way. Apply:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- treatment with folk remedies.
Drug treatment includes:
- antibacterial drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antihistamines (if swelling is present);
- cough medicines;
- antipyretic drugs (if the temperature rises).
The following antibiotics are prescribed:
- Bioparox;
- Ospamox;
- Azithromycin;
- Zinnat;
- Ceftriaxone (intramuscular injection, prescribed in severe cases).
Antiviral agents include:
- Theraflu;
- Strepsils;
- Travisil;
- Falimint;
- Inhalipt.
Among antihistamines, clinicians prescribe:
- Loratadine;
- Suprastin.
Medicines to eliminate cough can be for dry cough or for expectoration.
Expectorant medications:
- Alteyka;
- Bromhexine;
- Gerbion;
- Gedelix.
Drugs for the treatment of dry cough:
- Fluditek;
- ACC;
- Lazolvan.
Paracetamol or Nurofen may be prescribed to lower body temperature.
Physiotherapeutic treatment includes inhalations, electrophoresis and UHF.
Throat inhalations
Medication treatment is often combined with herbal medicine methods, since warm drinks and gargling will promote a speedy recovery.
The following variations of treatment with folk remedies are used:
- eat steamed garlic (if the person is hoarse);
- gargle with infusion of chamomile and sage, saline solution;
- potato juice helps relieve pain;
- inhalation on the bark of viburnum and oak or on lavender and chamomile flowers.
During treatment, sick people are contraindicated:
- drink alcohol;
- eat spicy, sour foods;
- breathe cold air;
- drink hot or cold drinks.
The room where the patient lies must be ventilated as often as possible. If you follow the recommendations of a specialist, you can recover quickly enough without additional complications.
Bronchodilators
Berodual
Berodual is a medicine for inhalation. It contains two potent ingredients: fenoterol hydrobromide and ipratropium bromide, which have bronchodilator activity. Therefore, the drug eliminates reflexes caused by the vagus nerve. Berodual is used for dry coughs in children and adults, for the prevention and complex treatment of bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis and other diseases associated with the bronchi. It prepares the airways for the use of aerosols in the form of antibiotics and mucolytics.
Application
It can be prescribed to children over three years of age. During treatment, one or two injections are made into the oral cavity 3 times a day. If it is used as a solution for inhalation, then take 2–8 drops and use 3–6 times a day, maintaining intervals of at least two hours. When adding it to an electrospray, you need to take 4 drops and combine it with 3 ml of solution. And then inhale this composition for 5 minutes until it completely evaporates. Atrovent is also used for inhalation.
How to treat laryngitis in children at home can be found in the article.
Erespal
Erespal is a bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory drug for children. It has an antispasmodic effect on the bronchi and stimulates the secretion of viscous mucus. It is produced both in tablets and syrup. Before use, we recommend that you read the instructions for Erespal cough syrup.
You can learn from this article which antibiotics are best for laryngitis.
Application
Not recommended for use by children under two years of age. And the tablet form is prescribed only to children over 14 years old; everyone else needs to drink it in syrup.
Before use, the daily dose is divided into 3 doses and consumed before meals. The dosage is calculated based on body weight. If the child weighs less than 10 kg, then you should drink from two to four teaspoons of syrup. And this is, respectively, from 10 to 20 ml of the product. With a body weight of more than 10 kg, the same amount of only tablespoons of medicine. And this will be from 30 to 60 ml of mixture.
Treatment should last at least 20 days, but no more than 30. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe a second course. The syrup is shaken each time before use.
What medications are needed to treat children from laryngitis can be found here.
Eufillin
Eufillin relaxes the muscles of the bronchi, contracts the diaphragm, improves the activity of the respiratory muscles and saturates the blood with oxygen. It has an antispasmodic, bronchodilator and diuretic effect on the body.
Application
Intravenously : for children over 14 years of age, a dropper is given at the rate of 2 - 3 mg per 1 kg of weight. For adolescents, the dose is taken on the upper scale.
Tablets: Children from 6 to 17 years old are prescribed to take one pill three times a day. The daily dose should not be more than 600 mg.
How to use tantum verde spray for laryngitis can be found in the article.