Eye contusion is a mechanical damage to the eyeball, which can be caused by many causes. According to oculists, it is this type of injury that becomes a catalyst for the development of many pathologies of the visual organs. Fortunately, this problem can be solved very simply if therapeutic actions were started in a timely manner. However, in order for the treatment of eye contusion to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to correctly classify the type of lesion and provide appropriate therapy.
Etiology
The etiology of injury plays a determining role in further prognosis and treatment tactics. Most often, eye contusion is a consequence of the following factors:
- Traumatic brain injury. The injury is indirect; there may be no visible defects. After a few hours or days, symptoms begin to appear - decreased visual acuity, headaches and dizziness.
- Direct hit. Injury can result from both physical and mechanical impact. The nature of the damage dictates the clinical picture and the severity of the disease.
- Blast wave. With such an etiological factor, the most severe consequences can occur, since damage occurs to both the internal and external parts of the organ of vision. The pathological process can develop symmetrically.
Specific pathological processes that can provoke such damage to the organ of vision have not been established.
Pathogenesis
After a mechanical shock, deformation of the ocular structures occurs, which provokes a sharp rise in intraocular pressure. This leads to the formation of hemorrhage in the eyeball and decreased visual acuity.
The severity of the contusion of the organ of vision will be influenced by the weight and shape of the traumatic object. If the area of the traumatic object and the speed are large, the severity of the injury increases significantly. The severity of the injury will depend on which part of the eye is hit.
General characteristics of the disease
Eye contusion is a violation of the integrity of the organ of vision as a result of exposure to a heavy object or mechanical force of increased intensity. Depending on the cause of the development of the disease, pathology is divided into direct and indirect forms.
The first appears due to the impact of mechanical force on the eyeball. For example, falling or being hit by powerful water pressure. An indirect anomaly is diagnosed as a result of damage to the area around the organ of vision.
In most cases, the contused eye returns to full function and continues to function uninterruptedly. But sometimes the injury leads to serious complications. The main danger of concussion is that there is a high risk of hemorrhage. According to statistics, approximately 30% of all cases end in complete loss of vision.
Classification
Based on their nature, there are two types of eye injury:
- straight;
- indirect.
According to the generally accepted medical classification, the following stages of damage development are distinguished:
- Eye contusion 1st degree (mild). There is mild swelling and possible bruising. There may be a decrease in visual acuity, but it is insignificant.
- Second degree. There may be a tear in the superficial membranes of the eyes, a rupture of the arch at the pupillary edge. The intraocular muscles may be spasmed.
- Damage 3rd degree. The cornea is saturated with blood, and there may be a tear in the eyelid. In some cases, there is a fracture of the skull bones in the orbital area.
- 4 or severe. Crushing of the eyeball, compression or rupture of the optic nerve may be present. The most severe contusion.
The consequences of the latter form of the disease, as a rule, lead to irreversible pathological processes: in the damaged organ, vision may disappear completely over time.
Determination of the severity and form of injury is carried out only by carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures. If you receive an eye injury, even a seemingly minor one, you should definitely contact an ophthalmologist.
Damage to various organs of the eye during concussion
The main components of the visual apparatus are the cornea, retina and lens. These elements are largely responsible for human vision. Therefore, they should be given special attention.
Pathological defects of the cornea
Stromal edema
As a result of contusion, the cornea can often be damaged. Defects indicating this are presented in the form of erosion deformations, differing in depth and area. The initial period, as a rule, lasts up to three days, and is characterized by the manifestation of such deformations of small size. After a week they become deeper.
Symptoms of such changes manifest themselves as:
- photophobia;
- unexpected attacks of lacrimation;
- sensations of the presence of a foreign body in the eye;
- blepharospasms;
- blurred vision (only with deformation of the center of the cornea);
- a sharp decrease in the acuity of the visual apparatus (this occurs with stromal erosion).
If the corneal endothelium has been destroyed, this causes swelling of the stroma (the clear layer of the cornea). At the same time, the purulent composition penetrates into the depths of the stroma and its other areas, and this leads to clouding of the cornea itself. It appears in the form of stripes or grids that appear before a person’s eyes.
With third-degree contusion, the stroma may become saturated with blood. The cloudiness in this case takes on a reddish tint, turning green, and ultimately becoming gray.
Cornea treatment
Treatment of corneal tissue involves the use of restorative type stimulants (corneregel, solcoseryl, methylene blue containing quinine). Blepharospasms are eliminated by blocking along the arteries located in the temple area. Lidocaine is also used for this. Toxoid, eye drops and ointments with disinfectant properties must be used.
Pathological defects of the lens
Cloudiness of the lens is a common consequence of contusion of the organs of the visual apparatus. Also, with serious injuries, a change in the location of the crystalline body may occur, that is, its dislocation.
The cause of cloudiness is usually moisture that enters the intraocular space through microcracks. It may appear a few days after the injury. When the cracks in the outer capsule are significant, the fibers swell and fill the intraocular space. This can lead to blockage of the outer chamber, which will increase the pressure inside the eye and may cause glaucoma.
Subluxation of the lens body can be diagnosed using the following series of symptoms:
- The anterior chamber has irregularities;
- Trembling of the iris is observed;
- The level of pressure inside the eye increases.
Dislocation is diagnosed based on the following signs:
- Deformation changes in the external chamber;
- Changing the location of the iris;
- The lens takes on a teardrop shape.
Pathological retinal defects
Also, often eye contusions can provoke clouding of the retina. This is usually caused by her concussion. The cloudy areas may be light gray in color and change to a milky color. The color change is explained by inflammatory processes occurring in the mesh structures.
Clouded areas most often appear at the periphery of the visible field of view and only for a short period of time. After their disappearance, a person’s vision is restored. If extensive swelling occurs, the risk of maculopathy (a disease affecting the center of the retina (macula)) increases.
As a result of trauma to the organs of the visual apparatus, various bleeding may occur:
- preretinal;
- retinal;
- subretinal.
This type of retinal bleeding can occur in the macular and paramacular areas, as well as around the disc and in large vessels. When the bleeding is stopped, the health of the visual apparatus is not restored to its previous state. The person will need to use correction tools.
Retinal detachment
Eye contusions often cause retinal detachment. This pathology is characterized by severe consequences. Detachment occurs when there is a blow to the retina. This may result in tearing or detachment from the jagged edges. The rupture is most often observed in the dimpled area in the form of holes. A large number of such gaps can form. Liquid seeps through them and the peeling process occurs.
Pathological changes in the retina lead to:
- a sharp deterioration in visual acuity;
- the occurrence of scotoma;
- narrowing a person's field of vision.
Important! In addition to the fact that contusions of the organs of the visual apparatus cause destructive processes in the lens, retina and cornea, they also entail destructive processes associated with other parts of the visual organs.
The following pathological processes may be considered particularly important:
- Conjunctival disorders;
- Violations of the integrity of the iris;
- Changes in the shape of the fundus;
- Violations of the integrity of the vitreous body;
- Destruction of the ciliary body;
- Optic nerve lesions;
- Contusion of the eyelids.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye contusion
The nature of the clinical picture will depend on the severity of the injury. At the initial stage, the following symptomatic complex may be present:
- pain and pain in the injured eye;
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- the victim cannot open his eyelids;
- visual dysfunction.
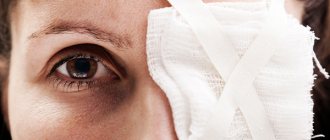
Visible signs of injury - hemorrhage in the eyeball, bruising, hyperemia of the skin around the organ of vision - may be absent. As a rule, this form of injury regresses on its own after 2 weeks.
Complicated forms of this type of visual damage may include the following symptoms:
- pain can radiate to the temporal, frontal region;
- the sensitivity of the cornea sharply decreases;
- visual acuity is significantly reduced, up to complete loss;
- spots, spots, and visual disturbances of a different nature appear before the eyes;
- headache and dizziness;
- mobility of the eyeball is very difficult, in other cases almost impossible;
- hemorrhage in the eyeball;
- swelling of the eyelid, hyperemia of the skin around the eye.
The specific clinical picture can in such cases be supplemented by general signs:
- headache and dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- impaired coordination of movements, orientation in space;
- loss of consciousness;
- memory impairment;
- hand tremors, paresis.
There may also be a clinical picture of problems with the nervous system. As a result, the complex of symptoms that appears will depend on the nature of the damage and the type of injury.
How to recognize an eyeball bruise? Symptoms.
The tissues that surround the eye have a tiny layer of fat, but a dense network of blood vessels that fit tightly to the bone component of the face.
As a result of trauma, fractures of the bone structures of the orbit often occur, and bleeding occurs. Bone fragments can compress soft tissue.
The symptoms of eye contusion are complex:
- lacrimation. Occurs due to irritation of the tear ducts, which are exposed to damage from the destroyed commissure of the eyelid. This symptom can be combined with inflammatory processes in the conjunctiva - if there is damage to the cartilaginous matter of the eyelid, due to which the latter closes/opens;
- hemorrhages. Blood accumulates in the layer of the eye fold, causing swelling and discoloration. Really complete closure of the eye opening. If a contusion of the eyeball occurs, hemorrhage can open at any point;
- accumulation of air masses in the subcutaneous layer of the damaged area, creaking of pieces of destroyed bone, pain when palpated. The eyeball is limited in its movements, penetrates deeper into the eye socket, the eye is half-closed. The described phenomena indicate a fracture of the bony projections of the orbit;
- inability to see anything. It is noted when the optic nerve is pinched between several bone fragments;
- the eyeball is bulging, the orbital vessels are bleeding. Occasionally, complete closure of the palpebral opening occurs, and the patient complains of double vision.
The ocular orbit consists of many components that are connected to the nasopharynx and the brain through a complex of blood vessels. The latter provide adequate nutrition to the specified orbit, but if it is damaged, an extensive hematoma can form, an accumulation of purulent masses - which, in turn, can cause a brain abscess.
The victim complains about:
- regular lacrimation;
- inability to stay in brightly lit rooms;
- gradual/rapid loss of vision;
- pain in the damaged area;
- increase in body temperature;
- uncontrolled closing of the eyelids;
- nausea;
- vomit.
The vulnerable location of the eyes leads to situations where accidental injuries can occur during everyday activities (drops of hot oil, steam, small solid particles, etc.). In addition, frequent neglect of safety precautions and ignoring personal protective equipment in the form of special glasses leads to frequent cases of injury during professional activities.
The main signs of eye injury are pain, burning and lacrimation. They are inherent in absolutely any damage and will be greater the more serious the injury. Many other symptoms can only be determined using special ophthalmic equipment.
Blunt trauma
Damage usually occurs during fights, falls, or accidents, when a blunt object hits the eyeball with force. In this case, a contusion of the eyeball develops, varying in severity.
Note! Blunt eye trauma is characterized by impaired pupillary response to light and the appearance of hyphema and hemorrhages.
Diagnostics
First of all, a physical examination of the victim is carried out: the doctor visually examines the injured eye and finds out how the injury was received and with what object.
To determine the severity of damage to the organ of vision and the risks of complications, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- visometry;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- gonioscopy;
- biomicroscopy;
- radiography of the facial part of the skull;
- MRI of the head;
- Ultrasound of the eye;
- non-contact tonometry.
Standard laboratory tests are carried out only when necessary, since in this case the tests themselves do not have diagnostic value.
Treatment
Initially, the victim should be given first aid: give pain relief, apply cold to the eye area, but not to the organ of vision itself. Treatment tactics will depend on the severity of clinical signs of injury and the severity of the injury.
Conservative treatment is based on taking the following groups of drugs:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiseptics;
- painkillers;
- mydriatics;
- hypotensive;
- antibacterial.
If necessary, a bandage is applied to the damaged organ of vision. Physical activity and alcohol intake are strictly prohibited during the treatment period. Factors that contribute to visual strain in victims should be excluded.
If conservative therapy does not give the desired result or a severe eye injury is diagnosed, surgical intervention is performed. In such cases, in addition to consulting an ophthalmologist, the intervention of a neurosurgeon will be required.
First aid
Any eye injury, even if it seems minor, requires medical attention. It is important to competently provide first aid to the victim at the scene of the accident. Chemical and thermal burns are dangerous, as they lead to damage to eye tissue. The treatment is lengthy because it is difficult to completely restore visual functions.
If you are burned by an acid, alkali or other chemical, rinse your eye thoroughly. This must be done under running water for 10-15 minutes. After the burning and stinging have subsided a little, you need to go to the hospital. If the chemical is solid, it should be removed before rinsing.
What to do as first aid for thermal eye damage? If a hot shard or hot liquid gets in, you need to remove it with a towel and rinse with cool water.
Then a cold compress is applied. Radiation burns are treated with cold application and anti-inflammatory drops.
First aid for eye injury depending on the severity of the injury:
- For superficial injuries caused by a foreign body, it is necessary to retract the eyelid and remove the object. Then rinse the eye.
- Dry ice helps with bruises.
- In case of a penetrating wound, if the eyeball falls out or there is bleeding, it is necessary to apply a gauze bandage.
- If a large foreign object is stuck, it is necessary to immobilize the eye. This is achieved by applying a bandage. You cannot move until the ambulance arrives.
What is prohibited to do when providing first aid for an eye injury? In no case should you rub the organs of vision, try to independently remove a foreign object in case of a deep penetrating wound, touch the mucous membrane with dirty hands, or use an eye patch made of cotton wool (only gauze or bandage is suitable).
Penetrating wounds are not washed. In case of an acid burn, alkalis should not be used for rinsing and vice versa.
While the eye is healing, you should stop wearing contact lenses. Instead, glasses are used to correct vision.