Why can the pubic bone hurt during pregnancy?
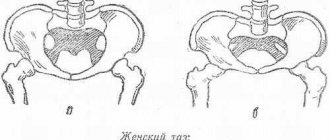
Let's first look at what the pubic bone is. The large pelvic bone consists of 3 bones, one of which is called the pubis. It, in turn, is steamed, looks like a roll as thick as a thumb and is formed by the fusion of two pubic bones, forming the pubic symphysis. They form the anterior wall of the pelvis. The female body begins to prepare for childbirth in advance. The hormonal background changes: relaxin has a softening effect on the pubic bone, helping to soften it.
REFERENCE! Relaxin is a preparation hormone for childbirth. It is intensively produced in late pregnancy. Relaxes the cervix, weakens the connection of the pubic symphysis with other pelvic bones, reduces uterine tone, softens other ligamentous tissues (which provokes, for example, joint pain in the last months of pregnancy).
But not only the pubic bones soften, but also the cartilage, the fusion site of the pubic symphysis. Wise nature took such care of both the woman in labor and the baby: it will be easier for the woman to give birth, and for the child to pass through the birth canal easier.
The distance between the two pubic bones in a healthy woman is within 5 millimeters. In a pregnant woman, the indicator may shift by a couple of millimeters and be 7-8. If the distance is more than 10 mm, a diagnosis of “symphysitis” is made. However, it is too early to panic - this is considered the initial stage, which does not threaten either the woman or the child, and does not require conservative intervention (of course, if the woman does not experience unbearable pain from which she cannot even walk). All that is needed is more careful medical supervision and the choice of the correct delivery tactics in the future. There are no contraindications to natural childbirth.
But with a discrepancy of 10 to 20 mm, they speak of the second stage of the disease. The pain becomes aching, moves to the groin, femoral and lumbar regions, and radiates to the tailbone.
Prevention of bone pain during pregnancy: general recommendations
You already know why bones hurt during pregnancy. If such a nuisance does not bother you, that’s great, but we recommend that you listen to some tips that will help you avoid pain in the future:
- try to climb stairs less;
- in later stages, sit less so as not to load the spine;
- do not lie on a hard surface;
- try to always keep your body in a symmetrical position (that is, distribute your weight evenly);
- buy a bandage and wear it from time to time (this will reduce the load on the bones).
If pain is already bothering you, you can relieve it with some exercises:
- Get on your knees and place your hands on the floor. Make sure that the vertebra, neck and head are at the same level, and then relax your back muscles. Stretch your back up like a cat backing up, then lower your head down and tighten your abdominal and thigh muscles. Do this 3 times.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees and bring your feet toward your butt. Gently begin to spread your knees to the sides and at the same time make sure that they are symmetrical. Do the exercise 5 times.
- Lie on your back and bend your knees 30 degrees. Slowly lift your pelvis up, stay in this position for a few seconds, and then lower it. Repeat the exercise 5 times.
Reasons for the development of symphysitis
REFERENCE! Under the general name “symphysitis” several changes and damage to the symphysis pubis are combined. There are more than 16 of them: loosening, softening, edematous impregnation, stretching, expansion, divergence, rupture, inflammatory process, symphysiopathy, symphysitis itself, and so on.
There may be several reasons contributing to the development of symphysitis. But it should be noted that it is not always possible to indicate a specific reason: one can only assume, taking into account both the anamnesis and the course of pregnancy as a whole.
- Firstly, scientists suspect that there is a genetic tendency, which can be inherited.
- Secondly, this diagnosis is more often made to those women who, before conception, had problems with the musculoskeletal system (for example, the pelvic bones were incorrectly positioned, were injured in the past, or had anatomical features: a saber-shaped pubis).
- The third reason is a severe hormonal imbalance, in which the hormone relaxin is produced in excess.
- And the last option is a deficiency of calcium and vitamin D in the body, an imbalance of magnesium, phosphorus and calcium.
REFERENCE! If the fetus is large, its head is low, plus polyhydramnios is present - pain in the pubis is almost always present (due to the load on the symphysis pubis).
Causes
In most cases, there is only one thing that is “wrong” - the density of the pubic bone, symphysis pubis, and ligaments has changed. And this is a difference from the state that the body is accustomed to recording as “normal,” and it hurts mommy. This change occurs because childbirth is coming, and soon 3-4 kilograms of happiness should squeeze through the birth canal. Not only muscles and ligaments are prepared. Under the influence of such a biologically active substance as relaxin (a hormone that only pregnant women have in excess), the joints of the pelvic bones relax. The pubic bone, which becomes more pliable, is most affected by “relaxation”.
The pubic bone itself is a paired bone; it consists of two pubic bones. They are connected clearly in the middle, and this is called the “pubic symphysis”, in medical terms – the symphysis. It is the pubic bone that bears the most load during pregnancy, and it is this bone that will prevent the baby from being born unharmed if measures to soften it are not fully completed. By the way, most often the pain is felt precisely in it, it’s just that the range of sensations extends to the entire pelvis.
If everything is fine, your term has passed 34 weeks, and you feel pain between your legs - you already know what causes this, this is a variant of a normal pregnancy. But if the pain is severe, sharp, and does not go away for days and nights, it is better to see a doctor. Because there are other causes of pubic bone pain during pregnancy, especially if you have just overcome the first weeks of the marathon of bearing a child or have just stepped into the second trimester.
In general, there are several pathologies in which pain in the pelvis and pubic bone is observed during pregnancy:
- Lack of calcium. The baby grows inside you, it begins to form its own skeleton. To build this skeleton, he takes calcium from the mother's blood. With an inadequate diet, calcium begins to be actively washed out of the bones - after all, the baby cannot be denied. Calcium deficiency makes bones brittle and brittle, a process also called osteomalacia.
- Lack of vitamin D. Everyone probably knows that calcium absorption is possible only if this vitamin is present in the body. There is no vitamin - no matter how much cottage cheese you eat, calcium will not be added to the body.
- Lack of magnesium and phosphorus . These microelements are also important in the process of building normal bone tissue, so their deficiency will primarily affect your bones.
- Growth of the uterus . Before pregnancy, the weight of your uterus did not exceed 40-50 grams. Now it contains a baby whose weight is already about 2 kg, several liters of amniotic fluid, and the placenta. And the wall of the uterus has become much larger and thicker. And all this puts pressure on the pubic bone.
- Woman's height . Well, what about growth... A woman in this position grows in breadth. And in addition to the weight that the baby adds to her, the mother also adds her own “extra” kilograms. And it’s one thing when the musculoskeletal system is used to carrying 60 kilograms, and quite another thing when it’s 70-75. All this mass “presses on the bones.” That’s why my back, lower back, and pelvis hurt during pregnancy.
- Symphysitis . This disease is also called symphysiopathy. Remember what a symphysis is? So, when this articulation of the pubic bones begins to diverge prematurely or occurs too intensely, the pubic bones become excessively mobile. And this is already dangerous for the mother (in this case the child is in little danger, and thank you for that). The symphysite has three stages, and each is filled with its own range of unpleasant sensations.
How is the problem diagnosed in pregnant women?
This disease is rarely asymptomatic. Listen to yourself and if:
- When walking (even slowly), your pubic bones hurt a lot.
- A sharp pain occurs when pressing on them, during sudden movements, stepping over a threshold, climbing stairs, even turning over from side to side in bed. You can hear crackling and clicking noises.
- When lying on your back, it is uncomfortable for you to lift your straightened legs up.
- The gait becomes like a duck waddling from foot to foot.
More on the topic
How to help a woman with pubic bone pain during pregnancy?
What is symphysitis after childbirth and how to treat it?
When do the pelvic bones begin to separate during pregnancy?
What is symphysitis during pregnancy?
Is it possible to avoid toxicosis during pregnancy?
IMPORTANT! Don't put off visiting your doctor. Among expectant mothers, there is an opinion that pain in the pubis a month before childbirth is the norm, and this must be endured. We hasten to dissuade you - no, this is not the norm, but a condition that requires medical supervision. If it develops into a disease, it will not go away on its own, the pain will only intensify, and serious inflammation may develop inside, which can cause fetal impairment and premature birth.
The doctors you need are a gynecologist, a surgeon and a traumatologist. You will probably be offered to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pubis, and, if necessary, an x-ray (for up to 16 weeks).
Is it normal for the pubic or pelvic bones to hurt during pregnancy?
If something hurts, this is a signal from the body about pathology, and this is not normal.
But in the case of pregnancy, everything is not so simple. The process of carrying a new family member in itself is a colossal burden on the mother herself. But the body knows that this process leads to procreation, which means it is necessary and important. Therefore, in the case of a curious situation, the organs and systems do not wait for everything to become completely bad, signaling the owner of the situation even at the first suspicion of pathological processes. Most often, pain in the pubic bone and pelvis begins in the third trimester of pregnancy. And she doesn't necessarily mean that everything is bad. Rather, it is simply a warning to a woman that she needs to be more careful and more attentive to herself, her lifestyle and diet. And do not make sudden movements. In fact, most young mothers encounter a similar range of sensations in the later stages, and in most cases such pain is a variant of the norm. But something is wrong if you are bothered by unpleasant sensations.
Basic treatment methods
- With the first degree of symphysitis, the woman does not need any treatment. The situation will normalize on its own, but after childbirth, in the meantime, some kind of painkiller will help alleviate the pain syndrome. The doctor may recommend rubbing the pubis with Menovazin or drinking No-shpu. Exception: thin, petite women with a narrow pelvis who are carrying a large child. The issue of obstetric care is decided in each case individually.
IMPORTANT! A woman will be prohibited from giving birth on her own if the pelvic bones diverge by more than 1 cm. The risk of complete rupture of the ligaments during pushing is too great, so the doctor will insist on a caesarean section.
- The second degree is already more serious. The birth may be unsuccessful and the woman will be forced to be placed in a cast for several months, and then in a corset for six months. It is difficult to predict the outcome of childbirth, so the doctor warns the mother in advance about the possible consequences and offers her to choose from two options: either a caesarean section, or take a risk and give birth herself.
- If there is a urogenital infection or internal inflammation, antibacterial therapy, pain-relieving suppositories or ointments will be prescribed.
- If the pubic bone hurts from the 32nd week of pregnancy and after childbirth, use the same antibiotics and ultraviolet irradiation of the pubis.
Which doctor should I contact if I have pain in the pubic bone and pelvis during pregnancy?
The first doctor who should know that you have pain somewhere is and remains your obstetrician-gynecologist. Any changes in your body, one way or another, are reflected in the course of your situation. And it doesn’t matter if it’s swelling during pregnancy, varicose veins in the legs or wild pain in the area of the pubic bone, sacrum and hips. And this specialist, believe me, will send you where you need to go without delay.
And you need to go where they will diagnose and prescribe treatment taking into account pregnancy. That is, an osteopath is a doctor who deals with bones. You may need to donate blood for a general analysis and for biochemistry and urine. Donate, this is the only way the osteopath will understand what is missing in your body for the normal condition of bone tissue. In addition, last but not least, it is worth “visiting” the surgeon and traumatologist. The first will rule out or confirm suspicions of symphysiopathy, the second will deal with suspicions of possible fractures and cracks. In any case, between examinations and surveys you will have to attend an ultrasound, based on the results of which the doctors will make a final verdict and tell you how to deal with this problem.
Prevention of pubic pain during pregnancy
- Be sure to review your diet. Add foods high in magnesium and calcium: nuts, legumes, dried fruits, dairy products, green leafy vegetables. Take quality vitamins or nutritional supplements.
- Exercise regularly. Naturally, only permitted and in moderation. This could be yoga for pregnant women, water aerobics, swimming. You can strengthen your ligaments with a set of special exercises – your doctor will advise you on them.
- Try to stay in a sitting position as little as possible; when sitting, do not cross your legs, avoid asymmetry, place your feet flat on the floor. The seat of your chair should be quite soft.
- Be careful with loads and movements. Do not make sharp turns or climbs. When going to bed, prepare a thick pillow: learn to place it under your feet (the pillow can be replaced with a rolled-up blanket).
- Watch your weight: extra pounds add stress.
Conclusion
Pain in the pubis does not always signal danger, but it always causes discomfort. A pregnant woman does not need unnecessary worries, therefore, if you notice deviations from the norm, rush to your doctor for a consultation. The specialist will answer all your questions in detail, conduct an examination, dispel your fears or prescribe the necessary treatment.
Especially for beremennost.net – Ksenia Dakhno
Treatment for pain in the pubic bone
Treatment as such is not carried out; after childbirth, the ligaments acquire their primary state. You can only temporarily reduce the pain by taking 1-2 tablets of No-shpa or rubbing the area above the pubis with Menovazin solution. And if there is swelling of the pubis due to an existing inflammatory process, then drugs such as Chondroxide gel or Betalgon ointment are also prescribed (the products must be applied over the affected area). And to replenish calcium reserves, Calcium D3-Nycomed or its analogs are prescribed.
Do not get carried away with taking medications containing calcium. This can lead to premature hardening of the baby’s skull bones, which can lead to birth injuries. Also, excess calcium puts additional stress on the kidneys and contributes to early aging of the placenta, which is not desirable during pregnancy.
By the third trimester, it is even recommended to reduce the consumption of foods rich in calcium and stop taking “tablet” calcium so that childbirth takes place without possible complications.
Also, with symphysitis, it is necessary to minimize physical activity such as climbing stairs, long walking, etc.
Sitting in one position for more than 1 hour and crossing your legs while sitting is also not recommended.
You need to stand firmly on both legs, and not put all your weight on one leg.
When turning over in bed, you need to turn first the upper torso, and then the pelvis itself.
An orthopedist/surgeon/traumatologist may prescribe wearing a special pelvic bandage and performing a set of special exercises that can strengthen the ligaments and increase the tone of the pelvic muscles, which will reduce pain with symphysitis.
The pelvic bandage secures the pelvic ring, preventing the pubic bones from moving and thereby causing pain.
In the last months of pregnancy or after childbirth, antibiotics and UV irradiation of the pubic area (the same solarium) may be prescribed to relieve inflammation of the symphysis. If there is no inflammation, then they simply carry on with the pregnancy and wait for the birth.
Causes of pubic pain in pregnant women
Doctors cannot name the exact reason for the development of this condition, but there are prerequisites that may cause the development of this condition:
- Large fetus - if the weight of the child in combination with amniotic fluid is quite impressive, the load on the pelvic bones is large. Under this weight, the bones can begin to separate.
- The release of a large amount of the hormone relaxin - in this case, the ligamentous apparatus is greatly softened, bringing pain to the mother in the pubis. But in this case, it will be easier for the child to pass through the birth canal.
- A woman’s predisposition to diseases of the musculoskeletal tract - during an interesting position, the bones experience greater stress and may be subject to deformation.
- A lack of vitamin D3, an imbalance of phosphorus, magnesium and potassium lead to the fact that calcium, so necessary for a pregnant woman for strong bones, begins to be poorly absorbed.
Pubic pain in early pregnancy
Early term is considered to be the period from conception to the end of the first trimester or the middle of the second. Any painful sensations in the early stages of pregnancy should alert you.
A visit to a gynecologist is a prerequisite , since only a qualified specialist can correctly diagnose the location and exact cause of pain.
If pain in the pubic area is accompanied by bleeding and nagging pain in the lumbar region, immediately call an ambulance, as the risk of miscarriage remains high until the 3rd month of pregnancy.
If the pain is localized only in the pubis, do not worry, eliminate the load on the spine and remain calm during the day, the painful symptoms should subside. Perhaps the pain in the pelvic area is affected by a lack of calcium in the body; consult a specialist about the possibility of taking a vitamin complex.
What is the condition of the pubic bone during pregnancy?
The symphysis pubis consists of cartilaginous tissue that connects the two pubic bones. In the normal state of the body, this entire complex is motionless, but with the onset of pregnancy the situation changes. The hormone relaxin, released by the body in large quantities, relaxes the ligaments. In this case, the bones lose their immobility and begin to move apart - pain in the pubis occurs.
Doctors already consider a distance of 6-8 mm between the bones to be grade I symphysitis, although this condition is natural. This does not pose a danger to the health of the mother and the child, but the doctor must make a note in the chart.
If the bones diverge further, then when the distance between them is 1-2 cm, a diagnosis of “second degree symphysitis” is made. A distance of more than 2 cm is stage III. There is only one thing that pleases future mothers - pain in the pubis during pregnancy is not terrible for the fetus, it only causes discomfort for the mother.
At 39 weeks
Severe pain in the pubic area may indicate the onset of labor . Contractions are accompanied by nagging pain in the lower back, contraction of the uterus, and slow movement of the fetus along the birth canal, which in turn leads to maximum divergence of the pelvic bones.
If the frontal joint diverges by more than 1 centimeter, it is recommended to maintain complete rest: do not engage in sports, avoid lifting heavy objects, and reduce long walks and climbing flights of stairs. At 39 weeks, labor can begin at any time.
Whenever possible, you should visit a gynecologist to make sure that the discrepancy of the frontal bones is not critical and a cesarean section is not required. If you neglect additional research (if indicated), pain in the frontal joint will accompany you for a long time after childbirth.