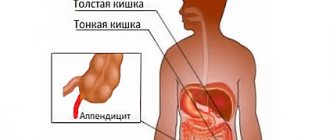
One of the most diagnosed pathologies of the abdominal organs is appendicitis - inflammation of the small vermiform appendix of the cecum (appendix). Most often, the disease occurs in patients 20-40 years old. In older people and children, inflammation is rarely diagnosed. Signs of appendicitis in women due to the presence of many organs in the pelvis and abdominal cavity are difficult to recognize. The first symptoms of the disease are often vague and similar to many gynecological diseases. Problems in the uterus, its tubes, and ovaries can provoke inflammatory changes in the bladder, urethra and intestines, compression of the digestive ducts, and ultimately lead to pathological changes in the appendix. It is very important to recognize the disease in time and receive qualified medical care.
Signs of the disease
The first symptoms of appendicitis in women are observed against the background of general normal health. Most often, abdominal pain appears in the evening or at night.
Symptoms of appendicitis in adult women differ from the manifestations of inflammation of the appendix of the cecum in young girls. They are constantly sick, but vomiting is rare, there is a change in the nature of the stool, painful cramping sensations on the right side of the abdomen (can be observed in the ribs, lower back, right thigh, around the navel), which intensify with physical activity, sneezing, coughing. The temperature is usually within normal limits, and it may even drop. Depending on the location of the appendix, other symptoms may indicate appendicitis:
- loss of appetite;
- yellow-coated tongue;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels (37-38 degrees);
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- flatulence;
- chills;
- tachycardia;
- frequent and painful urination;
- bloating;
- general weakness.
Sometimes the inflammatory process occurs in a chronic form. Manifestations of the disease in this case are less pronounced, but are similar to the above symptoms.
The most common symptoms of chronic appendicitis in women:
- paroxysmal pain;
- frequent stool disorders;
- During exacerbations, nausea and vomiting are observed.
In pregnant women, due to changes in the normal position of internal organs due to fetal growth, the first signs of appendicitis are often mild. Pain sensations are concentrated near the ribs, gradually covering the entire peritoneal area. The enlarging uterus compresses neighboring organs and disrupts their functioning. The process involves the renal pelvis, liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Inflammation often begins during the period of “critical days” in women due to the proximity of other organs and the likelihood of their infection.
Pain from appendicitis
The difficulty of making an independent diagnosis lies in the fact that the organ can be located in different areas of the peritoneum.
- Most often, the process is localized just below and to the right of the navel. There, during inflammation, pain occurs.
- Sometimes the appendix is located higher, where the liver is located, and accordingly, unpleasant sensations are associated with it.
- Pain in an organ that is too low can be confused with inflammation of the ovaries in women or the urinary tract in men.
- If the appendix is shifted towards the spine, appendicitis “gives” to the lower back, sometimes to the groin.
Causes of pathology
The main cause of the disease is stagnant processes in the appendix (mechanical blockage of the appendix opening with coprolites, seeds, bones, waste products of helminths or due to tumors). Other provoking factors may be:
- atypical structure of the process;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- bad habits;
- endocrine disorders;
- hormonal changes;
- constant stress;
- production of large amounts of serotonin;
- frequent constipation.
Rupture of the appendix of the cecum is dangerous and can result in death.
Features of blood supply and innervation
Blood supply to the appendix is possible in four ways:
- the only artery that supplies only the appendix (without the adjacent section of the cecum), occurs in half of the cases;
- more than one vessel, observed in ¼ of people;
- the process and the adjacent part of the cecum receive blood together from the posterior artery, found in ¼ of patients;
- the arterial branch goes into a loop - this is rare.
The practical importance of studying the blood supply can be seen in the example of applying ligatures (sutures) when removing the appendix. Incorrect consideration of the joint blood supply can cause necrosis of the adjacent area of the cecum and failure of the sutures.
A photo of the removed appendix quite eloquently indicates its inflammation
The outflow of venous blood goes through the superior mesenteric vein into the portal vein. Attention should be paid to collateral connections with the renal veins, ureteric veins, and the vascular network of the retroperitoneal space.
Lymphatic capillaries extend from the bases of the crypts and connect to the submucosal vessels. Penetrate through the muscular layer into the mesenteric nodes. The vessels of the cecum, stomach, duodenum, and right kidney are connected by especially close connections. This is important in the spread of purulent complications in the form of thrombophlebitis, abscesses, and phlegmon.
Nerve fibers to the appendix come from the superior mesenteric and solar plexus. Therefore, pain with appendicitis can be widespread.
Classification
The inflammatory process in appendicitis goes through several stages: catarrhal, phlegmonous, gangrenous and rupture of the appendix. It only takes some time for them to occur during inflammation.
The first stage is characterized by complaints of abdominal pain, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. The catarrhal stage lasts 6-12 hours.
In the next 24 hours, a phlegmonous period develops, ulceration and accumulation of pus in the appendix begins, temperature indicators increase to subfebrile values.
If the pathological process is not diagnosed at this stage, then the gangrenous stage occurs - necrosis of appendix tissue. Its duration is 24-48 hours.
The final stage is the rupture of the process of the cecum. Without immediate surgical intervention, death occurs.
Symptoms of appendicitis
- The main sign indicating an inflamed appendix is pain. It may increase gradually or appear suddenly. In most cases, it is a stabbing sensation that is almost impossible to endure. A person tries to lie down in a position that will reduce his suffering. It is especially dangerous when the pain disappears. You need to understand that appendicitis does not go away on its own, and the disappearance of this symptom indicates the beginning of necrosis and death of nerve endings.
- General malaise. It is difficult for a person to carry out his usual duties, he wants to lie down, and feels weak.
- With appendicitis, appetite disappears.
- Nausea appears, and in some cases vomiting, which does not bring a feeling of relief.
- The temperature rises and chills occur.
- The number of heart beats reaches 90-100.
- A white coating appears on the tongue.
Diagnostics
Making a correct diagnosis includes mandatory differentiation from other diseases. Appendicitis in women is similar in symptoms to:
- acute cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- abdominal muscle rupture;
- renal colic;
- adnexitis;
- adhesions;
- chronic gastritis;
- rupture of a cyst in the ovary;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- intestinal obstruction.
The examination of the patient begins with a general examination, during which the specialist palpates the abdomen, collects anamnesis and checks his suspicions for the presence of inflammation of the appendix using special techniques (Bartholomew-Mikhelson, Obraztsov, Shchetkin-Blumberg). Next, diagnostic procedures are prescribed to confirm appendicitis in women: blood and urine tests, abdominal ultrasound, laparoscopy, sometimes CT, MRI, contrast radiography. An examination by a gynecologist may also be necessary.
Laboratory blood tests show leukocytosis and increased ESR.
Urinalysis also reveals changes in the presence of pathology.
Other manipulations are necessary to differentiate the disease.
Home diagnostics and self-diagnosis
Even if you know in theory how appendicitis hurts, it is important to verify your fears or part with them. Every adult is able to find out whether the appendage is inflamed, and then take certain actions.
How to determine appendicitis yourself?
- Lay the sick person on his back on a flat surface.
- Feel the lowest rib on the right. Lightly tap slightly below the bone with your fingertips. Painful sensations indicate illness. You can perform the same manipulation with the subcostal area on the left. If pain is not detected there, this will only confirm fears.
- Ask the person to show you where the pain is most severe. Apply pressure to this area with your middle and index fingers. The pain should dull, but the moment you remove your hand, it will intensify significantly.
- Another sign of appendicitis is discomfort in the appendix area when trying to cough.
- If you recommend that a person assume the fetal position on his right side, with his legs bent and curled up, he will experience temporary relief. Rolling over and stretching his legs will make him feel worse.
If all the signs are confirmed, the main thing that needs to be done immediately is to call an ambulance. Only professional doctors in a hospital setting can help the patient.
However, even if, according to your calculations, appendicitis is not confirmed, it would be correct to send the person to the hospital. There are a considerable number of diseases of the digestive, reproductive organs, and genitourinary tract, the symptoms of which are similar to inflammation of the appendix. For cholecystitis, pancreatitis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, and diseases of the appendages, only professionals can help.
Treatment
Treatment of the pathological process is surgical only . Modern techniques make it possible to perform operations without incisions, by introducing special manipulators through the oral cavity, which remove the inflamed appendage. But the cost of such an operation is high.
Therefore, a classic or laparoscopic appendectomy is usually performed. The first option involves an incision on the right side of the abdomen. Through it, the diseased organ is removed. After treatment, a scar approximately 10 cm long remains. Laparoscopic appendectomy is performed through 2-3 small punctures using a laparoscope.
In case of peritonitis, the inflamed appendix is removed using both methods, as well as sanitation and drainage of the abdominal cavity. A course of antibiotics is required.
Postoperative recovery involves a two-month dietary restriction: a ban on eating fatty, fried, very salty foods, marinades, baked goods, and canned food. Alcohol is not allowed. Smoking is not recommended. It is recommended to give up sports for a period of 2 to 6 months.
A sick leave certificate is issued for a period from 2 weeks to 40 days. The hospital stay after appendicitis surgery lasts about 10 days; if complications arise, the period increases to 40 days.
Possible complications
Like any surgical procedure, appendectomy can have undesirable consequences. The most common complications are:
- abscesses in the abdominal cavity;
- formation of adhesions;
- peritonitis;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- necrosis of an organ area.
- infiltrate.
Such conditions require emergency removal of pathological tissue. Therefore, if women develop symptoms that are not typical for appendicitis or the postoperative period, then medical advice and assistance is necessary.
Prevention
To prevent appendicitis, it is important to eat a balanced diet and promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genital area in order to minimize the risk of infection of the appendix. It is useful to take a course of multivitamin complexes 1-2 times a year to strengthen the immune system. Prolonged stress should be avoided whenever possible. It is recommended to eliminate bad habits and carry out anthelmintic therapy. In this case, the likelihood of inflammation of the appendage of the cecum will be significantly reduced.
If appendicitis is suspected, it is prohibited to apply a heating pad to the painful area, take analgesics and laxatives, give an enema, be treated with folk remedies, physically exert yourself, eat and drink. It is necessary to seek medical help from specialists.
Signs of appendicitis in women do not always allow the pathology to be quickly recognized. The physiological characteristics of the body structure of the fairer sex make diagnosis difficult. However, contacting a doctor if discomfort occurs will help clarify the diagnosis and provide timely treatment.
Appendicitis in children: causes
Experts usually identify factors that directly cause acute inflammation and factors that are specific provocateurs that significantly increase the risk of disease manifestation. These groups include a large number of different reasons, both natural and caused by improper care of the child and monitoring his health.
The main reasons for the development of appendicitis
The appendix (that's right, not appendicitis, as many people believe) is a small extension of the large intestine. This process in its shape resembles a worm, with which it is usually compared, and ends with a completely blind end. The functions and purposes of this organ in the human body are not yet completely clear, and there are a huge number of assumptions about the functional significance of the appendix. For a long time, doctors promoted the theory of the mandatory removal of this process even before the appearance of any inflammatory processes, but after the idea appeared that this organ could play an important role in maintaining immune processes, this practice did not take root.
The cause of inflammation of the appendix and the development of appendicitis is usually two main reasons, very similar to each other:
- narrowing of the process;
- blockage of the appendix.
Subsequently, the active development of bacterial flora occurs in the cecum. Among the main reasons for such complete or partial blockage are the following options:
- small particles of fecal stones entering the cecum;
- ingestion of foreign small indigestible objects (for example, it is especially well known that large amounts of swallowed seed husks lead to appendicitis);
- development of parasites in the intestines;
- intestinal torsion, causing blockage;
- congenital anomalies and anatomical disorders in the correct structure of the cecum.
Such a mechanical blocking of the lumen of this same cecum ultimately leads to a disruption in its functioning - mucus begins to be removed with great difficulty, or getting rid of it stops completely, internal pressure increases sharply, the walls become tense, and the mucous membrane noticeably swells. The blood supply process sharply deteriorates, venous blood stagnates, and the same microflora and bacteria that accumulate in the appendix quickly multiply. In children, appendicitis usually becomes inflamed within 12 hours after the process “starts”.
Photo: Appendicitis in children
The development of appendicitis and the subsequent outpouring of pus and accumulated fecal matter occurs rapidly - it usually takes from 1 to 3 days before this process begins.
By the way, usually children under 2 very rarely suffer from the acute form of appendicitis. This is due to a more natural and soft diet at this age, and also in childhood, this appendix is wider and shorter - it is much easier to clean. With age, appendicitis seems to stretch, making it difficult to cleanse. Lymph nodes, which, when swollen, can also clog the appendix, are formed only by the age of 8, when a very large number of cases of exacerbation are usually observed.
Factors that increase the risk of developing appendicitis
Pathogenic microflora is always present in all parts of the intestine, so it can hardly be called the causative agent and cause of the development of inflammation. The reason for the development of inflammation is the creation of a favorable environment for bacteria, in which they begin to actively multiply, many times exceeding the natural quantities usually contained in the body. Another way to sharply increase their number in the appendix is for bacteria to enter there along with lymphatic fluid or already infected blood, which comes from already infected organs that act as foci of infection. Such foci may be located, for example, in the nasopharynx during the development of colds. The development of inflammation can also be caused by individual infections, such as sore throat and otitis media. Other diseases are directly related to appendicitis. These usually include typhoid fever, tuberculosis and other serious infectious diseases.
Factors that significantly influence the increased risk of exacerbation of appendicitis and, in general, the onset of inflammatory processes in the cecum are usually called:
- improper and too abundant nutrition, from early childhood allowing children to eat “harmful” foods such as chocolates, chips and other foods;
- a small amount of fiber in the daily diet, which stimulates the proper functioning of the entire intestine;
- too much harmful sugar consumed, all in the same chocolate, sweets and other treats;
- frequent constipation, which is often a consequence of poor nutrition, but in its own way affects the risk of inflammation (read the article on how to treat constipation in a child);
- developing intestinal dysbiosis, already affecting the normal number of bacteria in the human body;
- a variety of diseases of the entire gastrointestinal tract, both infectious and ordinary irritations or poisoning;
- the development of parasites in the child’s body, in particular helminthic infestations.