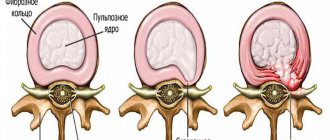
Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder in the transmission of signals in the brain due to damage to one or a group of nerves. There are several types of disease, which can be triggered by various factors.
For example, chronic neuropathy is often a concomitant disease with complicated diabetes mellitus.
ICD-10 Category: G90.0
G90.0 Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy
Etiology:
- Stimulation of hypersensitive carotid sinus baroreceptors (causes parasympathetic or sympathetic responses)
- Tumors of the carotid body
- Inflammatory and tumor processes in the lymph nodes of the neck
- Metastases to the area of the carotid node.
Risk factors:
- Organic heart disease
- Systemic atherosclerosis
- Mechanical irritation of the carotid nodes (tight collar on clothes, shaving the neck area, head movements)
- Emotional disturbances.
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Falls
- Veil before my eyes
- Tinnitus
- Bradycardia
- Arterial hypotension
- Pallor
- No symptoms after the attack.
Diagnostics:
- With the patient lying on his back with constant ECG monitoring, a careful massage of the carotid node is performed (before performing the massage, it is necessary to check whether the patient has any contraindications to this procedure). In carotid ganglion syndrome, there is a delay in systole of more than 3 seconds (cardiac inhibition) and/or a drop in systolic blood pressure of more than 50 mmHg. without reduction in heart rate (vasodepression)
- ECG
- Duplex scanning of the carotid arteries.
Differential diagnosis. Vagal reactions, postural hypotension, primary failure of the autonomic nervous system, hypovolemia, arrhythmias, pathological sinus syndrome and other conditions accompanied by low cardiac output, cerebrovascular insufficiency, emotional disorders.
Lead tactics. The method of choice is pacemaker placement (dual-chamber).
Drug therapy:
- Anticholinergics—atropine for cardiac inhibition
- Sympathomimetic drugs - ephedrine
- Theophylline.
Surgical treatment:
- Denervation of the carotid sinus surgically or with radiation therapy for selected patients
- In patients with elements of cardiac inhibition, pacemaker placement helps prevent relapse of symptoms
- For atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid sinus - surgical removal of atheromatous plaques.
- Persistent confusion after fainting
- Frequent falls lead to injuries and fractures.
Course and prognosis.
With atheromatous lesions of the carotid or basilar arteries, the prognosis is not very favorable.
Concomitant pathology:
- Sick sinus syndrome
- AV block.
Make an appointment via
Sign up for an appointment with the doctor
Any use of materials is allowed only with the consent of the publisher.
Certificate of registration of mass media EL No. FS3 dated 08/21/2017.
Peripheral autonomic failure (PVF) is a syndrome represented by a complex of pathological autonomic manifestations that develop with damage (usually organic) to the peripheral (segmental) part of the autonomic nervous system, which causes disruption of the innervation of internal organs, blood vessels, and endocrine glands. The causes of damage to the peripheral autonomic nervous system are primarily systemic, metabolic and endocrine diseases.
- The characteristic clinical manifestations of PVN are: Orthostatic hypotension, which is manifested by presyncope and syncope.
- Tachycardia at rest, fixed (rigid) pulse, arterial hypertension in the supine position.
- Dyskinesia or paresis of the stomach, intestines, constipation, diarrhea.
- Bladder atony, urinary incontinence, frequent imperative urination.
- Impotence.
- Hypohidrosis.
- Dry eyes.
- Dry mouth.
- Decreased vision at dusk.
- Sleep apnea.
There are primary (idiopathic, hereditary) PVN, caused by chronic slowly progressive degenerative diseases with an unrecognized etiology, and secondary peripheral autonomic failure associated with a primary neurological or somatic disease. The main symptom of primary PVN is orthostatic hypotension, i.e. transient clinically significant drop in systemic blood pressure when moving to an upright position or during prolonged standing.
Diagnosis is based on clinical data and identification of the underlying disease.
Treatment for peripheral autonomic failure is symptomatic, in addition to treatment of the underlying disease.
- Primary PVN. Idiopathic (isolated, “pure”) autonomic failure (Bradbury–Egglestone syndrome).
- PVN plus multiple system atrophies (Shy-Drager syndrome).
- PVN plus clinical manifestations of parkinsonism.
- Familial dysautonomia (Raily – Dey (Riley – Dey)). Other hereditary autonomic neuropathies (hereditary sensory-autonomic neuropathies (HSVN) and hereditary motor-sensory neuropathies (HMSN)).
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency).
- Primary PVN. Idiopathic chronic autonomic neuropathies.
- Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension (isolated autonomic failure).
- Chronic idiopathic autonomic neuropathy.
- Chronic idiopathic anhidrosis.
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.
- Autonomic failure in the elderly.
- Acute dysimmune autonomic neuropathies. Acute pandysautonomia.
- Acute cholinergic dysautonomia.
- Acute adrenergic dysautonomia.
- Familial amyloid neuropathy.
- Peripheral autonomic failure in metabolic neuropathies. Diabetic polyneuropathy.
- Alcoholic polyneuropathy.
- Acute inflammatory polyneuropathy (Guillain-Barré syndrome).
- Diphtheria polyneuropathy.
- Paraneoplastic dysautonomia.
- Polyneuropathy in diffuse connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, Sjogren's syndrome, systemic scleroderma).
- Neuropathy in chronic lung diseases.
There are no precise data on the prevalence of primary forms of peripheral autonomic failure, but it is known that they are relatively uncommon. The prevalence of multiple system atrophy is 1.9-4.9 cases per population. Among the secondary forms, the leader is PVN in diabetes mellitus. With amyloidosis, peripheral autonomic failure is detected in 80% of cases.
Autonomic neuropathy refers to disorders that affect the functioning of internal organs. With this pathological process, there is a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses from the central nervous system to the autonomic nerve endings that control the functioning of the stomach and intestines, heart and other systems.
The main symptoms of this type of neuropathy are:
- sudden pressure surges. With a pronounced decrease, the patient faints.
- Problems emptying the bladder. May manifest as difficulty urinating or urinary incontinence.
- Problems in the sexual sphere. Women experience anorgasmia and vaginal dryness. The stronger sex begins to have problems with erection and ejaculation.
- Gastric paresis with slower evacuation function. Diarrhea, constipation, bloating, heartburn, or vomiting.
- Impaired thermoregulatory function with high or decreased sweating.
- Changes in the accommodation of the pupils and the inability of the eye to adjust depending on the level of illumination.
- Inappropriate increase and decrease in heart rate in response to physical activity.
If such symptoms appear, patients should immediately consult a doctor, especially for the risk group, which includes people with diabetes.
Peripheral neuropathy or neuropathy includes several conditions that have one common feature - damage to the distal processes of nerve endings. There is no separate diagnosis for peripheral neuropathy (the exception is peripheral neuropathy as a complication of diabetes), therefore, when signs of neuropathy develop, doctors look for the cause of this condition.
Causes of neuropathy
Neuropathy is non-inflammatory damage to the nerves.
The name combines various degenerative-dystrophic changes in peripheral nerves. The nervous system is formed by peripheral nerves and various nerve plexuses, the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nerves, having a thin and at the same time complex structure, are unstable to damaging processes. There are mononeuropathy, which means damage to one nerve, multiple mononeuropathy, in which several nerves are involved in the process, but in different parts of the body, and polyneuropathy, which involves several nerves and is localized in one area.
Causes of neuropathy
· diabetic neuropathy is damage to nerve fibers and small vessels due to high levels of sugar and lipids in the blood.
· toxic neuropathy – the cause is nerve damage due to infectious diseases, among which are diphtheria, HIV, herpes, etc. The normal state of the nerve trunks is disrupted by poisoning with chemicals and the over-dosed use of certain medications.
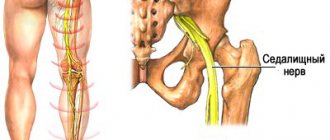
· post-traumatic – often a strong blow or other acute injury leads to disruption of the integrity of the myelin sheath of the nerve. This form is the result of compression of nerve fibers during bone fractures, improper formation of scars and tissue swelling. The most common lesions are the sciatic, ulnar and radial nerves.
Quite often the development of neuropathy is provoked by arthritis. osteochondrosis of the spine, liver and kidney diseases, insufficient levels of thyroid hormones in the body, tumors, etc.
Symptoms of neuropathy
peripheral form of neuropathy, i.e. damage to the nerves innervating the upper or lower extremities. In this case, there is a feeling of tingling on the side of the affected nerve, loss of sensitivity in the fingers and toes, and a feeling of numbness.
The proximal form is determined by a loss of sensation in the legs, particularly in the lower leg, thigh or buttock.
The autonomous form disrupts the activity of the digestive and genitourinary systems.
Found an error in the text? Select it and a few more words, press Ctrl Enter
Neuropathy is a rather complex disease, so anamnesis must be collected especially carefully, since such a disease can develop for a long time without showing symptoms. It is especially important to note whether viral diseases were present, what new medications may have been taken, or whether there was contact with chemicals.
The disease can be provoked by alcohol abuse or the presence of a systemic disease. A diagnosis is made based on many facts. Neuropathies progress in different ways, with rapidly increasing symptoms over several days or years. The disease is diagnosed by palpation of the nerve trunks, revealing the presence of thickening.
Traditionally, when examining polyneuropathy, blood is examined to determine ESR. Also included in the diagnostic complex is a chest x-ray and plasma glucose levels are measured after meals. Electrophoresis of serum proteins is performed.
Treatment of neuropathy
Treatment of non-inflammatory nerve lesions is selected individually and requires an integrated approach and constant prevention.
Methods and methods of therapy are selected depending on the degree, form and reasons contributing to the disruption of nerve fiber conduction. All efforts are aimed at restoring nerve function. The diagnosis of toxic nerve damage first of all implies the elimination of toxic effects. This may include stopping the medication or avoiding the use of toxic substances.
In diabetics, it is necessary to maintain normal blood sugar levels. If a post-traumatic form of damage to nerve fibers is identified, it is recommended to eliminate the traumatic factor. The complex of treatment must necessarily consist of taking painkillers, vitamins of certain groups, drugs that normalize metabolism and enhance regenerative ability.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are also prescribed. Prevention of neuropathy includes restoration of metabolic processes, timely treatment of systemic and infectious diseases. It should also be taken into account that this disease can become chronic, so it is advisable to take all necessary measures to prevent exacerbation.
Patients with such disorders, with a decrease in tangible symptoms of the disease and a possible chronic process, benefit from sanatorium treatment. Where they are prescribed psychotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, exercise therapy and massage, magnetic therapy, light and laser treatment, aromaphytotherapy.
Prevention of neuropathy involves every person taking care of their health. A healthy lifestyle and regular exercise can improve blood microcirculation in the limbs and other parts of the body. Prevention of complications of neuropathy is also important. You should avoid injuries and burns to your hands and feet, wash and examine your body parts daily, and if there are any changes, consult a doctor.
Neuropathy is any nerve disease that involves damage to parts of the spinal cord.
Neuropathy can be divided, depending on the neurons affected, into two categories:
- sensory, in which motor neurons are affected and motor disorders are detected and
- motor, in which the damage occurs mainly to the thick and thin fibers of the spinal cord.
The causes of this disorder may be: arthritis with rheumatoid symptoms, various forms of diabetes, hypothyroidism, tumors, renal or liver failure, which cause polyneuropathy.
Also, the cause of neuropathy is associated with increased sensitivity in the lower extremities and symmetrical disturbances of motor reflexes. There are cases when arthritis with rheumatic symptoms and amyloidosis appear, which are the cause of tunnel neuropathies. They occur through compression of the nerves. These include the following types of neuropathy: ulnar nerves, radial nerve, peroneal nerve and carpal tunnel syndromes.
Pathological diseases such as diabetes, tuberculosis, and polyarthritis can cause mononeuropathy, in which the lesion affects only one nerve and is most often accompanied by pain.
Also in medical practice, there are cases when neuropathies are not the result of diseases, for example, in the case of a lack of B vitamins, folic acid in the body, or as a result of the consequences of poisoning the body with mercury and other types of toxic substances, or the result of contraindications to taking any medicines.
Facial neuropathy is characterized by unilateral loss of facial muscle movement. In this case, one half of the face has normal sensitivity and mobility, while the other becomes like a mask. Damage to one part of the face manifests itself in smoothing of folds and wrinkles, widening of the palpebral fissure and drooping of the corner of the mouth. When the patient tries to make any movement with the immobilized part of the face, the asymmetry becomes more obvious.
With this type of pathology, the patient’s speech changes; food, while eating, may not stay in the mouth because the lips do not close tightly.
Three stages of facial damage:
- movements that convey an emotional state suffer;
- the mechanisms responsible for voluntary movements suffer;
- the mechanisms of facial muscles suffer.
These stages will help determine the treatment tactics and duration of therapy needed by the patient, as well as make an adequate prognosis for the course of the pathology.
Diabetes is the most common cause of neuropathy. High blood sugar levels in people with poorly controlled diabetes lead to nerve damage.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause neuropathy.
Some chemotherapy drugs and medications used to treat HIV cause nerve damage.
Poisons (toxins) - insecticides and solvents can cause damage to peripheral nerves.
Cancer - Neuropathy can occur in people with certain types of cancer: lymphoma and multiple myeloma.
Alcohol – Excessive alcohol consumption causes nerve damage.
Chronic kidney disease – If the kidneys are not functioning properly, an imbalance of salts and chemicals can cause peripheral neuropathy.
Chronic liver disease.
Infections—Nerve damage can be caused by some infections, including HIV infection and Lyme disease.
Connective tissue diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Certain inflammatory conditions—conditions including sarcoidosis and celiac disease—can also cause peripheral neuropathy.
Hereditary diseases - Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome and Friedreich's ataxia.
Diabetic neuropathy refers to metabolic polyneuropathies. A special role in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy belongs to neurovascular factors - microangiopathies that disrupt the blood supply to the nerves. Multiple metabolic disorders that develop against this background ultimately lead to swelling of the nervous tissue, disruption of metabolic processes in nerve fibers, disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses, increased oxidative stress, the production of autoimmune complexes and, ultimately, to atrophy of nerve fibers.
Increased risk factors for the development of diabetic neuropathy include age, duration of diabetes, uncontrolled hyperglycemia, arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity, and smoking.
Types of neuropathy and its manifestations
Content
Neuropathy is damage to nerve fibers and the development of disturbances in trophism and blood supply to tissues in the area of innervation.
The difference between this deviation and neuralgia is that as a result of neuropathy, the leading symptom is not severe pain, but a violation of muscle control, which is regulated by the damaged nerve.
There are different types of neuropathy, and they are divided so that in clinical practice it is convenient to make a diagnosis and apply one or another treatment.
Some types of disease
Neuropathy can appear for a number of unrelated reasons:
- metabolic disease;
- complicated diabetes mellitus;
- oncological diseases;
- toxic effects on the body;
- chemotherapy or treatment with potent antiviral drugs;
- severe injuries;
- diseases of joints and cartilage tissue;
- viruses and infections.
Neuropathy often accompanies diabetes mellitus. In this case, they talk about the chronic course of the disease.
Diseases of the joints and cartilage tissue, all kinds of arthritis and arthrosis, can cause neuropathy due to compression of a group of nerve fibers by damaged and deformed joints.
PNS disorders can also be caused by toxic substances, including excessive alcohol consumption and narcotic drugs.
The disease is often observed in HIV-infected people, due to the effect of drug therapy on the patient’s body.
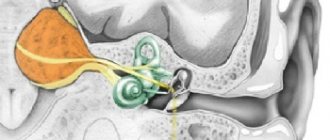
Doctors distinguish between a wide variety of PNS injuries. Acoustic neuropathy is common. The cause of this disease is nerve damage due to disruption of communication between the hair cells of the ear. As a result, the patient experiences hearing difficulties. Characteristic symptoms of damage to the auditory nerve:
- unintelligibility of words (“white noise”);
- extraneous noise in the ears;
- disruption of the sensitivity of the connection between sounds and words.
Features of the pathology of the auditory nerve are that the disease is observed both in infants and in older people. Hearing impairment may be mild, and in some cases the patient has no hearing at all. Often the speech apparatus is also affected.
Among the causes of human hearing loss are:
- congenital pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- immunity disorders;
- genetic diseases of the PNS and CNS;
- toxic effects on the body of various drugs;
- oncological diseases.
Diseases of the auditory nerve can be congenital, caused by negative factors at birth. The development of hearing impairment can be triggered by the baby’s low weight, lack of oxygen in the first days of life, genetic abnormalities, and birth trauma.
To make a diagnosis, a detailed examination of the patient’s hearing system is necessary. It should be remembered that progressive disease can lead to complete deafness.
Therapy includes wearing a hearing aid in cases of complete hearing loss, or installing a special electronic device that stimulates impulses sent to the brain.
What are the types of neuropathies?
At the moment, there is no unified classification of such a disorder as peripheral neuropathy. Experts have identified 100 types of this condition, each of which has its own symptoms, causes of occurrence and prognosis.
Function is impaired depending on the type of nerve that is compressed or destroyed. They are:
- Motor, or motor. This is a type of nerve that controls movement (moving the body in space, speaking, or picking up objects).
- Sensory. They are responsible for the process of perception - analyzing objects by touch, pain as a result of any violation.
- Vegetative. They help the functioning of internal organs and exercise control over breathing, the functioning of the digestive organs and heart muscle, and other actions that are not consciously regulated.
Most often, one or two types of nerves are affected, but sometimes in severe cases damage to all three types of fibers is observed.
Neuropathy can also be acute or chronic. In the chronic form, there is a gradual increase in symptoms and long-term progression. The acute form of the disease is characterized by severe, sudden pain and disorders that develop over a short time.
Symptoms of the disease
The following symptoms are typical for neuropathy of the peripheral nervous system:
- numbness in certain parts of the body;
- absence of pain as a reaction to an irritant;
- inability to perceive changes in temperature;
- violation of movement coordination;
- burning sensation or “lumbago” at night.
Symptoms depend on the location of the nerve damage. If the structure of the motor nerve is disrupted, the patient will experience difficulty coordinating movement. Also, this form of the disease is characterized by numbness of the limbs.
When the sensory nerve is damaged, the sensitivity to pain or temperature changes is impaired. Autonomic neuropathy is accompanied by pain and a burning sensation.
As the disease progresses, symptoms become worse. For effective treatment, it is very important to identify the cause of neuropathy, which is often complicated by the presence of a variety of symptoms inherent in other pathologies.
Symptoms of pathology
The disorders that occur in the human body with this pathology affect various areas. The extent of optic nerve damage may also vary from patient to patient. Much depends on the immune system and the general condition of the body. Sometimes it happens that neuropathy affects the oculomotor nerve completely. In some cases, a partial disruption of its functions occurs. Therefore, it is very important for the doctor to analyze in detail the symptoms, which can be varied. The main signs of the disease include:
- drooping eyelid;
- pain in the eyes;
- immobility of the eyeball;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dilated pupils;
- diplopia.
A common consequence of abducens neuropathy is heterotropia. Typically, the patient develops convergent strabismus. More often this occurs in advanced forms of the pathology. Some people complain of high blood pressure, which is often due to problems with the brain. Headaches are another common symptom of this disease. It often happens that patients do not pay attention to the malaise and associate it with prolonged visual work.
What does mononeuropathy mean?
For various reasons, all nerve fibers, or one nerve, can be damaged. In the latter case we are talking about mononeuropathy. It happens:
- Post-traumatic. Occurs when there is a significant blow, bruise, or cut of such intensity that it leads to nerve damage. Sometimes this happens due to the peculiarities of its localization. When it is located superficially, a minor injury is enough to lead to the development of neuropathy. So when you hit your elbow, you get a very unpleasant feeling.
- Mononeuropathy as a result of infection or hypothermia. Often in the latter case, pathology of the facial nerve develops. Viruses (herpes) and atherosclerotic lesions of blood vessels that feed nerve endings can lead to this disease. A typical example of postherpetic pathology is intercostal neuropathy.
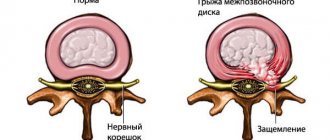
- Compression-ischemic neuropathy. It occurs when compression of the nerve fiber occurs in the area of the bone canal. The narrow space through which the nerve passes, together with blood vessels and muscles, can cause pinching as a result of sudden movement or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position. When pressure is applied, compression ischemia develops (the latter occurs as a result of disruption of blood flow through the vessel supplying the nerve). This phenomenon also has a second name - tunnel syndrome.
The most typical manifestation of this syndrome is pinched nerves in the wrist area. This phenomenon is often observed in people who are associated with work that requires them to constantly work with their wrists (sewing, knitting, typing, playing keyboards).
Polyneuropathy
It occurs when multiple nerves are damaged with the development of paresis and muscle paralysis. In this case, a change in pain, tactile and cold sensitivity occurs. Symptoms at the initial stage of the disease affect only the hands and feet, but as the pathological process progresses, it spreads upward. This is most often the case with diabetic neuropathy.
Patients with impaired sugar metabolism show signs of this abnormality as a result of changes in normal processes in the nerve fiber. The situation is further aggravated by the fact that blood vessels, including those supplying nervous tissue, also suffer.
Symptoms of peripheral polyneuropathy in the presence of diabetes mellitus are usually noted as follows:
- at an early stage of the lesion, only slight loss of sensitivity and decreased reflexes are noted. Only an experienced specialist can identify such deviations. For this reason, the endocrinologist refers patients with diabetes mellitus to regular consultations with a neurologist.
- There is a burning sensation, tingling and other uncomfortable sensations. Most often this is observed in the distal parts of the lower extremities, less often in the hands. Often the pathology is combined with deformation changes in small joints.
- In a neglected state, severe pain develops in the lower extremities and muscle atrophy develops. The lack of normal innervation and blood circulation leads to the development of gangrene.
A mandatory aspect in the treatment and prevention of diabetic polyneuropathy is careful and constant monitoring of blood glucose levels. It is very important to take insulin and the necessary medications in a timely manner to prevent sudden spikes in sugar.
For this purpose, glucometers are used at home. The more frequently fluctuations in glucose levels occur, the greater the likelihood of developing this disease. Type 1 diabetes requires a preventive examination by a neurologist five years after the diagnosis. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes should be tested annually as soon as it is diagnosed.
It is absolutely necessary to constantly check the feet for cracks or wounds, and treat them with antiseptics. Wearing tight shoes is not recommended. Failure to comply with these prevention rules can lead to disability with loss of a limb or death from septic complications.
In the presence of diabetes mellitus, other types of neuropathy can develop - autonomic and local.
Causes of abducens neuropathy
The disease rarely develops on its own. It is usually a consequence of other diseases. Most often, neuropathy of the abducens nerve occurs against the background of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, after traumatic brain injury and neurosurgical operations. Much less often, the disease is congenital. Cases of a hereditary form of pathology are not excluded, but they are not so common in medical practice. Doctors consider the main causes of the development of abducens nerve neuropathy
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism);
- neurological pathologies (osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, multiple sclerosis, stroke);
- complications of infectious diseases (encephalitis, diphtheria, meningitis);
- intoxication of the body (poisoning with ethyl alcohol, chemicals, alcohol);
- chronic arterial pathologies (atherosclerosis, arteritis, phlebitis);
- cardiovascular diseases (varicose veins, arrhythmia, angina).
Doctors cannot always immediately determine what exactly caused the development of neuropathy of the abducens nerve of the eye. Diagnosis of this disease is often carried out by several specialists simultaneously, including: neurologists, cardiologists, endocrinologists, and traumatologists.
The disease is easier to detect in children than in adults. One of the causes of abducens neuropathy is hydrocephalus. This disease allows doctors to immediately carry out procedures that will allow them to diagnose the pathology.
Establishing diagnosis
Making a diagnosis is fraught with some difficulties due to the vagueness of symptoms. Often, in order to determine the cause of the disorder, the patient is prescribed a full examination of the body.
The following diagnostic techniques are used:
- MRI – to detect disturbances in the structure of nerves in the muscle area;
- CT scan – to obtain a complete picture of the condition of all internal organs of the patient;
- Electromyography is a method that allows you to check muscle activity.
The doctor may refer the patient for a skin biopsy. This diagnostic method involves studying a small excised flap of skin to determine the condition of the nerve fibers.
To effectively treat the disease, it is important to determine the cause of the pathology. If diagnostic methods do not reveal the cause, the doctor diagnoses an idiopathic form of PNS disorder, that is, a deviation caused by unknown causes.
About diagnostics
Diagnosis is often difficult due to different symptoms; the patient must undergo a complete neurological examination.
Carrying out tests and analyzes will help identify how the nerves are affected due to common diseases.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Why double vision and the dangers of double vision
Information about the composition of the blood will help determine diabetes mellitus, vitamin deficiency, any deficiency, or pathology of the immune system. If you examine the cerebrospinal fluid, you can see the presence of antibodies that are related to neuropathies.
Other narrow-profile data determines:
- specific blood pathology;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- oncology.
Muscle strength tests reveal:
- convulsive activity or dysfunction of the motor type of nerve tissue;
- assess vibration, temperature and pain sensitivity;
- soft touch;
- body position;
- impairment of sensory sensitivity.
Instrumental diagnostics are presented:
- computer, magnetic resonance tomography;
- electromyographic study;
- skin and nerve fiber biopsy.
Clinics and treatment centers for idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy
Having discovered the first alarming symptoms, you should go for a consultation with a neurologist. Treatment begins with eliminating the cause of the PNS dysfunction. In cases where the cause cannot be identified (idiopathic form), treatment is carried out comprehensively and includes the following groups of drugs:
- sedatives;
- anticonvulsants;
- antioxidants;
- vitamin preparations;
- a potent pain reliever.
If symptoms do not go away after drug treatment, physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed to stimulate the functioning of the damaged area of the PNS.
The drugs are selected by the attending physician depending on the characteristics of the PNS damage. During treatment you should adhere to a balanced diet. If the disease is caused by complications of diabetes, it is very important to maintain blood glucose levels within normal limits.
If peripheral neuropathy affects the motor group of nerve fibers, the patient is advised to wear special orthopedic shoes, which will help normalize the distribution of load while walking.
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the pain and discomfort of the disease, as well as to eliminate the ailments that caused it. Drug treatment includes the following:
- corticosteroids that relieve inflammation;
- antiviral drugs;
- medications that relieve painful spasms;
- sedatives;
- drugs aimed at improving nerve patency;
- vitamin injections.
But the main result in the treatment of neuropathies comes from physiotherapy, which includes:
- therapeutic massage courses;
- warming up;
- electrophoresis;
- exercise therapy exercises;
- treatment with current and magnetic field;
- acupuncture;
- hydrotherapy.
To treat diabetic neuropathy, you need to keep your blood sugar levels under control for the rest of your life. There are no other ways to eliminate this type of disorder. In the alcoholic form, it is necessary to completely abstain from alcoholic beverages, and to restore the body, it is recommended to diversify your diet.
Surgical operations are used extremely rarely, only in cases where it is necessary to stitch a damaged nerve.
When diagnosing neuropathy, the doctor provides primary information by interviewing and examining the patient, as well as palpation, checking the sensitivity and motor activity of the affected area.
After receiving the results of all examinations, the doctor chooses the most effective treatment tactics in this case.
Surgical techniques for the treatment of neuropathy are used in cases where it is necessary to suture the damaged nerve.
Drug therapy involves the prescription of antiviral, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antispasmodic and sedatives, as well as drugs that improve nerve patency and vitamins. In the presence of a causative disease, treatment of the underlying disease is carried out in parallel with the treatment of neuropathy.
Physiotherapeutic methods are considered the most effective in the treatment of neuropathy:
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- hydrotherapy;
- massage;
- acupuncture;
- hydrotherapy, etc.
At the MedicCity multidisciplinary clinic, you can undergo comprehensive neurological diagnostics from the best specialists in this field at any time convenient for you. Entrust the solution of medical problems to professionals!
Diagnosis of the disease is based on identifying autonomic disorders and the causes that led to the development of this condition. First of all, the doctor collects anamnesis: the presence of symptoms, what diseases have been suffered, hereditary predisposition.
To identify the cause, it is necessary to take a general blood test and definitely a sugar level test, and consult with various specialists to rule out the presence of concomitant diseases.
The main instrumental diagnostic methods include:
Orthostatic test.- Valsalva test.
- Heart rate measurement.
- ECG.
- Nerve conduction study.
- Electromyography.
- Nerve and skin biopsy.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
Additional laboratory tests may be needed for diagnosis:
- cerebrospinal fluid puncture;
- immunogram;
- PCR for infections, antibodies to lupus and other diseases.
If the cause of the disorder is known, then the primary disease is treated first, in particular:
- If you have digestive problems, you should consult a gastroenterologist for nutritional recommendations. To treat autonomic neuropathy, various drugs are used depending on the symptoms that have developed:
For urinary incontinence, hormones with an antidiuretic effect (Vasopressin) and myotropic antispasmodics (No-shpa) are indicated, and muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) and alpha-1-blockers (Tamsulosin) are needed to relax the sphincter.- Men with impaired potency need to consult a specialist. In some cases, a vacuum device and stimulant drugs may be required. Women can benefit from special lubricants and ointments containing estrogen.
- For orthostatic hypotension, strong tea and coffee, split meals, increased salt intake and exercise can help. But if these methods are ineffective, drugs that normalize blood pressure (Gutron) are used.
Patients with autonomic neuropathy, regardless of the cause, need to take sedatives and antidepressants (Deprim, Sedafiton), vitamins and mineral complexes.
Physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises can be added to treatment - they have a positive effect not only on the nervous system, but also on the entire body as a whole.
Diagnostics
Identifying peripheral neuropathy is not difficult. The diagnosis is based on a careful collection of complaints and a careful neurological examination. The initial manifestations of neuropathy cannot be detected through a neurological examination, with the exception of some of its varieties. An example is neuropathy of the facial nerve, when facial asymmetry occurs from the first hours of the disease. Therefore, the initial stage of diagnosis is based solely on the patient’s complaints. Among additional diagnostic methods, electroneuromyography (a method of recording electrical potentials from nerve fibers) is used to confirm peripheral neuropathy. But identifying the true cause of neuropathy is a more complex task, which may require many research methods. First of all, this is a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test, determination of blood glucose levels, and a study of hormonal levels. Depending on the results of these analyzes, certain additional research methods are prescribed. Sometimes, despite a comprehensive examination, the true cause of neuropathy cannot be determined.
CM. SEE ALSO: Optic neuropathy
Forecast
If it is possible to identify the cause of the disease and begin treatment on time, the prognosis is usually positive. Everything will depend only on how accurately the patient adheres to the recommendations of the attending physician. In this case, medications are also prescribed for treatment that help get rid of the root cause that caused the disruption of the PNS.
If the disease is caused by genetic characteristics, treatment often does not bring the desired result.
The success of treating the idiopathic form of the disease, when the cause cannot be determined, depends only on what comprehensive treatment program the attending physician has selected.
It should be remembered that it takes time to restore nerve fibers. As a rule, the first acute symptoms of the pathology disappear several weeks after the start of therapy. However, it will take more than a month to fully restore the function of damaged nerves. You should be prepared that sensitivity to the affected area will not return soon; sometimes it may take years for the PNS to fully recover.
Treatment of abducens neuropathy
Treatment of pathology largely depends on the causes of its occurrence. The basis of treatment for this disease is strengthening the muscles of the eyeball. This allows you to activate blood flow. For this purpose, ophthalmologists prescribe eye drops, including:
- "Taufon";
- "Irifrin";
- "Emoxipin";
- "Vita-Yodurol";
- "Visiomax".
If pain occurs, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- "Tegretol";
- "Finlepsin";
- "Amelotex";
- "Dexalgin";
- "Baklosan";
- "Rekoksa";
- "Timonil."
These drugs have both an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, relieve muscle spasms, and reduce the excitability of nerve fibers. Any medications must be prescribed by a doctor. He will select a maintenance daily dose and frequency of administration.
Physiotherapy procedures, such as electrophoresis, have a good effect. To carry it out, doctors use the drug Neuromidin. It improves and stimulates impulse conduction in the nervous system. Treatment of neuropathy often includes wearing occlusive dressings and training glasses. In pediatric therapy, ophthalmologists often use stereo images, which they offer patients to view on a computer monitor.
It is very important to keep the muscles of the eyeball toned. To do this, doctors recommend that patients perform eye exercises. There are special complexes that are aimed at treating abducens nerve neuropathy. Most of them include exercises such as closing your eyes, alternate winking, and moving your eyes to the right side.
Content
Carotid sinus syndrome
Synonyms: syncope associated with irritation of the carotid sinus, hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus
Hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus (carotid sinus syndrome) is a common cause of syncope, accompanied by falls and injury to patients, especially the elderly.
Although the pathogenesis of carotid sinus hypersensitivity is not well understood, it is based on a paradoxical reaction of carotid sinus baroreceptors associated with the vasomotor center of the brain stem. When baroreceptors are irritated (the sensitivity threshold of which changes with hypertension and atherosclerotic vascular damage), the activity of the sympathetic nervous system is suppressed and vagal stimulation is increased, which is accompanied by bradycardia, AV block and/or vasodilation.
Carotid sinus syndrome is found in 5-25% of all persons over 60 years of age; 5-25% of them experience fainting or presyncope. Often combined with coronary artery disease and arterial hypertension. In addition, the syndrome is accompanied by enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes, thyroid gland, neck tumors, and can occur after neck surgery. Clinical picture: signs of cerebral ischemia, including fainting.
The most common type. Pathognomonic sign: massage of the carotid sinus leads to ventricular asystole lasting more than 3 s (due to sinus node arrest or AV block). Drugs that increase the sensitivity of sinocarotid receptors (for example, digoxin, beta-blockers, methyldopa, clonidine) are contraindicated.
A rarer type. Pathognomonic sign: massage of the carotid sinus leads to a decrease in systolic blood pressure by more than 50 mmHg. Art. without a decrease in heart rate (with or without the appearance of complaints) or a decrease in systolic blood pressure by 30 mm Hg. Art. with the appearance of complaints.
Carotid sinus massage causes bradycardia and decreased blood pressure. If there are bruits on the carotid arteries or a history of cerebrovascular accidents, carotid sinus massage is contraindicated.
Preventive measures
The following precautions will help avoid the development of PNS diseases.
- A balanced diet will provide full support to the entire body, including the PNS.
- Since neuropathy often develops against the background of a deficiency of microelements and vitamins, care should be taken to regularly take appropriate medications.
- It is important to prevent the development of metabolic diseases. Patients with diabetes should be very careful about their own well-being.
- Any injuries and fractures should be treated promptly. If you receive any injury, you should undergo examination at a clinic.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to prevent the development of a genetically determined disorder of the PNS. In this case, you should carefully monitor any symptoms of the disorder and, if necessary, immediately seek help from a clinic.
Timely treatment guarantees restoration of PNS function. This will take a long time, but you can get rid of the disease. It is important not to neglect your own health and seek help in a timely manner.
The information on the site is provided solely for popular informational purposes, does not claim to be reference or medical accuracy, and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. Consult your healthcare provider.