Most of us mistakenly believe that sclerosis is a disease of old people who lose memory due to age. Unfortunately, the reality is that this disease affects not only the elderly, but also the very young, and memory loss is just one of the symptoms, and even then it is quite rare.
What is sclerosis, what are its symptoms and types, who is at risk? This article will try to answer all the questions posed.
What is sclerosis?
The term “sclerosis” in medicine refers to a chronic inflammatory process that affects medium and large arteries due to their “overgrowth” with cholesterol deposits and manifests itself in the replacement of normal tissue of connective organs. The occurrence of sclerotic changes in the body can be provoked by:
- past inflammatory diseases;
- circulatory disorders;
- age-related changes.
It should be noted that sclerosis is a disease that can affect almost any human organ and tissue: brain vessels, lungs, heart, kidneys and others.
Classification of the disease
Sclerosis is classified depending on how much the disease has damaged the nervous system and which organs are affected:
- Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease in which, under attack from one’s own blood cells, the protective myelin sheath of nerve fibers is destroyed and their conductivity is disrupted. The following clinical forms of this disease are distinguished:
— stem;
- cerebrospinal;
— optical;
- spinal;
- cerebellar.
Basic therapeutic methods
In the patient management protocol, therapy is divided into two areas, one of which directly eliminates the exacerbation, the other is designed to slow down the development of the disease.
Attention. If the disease is not treated, the prognosis will be unfavorable and after some time you may become disabled. Statistics show that this condition can develop within three years or thirty.
You can learn about what plasmapheresis is and what other types of therapy are available for patients with multiple sclerosis here.
Medication regimen on how to deal with the disease
When the disease worsens, according to clinical recommendations, the doctor prescribes hormonal drugs (glucocorticosteroids) to the patient.
The patient is injected with Methylprednisoline (in the amount of 1-2 g for five or six days) or Prednisolone (1.5 mg per kg of total body weight). The general course of hormonal therapy lasts on average up to six weeks. In addition to hormonal therapy, the standard of treatment also includes the prescription of immunomodulators in order to enhance the activity of the immune system. Such medications include Rebif and Betaferon.
An alternative to immunomodulators are cytostatics . These medications are aimed at reducing the activity of the immune system, these include Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide.
Other medications are used to eliminate symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition:
- Cerebrolysin, Glycine, Glutamic acid, B vitamins are taken in courses to normalize the state of the nervous system (read about what vitamins and acids you need to take for multiple sclerosis here).
- Mydocalm, Sirdalud (drugs to reduce muscle tone).
- Finlepsin, Antelepsin (medicines to eliminate seizures).
- Phenazepam, Sibazon (medicines to reduce tremor and eliminate neurotic symptoms).
- Prozerin, Galantamine (drugs for urinary disorders).
- Paroxetine, Fluoxetine (medicines for treating depressive disorders).
Injections and vaccinations
Autovaccination is based on the isolation of leukocytes from the patient and their artificial stimulation by cells of the nervous system. As a result of such stimulation, T-lymphocytes should begin to multiply in the patient's body, which are exposed to radiation and reintroduced into the patient's body.
The body’s reaction is such that it begins to destroy foreign bodies, at the same time dealing with healthy T-lymphocytes. The effectiveness of the method has not yet been confirmed.
How to overcome a disease with the help of stem cells?
The method was developed in 2003.
It is based on such beneficial properties of cells as the ability to eliminate scar tissue and restore myelin fibers. When treated with this method , biomaterial is removed from the patient, stem cells are isolated from it , grown in a laboratory, and then reintroduced to the patient. Studies have shown that the effectiveness of this treatment method is at least 75-80 percent.
Puncture
Important! The puncture procedure is used to diagnose the disease. This method is aimed at analyzing cerebrospinal fluid; an increased amount of antibodies in it indicates a disease.
The process of taking a puncture lasts no more than 10-15 minutes and goes away with pain relief. Cerebrospinal fluid is taken for examination in an amount of 5-10 ml.
Bone marrow transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation is one of the most effective treatment methods . The transplant procedure is quite complex; before it is performed, the patient undergoes chemotherapy, then bone marrow cells removed from the bone are transplanted into him.
Pressure chamber
The barotherapy method involves treatment using pressure in a pressure chamber in combination with drugs. The procedure allows the patient to completely get rid of oxygen starvation of the brain, as a result of which its functioning is normalized.
This method of therapy is not only effective, but also safe. The course of treatment is 8-12 procedures.
Examination lamp
There are several ways to diagnose the disease. One of the most optimal examinations is MRI of the brain and spinal cord . Using this study, it is possible to accurately determine the location and size of sclerotic foci.
The disease is successfully diagnosed using superposition electromagnetic scanning. The method allows you to determine the total and focal loss of myelin, establish the state of ion exchange in tissues and the activity of neurotransmitters.
Multiple sclerosis
This is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the nervous system. Today it is incurable; there are only a number of methods that stop the development of this disease, as well as reduce the frequency and number of exacerbations. Despite many studies, scientists have still not been able to establish the exact cause of its occurrence. Today, doctors consider multiple sclerosis as a polyetiological disease, that is, having several causes that cause it. Thus, the disease mechanism is triggered only in a certain combination.
Medicines
Image from site zdrowie.dziennik.pl
Medicines for multiple sclerosis are prescribed by a doctor. Drugs may include corticosteroids, plasmapheresis, symptomatic drugs that relieve individual symptoms, drugs that control the immune system, and sometimes painkillers. The risk of developing multiple sclerosis is a low level of vitamin D, which is maintained taking into account the recommendations of an endocrinologist.
It is important for the patient to follow the treatment regimen not only during exacerbations, but also during periods of remission, since the body needs support even when the course of the disease does not appear outwardly.
Symptoms
This disease manifests itself in a very diverse manner, so much so that doctors had to identify 50 different signs of this disease that can manifest themselves in one case or another. When diagnosing multiple sclerosis, the most common symptoms considered are:
- feeling of constant fatigue;
- depression;
- dizziness;
- visual impairment;
- tingling and numbness in the hands and feet;
- tremor of the limbs;
- bowel and bladder dysfunction.
However, similar symptoms in one or another combination may indicate other diseases. That is why various laboratory tests are carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Problems in diagnosing MS in the early stages
How to recognize multiple sclerosis and seek help? As can be seen from the above signs of the development of the disease, the symptoms are quite vague. It is almost impossible to determine an accurate diagnosis on your own; moreover, there are various diseases similar to multiple sclerosis. They begin in exactly the same way as MS begins; to exclude them, the neurologist prescribes special tests (biopsy, blood test, MRI). Only a qualified specialist can determine whether a person has multiple sclerosis or not.
The list of diseases similar to multiple sclerosis is huge. Diseases similar to multiple sclerosis: Infections affecting the central nervous system. These include:
- Lyme disease.
- AIDS virus.
- Syphilis.
- Leukoencephalopathy
Inflammatory processes affecting the central nervous system:
- Sjögren's syndrome.
- Vasculitis.
- Lupus.
- Behçet's disease.
- Sarcoidosis.
Genetic disorders:
- Myelopathy.
- Cerebral arteriopathy is autosomal dominant.
- Leukodystrophy.
- Mitochondrial disease.
Deficiency of vital microelements:
- Copper deficiency.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency.
Lesions to tissue structure:
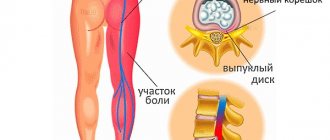
- Cervical spondylosis.
- Disc herniation.
Demyelinating disorders:
- Devic's disease.
- Disseminated encephalomyelitis.
In addition to these diseases, the first manifestations of the disease may be similar to the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, and it, unlike MS, is completely harmless to the human body. VSD is not fatal. It, like multiple sclerosis, is also characterized by dizziness, loss of coordination, spasms, and weakness.
Motor Neurone Disease
This is also called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It selectively affects peripheral and central motor neurons, which manifests itself:
- in increasing weakness of the pelvic and shoulder girdle, abdominal and torso muscles;
- damage to the bulbar muscles of the tongue, pharynx, larynx and palate paresis;
- in decreased or increased reflexes;
- in spontaneous and irregular contractions of muscle fiber bundles of individual muscles or their groups;
- speech disorder.
Lateral sclerosis in most cases develops in patients after 50 years of age, although this disease can affect a person of any age. Experts distinguish the following types:
- lumbosacral;
- bulbar;
- cervicothoracic.
How is it treated?
Current therapies cannot cure this disease. Patients with a similar diagnosis should be regularly monitored by doctors of several specialties. To maintain the vital functions of patients with a disease such as lateral sclerosis, treatment consists of taking many different drugs, including anabolic hormones. The disease lasts from 2 to 10 years and always, with the exception of the case of Stephen Hawking, has a poor prognosis. Patients die from exhaustion, concomitant infections or paralysis of the respiratory center.
What tests detect MS?
Spinal cord puncture with analysis for oligoclonal antibodies. The accuracy of diagnosis is 85-95%.
In terms of the degree of danger, the procedure is comparable to a regular injection (there may be a headache after the procedure; stories about when legs were lost after a spinal puncture are MYTH).
MRI – 70-90% when repeating the procedure every 3-6 months for a year. Once the diagnosis is established, there is no need to repeat the MRI.
Visual evoked potential – diagnostic accuracy is 50-90%. The method involves placing electrodes on the surface of the head to trace the path of the signal from the retina to the visual cortex. Effective if the patient has complaints to the ophthalmologist.
At the same time, multiple sclerosis must be distinguished from inflammatory diseases, hereditary and infectious diseases, which have a similar analysis pattern.
If the patient has been ill for a long time and the symptoms are clear, a diagnosis can be made without special tests based on a conversation with a neurologist.
In difficult cases, the patient may be prescribed additional studies (for example, genetic). In particularly difficult situations, diagnosis can take up to several years.
The scientific literature describes cases where patients with an incorrect diagnosis of MS were observed by doctors for more than ten years and even participated in clinical studies.
The “insidiousness” of MS is that over time, the foci of the disease are restored and look healthy on MRI. Thus, it is difficult to assess the course of the disease from each individual image.
Atherosclerosis
This is another name under which cerebral vascular sclerosis is hidden, a fairly common and often diagnosed disease.
Its first symptoms may appear after the age of 25, but usually this disease is diagnosed in people over 50 years of age. During the development of this disease, narrowing and deformation of brain vessels occurs under the influence of cholesterol deposits on their inner surface. As a result, there is a slowly increasing deficiency in the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the organ supplied by the affected vessel. Atherosclerosis has different symptoms, and their manifestation depends on the location of the disease and the spread of the process. Diagnosis is made by identifying lesions of individual vessels.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spine (the disease affects not only the brain, but also the spinal cord). It helps to determine the localization areas of sclerosis foci and the degree of demyelination of brain tissue. MRI using a contrast agent helps achieve the most accurate results.
For additional diagnostics and confirmation of the diagnosis, an analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid is also used - the presence of sclerosis will be indicated by an increased content of lymphocytes and myelin in it.
Causes
The development of this disease can be triggered by the following factors:
1. Heredity.
2. Staying in constant psycho-emotional tension.
3. Diseases of the endocrine system.
4. High blood pressure.
5. Bad habits, such as smoking.
6. Low physical activity.
During the treatment process, special attention is paid to regular physical activity, which promotes the development of alternative blood flow pathways, as well as proper nutrition.
Subchondral sclerosis
During the development of this disease, degradation of the articular cartilage occurs, which subsequently leads to changes in the surface of the joint. This type of sclerosis is divided into primary and secondary forms. In the first case, healthy cartilage is damaged under the influence of strong overloads of the spine. The secondary form occurs on cartilage that has been injured in some way. Thus, subchondral sclerosis is a disease that can occur both under the influence of injuries and diseases, and due to improper organization of physical activity.