Influenza is an acute respiratory infectious disease of a viral nature. Today, flu vaccination is not mandatory and is carried out at the request of the person. Its goal is to strengthen the immune system and prevent complications. Every doctor must know how the flu vaccine is administered, contraindications and undesirable effects of the drug. If the immunization technique is not followed or the body is hypersensitive, complications in the form of allergies and systemic reactions are possible.
Classification of contraindications
The following contraindications to the introduction of immunological drugs into the body of children and adults are identified:
- Absolute. These are conditions that cannot allow the vaccine to be administered under any circumstances.
- Relative. They are due to an increased risk of complications.
- Temporary (during an exacerbation of any disease). They are fickle. After the condition has normalized, the vaccine can be administered.
- Permanent. These are the contraindications that prevent a person from getting vaccinated for a long time.
- Are common. Suitable for all types of vaccinations.
- Private. Refer to a specific drug and its method of administration. Contraindications may be different for live and inactivated vaccines.
When influenza vaccinations are contraindicated, the doctor should tell the patient.
Effect of influenza vaccine
Vaccinations against infections that claim countless lives every year are not a cure. She cannot save those who are already sick. Any influenza vaccine is a means of helping the body's defenses fight infection.
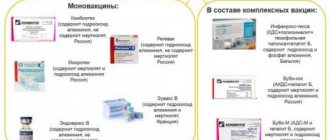
The composition of the vaccine may vary, so there are:
- live, consisting of weakened microorganisms or pathogens that allow the formation of immunity against influenza;
- inactivated (killed).
The latter are divided:
- to whole virion containing virions or virus particles;
- split, which do not contain chicken protein and lipids;
- subunit, which contains two viral proteins necessary for the formation of an immune response.
After the drug is administered, the body produces antibodies. When a virus enters, protective cells begin to act. Due to this, the symptoms of infection are not so pronounced, and most importantly, there are no complications.
How long the vaccination will last depends on the type of vaccine. Basically, this period is 6 months, some provide protection for up to a year.
When not to do it
Not everyone knows when the flu vaccine is not given, contraindications for adults and children. There is a whole table with restrictions on the use of the vaccine. Contraindications in children and adults to the administration of immunological drugs for influenza are:
- Acute infections (respiratory, intestinal, genitourinary). This is an absolute contraindication for flu vaccination.
- Exacerbation of existing chronic infectious diseases.
- Increased sensitivity of the body to the components of the drug.
- Intolerance to egg and chicken whites. They are part of many vaccines (Influvac, Begrivak, Vaxigrip). In this case, vaccination against influenza is contraindicated.
- Feverish state (high body temperature).
- Pathology of the endocrine and nervous systems.
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
- Age less than 6 months.
- Pregnancy.
- Lactation period.
- Severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system. In case of heart disease (heart attack, angina, heart failure), the possible risk is assessed.
- Signs of poor vaccine tolerance. A contraindication for influenza is the presence of severe post-vaccination reactions or complications during previous immunization.
Doctors recommend regular immunization for people with reduced immunity (children over six months old, the elderly, patients with HIV infection and diabetes).
How to use the vaccine
Instructions for use of the drug "Grippol" contain the following data:
- Packaging. The vaccine is available in 0.5 ml ampoules.
- Vaccination periods. The start of the vaccination campaign occurs in early autumn, that is, a month before the epidemiologically dangerous period, or at its very beginning.
- Dosage. The Grippol Plus vaccine is indicated for use in a dose of 0.5 ml in one injection for both children over three years of age and adults.
- Young children in the age group from six months to three years are also allowed to be vaccinated against influenza. The dose for them is divided in two, that is, two injections of 0.25 ml are given with a break of 28-30 days. If the child has already been vaccinated against influenza, it is allowed to administer the entire dose of 0.5 ml at once.
- Localization of the injection. The Grippol vaccine is injected into the brachial muscle or deep subcutaneously. For young children, the injection is given in the thigh.
The vaccine can only be stored at the correct temperature. Injections are given in strict accordance with antiseptic rules. If the ampoule is opened, it cannot be stored. Unused drug is disposed of along with consumables - syringes, needles, ampoules.
What side effects may there be?
When receiving a flu shot, side effects do not always occur. The risk group includes people with hypersensitivity. When using the flu vaccine for children and adults, the following undesirable consequences are possible:
- Moderate, short-term increase in body temperature. Occurs in response to the introduction of weakened viral particles or their genome (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase).
- Malaise. It lasts no more than 1-2 days, after which the condition returns to normal.
- A drop in platelet levels in the blood (thrombocytopenia).
- Cramps.
- Neuralgia-type pain.
- Paresthesia (impaired sensitivity). A person feels tingling, burning or goosebumps in various parts of the body.
- Symptoms of vasculitis (vascular damage) in the form of skin rashes.
- Skin itching. This is a manifestation of an allergic reaction in response to a foreign agent entering the tissue.
- Hives.
- Cyanosis of the skin.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Decreased appetite.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Exanthema (rash).
- Anaphylaxis. The most severe and dangerous manifestation of vaccine allergy. Manifested by swelling of tissues and fiber, impaired consciousness, and symptoms of shock.
- Local reactions in the form of skin hyperemia (redness), swelling and pain.
Vaccination may also cause headaches and neurological disorders.
How long does it take for a reaction to a vaccine to appear?
Side effects from vaccination occur both on the first day and after 1-2 weeks.
The time of their appearance is influenced by the following factors:
- reactogenicity of the drug;
- its composition;
- type of vaccine (live or inactivated).
In adults
Local (skin) symptoms appear several hours later (on the first day) after the flu vaccine in adults, provided that the vaccine is non-live.
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility?
Less commonly, side effects appear on the second or third day.
When using live preparations, a reaction may occur 5-14 days after immunization.
Peak manifestations are observed on days 8-11.
In children
Side effects occur more frequently and quickly in children. Children's bodies are more sensitive to influenza vaccination.
The reaction can be severe if the vaccine is given if you have an allergy.
Side effects from live vaccine
Live vaccines are distinguished by the fact that they contain live, weakened viral particles (the causative agents of influenza A and B).
They do not cause symptoms of the disease, but promote the production of antibodies. Their main disadvantage is the high frequency of adverse reactions. The main side effect after getting a flu shot is allergic reactions.
Release form and storage rules
The new generation flu vaccine Grippol Plus is available in the form of a suspension and is packaged in disposable syringes with an atraumatic needle. Due to this form of release, it is possible to minimize the risk of infection when taking the drug from an ampoule and reduce the vaccination time. This packaging of Grippol Plus allows you to vaccinate a large number of people in a short time in compliance with all the rules.
The traditional packaging of Grippol Plus is also used in sealed glass bottles or vials with a rubber cap.
Description of the dosage form: colorless or yellowish, slightly opalescent liquid.
The medication leaflet describes in detail the conditions of storage and transportation. They are as follows:
- store the drug for no more than 12 months;
- Avoid using the freezer as a storage place;
- maintain temperature conditions in the range of +2…+8 °C;
- transport ampoules and syringes filled with suspension in sealed containers at a temperature of +2...+8 °C;
- transport the drug at a temperature of 25 °C for no longer than six hours.
The Russian manufacturer Grippol Plus uses different types of influenza strains every year, so even with proper storage, the medicine is disposed of after the end of its use.
Possible complications
Flu vaccination sometimes leads to complications. Risk factors for side effects from the flu vaccine include:
- high reactogenicity of the drug (strong effect of the vaccine on the body);
- incorrect technique for administering the vaccine (needs to be administered intramuscularly or deep subcutaneously);
- drug contamination;
- use of expired vaccine;
- improper storage;
- ignoring indications and contraindications for vaccination;
- self-administration of the vaccine at home (you cannot vaccinate intravenously);
- the presence of somatic diseases in a person;
- allergy;
- autoimmune pathology;
- medical errors (when administering a flu vaccine, side effects occur due to lack of skills in administering the drug and failure to follow the instructions);
- improper dilution of the immunological drug;
- violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during vaccination;
- exceeding the permissible dosage.
The following complications are possible after receiving a flu vaccination:
- Swelling of soft tissues. Occurs at the injection site. This disorder is transient and disappears within 1-2 days.
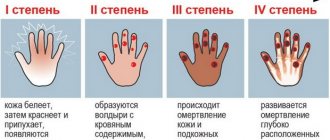
- Decreased skin temperature in the extremities. It is felt in the form of their cooling.
- Insomnia.
- Fever. The temperature can rise to +38…+39ºC.
- Fainting conditions.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Suppuration. Occurs when the drug is injected under the skin and not into the muscle.
- Anaphylactic shock. This is a rapidly developing allergic reaction. Shock is manifested by itching, fear of death, rash, swelling in the face and neck, respiratory disorders (cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, change in voice), drop in blood pressure, dyspepsia and neurological symptoms (convulsions, headache, weakness, visual disturbances).
- Chills.
- Lethargy.
- Anorexia (weight loss).
- Nosebleeds.
- Vomit.
- Hallucinatory syndrome. Occurs rarely against the background of hyperthermia.
- Exacerbation of asthma and atopic dermatitis. Seen in children.
- Hemorrhagic vasculitis.
- Quincke's edema. Develops when allergy sufferers are vaccinated.
- Hives.
- Post-vaccination encephalitis. Characterized by inflammation of brain tissue. Most often it develops on days 7-12. Encephalitis has an acute onset and is manifested by psychomotor agitation, fever, impaired consciousness, meningeal symptoms of Kernig and Brudzinski (with the involvement of the meninges in the process), focal symptoms (paresis, paralysis, impaired coordination of movements and sensitivity). Sometimes bulbar syndrome occurs.
- Arthritis.
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle).
- Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Grippol plus during pregnancy and lactation
A variety of the Grippol vaccine, called Grippol Plus, is subjected to multiple purifications and does not contain preservatives. Therefore, experts recommend it for use in women starting from the second trimester of gestation.
You need to make a decision about the possibility of vaccination together with a doctor who will evaluate:
- risks for a pregnant woman of catching the influenza virus;
- the woman's health status;
- possible complications that may occur during influenza illness.
The flu vaccine Grippol Plus can be administered to pregnant women after the second trimester of gestation. Before this period occurs, the woman is advised to take preventive measures to prevent infection with influenza.
What to do in case of adverse reactions and complications
You need to know not only who should not be vaccinated and what the side effects may be, but also how to eliminate them. If side effects of the vaccine are pronounced, you should consult a doctor (general practitioner or pediatrician). It is important to differentiate complications from post-vaccination reactions. You will need:
- General clinical blood and urine tests.
- Measuring body temperature.
- Pressure measurement.
- Survey. The time of occurrence of complaints is established.
- Examination of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Virological research.
- Physical examination.
- Blood test for antibodies to pathogens of infectious diseases. It is carried out to exclude infections.
- Blood chemistry.
- Study of the ionic composition of blood.
- Instrumental studies (carried out according to indications). MRI, CT, electromyography, electroencephalography, and lumbar puncture may be required.
To eliminate side effects after getting a flu shot, you need to:
- Carry out local procedures (for skin redness, swelling and infiltrates). Ointment dressings with anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy (UHF therapy, ultrasound exposure) are used.
- Carry out detoxification measures (at high temperatures). You need to drink enough fluids and use antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Efferalgan, Panadol). In severe cases, infusion therapy is required (glucose-salt agents are administered).
- Reduce allergy symptoms. For this purpose, antihistamines (H1-histamine receptor blockers) are prescribed. For anaphylaxis, they are administered by injection.
- Use symptomatic and other medications (adrenergic agonists, systemic corticosteroids, anticonvulsants).
To avoid complications, flu vaccination must be approached responsibly. A child should be vaccinated only after consultation with a pediatrician.
Flu vaccination: contraindications. Do you need a flu shot?
Seasonal influenza is a disease that affects millions of citizens every year. The most favorable time for the disease is autumn and winter, when the human immune system is weakened and does not cope with viruses as effectively. Different strains of viruses can cause the development of acute respiratory disease, but, despite the nature of the pathogen, the symptoms are very similar in all cases. The patient has a fever, sore throat, runny nose, cough and headache.
Flu shot
In order to prevent the onset of many infectious diseases, vaccination is carried out. Since the discovery of the first vaccine, doctors have saved hundreds of millions of lives. Millions of people are vaccinated against influenza every year, because the vaccine is still considered the main preventive method in the fight against infections.
Sometimes potential patients have a question: do they need a flu shot? The vaccine is a weakened viral material that is not able to multiply in the body. When a person is injected with a vaccine whose set of proteins is identical to the active virus, his immune system begins to produce antibodies against this virus.
Time for vaccination
It is best to get vaccinated against the flu in the fall (from September to November), because the epidemic of this disease becomes widespread at this time. Flu vaccinations are given to children and adults. It is not recommended to vaccinate in the spring or summer, as the number of antibodies decreases over time and the effect is no longer as strong.
You can get a flu shot even after the outbreak of an epidemic. If vaccination was carried out, and the next day the person was struck by an infection, then the vaccine will not worsen the course of the disease. The flu will be much worse if such a vaccination is not given, and there is even a risk of serious complications.
Who needs vaccination
Today, vaccinations are given to infants from 6 months of age. There is a category of people who need a flu vaccine first. Those at high risk include elderly people, patients who are in hospital, and pregnant women. It is necessary to vaccinate children and adolescents (from 6 months to 18 years), especially if they have been using aspirin for a long time for treatment. These patients may have severe complications from influenza. This category includes people with kidney, lung, heart problems, metabolic disorders, patients with immunodeficiency, hemoglobulinopathies, staphylococcal infections, as well as students and schoolchildren who are constantly in society.
Flu vaccination: contraindications
The main material for making the vaccine is chicken embryos. Not every body is susceptible to them, and there are a number of cases when a flu shot is not recommended. Contraindications apply primarily to those patients who suffer from an allergic reaction to chicken protein. People should not be vaccinated during periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases. Vaccination is not advisable for another two weeks after final recovery, because the body is weakened and may react incorrectly.
Patients with progressive forms of neurological diseases, as well as those with allergies to influenza vaccines should not be vaccinated.
What is the flu?
The disease belongs to the category of acute viral infections, is accompanied by a general infectious syndrome in a pronounced form and affects the respiratory tract. Not all patients are aware of the danger of this disease. In some cases, the flu begins with a cough, fever and runny nose, and can end in the death of the patient. Statistics show that every year about 40 thousand people from developed countries die from influenza and complications caused by it.
Types of influenza pathogen
The causative agent of the virus is divided into three independent types: A, B and C. Constant mutation of the virus, which leads to a change in its antigenic structure, leads to the fact that qualitatively new varieties of the influenza virus actively appear and multiply. The danger for the population lies in the fact that the human body has not yet developed immunity to them, so the virus affects the patient and can cause unpredictable complications. The influenza virus is transmitted from a sick person by airborne droplets, which allows it to spread to all categories of the population.
Influenza type A instantly spreads over large areas and is pandemic or epidemic in nature. The local spread of type B influenza virus makes it possible to detect its individual outbreaks and take timely measures. Influenza type C causes sporadic outbreaks of infections.
Benefits of vaccination
Vaccination helps the body develop lasting immunity, which will help avoid infection with the flu. Even if a vaccinated person catches an infection, his disease proceeds without complications and in a milder form than in those who refused vaccination. Specific prevention is carried out with live and inactivated vaccines. The flu vaccine for children over three years of age is of domestic origin. Imported vaccines that have all the necessary licenses are intended for children aged 6 to 12 months.
The maximum amount of antibodies is reached 14 days after vaccination. Annual vaccination is explained by the fact that the vaccine provides the body with short-term immunity (6-12 months). Vaccination should be carried out before and during the epidemic season.
Flu vaccines
Vaccines aimed at combating influenza are divided into several types. The first is live vaccines. They are made from virus strains that are safe for humans. When administered intranasally, they contribute to the development of local immunity. Vaccination is carried out before the start of the epidemic period. Live vaccines vary depending on whether they are intended for children or adults.
Inactivated vaccines are intended for persons over 7 years of age. This is a concentrated and purified influenza virus grown in chicken embryos and inactivated by UV radiation and formaldehyde. Inactivated vaccines include influenza liquid chromatographic, centrifugal and eluate-centrifuge vaccines.
Subunit and split vaccines have domestic and imported varieties. These include drugs such as “Grippol”, “Agrippal”, “Begrivac”, “Vaxigrip”, “Influvac”, “Fluarix”.
Refusal of vaccination
More and more people are refusing vaccination. This is explained by the fact that often after a flu vaccination, undesirable reactions of the body to the material occur. Illiterate administration, poor quality of the vaccine or non-compliance with the rules after vaccination leads to complications. Another reason for refusing vaccinations is that parents consider it harmful to the health of their child.
You can refuse all vaccinations or a specific one. Refusal to get a flu shot must be justified and the clinic staff must be notified of this decision.
There are a number of cases where medical professionals confirm that the flu vaccine is not advisable. Contraindications relate primarily to the child’s health status when he has suffered an injury or is sick. But after the baby’s condition returns to normal, the vaccination will still have to be done.
To refuse vaccination, you must write a special application in two copies (one for yourself, and the second for the school, kindergarten or clinic). The application must be registered in the institution's document journal, and it must contain: a decrypted signature, number, document number, and seal. It is also worth remembering that refusing vaccinations is a decision to take responsibility for the diseases against which vaccinations are carried out.
Consequences of refusing vaccinations
Refusal to get a flu shot (sample below) is not always the right decision on the part of parents. Preventive vaccinations are protected by law, and their absence makes life difficult for citizens. Thus, they are prohibited from traveling to countries that require specific vaccinations. Citizens may be temporarily denied admission to health or educational institutions, especially if there is a threat of epidemics or infectious diseases. In the absence of the necessary vaccinations, citizens have problems applying for jobs where there is a risk of contracting infectious diseases. In other words, unvaccinated children and adults are not allowed into the group if there is a suspicion of an epidemic.
Consequences of the flu shot
The flu vaccine, the contraindications to which have already been studied quite thoroughly, can also have a negative impact on human health. We are talking about the occurrence of side effects. Before getting vaccinated, you must undergo an examination and consult a doctor. Maximum caution should be exercised when vaccinating children, pregnant women and the elderly. Vaccination does not protect against all diseases (in this case, the flu) at all, but it significantly reduces the possibility of infection. Delayed vaccination can lead to flu. But even in this case, it will be much easier to transfer the disease than by refusing the vaccine.
After vaccination, allergic reactions and chronic diseases may worsen. To avoid this, you need to warn your doctor about their presence. Only healthy children should be vaccinated, because even a slight runny nose during vaccination can result in insomnia, loss of concentration and decreased immunity for the child. You also need to follow the rules for caring for the vaccine to avoid local skin problems. If the body somehow reacted to previous vaccinations, then you should refuse subsequent ones.
fb.ru