For the patient and his relatives, the diagnosis of “pneumonia” is scary in itself, especially if we are talking about atypical pneumonia in children, the symptoms of which do not appear immediately. Especially if the sick child has relatives who have reached old age and well remember the times when antibacterial therapy was not yet sufficiently developed, and a large number of people died from this disease. When a child falls ill with pneumonia, it generally makes parents panic.
In the figure: a schematic representation of cell damage by chlamydia.
Of course, pneumonia is a dangerous disease that is characterized by inflammation of the lower respiratory tract and lung parenchyma, however, in most cases it has typical symptoms and is amenable to conventional therapy. Naturally, this cannot be done without professional medical help, and in some cases hospitalization in a hospital will still be required, but this disease is perfectly treatable and there is no reason for excessive concern (of course, with properly prescribed therapy).
In the picture: mycoplasma under a microscope.
But there are a number of exceptions. As is clear from the title of the article, we will talk about atypical pneumonia in a child. So, what is this pathology and why is this type of lung inflammation called atypical? What are the symptoms of chlamydia pneumonia?
General information
Left-sided pneumonia in children
When the inflammatory process develops in the segment of the left bronchus, this indicates that the child’s body is weakened by a previous disease. This could be acute respiratory infections, bronchial asthma, various surgical interventions. As a result, the immune system becomes weak and is unable to prevent the appearance of pathogenic bacteria.
In children, bacterial left-sided pneumonia is often formed by airborne and droplet infection.
It happens that the onset of infection occurs in the area of the circulatory system. This happens if viruses have affected an organ other than the lung area. Or in situations where there are disorders of the swallowing apparatus.
Reasons for development
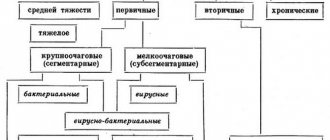
Segments are the morpho-functional parts that make up the lobes of the lungs. The left lung consists of 2 lobes and 8 segments, and the right lung is formed of 3 lobes and 10 segments. Each segment is ventilated by a separate bronchus and fed by its own part of the pulmonary artery. The defeat of one of these areas is called segmental pneumonia. If two or more segments are involved in the process, the disease is called polysegmental inflammation.
Streptococci
Most often, the causative agents are bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococci, streptococci) and viruses (influenza, adenoviruses, viral respiratory infections). Inflammation in the lung segment may develop under the influence of fungi or protozoa.
Most often, pathogenic microflora enters the child’s body through inhalation. An aspiration route of infection is also possible, when microorganisms enter the respiratory tract from the nasopharynx. In some cases, infectious agents penetrate the lung tissue from distant foci through the bloodstream.
The development of inflammation of the lung segment is facilitated by a decrease in immune status and hypothermia. This form of pneumonia is often diagnosed in children prone to allergic reactions.
Causes
Causes of left-sided pneumonia in children
Left-sided pneumonia spreads from a sick person to a healthy person. Pathogenic bacteria leave the respiratory tract when you sneeze and pass into the lungs of another person. When the body is weakened, they instantly begin to multiply, which leads to further inflammation. It is at this stage that it is possible to easily cure the disease with antibacterial agents.
The causes of lung pneumonia developing on the left side are:
- weak immunity;
- existing chronic pathologies;
- close relationship with a sick person;
- hypothermia.
Therapeutic measures for pneumonia in a child are carried out exclusively in a hospital setting, the patient is hospitalized. When the patient seeks medical help at an early stage of development, then treatment can be carried out at home.
Causes of pneumonia in children
Damp, cold weather, temperature changes in spring and autumn lead to colds, which reduce the child’s immunity. At this time, any provoking factors can lead to the development of pneumonia, for example:
- chronic respiratory diseases – laryngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis;
- ARVI;
- allergic reactions;
- obstruction (impaired patency) of the respiratory tract;
- stressful situations;
- immunodeficiency state.
Advanced bronchiolitis and bronchitis lead to infection in children. The cause of the inflammatory process is the exhaustion of the body in frequently ill children. Pathology is caused by:
- dust in the room;
- unbalanced diet;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- lack of vitamins;
- inhalation of chemical fumes;
- high room temperature;
- fungal damage to walls;
- aspiration – entry of a foreign body into the respiratory system;
- rare walks in the fresh air;
- passive smoking – when the baby is forced to breathe cigarette smoke.
There are reasons for the appearance of pneumonia related to the developmental characteristics of the child’s body. Premature babies are at risk of infection. This is due to the following factors:
- immaturity of the respiratory system;
- underdevelopment of lung tissue, epithelial cilia;
- increased vulnerability of mucous membranes;
- abdominal type of breathing;
- Congenital heart defect;
- rickets;
- birth injury;
- ingestion of amniotic fluid and vomit into the respiratory tract;
- artificial feeding;
- overheating, hypothermia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of left-sided pneumonia in children
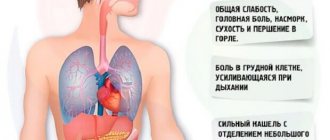
The symptoms of left-sided pneumonia are the same as with right-sided inflammation:
- the presence of a wet cough with sputum, associated with sore throat, shortness of breath, and malaise;
- high body temperature (38-40°C) and chills;
- Nausea, headache appear, and aching or stabbing pain occurs in the left region of the sternum.
With the development of pathology, cough in children can transform into purulent, sometimes with blood streaks. When you take a deep breath, the pain increases. Dizziness and loss of consciousness may occur.
But, there are cases when pneumonia at an early stage passes without any symptoms. And this is very dangerous, since treatment of the late stage of the disease is quite difficult, especially if a similar situation occurs in an infant.
The main danger is that young children cannot describe all the symptoms necessary to diagnose the disease. Therefore, detecting pathology at the initial stage is impossible.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of left-sided pneumonia in children
Left-sided pneumonia in a child can be detected using an x-ray. This method is the most optimal for children.
Bronchoscopy is also considered effective. However, this procedure is not pleasant, since it is carried out through a thin video tube, which is inserted through the nasal or oral cavity into the lung area. But manipulation has many advantages, because... You can clearly see the bronchial condition, and also take an analysis of the mucous membranes.
Diagnosing left-sided hilar pneumonia in children is quite difficult due to its unusual location. Especially in infants at the initial stage of development of the disease. Left-sided hilar pneumonia affects the lung tissue and is located in the area of the pulmonary root.
To establish a diagnosis you will need:
- blood and sputum tests;
- additional tests - cultures, which can identify the type of bacteria or virus, this will help for further treatment.
Complications of pneumonia
If the treatment was incorrectly prescribed or the course was not completed, severe consequences cannot be ruled out. Lung damage in newborns due to pneumonia causes oxygen starvation. As a result of pathological processes in the baby:
- the functioning of all organs is disrupted;
- acute cardiac and respiratory failure develops;
- shock occurs;
- death comes.
If the disease is severe, the baby’s body copes poorly with the pathology, treatment does not produce results for a long time, and serious pulmonary complications arise. The following consequences appear:
- pneumonia becomes chronic;
- bronchial patency is impaired;
- pleurisy develops - accumulation of fluid in the space between the chest and lungs;
- an abscess occurs - purulent tissue damage;
- secondary inflammatory processes develop;
- destruction occurs - complete progressive destruction of the pulmonary parenchyma (tissue).
If the treatment of pneumonia in children does not achieve complete recovery, infectious agents accumulate in the body and cause intoxication. The child has a hard time tolerating this condition. This is facilitated by the influence of medications, which in the treatment of pneumonia negatively affected the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and decreased immunity. Extrapulmonary consequences in children include:
- sepsis – spread of infection through the blood;
- development of myocarditis - inflammation of the heart muscle;
- neurotoxicosis - the effect of toxins on the cerebral cortex;
- the occurrence of meningitis;
- the appearance of anemia.
In order to avoid the development of complications, it is extremely important to strictly follow all the pediatrician’s recommendations and not to interrupt the course of treatment on your own, even if the patient’s condition appears to improve and symptoms disappear.
Possible complications
Complications of left-sided pneumonia in children
Still, is pneumonia dangerous? The disease is serious with its unpleasant consequences, and in severe cases – even death. Other most dangerous diseases can also become complications:
- formation of pleurisy;
- gangrenous accumulation of the lungs;
- damage to the respiratory process;
- development of pulmonary edema.
Prevention
Specific measures to prevent left-sided pneumonia include immunization - that is, the use of vaccines against pathogens.
General prevention of left-sided pneumonia requires adherence to the following guidelines:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- prevention of hypothermia;
- maintaining the functions of the body's defenses;
- timely initiation of treatment for diseases that can subsequently provoke pneumonia;
- regular medical examination.
In 70% of cases, early diagnosis and complex therapy helps to completely cure left-sided pneumonia. The prognosis will not be as favorable if pneumonia develops against the background of another pathology - there is a high risk of complications of the primary disease. The fatal outcome in children is 10–30%.
For highly effective treatment of left-sided pneumonia, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions of a specialist and maintain the correct daily routine. Thus, complete recovery occurs after 14 days. After this, you will need to be more attentive to the child’s health, because the body still remains weakened and a relapse may occur.
Features of treatment
Treatment of left-sided pneumonia in children
Without parental support and control, therapy will not bring the desired result. You should strictly follow all doctor’s orders, take all necessary medications, and drink plenty of fluids.
Do not self-medicate under any circumstances, as this can only harm the child. Take medications prescribed by a specialist in a timely manner and do not violate the dosage.
Drug therapy
Having received the results of the study, the doctor draws up the necessary treatment regimen:
- Bacterial drugs (Amoxicillin, Levafloxacin, Cephalosporin), the choice is made depending on the causative agent of the disease.
- Expectorants, the respiratory tract should be cleared of sputum.
- Anti-inflammatory medications are used to relieve inflammation, fever, and pain.
- Vitamins of groups A, C, B are prescribed to increase and strengthen the body's defenses, and are administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
In addition, the child needs to be surrounded with attention. The room should be regularly ventilated and provide healthy and nutritious food.
It is worth noting that the treatment of left-sided or, for example, right-sided hilar pneumonia is carried out almost the same.
Additional treatment
In order for the treatment to have a positive effect, some more procedures will be needed:
- physiotherapeutic measures;
- inhalations with the addition of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- electrophoresis;
- certain breathing exercises;
- therapeutic massage in the chest area.
Doctors recommend intense massage by rubbing, kneading, and patting the lungs.
Pneumonia in children is carried out in a hospital setting. After all, the body is very weak at this time, so various complications cannot be ruled out.
The therapeutic course often lasts 7-10 days, and medication use lasts 2 weeks. To prevent re-inflammation, a biochemical blood test will be required. Because The child’s immunity is reactive, then the possibility of recurrent disease cannot be ruled out.
Treatment with folk remedies
Along with medications, folk recipes are used. The most common are:
- To get rid of pneumonia, inhalations with the addition of horseradish are used. The roots of the plant are washed, peeled, and grated. 1 tsp. The prepared mixture is placed in a container with warm water and inhaled through the nose for 2 hours (breathe for 10 minutes, then take a break for 5 minutes).
- You can treat pneumonia in children with the aloe plant. You need to grind it, then add 0.1 tsp. salt, insist a little. Take 30 ml 1 hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
- To normalize breathing, use eucalyptus tincture. Can be used as inhalations and rinses.
- Garlic relieves inflammation well. It is possible to make jars or mustard plasters, but only if there is no temperature.
- Horseradish with lemon provides excellent results. To prepare the medicinal mixture you will need 1 tsp. finely chopped horseradish and lemon juice, mix everything thoroughly. About 20 min. the resulting composition is infused. You need to drink 20 ml 0.5 hours before meals 3 times a day.
- Horseradish is also used for coughs. The finely crushed plant is poured into a teapot, 80% alcohol is added there and infused for 0.5 hours. Then inhale the vapor over the kettle at least 5 times a day.
- Chop 2 onions, pour in 1 cup. milk, put on fire for about 5 minutes, it should be infused for 4 hours. Consume 1 tbsp. l. every 3 hours
- The use of dried fruits to treat this disease is suitable for both children and adults. 0.5 stack. pour 1 cup of ground raisins. boiled water. For 10 minutes. keep on low heat, then filter. The resulting composition is taken in 0.5 cups. 3 times a day.
- Wash plantain leaves thoroughly and dry. Then take a towel, run an iron over it and put leaves on it. Place a towel on the child's chest area, leaves side down, cover with a woolen scarf on top. With this compress, the child sleeps all night. The main thing is to fix it so that it does not move from the chest at night.
During the treatment process, the child must be provided with rest and appropriate hygienic care. A daily warm bath before bed helps a lot. It will have a calming effect, restore blood circulation and breathing.
To prevent the formation of left-sided pneumonia, some recommendations should be followed. First of all, treat viral diseases in a timely manner and constantly harden the body. Nutrition should be healthy and balanced. Consume vitamins regularly to strengthen your immune system.
Editor
Daria Tyutyunnik
Doctor, forensic expert
Pneumonia is an infectious disease caused by the activity of viruses, bacteria or fungi. Some types of bacterial infections are typical only for a certain age of the child. When the disease occurs, the infection reaches the lowest parts of the respiratory tract, as a result of which the lungs cannot properly perform their respiratory function.
In this article we will focus on the left-sided form of pneumonia, the characteristics of its manifestation and why children are more often affected by it.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis is carried out on the basis of complaints from the patient; if the child is small, then the parents describe the symptoms. After this, the doctor performs auscultation and percussion of the lungs (listening with a phonendoscope and tapping the lungs to determine the characteristic sound).
The following are prescribed as additional diagnostic procedures:
- Clinical and biochemical examination of blood and urine . In this case, attention is paid to the number of leukocytes, ESR and the state of the neutrophil blood count.
- Frontal and lateral projections of radiography make it possible to recognize diffuse or focal lung damage.
- Bacterial culture makes it possible to determine the type of pathogen and establish its tolerance to antibacterial drugs.
- Microscopic examination allows you to recognize gram-positive or gram-negative microflora (Gram staining is performed).
- To differentiate from tuberculosis, a Ziehl-Neelsen stained smear is examined under a microscope.
If the diagnostic measures taken turned out to be uninformative, then the following is prescribed:
- Bronchoscopic examination with possible biopsy.
- Paracentesis of the pleural cavity is performed, followed by a pleural biopsy.
- Using MRI or CT techniques.
- Blood cultures for sterility and blood culture.
- Diagnostics using the PCR method.
How is it different from right-handed?
Left-sided pneumonia is much less common than right-sided pneumonia and is considered a specific diagnosis, as it manifests itself in the autumn-winter period.
Most often, children suffer from left-sided pneumonia. This is due to the fact that they have a fragile body and a rather weak immune system, which makes it easier for viral agents to penetrate into the main left bronchus. Left-sided pneumonia mainly develops against the background of viral diseases, influenza and hypothermia. It is extremely difficult to treat this type of pneumonia, because due to poor blood supply to the left bronchus, the delivery and absorption of medications is difficult.
The danger of the lower lobe form
Left-sided pneumonia is divided into:
- lower lobe,
- upper lobe.
Important! Left-sided lower lobe pneumonia is considered a more dangerous form, since it is quite difficult to treat (especially in childhood) and can lead to acute respiratory failure. This is due to the fact that the lungs have an asymmetrical shape and the airways on the left side are much narrower than on the right. Because of this circumstance, the removal of mucus becomes difficult, causing an infection to develop.
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammatory process that involves the respiratory tract, impairing the functionality of the alveoli.
In a healthy person, the air flow enters the alveoli, where oxygen enters the systemic circulation and carbon dioxide is removed from the body. The development of pathology in the alveoli causes disruption of this process, as they become inflamed, swollen and filled with liquid contents.
This condition makes natural breathing difficult, causing all organs and systems to suffer from hypoxia.
You need to know that pneumonia most often occurs in infectious forms that are transmitted through the air (airborne infection). Therefore, a sick person is a source of infection and prolonged contact with him, without observing personal hygiene rules, can cause illness.
Features of the course in childhood
The fact that children are much more likely than adults to suffer from pneumonia has certain reasons. First of all, this is due to the fact that young children, unlike adults, have much weaker immunity. The second reason is the underdeveloped respiratory system in children compared to adults.
In infants, frequent cases of pneumonia are associated with the occurrence of congestion in the lungs, which lead to an increase in the number of pathogens. This is due to the fact that in young children breathing is carried out due to the movements of the diaphragm, which, in turn, is greatly influenced by the state of the gastrointestinal tract and any disorders associated with it greatly affect the condition of the lungs.
Symptoms
No one, even the most effective preventive measures, can stop the inflammatory process when the infectious agent is at its peak of activation. The child’s well-being will rapidly deteriorate and parents in this case need to carefully monitor the symptoms that appear and also immediately consult a doctor. The symptoms of left-sided lower lobe pneumonia in children of different ages are slightly different.
In children aged 2 years and older
If after a child has had the flu or acute respiratory viral infection, there is no improvement in the condition within 5 days, or some time after a slight improvement, the temperature rises again and intoxication increases, it is important to consult a doctor. It is these signs that may indicate the onset of the disease.
More severe symptoms include:
- Apathy, loss of appetite, mood swings and sleep problems continue to persist for a week after the onset of the disease.
- Powerful cough , which is the primary symptom of respiratory tract disease.
- Low body temperature, which is accompanied by shortness of breath . In this case, it is necessary to carefully monitor the number of breaths the child takes. The norm for breaths in children aged 1 to 3 years is considered to be 25-30 per minute. In children aged 4 to 6 years, the rate of breaths is 25 times per minute at rest. If the number of breaths has increased, then this is one of the main signs of pneumonia.
When other symptoms appear in children, demonstrative pallor of the facial skin .
Also a symptom of pneumonia is high temperature , which lasts for 4-5 days and is susceptible to the action of antipyretics.
In infants up to one year old
In infants, the onset of the disease can be detected by how the baby’s behavior has changed. If a child begins to cry frequently, loses appetite, becomes very lethargic and, among other things, has a fever, you should immediately consult a pediatrician.
In addition, clear signs of the onset of pneumonia are high fever, shortness of breath and cyanosis. Let's take a closer look.
Increased body temperature . High temperature should be considered a sign of acute infectious diseases. However, in children under 1 year of age the temperature is not very high and sometimes may not reach 37.5 degrees.
Breathing . It is quite difficult to understand that a child is experiencing pain in the lungs when breathing or coughing; in this case, you need to pay attention to other signs.
Firstly, this is the presence of sputum. With a wet cough that accompanies pneumonia, the child develops green or yellow purulent sputum.
Secondly, you should closely monitor for shortness of breath and increased respiratory movements. During shortness of breath in infants, the head begins to sway in rhythm with the breaths.
Some babies may puff out their cheeks and pull out their lips, and sometimes develop a foamy discharge from their nose and mouth.
The normal norm for shortness of breath in young children under 1 year of age is:
- 50 breaths per minute in children under 2 months;
- 25-40 breaths per minute in children from 2 months to one year;
- If children over one year old take more than 40 breaths per minute, this is considered shortness of breath.
In addition to shortness of breath and sputum production in young children, changes in skin texture can be observed during breathing. During inhalation, the skin on the side of the left lung seems to be inhaled inward. In order to detect this, you need to remove the baby’s clothes and carefully monitor the skin on the ribs.
Also, with pneumonia, children under one year of age may experience rhythm disturbances during breathing, as well as the child’s desire to lie on his side.
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle . This symptom is very important, as it will help determine the presence of the disease in infants. During the disease, the skin between the baby's lip and nose acquires a blue tint. This symptom mainly appears during breastfeeding. In severe cases of the disease, blue discoloration can occur not only under the nose, but also on the surface of the body.
In addition to the above symptoms, with left-sided lower lobe pneumonia, regardless of age, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and pain in the side or abdominal area are observed, which can only occur when the lower lobe of the lung is affected.
Read more about symptoms in children under one year of age.
Causes and pathogens
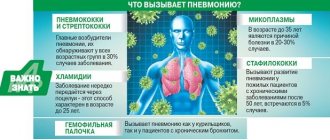
Mycoplasmas are considered the most common causative agents of atypical pneumonia in children. They become the culprits of the disease in 40% of cases in children under 7 years of age , 25% in children 7–15 years of age . To a lesser extent, pneumonia in children is caused by chlamydia and legionella.
The disease is classified as infectious, therefore the main cause of atypical pneumonia in children is considered to be the entry into their body of a viral, fungal or bacterial pathogen.
Newborn babies get sick due to the penetration of various herpes viruses, smallpox, cytomegaloviruses and chlamydia into their bodies. Against the background of their introduction, the immune system weakens and a secondary disease develops. Infection can be intrauterine, from mother to fetus, or when the virus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococcus, or staphylococcus is introduced during treatment of another disease in a child.
The age group 1 – 5 years are most often infected outside the hospital walls (statistically up to 80%), and the causes are pneumococcus, less commonly Moraxella and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
In children over 3 years of age, a lobar type of pneumonia caused by pneumococci is often detected. It affects only the lower part of the left lobe of the lung and very rarely affects the right.
Preschool children 5–7 years old become ill due to E. coli, Klebsiella, staphylococcus and enterobacteria.
In schoolchildren and adolescents, doctors diagnose atypical pneumonia against the background of pneumonia, and the disease is caused by viruses such as legionella and mycoplasma.
In general, children of any age are vulnerable to any stress.
Psychosomatic causes of pneumonia often include:
- negative emotions of a teenager;
- grief or stress;
- depression;
Diagnostics
Left-sided lower lobe pneumonia can be completely asymptomatic in children. The only sign indicating that there is a danger of illness is the child’s general poor health, which is expressed in loss of appetite, apathy, weakness and slightly elevated temperature.
That is why it is necessary to call an experienced therapist in time, who can determine the source of inflammation while listening to the lungs for noise and wheezing, as well as by tapping the chest.
Also, in order to recognize the disease, the doctor can use diagnostic signs such as:
- respiratory failure;
- damage to the upper respiratory tract;
- nature of hypothermia.
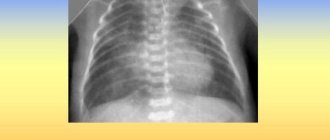
However, in order to unambiguously make a diagnosis and determine the location of the source of pneumonia, it is necessary to take an x-ray. An X-ray will provide an opportunity to examine the extent of damage to the respiratory tract and determine the area of distribution of the pathological process. Namely, this sign is key in diagnosis.
However, x-rays do not always help determine the source of the disease, and the strategy for future treatment and the possibility of recovery depend on this information. To determine the pathogen, special bacteriological tests are used, during which antibodies to the pathogen are isolated, or the pathogen itself is isolated from sputum or blood.
Features of treatment
The basis of treatment for left-sided (including lower lobe) pneumonia is the use of antibiotics. Many years ago, in a time before antibiotics, pneumonia was a common cause of death in adults and children. Therefore, you should not refuse to use them, and even more so, you should not completely shift treatment to traditional methods, since in this situation they are absolutely ineffective.
If your child gets sick with pneumonia, you must strictly follow all the instructions prescribed by the doctor, as well as follow proper care and monitor drinking and nutrition. As treatment, the doctor may give the following recommendations:
Taking antibiotics
Antibiotics are the main point in the treatment of a disease such as pneumonia, which must be strictly observed in time and dosage. If the doctor has prescribed the drug to be taken twice a day, then the interval between doses should be 12 hours. If you need to take medications 3 times a day, then the interval will be 8 hours.
Basically, antibiotics are prescribed such as penicillins and cephalosporins, which are taken for 7 days, or macrolides, which are taken for 5 days. The effects of taking antibiotics can be seen within 72 hours of starting treatment. This is expressed in a decrease in temperature and the appearance of appetite.
The image is taken as an example. The medications prescribed by your pediatrician may vary.
Antipyretic medications
They are used if the body temperature rises above 39 degrees, and in infants above 38. In the first days of taking antibiotics, drugs to reduce fever are not used, as this may interfere with the assessment of the effectiveness of the drugs. It is also necessary to remember that at high temperatures the body produces antibodies that are able to fight against the causative agent of the disease, and therefore if a child is able to tolerate a temperature of 38 degrees, then it is not worth knocking it down.
Diet
Lack of appetite and a child’s refusal to eat food is a natural symptom, which is explained by an increased load on the liver caused by the body’s fight against infection. During illness, it is necessary to prepare light food for the child, completely eliminating ready-made chemicalized foods, as well as fatty and fried foods. The best option would be to feed the child easily digestible food, such as broth, porridge, steamed cutlets, boiled potatoes and various vegetables and fruits.
Read more about diet in children with pneumonia.
Room ventilation and daily wet cleaning
In order to help a small organism get rid of infection, it is necessary to keep the room clean and fill it with fresh air.
The course of treatment for left-sided lower lobe pneumonia can take from 2 to 4 weeks and is carried out on an outpatient basis. But due to the fact that the onset of the disease is often asymptomatic, parents do not go to the clinic in a timely manner and in this case, many pediatricians insist on inpatient treatment.
Important! It is undesirable to take synthetic vitamins and immunomodulating agents during illness, as this may cause side effects.
Treatment
To ensure positive dynamics of the treatment process of pneumonia in a child, complex therapy is performed using dosage forms of different pharmacological groups.
To do this, use the following treatment regimen:
- Antibiotics are the drugs of choice. If, as a result of laboratory research, it was possible to establish the type of pathogen, then one type of antibacterial agent is used. Two antibiotic drugs of different pharmacological groups are prescribed in the absence of such data. Pneumonia in a mild form requires the appointment of an antibacterial course for a seven-day period, severe forms are subject to therapy for at least 14 days. To suppress bacterial pathogens, medications are used: Flemoxin Solutab.
- Amoxiclav or Amoxicillin.
- Ceftriaxone.
- Azithromycin.
- Summed.
Flemoxin Solutab
Amoxiclav
Amoxicillin
Azithromycin
Ceftriaxone
Sumamed
- Bronchodilators and expectorants can cope with paroxysmal cough and facilitate the discharge of viscous sputum, which accumulates in the respiratory tract as a result of stagnation. For this purpose, the following is prescribed: Lazolvan syrup.
- Herbion syrup.
- The drug Prospan.
- Fluditeca.
Lazolvan
Herbion with primrose
overslept
Fluditek
- Antipyretic medications are prescribed when the temperature exceeds 38 degrees. If a child has a tendency to have epileptic seizures, then the temperature should be lowered starting from 37.5 degrees. In this case, the prescription of the following dosage forms will be justified: Panadol or Efferalgan.
- Rectal suppositories Tsefekon D
- Ibuprofen.
- Nurofen.
Panadol
Efferalgan for children
Tsefekon
Ibuprofen
Nurofen
- Immunomodulators. This type of Interferon-based drugs will increase the body's protective function. To minimize the toxic effects on the child’s body, the following types of rectal suppositories are prescribed: Viferon.
- Laferobion.
Viferon
Laferobion
- To eliminate the symptoms of rhinitis, use: Naphthyzin.
- Pinosol.
- Xylene.
- Otrivin.
Naphthyzin
Xylene
Pinosol
Otrivin
- Even if the child was not hospitalized in a hospital, bed rest must be observed in the first days of illness. The indications for its cessation are normalization of temperature.
- During this period, it is especially important to drink large amounts of hot drinks. This can be weak tea with the addition of honey or lemon, compote from natural or dried fruits, or a decoction of rose hips. This will speed up the removal of mucus and ensure the removal of toxins from the body.
- It is also necessary to focus on the child’s diet. Due to the manifestation of weakness as a result of intoxication of the body, the child may completely lose his appetite (anorexia). Therefore, it is necessary to give food in liquid form (meat broths with pureed meat, rare slimy porridges).
- Prescribing antibacterial agents can lead to intestinal dysfunction (dysbacteriosis). Therefore, in parallel with the prescription of antibacterial agents, it is recommended to use probiotics: Linex.
- Acipol.
- Bifiform.
Bifiform
Linex
Acipol
Traditional healing recipes
Adherents of methods using traditional healing recipes need to know that the priority in the treatment of this pathological process is medicines.
Traditional recipes can be used as additional treatment, and this occurs by coordinating their use with a doctor. This position is explained by the impossibility of achieving complete recovery using only infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs.
In addition, home preparation of medicinal products can occur with an increased concentration of natural ingredients. In this case, there is a possibility of developing allergic reactions, which significantly complicates the child’s condition.
As a supplement, the use of the following formulations is recommended:
- A decoction based on honey with the addition of aloe. Add half a glass of water with crushed aloe leaves to 300 grams of honey. This composition must be simmered over low heat for 2 hours. Apply after cooling three times a day, one large spoon.
- Butter with added garlic. Garlic in the amount of 2 cloves is passed through a meat grinder or blender. After this, the resulting slurry is mixed with butter of soft consistency (100 g). It should be consumed two or three times a day, during meals, spread on a piece of bread.
- Decoction of rose hips. Two dozen dry fruits are placed in a thermos and poured with a liter of boiling water. After infusion for 20 minutes, the decoction is considered ready. You can drink it instead of tea several times during the day. To improve the taste and diaphoretic effect, you can add a slice of lemon or a small amount of honey.
- Instead of tea, a hot drink with honey and raspberries is recommended as a hot drink.
The following medicinal compositions are prescribed for inhalation:
- Honey diluted with propolis.
- Sage tea.
- A decoction of chamomile or calendula inflorescences.
- Inhaling vapors from peppermint or eucalyptus oil.
Massage
Starting from the age of six months, the child can have a massage using honey.
This improves sputum discharge. It is important that the massage is accompanied by vibration (percussion) techniques.
They are applied to the area of the shoulder blades and intercostal spaces.
They are alternated with stroking and rubbing techniques (all techniques are performed only according to the flow of lymph).
After the massage session, the child needs to remain under a warm blanket.
Danger of left-sided pneumonia
Left-sided segmental pneumonia on x-ray
Unfortunately, left-sided pneumonia is not always diagnosed on time. Sometimes symptoms go unnoticed by doctors.
Why does this happen and what does it lead to:
- the clinical picture is weak, and an incorrect diagnosis is initially made;
- the consequence of an erroneous diagnosis is incorrect treatment (as a result, the illness becomes chronic, and the tragic outcome is the logical conclusion of a negligent attitude towards a serious problem).
There are deplorable statistics regarding this disease in Russia: it causes the death of the patient in 5 cases out of 100 (6th line in the list of fatal diseases).
And if the adult body is even more or less ready to fight the disease, then the child’s chances are much less. Infants are especially at risk of death.
Unfavorable development of events:
- in the absence of qualified doctors near the patient, acute respiratory failure occurs;
- emergency treatment in the form of artificial ventilation is required;
- If the patient is outside the walls of a medical institution equipped with appropriate equipment, death occurs.
Reviews
Reviews about the treatment of pneumonia in a child:
- about the author
- Recent publications
Vladimir Ilyin
Otolaryngologist of the highest category and author of the website vdohvidoh.com. For many years she has been successfully helping adults and children get rid of ENT diseases.
Causes of left-sided pneumonia
Left-sided upper lobe pneumonia on x-ray
For what reasons does left-sided pneumonia develop? The root of evil is represented by bacteria and viral fungi.
The infection algorithms for an adult and a child are approximately the same:
- Pneumonia is spread by airborne droplets. The pathogen is found in the environment and, theoretically, is safe for people with extremely high immune status;
- infection is provoked by the slightest decrease in immunity (which is typical for a newborn child or an adult weakened by other ailments);
- sources can be either clearly infected people (who have obvious symptoms), or hidden carriers - fungi and bacteria are contained in sputum secreted during a wet cough or during sneezing;
- pathogens that enter a new organism begin to actively multiply.
Attention: for primary local inflammation of the lung tissue, treatment with antibiotics is 100% effective. The problem is that early signs are often ignored. Much of the responsibility lies with the patients themselves.
Symptoms of left-sided pneumonia
Left-sided lower lobe pneumonia on x-ray
Ideally, the patient should have a chest x-ray. In the image, left-sided pneumonia will appear as focal infiltrates in the lungs on the left.
However, the reality is that:
- there seems to be no reason to send a person to an X-ray room (after all, at the initial stage of tissue infection by a pathogen, symptoms often remain without proper interpretation);
- precious time begins to be lost - viruses and bacteria rapidly conquer more and more areas of lung tissue;
- the process deepens and becomes more extensive.
Attention: the same pathogen leads to different symptoms in different people. Much depends on the individual characteristics of a particular human body.
General signs of left-sided pneumonia
What you should pay attention to as soon as possible:
- weakness;
- sweating (excessive sweating at night should be the first thing to worry about);
- cough;
- increased breathing;
- cyanosis of nails, lips;
- fever, fever, chills;
- increased body temperature;
- sputum production when coughing.
Caution: the peak of the disease appears as a severe cough, high fever and fainting. But it may be too late for medical care with a guaranteed effect. Do not bring the process to a critical point.
Bacteria or virus
Please note that the symptoms of left-sided pneumonia differ depending on whether the infection has a bacterial or viral etiology.
The correctness of the definition influences what treatment will be optimal.
With a bacterial infection, the symptoms are as follows:
- moist cough;
- copious sputum;
- elevated temperature (from 37.8 to 39.0 °C);
- chills.
Attention: according to all medical canons, fever and chills for more than 3 days indicate bacterial infection.
When infected with a viral fungus, the following picture is observed:
- fever, chills;
- dry cough;
- headache;
- muscle weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- small amount of sputum;
- severe shortness of breath.
In any case, the cough is obsessive (not to be confused with smoker's bronchitis).
In addition, with left-sided pneumonia, other signs cannot be excluded:
- constant, intense stabbing and cutting pain in the left side of the chest;
- vomit;
- nausea;
- chest pain increases with deep inspiration;
- sputum discharged when coughing may contain streaks of pus or blood.
Symptoms of left-sided pneumonia in children
In a child, the clinical picture takes on the most acute manifestations:
- Severe shortness of breath appears quite quickly (not only from physical exertion, but also at rest);
- already in the first stages of development of left-sided pneumonia, the temperature rises to 39-40 ° C;
- the leaves of the diaphragm become irritated, which leads to hiccups;
- there is pain in the chest.
Clarifying diagnostics
The most dangerous option is the asymptomatic development of the disease (in both adults and children):
- the problem escapes the doctor’s field of vision even when listening;
- in most cases, treatment is prescribed, although effective, but with a delay;
- as a result, a number of complications arise;
- only an x-ray provides an accurate diagnostic guarantee of the presence of a pathogen;
- it is necessary to conduct a laboratory test of blood and sputum (the presence of bacteria or a virus will be indicated by an increased number of blood cells in the blood);
- excellent results are obtained by a modern examination method known as bronchoscopy. A thin video tube is inserted through the nose or mouth, with which the bronchi are examined, and mucus is collected for analysis.
Warning: bronchoscopy is very unpleasant (especially for a child). But the diagnosis is most accurate.
Inflammation of the respiratory system by chlamydia
According to statistics, about 11% of people experience this type of disease. Often, signs of atypical lung damage, which are caused by chlamydia, manifest themselves weakly or are absent at all.; It happens that the development of a severe form of the disease is recorded.
Signs of illness
The onset of symptoms is nonspecific for this disease, manifesting itself with acute respiratory symptoms characteristic of rhinitis and pharyngitis.
- General malaise.
- Runny nose.
- Pain in the throat.
Further, the patient notices:
- temperature rise to 39 degrees;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- dry cough;
- wheezing is initially wet, with a transition to moderate dry wheezing;
- low-grade fever;
- intoxication of varying severity;
- dyspnea;
- Possible cervical lymphadenopathy.
The disease often develops severely, but is easily tolerated. A long stay of chlamydia in the body can lead to allergies to infection antigens with the occurrence of chronic obstructive bronchitis and bronchial asthma.
When listening to a child, wet and dry wheezing can be heard for 10 days. X-ray shows the presence of small focal or interstitial infiltration, often bilateral.
Treatment of the disease
The basis for combating pneumonia is antibiotic therapy. Children over 9 years of age use tetracycline antibiotics for 14 days. For complete correction, macrolides are prescribed. Children under 9 years of age can only use macrolides.
In some cases, fluoroquinolones may be prescribed.
- Sparfloxacin.
- Ofloxacin.
It is important to remember that the dose of the drug is prescribed depending on the weight and age of the patient.
Treatment of left-sided pneumonia
Antibiotics are used to treat left-sided pneumonia
The treatment goal is complex and consists of:
- relieve the inflammatory process as soon as possible (antibiotics);
- significantly increase immune defense in tissues (rubbing legs, arms);
- support metabolic processes in the chest area (intensive massage in the form of tapping with palms, rubbing, kneading in the lung area).
Attention: the correctness of the massage is indicated by the disappearance of pain in the lungs. Massage practices are famous for their effectiveness against congestion.
When damage to the bronchopulmonary system is on the agenda, it is unacceptable to discuss any methods of traditional medicine.
Effective treatment is possible only with new generation antibiotic drugs.
You should also remember about the rapid development of infection, especially in a child or an elderly person (their bodies are weakest, unlike middle-aged people).
Medical or home care
Moderate focal infiltrates, if they are detected by x-ray and correctly assessed by a doctor, do not pose a great danger:
- if the immune system is in a normal state, it is quite possible to be treated at home;
- of course, under the supervision of a doctor;
- strictly in accordance with his instructions;
- only if the adult or child has no symptoms of secondary diseases.
If the disease develops seriously, hospitalization is necessary.
What does it give:
- 24-hour supervision by qualified doctors and staff;
- availability of special equipment (in particular, artificial ventilation systems);
- complete control of the condition of a weakened child or adult whose body suffers from some other ailments (allergic reactions, disruption of the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, liver).
Antibiotics for left-sided pneumonia
Both at home and in hospital settings, the use of new generation antibiotics is mandatory.
What is pneumonia
This disease has an acute form. Pneumonia is an infectious and inflammatory process that occurs in the lungs. The development of pathology is characterized by:
- damage to the alveoli and connective tissues;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- focal form of damage to the lungs;
- intra-alveolar exudation - the release of fluid from the blood through the vascular wall into the inflamed tissue;
- violation of gas exchange;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- oxygen starvation of tissues of the whole body;
- change in thermoregulation.
When treating infectious inflammation, it is important to determine the causative agent of the disease. This will help you choose the right treatment regimen and shorten the treatment time for pneumonia. The pathology is often caused by rubella viruses, chickenpox, influenza, herpes simplex, and adenovirus. The infection is provoked by:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- pneumococci;
- legionella;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- fungi;
- staphylococci;
- mycoplasma;
- chlamydia;
- coli.