- Features of cardiac arrhythmia in men
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Prevention of arrhythmia in men
Arrhythmia in men occurs 2 times more often than in women and more often leads to strokes. The disorder has its own characteristics and occurs at each age for its own reasons. Sometimes the pathology occurs without symptoms, but affects the functioning of the whole organism.
Classification of pathology
Atrial fibrillation is subject to a certain classification according to its clinical course, special electrophysiological mechanisms, and etiological factors.
It is customary to distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- Paroxysmal form - the duration of its course does not exceed 7 days. But in standard situations it lasts about 24 hours.
- Chronic or persistent arrhythmia - duration can reach more than 7 days. With such a manifestation, the ineffectiveness of electrical cardiotherapy is clearly visible.
- As for the permanent one, it is expressed by recurrent consequences.
Arrhythmia is usually divided according to the type of rhythmic disturbances in the atria, in particular flutter and fibrillation.
Atrial fibrillation
If fibrillation occurs, individual muscles contract, resulting in a lack of coordination of contractions. At the same time, electrical impulses make themselves felt, partially delayed or intensively spreading to the myocardium and creating various ventricular contractions.
According to the frequency of the last measurements, tachysystolic (90 beats and above), normosystolic (beats vary from 60 to 90), bradysystolic (beats below 60) arrhythmia are distinguished.
When paroxysm is detected, there is no normal blood supply in the cardiac ventricles. Contractions are ineffective; during diastole, the ventricles are systematically filled with flowing blood, but not completely. Due to this pathology, there is a periodic lack of release of blood masses into the aortic system.
Atrial flutter
This type of disease is accompanied by rapid contractions up to 350-450 beats. At the same time, a coordinated heartbeat rhythm is maintained. The myocardium contracts synchronously and almost continuously, with almost no diastolic interruption.
As for the atria, they do not relax and are always in a systolic state. Poor filling of these areas with blood masses occurs, which causes failure of the filling of the heart ventricles.
What is atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disorder (atrial fibrillation) in which the atria lose their ability to contract normally and instead twitch asynchronously. This condition is also called atrial fibrillation (AF), in which only certain groups of muscle fibers contract.
The risk of atrial fibrillation increases with age. Although both women and men are affected by the condition, the male gender is most susceptible. Below are examples of pulsed sounds.
The main danger of atrial fibrillation is an increased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system (the organ system that ensures blood circulation).
At the moment of atrial fibrillation, blood stagnates in the heart and blood clots (thrombi) form. When the heart rhythm returns, the blood clots travel throughout the body and can clog blood vessels.
Most often, blood clots provoke a cerebrovascular accident, which leads to a stroke. When the intestinal vessels are blocked, necrosis (death) of the organ can occur, which has life-threatening consequences.
The prevalence of the pathology is higher in older age groups - for example, at the age of 60 years, atrial fibrillation occurs in 6% of the population and in 8% of people over 80 years of age, mainly in men, 1.7 times more often than in women.
Main reasons
The described arrhythmia is provoked not only by heart disease, but also by disruption of the functioning of other organs.
Most often, arrhythmia accompanies the following disorders in the body:
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Heart defects.
- Cardiosclerosis.
- Heart attack condition.
- High blood pressure.
- Myocarditis.
- Complicated heart failure.
Less commonly, fibrillation occurs due to oversaturation with alcohol, poisoning when taking cardiac glycosides, adrenomimetics, as a result of hypokalemia, mental and nervous disorders, and thyrotoxicosis.
When idiopathic arrhythmia is diagnosed, its causes often remain incompletely understood, despite careful and lengthy examination.
About the main symptoms
The disease manifests itself in different ways, it all depends on its progressive form, the physical state of the valve apparatus and myocardium, certain characteristics of the human body and his mental behavior. Tachysystolic arrhythmia is difficult to tolerate. It is accompanied by shortness of breath, frequent and uncomfortable heartbeat, and characteristic pain in the heart.
Initially, the described pathology manifests itself in paroxysms, but the frequency of paroxysms is strictly individually dependent. Practice shows that some patients who have suffered a couple of atrial fibrillation attacks are diagnosed with a persistent form of the disease.
Other people suffer only short and extremely rare paroxysms that do not lead to progression of the pathology.
The causes of arrhythmia manifest themselves in various ways. When the disease is detected only after a medical examination, a person has increased fear, sweating, trembling, general weakness, chaotic heartbeat, and polyuria.
If the heart rate increases greatly, fainting, dizziness, and Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks occur. As a result of normalization of sinus rhythms, the symptoms of the pathology disappear. If there is a permanent form of arrhythmia, a person no longer feels the characteristic signs over time.
Causes, symptoms and risk factors
Atrial fibrillation occurs as a result of various diseases of the heart and other systems. The most common causes of arrhythmia are the following diseases:
- mitral valve defects;
- ischemic disease;
- diabetes;
- high blood pressure;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- alcohol intoxication;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- deficiency of potassium and magnesium.
Regardless of the quality of the examination, in some cases it is impossible to determine the cause of the arrhythmia. In this case, the doctor diagnoses idiopathic atrial fibrillation and prescribes restorative treatment, as well as drugs to relieve attacks.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the degree of its development and the cause. Therefore, in each specific case the set of symptoms may differ. The most common symptoms include:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- frequent urination;
- sweating;
- fainting;
- chest pain;
- weakness in the mice;
- panic attacks.
In only 0.01% of patients the disease does not cause symptoms. In this case, it is called hidden arrhythmia.
There are risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- people over 60 years of age;
- high pressure;
- heart disease;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- pulmonary embolism;
- thyroid diseases;
- drug use;
- taking decongestants;
- heart or lung surgery;
- smoking.
Possible complications
The main complications of the described arrhythmia are represented by diseases such as heart failure and thromboembolism. If mitral stenosis develops, the atrioventricular opening becomes clogged with the resulting thrombus, which will cause cardiac arrest, that is, sudden death occurs.
When intracardiac thrombi enter the bloodstream, thromboembolism of various organs often occurs. Most of them enter the cerebral vascular system. It is known from practice that every 5th ischemic stroke is the result of the described pathology.
The risk group includes elderly patients, people with a history of thromboembolism of varying severity, unstable blood pressure, and diabetes mellitus. The latter disease manifests itself as a complication in patients with impaired function of the cardiac ventricles who suffer from heart defects.
In the presence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and mitral stenosis, heart failure can lead to pulmonary edema and cardiac asthma.
Left ventricular failure manifests itself as a result of improper emptying of the corresponding part of the main organ, which causes an increase in pressure in the pulmonary vessels. In complex cases, arrhythmogenic shock occurs as a consequence of low cardiac output.
Ways to Help You Control the Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
Visit your doctor
It's important to visit your doctor frequently as you get older, especially if you have a family history of heart disease or other known risk factors. Research shows that women are more susceptible to risk factors that contribute to the development of heart disease and atrial fibrillation, and they also have a higher risk of mortality associated with such diseases.
Another reason for an annual visit to the doctor, research shows, is the fact that procedures used to correct heart rhythms work better if they are implemented soon after diagnosis. Treatment for atrial fibrillation usually begins with lifestyle changes and medications, but other treatments may also be required. Similar procedures include ablation , which is minimally invasive and uses heat or cold to apply it to the veins that are causing atrial fibrillation.
According to scientists from the Cleveland Clinic; “... if ablation was used after the diagnosis of AF, then the success of this procedure is approximately 80% if the duration of atrial fibrillation is up to 1 year... but it drops to 50% if at the time of ablation the duration of AF symptoms is 6 or more years…".
Therefore, it is worth understanding that if ablation is necessary in your case, then it should be performed as early as possible to improve results and avoid the appearance of scars on the heart.
Switch to an anti-inflammatory diet
Another significant problem in the occurrence of heart problems and the development of cardiovascular diseases is inflammation. Such inflammation leads to serious damage to both the heart and the entire cardiovascular system.
Increased weight, like obesity, contributes to the development of heart disease and atrial fibrillation through induced inflammation. This is why a diet with anti-inflammatory foods may be beneficial. When switching to an anti-inflammatory diet, first of all, you should give up those foods that contribute to the growth of inflammation:
- refined vegetable oils (such as corn, safflower and soybean)
- refined carbohydrates and processed foods (fast food and processed foods)
- sugar and fructose
- trans fats
- pasteurized dairy products that do not contain real beneficial bacteria
- foods high in salt
- large amounts of caffeine and alcohol in the diet, which can aggravate the health problem (5 alcoholic drinks within 2 hours for men and 4 alcoholic drinks for women are known to seriously increase the risk of atrial fibrillation)
These unhealthy foods can also increase your risk of gastrointestinal disorders, thyroid disease, autoimmune disorders (leaky gut syndrome), and diabetes. Most of these diseases contribute to the development of AF.
The healthiest type of diet that helps prevent heart disease and complications with an existing diagnosis is the list of anti-inflammatory foods included in the Mediterranean diet . Today, this diet is considered the healthiest diet and is one of the most popular and effective anti-inflammatory diets. Adopting a Mediterranean diet with adequate vitamin D helps reduce symptoms of various cardiovascular diseases and lowers cholesterol, blood sugar and triglyceride levels.
An anti-inflammatory diet may include:
- Vegetables rich in fiber and antioxidants: leafy greens, beets , carrots, cruciferous vegetables (Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower), artichoke, onion, etc.
- Fruits: all types, especially berries and citrus fruits
- Herbs and spices: especially anti-inflammatory, such as turmeric (curcumin), raw garlic, basil, chili peppers, cinnamon, ginger, rosemary and thyme
- Traditional teas: green tea , black tea and white tea (not in bags)
- Sprouted legumes and beans
- Organic, low-fat protein foods: raw, unpasteurized dairy products, eggs, free-range meat
- Natural fats (fatty acids): nuts, seeds, avocados, wild ocean fish, olive oil, coconut oil (minor amounts)
- Coffee in moderation (need to see your doctor)
- Natural red wine (doctor's approval required)
Reduce your stress
Stress contributes to inflammation and atrial fibrillation, not to mention promoting many other forms of chronic disease, including heart disease. A 2010 report in the American Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing found that patients diagnosed with AF show more psychological distress than the average healthy person . Unfortunately, psychological disorders such as anxiety and depression in patients with heart failure or coronary artery disease have been found to increase the risk of death and complications.
Severe stress and anger can also lead to abnormal heart rhythms. Sleep, relaxation and rest are very important for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, as they help balance the production of stress hormones, in particular cortisol . These stress hormones can disrupt the normal functioning of the immune system and heart function when present in abnormally large quantities.
There are several simple ways to reduce stress:
- Reducing caffeine intake
- To give up smoking
- Quitting alcohol
- Prayer practice
- Meditation practice
- Blogging on the Internet
- Creative work (hobby)
- Family holiday
- Spending time with pets
- Using essential oils (lemon, frankincense, ginger and helichrysum)
FOR PATIENTS WITH AFIBLIAR ARRHYTHMIA, AEROBIC PHYSICAL EXERCISE WITH A PULSE RATE CLOSE TO MAXIMUM IS EFFECTIVE (https://circ.ahajournals.org/content/133/5/457)
Practice physical activity regularly
One of the best ways to combat stress is through exercise, which can be beneficial for improving heart health for a very long time, almost throughout your life. A 2013 study published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology demonstrated that short, sustained exercise at low, moderate or high intensity in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation significantly improved heart rate, cardiac function, muscle strength, daily activity and quality of life. life.
Practice shows that athletes can also experience rapid heartbeat, which is called supraventricular tachycardia. Therefore, if you are actively involved in sports, it is always better to get checked by a doctor if you notice a change in your heartbeat during exercise.
Talk to your doctor about taking a safe route to a regular exercise routine that you enjoy and can stick to. But it is better if you pay special attention to physical activities such as swimming , cycling and brisk walking.
Minimize exposure to harmful chemicals, toxins and air pollution
Heart disease and inflammation are associated with free radical activity (also called oxidative stress) and low levels of antioxidants in the body. Free radicals can accumulate in the body due to poor diet, pollution, alcohol, smoking, unhealthy trans fats and lack of sleep.
Research shows that air pollution is associated with thrombosis, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Pollution causes oxidation, which wreaks havoc on the body, damaging cells, destroying tissue, causing DNA mutation and overloading the immune system. You can significantly reduce your exposure to toxins by eating organically grown foods, getting outdoors frequently outside of cities, and reducing your consumption of cigarettes or medications.
Use anti-inflammatory supplements
Taking aspirin can sometimes help reduce inflammation, which helps blood clot. This can be helpful when there are already symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia, but it is still important to consult with your doctor and discuss what other medications may be needed to reduce complications.
Some dietary supplements can also help improve the body's ability to detoxify, reduce inflammation, and heal itself.
Anti-inflammatory supplements include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (eg, tablespoon fish oil daily)
- Turmeric
- Garlic
- Coenzyme Q10
- Carotenoids
- Selenium
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E (it is better if this vitamin comes from food, due to the increased risk of developing cancer with artificial vitamin E)
Information sources
- https://circ.ahajournals.org/content/133/5/457
- https://keranews.org/post/new-study-says-atrial-fibrillation-riskier-women-men
- https://www.mayoclinic.org
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24267810
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19935428
- https://www.heart.org
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22237295
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/af
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0062932/
- https://www.heart.org
- https://www.hrsonline.org/Patient-Resources/Heart-Diseases-Disorders/Atrial-Fibrillation-AFib
The information on this site has not been evaluated by any medical organization. We do not seek to diagnose or treat any disease. The information on the site is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your physician before acting on information from this site, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medications, or have any medical condition.
Rate this article
Average 3.5 Total votes (2)
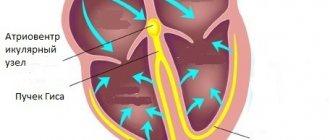
Determining the diagnosis
Typically, atrial fibrillation is detected during a physical examination. A disordered characteristic rhythm is felt when checking the peripheral pulse.
There is also irregularity in heart sounds, in particular, fluctuations in their volume are noticeable. If such abnormalities are detected, the person is referred for examination to a cardiologist.
The diagnosis is established through an electrocardiographic examination. If atrial fibrillation occurs, the ECG shows a chaotic arrangement of ventricular QRS complexes, while there are no P marks indicating atrial contraction.
In the presence of flutter, atrial waves are observed instead of P waves. A 24-hour ECG allows you to monitor heart rhythms, while determining the form of arrhythmia and the length of paroxysms, their relationship with the loads applied.
If we talk about tests with a focus on physical activity (treadmill test, bicycle ergometry), they are aimed at determining the symptoms of myocardial ischemia. Using these studies, a specialist selects antiarrhythmic medications.
During echocardiography, the dimensions of the heart cavities are determined and possible blood clots are detected. You can also determine the degree of damage to the pericardium, valves, cardiomyopathy, and evaluate the systolic and diastolic function of the left cardiac ventricle.
EchoCG makes it possible to prescribe the most effective antiarrhythmic and antithrombotic therapy. More detailed visualization of the organ can be obtained using MRI and MSCT procedures.
The choice of treatment method for the described pathology is determined using an electrophysiological transesophageal study. This establishes the progression of arrhythmia, which is important when planning the introduction of a pacemaker (artificial pacemaker) and performing catheter ablation.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “atrial fibrillation” is made after a set of diagnostic measures: a description of the patient’s complaints, an external examination, tests. Upon examination, an irregular or flickering pulse is observed; the same irregular contractions are detected when listening to the heart.
The heart rate can be either normal or increased (tachyform).
The main methods for diagnosing the disease are cardiogram, Holter monitoring, blood tests, and chest radiography.
On the ECG with atrial fibrillation, there are no P waves (instead, f waves of different heights and shapes appear). In addition, there are unequal RR intervals, changes in the ST segment and T wave.
How to treat the disease?
The choice of medications and drugs is aimed, first of all, at restoring sinus rhythms and maintaining them at the proper level.
With properly organized therapy, the following is prevented:
- Recurrence of fibrillation attacks.
- The frequency of contractions in the heart is controlled and normalized.
- Effective prevention of thromboembolic pathologies is carried out.
To stop paroxysms of arrhythmia, it is recommended to use Novocainamide, which is used intravenously, Amiodarone (orally and intravenously), Himidin (also orally). Monitoring during such treatment, regulation of the electrocardiogram and normal blood pressure levels is important.
Less pronounced is the use of Digoxin, Verapamil, Proplanolol. Treatment with such medications and tablets improves a person’s well-being by reducing contractions of the heart muscle. Less common symptoms include weakness in the body and unusual shortness of breath.
Important! If there is no positive result from the therapy, electrical cardioversion is performed as standard. This is the use of a pulsed discharge to restore normal functional rhythms.
During an arrhythmia that lasts more than 48 hours, thrombus formation may develop. To prevent such an undesirable process, experts recommend the use of Warfarin.
It is possible to arrest or stop a repeated recurrence of an attack after stabilization of sinus rhythms with the help of medications aimed at eliminating arrhythmic signs (Propafenone, Amiodarone).
If the chronic form of the disease is determined, regular use of adrenergic blockers is indicated. In particular, these are Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Atenolol. Calcium antagonists help if the results of the coagulogram are monitored.
In an advanced form of arrhythmia of the type described, treatment of the main cause of its occurrence, which led to the disruption of heart rhythms, is indicated. A method that effectively eliminates the “flicker of the heart” is radiofrequency elimination of the affected pulmonary veins (isolation of their mouths).
This is an invasive method of relieving pathology, the effectiveness of which, judging by medical practice, is more than 60%. When a permanent form of arrhythmia is diagnosed, the patient may be prescribed RFA of the heart, during which the offending organ is “cauterized” with special electrodes.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
The functioning of all vital organs depends on the normal functioning of the heart, and with atrial fibrillation, the blood supply to the body will be disrupted. Here are the main signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation:
- muscle weakness and dizziness;
- sweating (hyperhidrosis), fatigue;
- symptoms of angina pectoris (angina pectoris);
- panic attacks, fear;
- frequent urination;
- chest pain, feeling of “fading” of the heart;
- increased heart rate, when the heart seems to “jump out of the chest.”
It should be remembered that if atrial fibrillation is not combined with tachycardia - one of its most striking manifestations, in which the heart rate (HR) increases significantly - it can be difficult to recognize it in time. Any disturbance in heart rhythm is potentially dangerous, as the heart is subjected to additional stress and blood circulation deteriorates.
If an arrhythmia attack began more than 24 hours ago, and the heart rhythm has not returned, immediate medical attention is necessary.
From traditional medicine
Affordable and simple recipes will help relieve illness at home and restore heart rhythms:
- Green horse chestnut fruits must be crushed in the amount of 1 cup and left for 20 days in 300 ml of medical alcohol. The strained tincture is taken before night's rest, 10 drops.
- It is recommended to use 1 tbsp. spoon of fresh yarrow juice once before meals, wash down with a small amount of plain water. The course of treatment is 8-10 weeks.
- An alcoholic tincture of hawthorn prepared at the rate of 2 cups of crushed raw material per 500 ml of vodka will be useful. Dosage: 2 teaspoons 2 times a day, washed down with water.
- A herbal mixture that contains sweet clover, mint, calendula (flowers), adonis, rose hips, and chicory is effective against atrial fibrillation. These plants have a beneficial effect on the nervous system, as a result of which the heart rate stabilizes (about 60-100 beats). Moreover, the described collection improves blood flow, enriches important systems and organs with potassium, calcium, and oxygen.
- According to the recommendations of old-timers, strawberries should be used for arrhythmia. Dried stems and berries in the amount of 2 tbsp. spoons must be brewed in 500 ml of hot water in a thermos.
What is traditional treatment?
For many centuries, medicine was perceived as a single direction, the purpose of which was to help a person cope with various ailments. At the same time, alchemists, as a rule, acted in urban conditions, who created a certain substance with the necessary properties from various substances. In the villages, healers were more trusted, who studied the healing properties of various herbs and plants and prepared various medicines based on them.
Traditional medicine represents a wealth of healing experience, based on the trial and error of many generations of healers who mainly used herbal medicine in their practice.
From the beginning of the 13th century, everything changed, as the first attempts to influence diseases with the help of spells and incantations appeared. Such occult actions were perceived extremely negatively by many representatives of “official” medicine, which provoked its separation from the so-called alternative. Nevertheless, over time, scientific research has proven the benefits of traditional medicine, as evidenced by the appearance of memories about it from about the 19th century. As a result, the accumulated knowledge in the field of traditional medicine began to be further enriched, and there was a clear separation of this direction of therapy from superstition and obscurantism.
How long do people live with arrhythmia?
The development and course of the disease directly depends on the causes of its occurrence and possible complications. If arrhythmia develops due to severe myocardial damage or heart defects, there may be a high risk of heart failure. It is known from practice that complications of the thromboembolic type are unfavorable; with arrhythmia, mortality increases.
If a person does not have chronic severe heart pathologies, he feels satisfactory, and the life prognosis is more satisfactory. It is important that paroxysms are repeated infrequently; a striking example of this is idiopathic arrhythmia, which proceeds more loyally and allows a person to withstand normal everyday stress.
Symptoms depending on the type of disorder
The list of manifestations depends on the type of deviation.
If the problem is in the natural pacemaker (sinus node):
- Acceleration of cardiac activity. Up to 180 beats per minute, it practically never gets higher.
- Sweating, hyperhidrosis. The patient can be squeezed.
- Weakness, drowsiness, desire to lie down.
- Feeling of pain in the chest, not significant in intensity.
- Dyspnea. Against a background of complete peace.
- Inability to sleep. Sinus tachycardia can occur at any time. When developing at night, the sensation of heartbeat interferes with rest.
Duration - from 10 minutes to several days. Neglected organic forms give constant, continuous symptoms. However, patients get used to their own condition and no longer complain.
The paroxysmal variety is much more characteristic and dangerous:
- Chest pain. Pressuring. Burning. They do not respond to changes in body position and worsen with little physical activity.
- The acceleration of cardiac activity is significant. At the level of 300-400 beats per minute. Subjectively, fibrillation is not felt. Manifestations: turning over in the chest, skipping, freezing.
- Nausea.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Blue discoloration of the area around the mouth.
- Increased sweating.
- Vomit.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Urinary disorders.
The paroxysmal form always occurs in attacks. The episode begins with a sharp blow in the chest, a jolt. Darkening in the eyes. It takes my breath away. Heart rate increases until it reaches a peak.
Duration - from a couple of minutes to several hours. Progression leads to stabilization of the lesion.
Attention:
The condition can become permanent or chronic, in which case the paroxysm lasts indefinitely. Constantly accompanies the patient.
The cause of tachyarrhythmia of this kind is often a violation of cardiac conduction, blockade, a previous heart attack, or peculiarities of the nervous system. They eliminate probable factors one by one until they get to the truth.
Disease prevention
Primary preventive measures consist of intensive and extremely early treatment of “possible precursors” of arrhythmia. This could be heart failure or high blood pressure.
As for secondary prevention, it is aimed at:
- Maintaining specialist advice regarding anti-relapse drug therapy.
- Limiting psychological and physical stress.
- If necessary, undergo intervention by cardiac surgeons.
- Categorical refusal of alcohol and smoking.
If you suspect atrial fibrillation, you should immediately be examined by a doctor. It is important to promptly identify deteriorating health, establish the most accurate diagnosis, and undergo the necessary therapy.
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)