Scientists have long proven that the number of cells in a child’s blood can constantly change; in children this process occurs much faster, therefore, when the number of cells increases, this is called leukocytosis. Leukocytosis in children can manifest itself temporarily; if you take tests after some time, you can say with confidence that everything has returned to normal, but there are cases when leukocytosis has to be treated, or rather, the cause that could cause it has to be eliminated.
What causes leukocytosis?
As a rule, doctors claim that leukocytosis in the blood of children can manifest itself on the basis of non-physiological reasons, but also not pathological ones. Parents, if tests have shown an increase in leukocytes in the child’s blood, should not panic under any circumstances; it would be more correct to look for the reason why this could happen.
If you carefully study the individual characteristics of the body, you can highlight the following points that can provoke an increase in leukocytes:
- First of all, physiological factors are taken into account. If a child is actively involved in sports and there is a lot of physical stress on the body, if the child is overheated in the sun or took a bath that is too hot, the level of white cells may increase. Also, sometimes the reason is hidden in long-term use of the drug.
- Often, leukocytosis in children can appear before the age of one year, this is due to the fact that it is during this period that the immune system of a small person begins to form. When a child feeds on mother's milk, he receives antibodies from breast milk; when complementary feeding begins, the immune system becomes weaker, which provokes leukocytosis.
- Children, like adults, can be exposed to stress, so any stressful situation or experience can lead to jumps in the number of white blood cells in the body.
- An allergic reaction also becomes the main cause of changes in white blood cells.
- If leukocytosis is detected in the blood of children, the causes should be looked for in infectious diseases, for example, these could be viral infections, as well as diseases of a fungal and bacterial nature.
- The level of white blood cells increases and when a child receives some kind of injury, especially if it is associated with a burn, in order to counter this condition, the immune system triggers such a reaction as a defense.
- The worst cause can be cancer, in which case we should talk about leukemia and leukemia. A doctor can make an accurate diagnosis by taking cells for cytology.
Leukocyte formula
An upward change in the number of neutrophils indicates the penetration of pathogenic bacteria or microscopic fungi. With severe infection, active production of segmented neutrophils occurs, but they do not have time to mature and enter the bloodstream in an immature form. This condition is a signal about the active work of the body’s defenses to fight infection.
In addition, the number of neutrophils increases with extensive burns, in the acute stage of pancreatitis, as well as with oncological pathology affecting the red bone marrow.
Lymphocytes react to a greater extent to the development of a disease of viral etiology. Thus, when a patient is infected with cytomegalovirus, rubella virus (Rubella virus) or chickenpox virus (Varicella Zoster Virus), an enhanced humoral response of the human immune system is observed. Oncology is another justification for abnormal lymphocyte counts as a result of the analysis.
Monocytes increase when:
- acute infectious process of viral etiology;
- oncopathology, which affects the bone marrow and lymph nodes, as well as the stomach and ovaries;
- pathologies of connective tissue of various etiologies;
- Besnier-Böck-Schaumann disease primarily affects lung tissue. The peculiarity of the disease is a long asymptomatic course and the impossibility of transmission to other people.
In turn, eosinophils are most sensitive to the penetration of allergens, which can cause the development of allergic shock. More than 1 thousand allergens are known; they can be inhalant, animal, plant, medicinal, mold or food. In addition, segmented eosinophils also respond to parasitic infestation by helminths.
According to statistics, basophils relatively rarely rise to critical values. Possible justifications: severe oncological lesions of the patient with the development of concomitant diseases, as well as allergic shock.
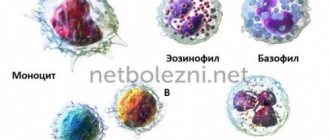
Leukocytes are a group of cells, united by a common name, and belong to the immune system. Shaped cells not only have different structures, but also perform different functions. For example, lymphocytes act to protect the child’s body during a viral infection, and neutrophils act to fight bacteria.
A clinical blood test contains data on the number of white cells, and the leukocyte formula will tell you about their percentage.
A high level of white blood cells in the blood indicates the presence of an infection in the body, but thanks to the leukogram you can determine its type:
- Neutrophilia (there are many neutrophils in the blood) with general leukocytosis indicates a bacterial infection.
- In cases of viral etiology, lymphocytosis is observed in the blood.
- An increase in eosinophils and leukocytes is characteristic of helminthic infestations or allergic diseases.
- Monocytosis is observed in prolonged and indolent infections, such as tuberculosis. An increase in monocytes is a specific sign of infectious mononucleosis.
How can leukocytosis be recognized?
A child may not have any symptoms; sometimes leukocytosis can be detected only through diagnostics, which is why doctors recommend taking a baby’s blood test at least once every six months so that you can respond to such a deviation in the body in a timely manner.
Of course, sometimes you can recognize increased leukocytosis in a child if you pay attention to the following symptoms:
- A small child may get tired quickly, vision deteriorates, dizziness appears, the baby may complain of pain in the legs and sleep often.
- Sometimes low-grade fever occurs.
- The baby sweats a lot, but his body remains cold.
- Weight loss quickly and appetite completely disappears.
- At night the child sleeps restlessly.
You should pay attention to all these signs, as this may primarily indicate an inflammatory process in the child’s body, and this is also how a viral infection can begin. As we can see, if a diagnosis reveals leukocytosis in a child, the causes can be looked for in completely different directions, so a qualified specialist must prescribe treatment.
What are the age norms of leukocytes?
Each age has its own standards for the content of leukocytes in the body. A newly born child faces a huge problem, because he finds himself in a world full of germs and bacteria, so the immune system, which has not yet formed, tries in every possible way to fight the load placed on it. In newborn children, the leukocyte level can reach up to 24.5 leukocytes per 109/l; over time, naturally, these figures begin to decrease. So, at the age of six months this figure is only 13.5 per 109/l. By the age of one year, the level of leukocytes decreases to 12 per 109/l. And by the age of 12, the level of leukocytes in the blood fully reaches the level of an adult and should not exceed 4 leukocytes per 109/l.
It is worth noting that the number of leukocytes in a child’s body can constantly vary, this is also considered normal.
What are leukocytes and how many of them should be in the blood
Leukocytes are white blood cells, the main cells of the immune system.
As the body's "police", they are responsible for catching, containing and destroying any danger to the body. To perform these functions, there are 5 types of leukocytes:
- Neutrophils. They quickly move to the source of infection and eat pathogenic microorganisms. They are also capable of producing antimicrobial substances. In case of mass death, they become the basis for pus.
- Monocytes. These are the largest white blood cells that can eat large bacteria and the body's own cells infected with viruses.
- Eosinophils. Destroy excess histamine released during an allergic reaction. They are also capable of destroying parasite larvae that have entered the body.
- Basophils. They trigger an immediate reaction (rash, swelling, cough) upon contact with an allergen.
- Lymphocytes. There are T-lymphocytes that recognize infection and direct the activity of all components of the immune system, and B-lymphocytes that produce specific antibodies to destroy the cause of the disease. There are also zero lymphocytes in the blood as a reserve in case of mass death of leukocytes.
On average, an adult has 5.5-8.8 x 109 leukocytes per 1 liter of blood. This indicator is not suitable for children, and the norm is taken from the table by age.
Types of leukocytosis
In medicine, there are several forms of leukocytosis.
- Most often, a short-term type is determined, when there is a sharp release of leukocytes into the blood due to stress, this condition quickly passes, but there are cases when leukocytosis is observed during infectious diseases, and the level of leukocytes returns to normal along with the recovery of the little patient.
- High leukocytosis in the blood of a child can be directly related to pathologies; they can be hereditary.
- The lymphocytic appearance most often occurs when the level of leukocytes in the blood is much different from the norm, for example, this is observed when a child has been suffering from a chronic disease for a long time.
- The basophilic form can occur with frequent colitis in a child.
- The monocytic appearance is characteristic of malignant formations in the body.
How is the analysis carried out?
Various pathological factors distort the results of blood tests. To obtain reliable survey results, you must adhere to the following rules:
- The day before the blood sampling procedure, exclude fatty and spicy foods from your diet.
- Refrain from taking medications for 24 hours (if the use of medications cannot be ruled out, then you should inform your doctor about this).
- Before taking blood, you need to limit the child from emotional stress.
- Physical overload should be avoided.
- Stop eating 8 hours before taking blood (for infants - 2 hours). Drinking water cannot influence the test results, and children can be given non-carbonated and unsweetened water.
Capillary blood is most often used for analysis. It is taken from the fingers. In infants, it is obtained from the heel (a scarifier is used for this). The child should be psychologically prepared for the blood sampling procedure, because stress negatively affects the results of the analysis.
To reduce stress and discomfort, mini-vacuum blood sampling systems are used. They hardly fix the child’s limb, and the doctor or nurse can draw the required amount of blood into the tube.
Important information: What does increased lymphocytes in the blood mean in an adult (causes and consequences)
In the blood test results, all white blood cells are designated as WBC. Additional blood diagnostics are prescribed for severe illnesses or questionable results.
What to do if leukocytosis is detected in a newborn baby?
For a newborn child, abnormalities in the level of leukocytes in the blood are often considered normal, so parents should clearly understand that the immune systems of an adult and a small child are very different. The baby may suffer from frequent infectious diseases, poor nutrition, and also from heredity. Of course, if an increase in leukocytes in the blood is accompanied by any other disease, then first of all it is necessary to eliminate the disease, after which the leukocytes can return to normal.
Pediatricians recommend donating blood for analysis at least once every six months; this helps to identify serious abnormalities in the body in the early stages, especially since in some cases leukocytosis in children under one year of age occurs hidden.
Diagnosis of leukocytosis
First of all, of course, it is worth doing a detailed blood test, which can show the level of leukocytes in the blood; different types of leukocytes are indicated as a percentage, which is derived using a special formula, it is called a “leukogram”. The leukogram is compiled taking into account the age of the child, because each age has its own norm. If the number of eosinophils in the body increases, this indicates that the child is experiencing an allergic reaction; neutrophils increase during inflammatory processes in the lungs. It is best to donate blood for analysis in the morning, and it is advisable that the child does not eat anything. Increased leukocytosis in a child’s blood may not always indicate pathological processes in the little person’s body, so after a while it is recommended to undergo repeated tests.
How to treat leukocytosis?
Treatment can be prescribed only after the exact cause of this phenomenon has been established, for example, physiological leukocytosis is considered to be the norm. As soon as the causative agent of the infection is detected, the following drugs may be prescribed to the small patient:
- Antiviral agents that effectively fight viruses.
- In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed, but they are taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Chemotherapy drugs that are aimed at maintaining the immune system.
Sometimes, when leukocytosis is detected in children and the blood has a viscous consistency, leukapheresis is prescribed, during which the blood is purified.
Dangers of Increased White Blood Cells
Leukocytosis does not pose a health hazard, according to Dr. Komarovsky, if its occurrence is associated with physiological reasons. This sign in some cases indicates a certain disease that negatively affects the quality of life and leads to complications. The main place is given to tumor processes, which can be asymptomatic for a long time and are often discovered by chance during a routine examination.
The main treatment of leukocytosis in children is aimed at eliminating the causes that provoked the appearance of this symptom. It includes:
- antihistamines;
- antibiotics;
- antiviral;
- immunomodulators;
- chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant for leukemia.
The main stage from which children begin to be treated is proper nutrition, including foods that are responsible for stimulating the formation of hemoglobin. You should eat legumes, B vitamins, and milk.
By analyzing peripheral blood and examining urine for leukocytes, a diagnosis can be suspected. Its confirmation is provided by additional instrumental examination methods, examination and information received from the mother. If leukocytosis is detected in time, if the disease is present, treatment can be started at an early stage.
Watch the video of Dr. Komarovsky - clinical blood test:
Traditional methods of treating leukocytosis
All folk methods are aimed at increasing the child’s immunity, so it is recommended to eat a large amount of vegetables and fruits. Before bedtime, it is recommended that the child be given vegetable salads, which help the little person absorb more nutrients into the intestines, and everything else is easily excreted from the body. You should also eat more foods that are full of proteins, including nuts, cheese, seeds, beans and soy.
As you can see, leukocytosis in children is not considered a major deviation in the body, but it is also not recommended to ignore it. As a preventive measure, it is necessary from childhood to teach the child to lead a healthy lifestyle, provide him with proper nutrition, but also, of course, donate blood for analysis at least once every six months.