How does the expectant mother feel in the second trimester?
After three months of the gestational period, many organs and systems in the body of a pregnant woman have been rebuilt to meet the growing needs of the fetus. Some of these changes occur unnoticed by the woman, some changes were expected and are tolerated quite well, some cause problems.
Feelings in the second trimester:
- Enlargement of the mammary glands.
Hormonal changes affected the breasts starting from the first trimester. Now the mammary glands have significantly increased in size, a venous network has appeared on them, colostrum is sometimes released from the nipples, the areolas of the nipples have darkened, and their diameter has increased. To prepare your breasts for upcoming breastfeeding, you need to gently rub your nipples with a terry towel and leave the mammary glands in the open air for some time. The bra must reliably support the breasts; it is selected according to size, giving preference to natural fabrics.
- Abdominal enlargement.
At the beginning of the second trimester, the volume of the hips and waist increases slightly, but by the end of this period, the mobility of a pregnant woman will decrease significantly due to the growing belly. To alleviate the condition, you should wear a prenatal bandage.
- Training contractions.
From time to time, pulling, painless sensations or false contractions appear in the lower abdomen. They are not accompanied by pain; during these contractions, the uterus seems to “turn to stone” and become dense. In this way she is preparing for the upcoming birth. False contractions do not cause any harm to the fetus.
- Pigment spots and darkening of the skin.
Pigmentation appears on the skin of the face and neck during pregnancy, which disappears after childbirth. In the second trimester, the strip of skin from the pubis to the navel becomes darker, as well as the skin of the perineum. This is due to increased secretion of melanin.
- Striae
(stretch marks) on the chest and abdomen.
Pinkish-red skin defects, the appearance of which is sometimes accompanied by itching, occur during intensive tissue growth. Over time, they become paler or disappear completely. To prevent the appearance of stretch marks, you can lubricate the skin with olive or almond oil, moisturizing cream from a series of pharmacy cosmetics. - Dizziness.
This symptom in the 2nd trimester is associated with arterial hypertension, when the total volume of circulating blood in the body of the expectant mother increases significantly, and due to the action of progesterone, the tone of the blood vessels decreases. To prevent such vascular pathologies, you should not get up suddenly from a lying position, it is advisable to rest more and follow a drinking regime.
- Snoring and bleeding gums
. Swelling and looseness of the mucous membranes due to the increased volume of blood circulation leads to the fact that the mucous membrane of the palate and larynx increases in size, which leads to snoring. For the same reasons, the oral mucosa swells and loosens, the gums soften and become easily wounded, bleeding.
- Dyspnea.
The need to transport increased amounts of oxygen to the placenta through the blood increases the intensity of exhalations and inhalations. In addition, the enlarged uterus affects the diaphragm, lifting it and the respiratory system upward from its normal position. To make such changes less likely to lead to shortness of breath, you should often walk and ventilate the room where the woman is.
- Cramps in the calf muscles.
Increased consumption of minerals for the formation of organs and tissues of the unborn child can lead to their lack in the woman’s body. This deficiency manifests itself as nighttime cramps in the leg muscles. To prevent them, you should take vitamin and mineral complexes on the advice of a doctor.
To get through the second trimester of pregnancy without complications, you should rest more often, treat possible problems with optimism, avoid stress, remembering that the mother’s condition will certainly be passed on to the child.
Causes and treatment of lower back pain during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s body must “adapt” to the upcoming loads and compensate for all the changes occurring with the expectant mother.
This means that the gradual growth of the fetus should not cause pathological changes in the balance of the female general condition. And pain in the lower back or tailbone, which often accompanies pregnancy, may reflect adaptive processes.
Contents of the article: Mechanism of development Treatment of low back pain during pregnancy Precautionary measures Prevention
Development mechanism
Lower back pain during pregnancy can occur at different stages. It is a mistake to think that in the early stages of gestation a woman’s back is not subject to certain loads. So why do women often complain that their lower back “aches” or their tailbone hurts during pregnancy?
In fact, the manifestation of cramps in the lower abdomen during pregnancy is not considered any serious abnormality. This symptom is inherent in almost every pregnant girl and is considered the norm, such as toxicosis, breast enlargement, growth of the tummy and pelvis in it.
As a rule, discomfort in the lower abdomen occurs for the following reasons:
- increased uterine tone;
- problems in the digestive system (bloating, flatulence, constipation);
- Braxton Hicks training contractions;
- painful tingling in the lower abdomen at the end of pregnancy, signaling the beginning of the labor process.
Along with the usual causes of abdominal cramps, there are certain points that require increased attention from expectant mothers. For example, if brown/bloody discharge, loss of consciousness, general malaise, elevated body temperature, vomiting, nausea, and painful urination are observed with spasmodic pain. These symptoms may indicate the following:
- possible ectopic pregnancy;
- premature birth, possible miscarriage;
- cystitis;
- inflammation of appendicitis;
- intestinal flu, rotavirus infection.
It should be noted: most of the above signs, causes of discomfort, and the occurrence of cramps in the abdominal area can be observed in every pregnant girl (healthy, sick, physically fit, weak) and accompany a pregnant woman at any stage.
Abdominal cramps in the early stages of pregnancy primarily occur due to pregnancy itself, a large-scale restructuring of the body as a whole. Due to hormonal changes in the wall of the uterus, the ligaments that support it become more elastic and stretch, which causes some discomfort in the lower abdomen.
You should be wary if contraction and hardening of the lower abdomen are accompanied by sharp, acute pain with bleeding, nausea, and loss of consciousness. These symptoms may indicate the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, or if the ultrasound does not confirm the fetal heartbeat, a missed abortion. In such circumstances, it is necessary to urgently seek professional help.
Muscle spasms in the lower abdomen at the beginning of pregnancy can be felt by girls whose monthly cycle was painful, and various types of diseases of the reproductive organs were observed. Sometimes spasms of the lower abdomen occur at lightning speed with sudden movements, coughing, sneezing. Often, spasmodic pain appears in repeatedly pregnant women after cesarean section, who have a scar on the uterus.
Abdominal cramps in late pregnancy are usually caused by the same hypertonicity of the uterus. Only, if the main reason for the increased tone of the uterus in the first trimester is changes in hormonal levels, the formation of the embryo, then in the second and third trimester, spasms appear due to the rapid growth of the baby, an increase in the size of the uterus, due to preparatory contractions (from about the 20th week), at the end of pregnancy, discomfort is considered one of the signs of imminent labor.
As the volume of the uterus increases, the organs of the abdominal cavity shift and shrink, so in the later stages, abdominal cramps during pregnancy can signal a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, a pregnant woman, along with cramps, often experiences a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, and bloating. Due to the uneven passage of food through the intestines, flatulence (gas formation) and constipation occur.
Therefore, nutritionists recommend that mothers review their menu and adjust meal times: eat often, but in small portions. Include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet, and do not neglect dairy products and dried fruits. But it’s better to forget about smoked meats, pickles, and fried foods for a while.
Experts primarily attribute inflammation of the appendix, the vermiform appendix of the rectum, to non-obstetric causes of abdominal cramps at the very bottom. Increasing, prolonged pain (more than twelve hours) in the right lower side, radiating into the umbilical region with a spasm, indicates inflammation of appendicitis.
Similar symptoms with inflammation of appendicitis occur with rotavirus infection. However, in addition to sharp cramps and nagging pain, intestinal flu is characterized by frequent vomiting and diarrhea. As a result, while waiting for an ambulance, it is necessary to drink still water or sweet tea often, but in small doses. It is prohibited to take any medications without a doctor's prescription. This can worsen the situation and harm the baby.
If muscle spasms in the lower abdomen during pregnancy are accompanied by tingling and painful urination, this is due to the occurrence of cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), which is caused by a bacterial infection entering the body.
Pregnant women have a highly developed “sixth sense”, so they can easily determine in which situations cramps in the lower abdomen are not significant, and which symptoms should be heeded. In any case, expectant mothers need to take care of themselves, and at the slightest hint of problems, consult a leading doctor.
Cramps are voluntary muscle contractions. This phenomenon occurs in pregnant women in most cases in the morning or at night. Numbness is most common in the second trimester of pregnancy. What are the causes of leg cramps during pregnancy at night and not only?
Every woman experiences painful symptoms while expecting a child. This is due to the restructuring of the body at the hormonal level, internal organs are rebuilt. This may also be a symptom of increased uterine tone.
It is permissible to simply lie down for mild spasmodic phenomena; the pregnant woman needs to relax and rest. Sharp pain requires serious treatment and mandatory medical care.
Fetal development in the second trimester of pregnancy
The countdown of the second trimester begins from the 13th obstetric week, and its end occurs in the last days of the 28th week of pregnancy. By the 13-16th week of intrauterine development, all the internal organs of the fetus have already been formed, and the placenta has completely taken over the functions of the life-support organ of the unborn child. From this time on, the functioning of the central nervous system, respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems of the fetus is improved.
He has already established a sleep and active wakefulness pattern. With the development of the nervous system and brain, the unborn child improves his perception of the world available to him. He can react to the bright light of a lamp brought to the mother’s belly, flinch from sharp sounds, and feel touches to the belly from the outside.
The fetus's facial expressions develop; he can wince and smile, swallow amniotic fluid, touch the umbilical cord, his face and suck his finger. The main achievement of the second trimester is that the mother clearly feels the baby’s movements. For her, he is no longer an abstract being, but a living child who moves, hiccups, pushes from the inside of the uterine wall with his strengthened arms and legs. The fetus moves so intensely that it changes its position several times a day. Sometimes a pregnant woman's belly becomes asymmetrical because the baby is predominantly in one part of the uterus.
Fetal parameters:
- Fourth month – weight 140 g, height 15 cm;
- Fifth month – weight 350 g, height 21 cm;
- Sixth month - weight 900 g, height 34 cm.
By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is already beginning to open its eyes, until that moment hidden under the eyelids. Thin and delicate hairs (lanugo) grow on the skin of the body and head, outlining the eyebrows and eyelashes. The entire fetus is covered with vernix, which protects the epidermis from the action of amniotic fluid. His urinary system works clearly, passing through itself the products of processing amniotic fluid swallowed by the baby.
Meconium has formed in the intestines - original feces, which will be released after childbirth. By the end of the second trimester, the baby's respiratory system is not fully formed, although its main sections are already there, and the unborn child has imitated breathing movements more than once.
The formed nervous system makes the fetus very susceptible to the mother’s condition. If she experiences negative emotions, he calms down, or, conversely, makes a series of sudden movements. Therefore, you should protect yourself from stress and conflicts with others. Most women feel a surge of strength in the second trimester, they are active and full of energy due to stable hormonal levels.
Second trimester workout - contractions
For some pregnant women, resting their legs will be enough to stop the pain.
Pelvic pain during pregnancy can be distributed across the lower and upper pelvis and may manifest as morning stiffness. It’s good when pain goes away with rest and relaxation, but sometimes you need to put in a lot more effort to reduce the unpleasant sensation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gDCXvI9FCnU
Nagging pain is typical at the very beginning of pregnancy, at about 2 weeks. This is due to the passage of the fertilized egg (fertilized egg) through the fallopian tubes and its subsequent implantation in the woman’s uterus.
Adapting to new conditions, the muscles and ligaments of the uterus stretch, causing discomfort in the woman. This is one of the first symptoms of pregnancy. Suddenly your stomach feels tight - congratulations, you are pregnant!
If discomfort in the lower abdomen starting from 2 weeks is accompanied by
then this is an ectopic pregnancy.
An ambulance should be called immediately, as an ectopic pregnancy poses a threat to a woman’s life.
In pregnant women, under the influence of hormones, taste changes dramatically. They are overwhelmed by the irresistible
(for example, herring with milk), resulting in
. Pain in the lower abdomen can be caused by this. They may be accompanied
- bloating
- flatulence
- constipation
- and dysbacteriosis.
4. If your stomach feels tight when you are pregnant for more than 4 weeks and there is bloody discharge from the genital tract, then there is a threat of spontaneous miscarriage, or frozen pregnancy. In this case, it is also necessary to immediately call an ambulance.
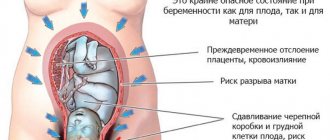
1. As pregnancy progresses and the baby grows, the uterus continues to stretch, which increases pain. Attacks can last up to a week. It increases even more as labor approaches, especially from 36 to 38 weeks, when the baby begins to descend into the pelvis.2. As the end of pregnancy approaches, a pulling in the lower abdomen along with bloody discharge from the genital tract may indicate premature placental abruption. Through the placenta, the baby receives nutrients and breathes.
Detachment before birth means that it is fatal for the baby.
You should seek medical help immediately.
Pain in the lower abdomen can also be a consequence
. What it is? The four pelvic bones are attached to each other by a joint called the symphysis. It is responsible for stabilizing the pelvis during walking and sitting.
During pregnancy, the hormone relaxin is secreted, which softens the joints, thereby allowing the birth canal to dilate. When relaxin is released excessively, the joints soften and stretch too much, which causes pain in the lower abdomen. In severe cases, pain significantly complicates the course of pregnancy. Frontal dysfunction syndrome is estimated to affect one in 35 pregnant women. There is pain in the area
- pelvis
- groin
- lower back
- inner thigh.
It becomes difficult for a woman
- stand on one leg
- walk up the stairs
- move while lying on your back
- get out of the car and get into it.
Symptoms are more pronounced in the second trimester, from 12 weeks. Some pregnant women will have less of a problem with the syndrome, and some will have severe difficulties
- sitting
- lying down
- during sleep
- movements.
There is no prevention in this case, and it is difficult to predict whether it will hurt in subsequent pregnancies, but at least you will know and can be better prepared.4. Well, the main reason for nagging abdominal pain after 38 weeks. Labor has begun! But before you grab your things and rush to the hospital, check whether your contractions are real or false.
During this period, from time to time the woman feels pain or discomfort in various parts of the body. As a rule, they indicate changes in hormonal levels or are associated with abdominal growth. But sometimes abdominal pain indicates an exacerbation of previously dormant diseases or the emergence of other problems.
The abdomen does not belong to a single organ; pain in this area can be associated with pathologies in various body systems. If you experience any unpleasant painful sensations, it is best to consult a doctor.
As you can see, abdominal pain during pregnancy can occur for various reasons. Some of them can threaten the health of both the expectant mother and the child. During the normal course of pregnancy, there may be minor pain in the abdomen without dynamics. In this case, the body simply adapts to a new physical state.
You should not self-medicate abdominal pain during pregnancy, as you can harm yourself and your baby. It is best to consult your doctor first.
Physiological pain during pregnancy can be relieved by staying in the knee-elbow position for 10 minutes several times during the day. Taking a warm shower, chamomile tea or aromatic relaxing oils (rose, mint, jasmine, lavender) will also help. After your doctor's permission, you can drink a glass of mint infusion or lemon balm decoction at night. The product will help you relax, eliminate pain and fall asleep quickly.
For pain caused by digestive problems, normalizing your diet and including a large amount of fresh vegetables, fruits and dairy products in your diet will help. You need to try to stick to the regime and eat food at the same time every day. It is important to avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods.
In case of inflammatory processes in the body that cause abdominal pain, the woman is prescribed pregnancy-compatible antibiotics, as well as acceptable antispasmodics. If there is a threat of miscarriage, uterine hypertonicity and initial placental abruption, bed rest and sedatives are indicated. Antispasmodics, which also reduce the tone of the uterus, help relieve pain in the abdomen.
If surgical intervention is necessary, they try to postpone it until the end of pregnancy, relieving the symptoms of the pathology. In emergency cases, they try to resort to laparoscopy rather than strip surgery.
You should never despair, everything will definitely be fine
One of the most difficult tragedies for any patient is a frozen pregnancy. Usually, fading and further fetal death occur in the early periods of gestation, however, a fairly high risk of such a complication remains in the middle of gestation. A particularly dangerous period in this situation is 16-18 weeks.
One of the frequent, but not obligatory, signs of frozen is the appearance of painful discomfort in the uterine area. If the baby suddenly stopped showing signs of activity, signs such as fullness of the mammary glands disappeared, painful tingling appeared in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, and ultrasound diagnostics did not detect the baby’s heartbeat, then there is every reason to believe that intrauterine fetal death has occurred. Also, one of the signs of frozen tissue may be a thick brown smear.
All unpleasant sensations during pregnancy can be divided into physiological and pathological. If you just need to get used to the former, the latter signal certain deviations. It's time for you to learn to understand your body.
Acceptable pain includes discomfort in the lower abdomen or back after walking or staying in one position for a long time.
- During pregnancy, not only your mood and the size of your belly changes, but even your gait. During this period, the pelvic bones gradually expand, becoming softer, and the joints? respectively? weaker, hence the pain when tired;
- The location of pain in the second trimester of pregnancy is the lower abdomen, namely the place where the uterus is supported. Short-term sensations that go away on their own are the norm;
- The cause of painful sensations may also be banal bloating or flatulence, which are not alien to pregnant women (read the article on the topic Bloating during pregnancy{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;);
- You may also feel pain in the sacral area or lower back: during this period, the load on the spine is increased, the center of gravity is shifting, in addition, the increasing size of the uterus and its contents puts pressure on all internal organs.
Pathological pain
All painful sensations that do not go away, but only intensify over time, are pathological in nature.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, which lasts more than 2 minutes and is systematically repeated up to 10 times a day, is a signal of increased uterine tone, which is fraught with the threat of miscarriage. Spasms that accompany uterine contractions can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus, the development of intrauterine anomalies and even termination of pregnancy;
- Heartburn, which you can experience as early as the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, is both a physiological and pathological phenomenon. It appears due to weakening of the muscle tone of the gastrointestinal tract under the influence of the hormone progesterone and the release of gastric juice into the esophagus, but the intensity of the discomfort may depend on what you eat and how (more about heartburn during pregnancy{amp}gt;{amp} gt;{amp}gt;);
With proper nutrition in small portions, heartburn can be minimized, in addition, you can take acceptable medications, like Rennie or Galstena, the main thing is to study the instructions with contraindications (read the article Rennie during pregnancy{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp} gt;). In addition, be sure to pay attention to our book on proper nutrition: Secrets of proper nutrition for an expectant mother{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
- Headaches and dizziness can signal you about the development of anemia and low blood pressure. Monitor these indicators in order to take the necessary measures in time;
- But pain and heaviness in the legs can be caused by swelling and venous insufficiency. Drink clean, still water, eat less salt and preservatives, and get plenty of rest during the day. Please note that excessive swelling can be caused by kidney disease, so additional tests should not be avoided;
- Cramps that may bother you in the 2nd trimester directly indicate vitamin starvation. Calcium, Magnesium and Potassium in any form will help you forget about unpleasant numbness in your limbs. Also study the article on the topic: Arms and legs go numb during pregnancy{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;;
- Local pain in the side with discharge can signal you about inflammatory processes. Do not forget to tell your doctor about this phenomenon (current: Right side hurts during pregnancy{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;).
Is nausea possible in the second trimester?
Although in most women early toxicosis no longer makes itself felt, sometimes its symptoms drag on and go into the second trimester. More often than others, nausea is felt in women with multiple pregnancies - almost up to the 20th week. In order to experience such an unpleasant symptom as rarely as possible, you need to have breakfast without getting out of bed. Tea with lemon and crackers or cookies is great for this.
It is advisable to limit the consumption of fatty foods and eliminate intensely perfumed cosmetics from everyday use. If nausea continues for too long, accompanied by debilitating vomiting, this condition requires immediate medical attention. Perhaps this is a sign of gestosis, a dangerous pathology of pregnancy.
Why may abdominal pain occur in the 2nd trimester?
During pregnancy in the second trimester, most expectant mothers feel quite tolerable, but often women begin to experience aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, as during menstruation (we recommend reading: why does the lower back often ache during pregnancy?). As a rule, this condition does not cause concern among specialists. Unpleasant sensations arise due to an increase in the size of the uterine body. It’s another matter when the patient experiences sharp stabbing pains, accompanied by vaginal discharge. In such situations, you should not hesitate, because the risk of miscarriage is high.
Sometimes abdominal discomfort can be associated with malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. The enlarging uterus puts pressure on the stomach and intestines, which causes heartburn. Constipation is a common companion for a pregnant woman. Fecal stagnation contributes to the penetration of toxins into the blood, causing intoxication of the body. Constipation is accompanied by abdominal pain and often provokes the development of hemorrhoids. Sometimes discomfort in the intestines occurs in expectant mothers who have never encountered such a problem before.
Physiological pain in a pregnant woman
Experts say that almost all women experience periodic pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy. Physiological pain is explained by the growth and development of the fetus. In addition to unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen and lower back, a pregnant woman has to put up with chest pain, increased sensitivity of the nipples and frequent mood swings.
By the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy, the center of gravity changes. The developing fetus affects nearby organs, which often causes discomfort when walking.
Training contractions can also cause physiological pain. A woman must take into account her character. If the contractions are pronounced, and the discomfort only intensifies over time, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
No need to worry if:
- pain is temporary and disappears after changing body position;
- no bleeding;
- the lower abdomen is slightly tight, the pain is mild, as during menstruation;
- the pain that occurs in the abdomen is moderate and easily tolerated.
Pathological pain
Sometimes discomfort in the abdomen in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy can be a symptom of the development of pathology of internal organs. Unpleasant sensations in the iliac or groin area often occur in women with diseases of the digestive, genitourinary, cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems. Also, sharp stabbing pain in the lower abdomen can be a symptom of premature birth.
If a woman, in addition to abdominal pain, has swelling in her extremities, the doctor may suspect a kidney pathology, which is why the expectant mother should regularly have her blood and urine tested throughout her pregnancy. Often the stomach is pulled, it hurts and seems to become like stone in women at 4-6 months of pregnancy with increased tone of the uterus. This condition requires monitoring by a specialist; the patient may have to undergo a course of inpatient treatment.
If the expectant mother experiences acute pain in the lower abdomen, and then spotting appears, you should immediately call an ambulance. This condition is not only dangerous for the health of the fetus, but also threatens the life of the mother.
Causes of pain in the second trimester
The increased risk of miscarriage remains in the first trimester, and pain associated with the risk of miscarriage should not be felt. However, there are many reasons for concern.
Causes of pain:
- Pain due to sprain of the round ligament.
If pain sensations are concentrated in the lower abdomen, and they appear sporadically, this is a manifestation of the pressure of the uterus on the round ligament that supports it from below. Such unpleasant sensations pass quickly and are not accompanied by spasms.
- Lower back pain due to a shift in the center of gravity.
Almost all pregnant women feel such pain; they are associated with the fact that the growing uterus shifts the balance, and the spine has difficulty regulating the increased load on the lower back and spinal column. The growing uterus adds stress to the spinal discs, pushing all organs apart.
- Pain due to diseases of the urinary system.
Impaired immunity often leads to pregnant women developing a specific type of cystitis. If left untreated, the infectious process progresses along an ascending path and affects the kidneys, causing pyelonephritis. Impaired kidney function is dangerous for the health of the woman and child; it negatively affects the course of labor, so this pathology should be treated immediately.
- Pain due to softening of the joints.
After a long walk or a forced sitting position, a pregnant woman may feel pain in her joints. This is due to the fact that in preparation for childbirth, hormonal regulation somewhat softens the pelvic bones and articular ligaments. If a woman does not wear a support bandage, after every walk she feels pain in her hip joints.
- Pain due to intense fetal movements.
Increased fetal activity causes a woman to feel sudden pain in the right and left hypochondrium. It changes its position in the uterus and its movements cause slight painful sensations.
You should be wary if the pain is severe, cramping, and accompanied by bloody discharge. These symptoms should promptly seek medical attention.
Other causes of pain
Abdominal pain may occur in the second trimester with a displaced pregnancy or an ectopic pregnancy. Very rare, but attacks of acute appendicitis, acute inflammation of the pancreas, and intestinal obstruction are possible. Such disorders are accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If such signs are present, immediately call an ambulance.
In any case, if you feel something, do not rush to panic and get upset. Calmly observe yourself and be judiciously aware of your sensations. If something confuses or worries you, go to the doctor. Even if it is not so scary, you will see for yourself that your fears are groundless. If the pain is systematic and intense, again, go to the doctor. The sooner you find out the reason, the sooner you can solve it. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, take baths or do any other procedures you have heard or seen. Just solve the issues with the doctor, and everything will be great.
Vaginal discharge
Hormones influence the nature of vaginal discharge in the second trimester. Leucorrhoea increases in volume and acquires a milky white color. They are not accompanied by itching or burning.
If vaginal discharge takes on an atypical appearance, the woman has a pathology of the reproductive system:
- Green or yellow tint, foamy structure - infection with a sexually transmitted infection (trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea);
- Scanty bleeding is a sign of cervical erosion, fading pregnancy;
- Curdled discharge accompanied by itching and burning is a sign of vaginal candidiasis.
- Copious transparent discharge – leakage of amniotic fluid, the condition requires hospitalization;
- Clear discharge with an unpleasant odor is a sign of bacterial vaginosis.
Any vaginal discharge that differs from the norm should be diagnosed by taking a smear for urogenital infections. If a pathology is detected, it is immediately treated, blocking the spread of pathogenic microorganisms, some of which can penetrate the placental barrier.
To avoid the appearance of thrush, or vaginal candidiasis, you should wear cotton underwear, avoid carbohydrate foods, and practice condom-protected sexual intercourse. Treatment of thrush is carried out under the guidance of a gynecologist.
Treatment of intestinal colic during pregnancy
Mild, quickly passing intestinal pain does not require treatment, but be sure to inform the gynecologist about the discomfort. In other cases, when intestinal pain is a sign of some other disease, it is necessary to begin treatment under the guidance of a doctor. Even pharmaceuticals such as No-shpa or Espumisan, which can relieve spasms, are prescribed only by a specialist. He selects the dosage for the pregnant woman and sets the course of taking the medicine.
To treat colic and reduce gas formation, doctors can recommend the following drinks and foods, only taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient:
- Tea with mint or lemon balm
. During a normal pregnancy, doctors recommend drinking no more than 4 cups of tea per day, and the course of taking mint should not last more than 3 months. It should be used with caution, especially for women with a difficult pregnancy, since in case of an overdose, mint can provoke premature birth, since it contains estrogen. This tea is also contraindicated for women with low blood pressure. - Dill in any form
. It is recommended for postterm pregnancy or weak labor, since it enhances the contractile activity of smooth muscles, and the uterus is just a smooth muscle organ. Therefore, if in the early stages a woman is at risk of spontaneous abortion, then it is worth limiting the use of dill. In the second half of pregnancy, it is better to replace it with less harmless greens to replenish the body with vitamins and minerals. - Pharmaceutical chamomile
. It has antispasmodic, analgesic and carminative properties, that is, it is an ideal remedy for combating intestinal colic. However, this herb, although weak, is still an abortifacient, therefore, like peppermint and lemon balm, it increases the production of hormones - estrogens, which leads to uterine tension. Therefore, especially in the first trimester, use it only as prescribed by a specialist, observing all dosages. Chamomile is drunk in short courses, lasting no more than 7 days. Take up to 3 tablespoons of decoction no more than 3 times a day. - Motherwort
. According to doctors, it is one of the safest folk remedies when used correctly and without individual intolerance. It does not have a negative impact on the development of the child and the health of the mother. Unlike previous medicinal herbs, on the contrary, it relieves uterine tone. There are enough drugs based on it, but only a specialist can determine how to take it, the dosage and duration of the course.
Hypertonicity of the uterus
Most often, the uterus in the second trimester is in a relaxed state. If it contracts frequently, and this is not associated with training contractions, it is considered that the pregnant woman has uterine hypertonicity.
Its possible reasons:
- Conducting intravaginal ultrasound;
- Exercise stress;
- State of chronic stress;
- Lack of progesterone – the main “pregnancy hormone”;
- History of uterine fibroids, endometriosis.
Constant pressure on the fetus can lead to its hypoxia and subsequent complications, so treatment of uterine hypertonicity is carried out under bed rest. The doctor prescribes antispasmodics, drugs that relax tone, and vitamins.
Renal
The doctor differentiates hepatic colic from renal spasms. Renal colic during pregnancy threatens to increase the tone of the uterus - a risk factor for premature birth.
Unpleasant sensations and pain in the kidney area can be a consequence of exacerbation of chronic diseases of the urinary system: urolithiasis and pyelonephritis. A sudden attack occurs at the location of the stones.
Self-medication and the desire to “endure” unpleasant sensations are dangerous for both the expectant mother and the child!
The attack is accompanied by a slow heartbeat and increased blood pressure. Sometimes a semi-fainting state occurs. The attack lasts from ten minutes to several hours. The use of heating pads, hot baths and medicinal self-medication to relieve spasms is strictly contraindicated.
Second trimester screening
In order to timely diagnose pathologies of fetal development and provide therapeutic and preventive care to mother and child, screening studies are carried out every trimester. In the second trimester it is:
- Triple test, or biochemical screening for the study of special markers (hCG, estriol and β-fetoprotein);
- Ultrasound examination to identify genetic and chromosomal pathologies of child development.
A biochemical blood test allows you to determine the likelihood of the presence or absence of Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome - irreversible genetic disorders. A high degree of risk identified by test results cannot serve as a basis for making a diagnosis. To clarify it, a full examination of the woman and her child is carried out.
An ultrasound performed at 20-24 weeks allows us to evaluate the following indicators of the course of pregnancy:
- The exact date of the gestational period;
- Correspondence of fetal size to gestational age;
- Possible malformations (heart defects);
- Volume of amniotic fluid;
- Assessment of the condition of the placenta, uterine myometrium, risk of possible presentation;
- Gender of the unborn child.
If the screening results are favorable, the woman can be confident that the pregnancy will be successful.
An obstetrician-gynecologist will answer the questions: what changes should you expect in the second trimester of pregnancy? Video about prenatal screening and other tests:
Stretching or pain in the lower abdomen
Nagging pain and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen in the second trimester of pregnancy often indicate natural physiological causes:
- At 12-13 weeks, the uterus begins to actively enlarge. Blood circulation increases, muscle structure softens. This leads to unpleasant abdominal symptoms, which can get worse over time. Single and scanty bleeding in this case is not always a sign of a disease; they can be confused with menstruation, but confirmed pregnancy no longer allows such processes to occur.
- At the end of the 2nd trimester, the rate of divergence of the pelvic bones and the pubic symphysis increases. Because of this, the pain in the lower abdomen worsens and can radiate to the lumbar region and perineum. However, these are not acute symptoms, but mild sipping sensations.
- Disturbances in the digestive process occur in both early and late stages of pregnancy. In the sixth month, the intestines, liver and other gastrointestinal organs take on an unnatural position, causing diarrhea and other disorders. During the same period, flatulence and constipation may increase.
- By the sixth month, the baby begins to actively grow and move. Its actions sometimes turn out to be painful for women - blows to the kidney, liver and intestines cause severe discomfort, but quickly recede. Pain also appears due to the fact that the uterus reacts to fetal movements with increased contractions.
Functional pain does not require emergency medical intervention. However, some women are prescribed certain medications to relieve symptoms.
The ultrasound results determine the growth and development of the fetus
A fairly common complaint among mothers is nagging pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy. Although this stage of gestation usually proceeds quite calmly for pregnant women, the uterus still continues to grow and stretch muscle tissue, which explains the pain in the lower abdomen. With the development and growth of the fetal organism, a displacement of organs localized in the peritoneal cavity occurs.
Huge loads are placed on the intestinal structures, which are also compressed by the enlarged uterine body. As a result, natural difficulties arise with the movement of food masses through the intestinal tract, which leads to disruption of digestive processes, flatulence and bloating, constipation and other unpleasant conditions that cause abdominal pain.
The doctor will be able to detect the tone of the uterine muscles during a visual gynecological examination and palpation of the uterus. Ultrasound diagnostics are also prescribed. But even if an ultrasound shows the presence of uterine contractions, hospitalization of the patient is not necessary at all, since uterine contractions can only occur periodically.
If the stomach constantly hurts during pregnancy, a mandatory examination is necessary aimed at eliminating hypertension, which quite often occurs against the background of progesterone excess. Such a hormone in excessively high concentrations can cause irreparable harm to the baby and mother. Therefore, this condition requires mandatory laboratory and hardware examination.
Particularly dangerous are clinical situations in which not only does the stomach hurt, but also red-brown discharge occurs. Such symptoms require mandatory intervention by specialists, and urgently, in order to clarify the patient’s diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
One of the common factors explaining why painful tingling in the lower abdomen occurs during pregnancy or severe uterine pain is the threat of miscarriage. In the second trimester, the dangerous period is 12-22 weeks of gestation, when late spontaneous abortion may occur.
The patient can be warned about the impending threat of interruption by various manifestations.
- Feeling of heaviness and pain in the lumbar area and lower abdomen.
- The uterus noticeably tenses and cramping sensations occur.
- Vaginal discharge of various shades appears - from scarlet to burgundy-brown. In this case, the amount of mass released is not particularly important; heavy bleeding or minor spotting equally often indicate an impending tragedy;
- Sometimes the threat of miscarriage can be detected in a timely manner during a routine ultrasound examination, when a disturbance in the fetal heart rhythm, an increase in uterine tone and a discrepancy between the size of the uterine body and the actual gestational age are detected.
- Painful symptoms in the abdomen are varied and ambiguous. Usually the pain is concentrated above the womb and in the sacrolumbar area. They can be constant or intermittent, aching or increasing, cramping, etc.
In some patients, as the threat of termination increases, the temperature may rise, but not very much, about 37.5 degrees.
A particularly critical stage in the second trimester in terms of the high risk of miscarriage is considered to be weeks 18-22, when the uterine body begins to rapidly increase. In addition, the risks of interruption increase on the days when the patient was supposed to start menstruating. Therefore, during these periods of gestation, the mother should be extremely careful.
- Enlarged uterus. Changes in the uterus begin from the very beginning of pregnancy. By the beginning of the second trimester, it increases to the size of a newborn baby's head and begins to take up much more space. In the later stages (about 38 weeks), the fundus of the uterus rises to the level of the tenth pair of ribs and the xiphoid process of the chest. The enlarged uterus puts pressure on all neighboring organs. The bladder and intestines are most affected, which is why tingling occurs.
- Stretching and separation of the supporting ligaments of the uterus and pubic symphysis during pregnancy. This is a natural process. Gradually stretching ligaments help the baby pass through the birth canal more easily. Sometimes pregnant women are diagnosed with symphysitis - excessive stretching or rupture of the ligaments of the symphysis.
- Increased gas production. The problem is familiar to every pregnant woman, as the uterus puts pressure on the intestines, causing excessive gas formation.
- Constipation. Another common problem. The longer the period, the more often difficulties arise with bowel movements. If there is no stool for more than 3 days, a stabbing, sharp pain appears.
- "Training" contractions. Thus, in the third trimester, the body prepares for childbirth.
- Embryo attachment. If the expectant mother has a tingling sensation in the lower abdomen in the early stages, this may indicate the process of implantation of the fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus. In this case, the discomfort lasts for a short period of time. In addition, many changes occur in the uterus itself (gradual growth, increased blood supply to the organ).
Pathological causes of stabbing pain:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- urinary tract infections;
- intestinal obstruction;
- gastrointestinal infections;
- ulcerative colitis;
- appendicitis;
- cholecystitis;
- freezing of the embryo.
In 1st trimester
Stitching and bursting sensations may appear in the early stages of pregnancy. Sometimes this happens even before the expectant mother finds out about her “interesting” situation. In most cases, by the end of the 12th week, the discomfort goes away on its own. The pain is associated with an enlarged uterus and increased blood flow to it.
Pain may also be present with gastrointestinal pathologies. For example, with flatulence, pancreatitis, gastritis, ulcerative colitis, constipation, dysbacteriosis, etc. You need to contact a gastroenterologist, the doctor will prescribe a diet and treatment.
In the 2nd trimester
Doctors note that the largest number of complaints from expectant mothers occurs in the 2nd trimester. Women complain of slight discomfort, colic, pain, feeling of fullness, etc.
These symptoms can be caused by two reasons:
- Around the fourth month of gestation, the fetus begins to grow rapidly, as a result of which the uterus sharply stretches. She puts pressure on the bladder. A pregnant woman feels tingling and constantly wants to go to the toilet.
- The uterus puts pressure on the intestines, worsening patency in some of its sections. There are difficulties with defecation and flatulence.
In the 3rd trimester
Most often, stabbing, pulling or cutting sensations occur during contractions of the uterus. These are called false contractions. Women cannot always distinguish them from real ones. False uterine contractions are irregular and do not increase over time. Also, before childbirth, the uterine ligaments are stretched to the limit, which causes pain.
Episodic acute pain occurs when the baby is active. It rolls over, kicks with its arms and legs, and often hits the ribs or bladder. In this case, the expectant mother feels acute pain, which quickly passes.
Sensations similar to contractions or tone are caused by the usual physiological stretching of muscles to the size of the child. The entire bottom may hurt - from the sacrum and tailbone to the stomach; it is possible that only one side will hurt or each side will hurt alternately. In addition, a sensation similar to menstrual pain will appear in the lower back, and the pubic bone will cramp.
Proper functioning of the ovaries ensures normal hormonal levels for the development and growth of the fetus. However, in the second trimester of pregnancy, most women experience unusual and previously unfamiliar conditions - the lower back or kidneys may begin to hurt, either simultaneously or alternately on each side separately. It may also begin to bother the intestines - stabbing in the stomach, navel. In this case, the pain will radiate to the ribs.
Colds in the second trimester
During this period, viral infections no longer pose a great danger to the development of the child, as in the first months of pregnancy. Reduced immunity makes pregnant women a frequent target of respiratory infections. They need to be properly treated under the guidance of a doctor to avoid the development of fetoplacental insufficiency.
The consequences of a cold are especially dangerous for a child’s developing nervous system. At 14 weeks, the endocrine system of the fetus may be affected; at 16-18 weeks, a viral infection negatively affects the musculoskeletal system, which is actively strengthened during these periods. At 19-20 weeks, acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections can cause pathology in the development of the reproductive system in a female fetus, since female fetal eggs are formed during this period.
In the 2nd trimester, the list of medications that can be taken during pregnancy expands.
However, it is better to give preference to neutral cold treatments:
- Drink plenty of fluids to remove viral intoxication products;
- Rinsing your nose and throat with sea water or saline solution;
- Drink herbal teas as recommended by your doctor.
Colds are treated with bed rest.
What to do?
What to do in the second trimester of pregnancy? Nothing special: this is a period of special self-care and good nutrition. Fears about miscarriage are becoming less and less, but you should still be reasonable about overload and avoid stress. Sex in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy begins to be enjoyable, so sexual activity can be practiced without problems, except for the presence of complications. Of course, regular visits to your doctor are necessary to monitor the progress of your pregnancy.
Vaginal discharge. You may have noticed intense white discharge from your vagina during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. Don't be alarmed—they help inhibit the growth of potentially harmful bacteria or yeast. You can wear pads for comfort. Contact your doctor if the discharge is strong-smelling, green or yellowish, or if it is accompanied by redness, itching, or irritation. This may indicate a vaginal infection.
Fever
Hyperthermia in the 2nd trimester no longer has a pronounced negative effect on the fetus and does not stimulate the threat of miscarriage, as at the beginning of pregnancy. The baby is reliably protected by the placenta, which does not allow viruses and microbes to reach it. Elevated temperature is most often a sign of trouble in the body of a pregnant woman. Rarely, but still there are cases when a low-grade fever of about +37+37.5? C is a sign of increased metabolism and hormonal influence, as was the case in the first trimester.
Most often, hyperthermia is accompanied by the following pathologies:
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- Herpes;
- Tuberculosis;
- Pyelonephritis.
If the doctor has not yet prescribed treatment, and the temperature needs to be lowered, you should not take the usual medications such as Aspirin, Nurofen, Analgin. During pregnancy, it is permissible to use Paracetamol as an antipyretic if the temperature remains stable at +38.5? C and above these values. Low temperatures are reduced with tea with raspberries and honey, and cold compresses.
Why do cramps occur during pregnancy?
In fact, there are many reasons why your calves, feet, and stomach cramp at night during pregnancy. The most common:
- toxicosis: at this time, the female body is greatly weakened and is not able to absorb the necessary substances and vitamins in the required volume. During the period of toxicosis, the expectant mother eats little and meals are often accompanied by vomiting;
- deficiency of calcium and magnesium: these microelements are washed out of the body during toxicosis. As the baby grows, calcium and magnesium are increasingly lacking. According to experts, a lack of these elements is the cause of leg cramps;
- lack of glucose: an unbalanced diet helps reduce blood sugar levels;
- varicose veins: exacerbation of the disease occurs due to increased pressure of the fetus on the pelvic veins. The female body is not able to control this situation. That is why the expectant mother may feel cramps and numbness in her legs;
- seizures may occur due to the abuse of drinks such as coffee and tea;
- Diuretics remove not only excess fluid from the body, but also useful substances. Even if this type of medication is prescribed by a doctor, the medications can have negative effects on the body.
If your legs cramp during pregnancy, or unpleasant sensations appear in your stomach, then in some cases you can do without the help of a doctor and eliminate the unpleasant sensation yourself:
- The most important thing is not to make sudden movements. Carefully roll over onto your side and gently lower your legs. Try to press your feet as hard as possible onto the floor. You need to stay in this position for about 30 seconds;
- For 60 seconds, slowly stroke and knead the cramped area from the foot to the knee;
- Holding on to the bed, for example, try to stand up;
- While continuing to hold on to something, you need to carefully walk around the room. You need to walk until the painful sensation goes away completely;
- As soon as the pain subsides, rub your feet with a warming agent (for example, “Star”) and put on warm socks. This way you can prevent the recurrence of seizures;
As for abdominal cramps during pregnancy, if they occur, it is still better to call a doctor, as they may mean a threat of miscarriage. If you do not have the opportunity to call an ambulance, then take antispasmodics and sedatives. Separately, it is worth mentioning that in the third trimester of pregnancy, infrequent cramps are a completely normal phenomenon, indicating an approaching birth.
Frozen pregnancy
Fetal death is the cessation of its development and death, most often occurring at 16-18 weeks of pregnancy.
Signs of a frozen pregnancy:
- Inability to listen to the fetal heartbeat;
- Stopping movements;
- Softening of the mammary glands, cessation of painful sensations in the chest;
- The appearance of brown or bloody discharge;
- During a gynecological examination, the opening of the cervix and the coloration of the vagina in a red-pink color are noticeable.
The woman is freed from the dead ovum and given a course of antiseptic treatment. The causes of pregnancy failure may be genetically determined abnormalities of fetal development, Rh factor, history of abortion, consequences of infection of the uterus.
If your stomach hurts in the first trimester of pregnancy
As a rule, this is a normal condition in the first weeks. But sometimes, in combination with other symptoms, pain may indicate an early miscarriage. Unfortunately, such cases have been happening frequently lately. The main reason is that the fetus does not develop properly. What are the features of early miscarriage:
- Feel. Spasmodic pain in the lower center of the abdomen, bleeding.
- Deadlines. Can happen any time before 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- What to do? Call your gynecologist or urgent care for advice. Sit or lie down. Relax. In case of heavy bleeding (more than one pad per hour), you should urgently go to the hospital emergency department.
Interesting: How Long After an Ectopic Pregnancy Can You Exercise
Sometimes pregnancy can develop outside the uterus. This pathology is called ectopic pregnancy. Unfortunately, this embryo cannot be saved in any way and an urgent termination of pregnancy is necessary. This is a serious condition and occurs in 1% of cases. Features of this pathology:
- Feel. The pain is of a cramping nature, which is localized on one side, but during the contraction it spreads to the other part of the abdomen. Watery bleeding is quite dark in color.
- Deadlines. Usually from 4 weeks to 10.
- What to do? Call an ambulance immediately. Treatment in this case should be started immediately.
Organization of proper nutrition
In the second trimester, the fetus begins to actively develop subcutaneous tissue, and it itself experiences a period of rapid growth, so special attention is paid to the woman’s proper nutrition. The basic principle of menu formation is a balanced diet of nutrients, vitamins and microelements.
An important source of protein is lean boiled or baked meat, sea and river fish, and eggs. The source of calcium, necessary for the formation of bones and teeth of a child, is dairy products (kefir, fermented baked milk, cheese, cottage cheese). To saturate the blood with iron and prevent anemia, you need to eat liver and buckwheat porridge, pomegranates and apples, drink tomato and pomegranate juices. To avoid constipation, it is recommended to include increased portions of plant fiber, vegetables and fruits in any form in your diet.
In order to prevent the development of diabetes in pregnant women and maintain optimal weight, it is advisable to limit the consumption of sweets and products made from wheat flour. They are replaced with bran bread and whole grain baked goods. You should not buy products with dyes and preservatives, or include marinades, ready-made sauces, or smoked meats in the menu. Such foods are often very salty, and their consumption leads to swelling. It is strictly forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages of any strength, since alcohol immediately penetrates into the blood of the fetus.
Symptoms of intestinal colic during pregnancy
Some women may believe that such pain is a harbinger of a threatened miscarriage, which will have an extremely negative impact on their psychological state. To avoid unnecessary stress, you need to know the symptoms of intestinal cramps.
In the early stages they are joined by:
- increased gas formation;
- rumbling or grumbling;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- problems with stool - constipation, diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
All these signs are moderate in nature, but with poor nutrition and an inactive lifestyle they can intensify. If you feel unwell or have persistent concerns, be sure to consult your doctor.
At later stages, the symptoms of intestinal colic are more pronounced and bring more concern, as they are accompanied by dizziness or weakness.
Taking vitamins correctly
The need to form a child’s body and ensure its growth requires an increased amount of vitamins. In modern gynecology, they are abandoning the previous practice of prescribing multivitamin preparations to all pregnant women. According to medical research, such methods lead to an increased number of large-fetal pregnancies, which can only be resolved with a cesarean section.
A varied diet without additional inclusions can provide a woman and child with the necessary nutrients, macro- and microelements, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. However, for the formation of the fetal nervous system, the prevention of hypertension and preeclampsia, additional intake of vitamin E and folic acid is recommended.
Possible need for vitamins in the 2nd trimester:
- A – development of visual receptors, skin, bones;
- C – increasing immunity, preventing premature birth;
- D — formation of the musculoskeletal system, tooth buds;
- B – development of the central nervous system, protein absorption.
The advisability of taking vitamin preparations can only be assessed by the doctor leading the pregnancy.
Pathological causes
If you feel pain in the lower abdomen in the 2nd trimester, it is necessary to exclude a dangerous pathology. The following signs indicate it:
- Pulling sensations on one side only.
- Blood in the discharge.
- Severe cramping pain.
Bloody discharge and an increase in pain are a serious sign that requires immediate hospitalization.
Hypertonicity
Increased uterine tone is associated with a lack of progesterone, concomitant diseases, physical and emotional stress. It is characterized by nagging pain, without clear localization. Sometimes hypertonicity radiates to the sacrum and perineum.
A woman can independently determine increased tone by placing her hands on her stomach. The uterus feels dense with clear boundaries.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a dangerous condition for the fetus and the woman. It manifests itself as high blood pressure, swelling, and headache. During examination, protein is detected in the urine. Without treatment, eclampsia develops - loss of consciousness and convulsions. It can lead to fetal death.
Premature abruption of a normally located placenta
Abruption is the separation of the placenta from the wall of the uterus. It often occurs against the background of autoimmune diseases, Rh conflict, chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, heart defects). The pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- red or brown discharge;
- cramping nature of pain;
- increased symptoms with movement;
- decreased blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness.
Detachment of a small area may stop on its own. The vessels thrombose, and a retroplacental hematoma forms in the uterus. With significant detachment, blood completely saturates the walls (Kuveler's uterus). This leads to disruption of the contractility of the organ.
Placenta previa
There are complete and incomplete presentations. When it is complete, heavy bleeding suddenly occurs; when it is incomplete, the discharge is light. Complications of the pathology are premature birth, placental abruption.
Cystitis and pyelonephritis
Diseases of the urinary tract, in addition to nagging pain, are accompanied by changes in the color of urine, frequent urges, swelling, and fever.
Acute surgical pathology
During pregnancy, surgical diseases occur hidden. This is due to stretching of the peritoneum and changes in the location of some organs. Aching sensations in the hypogastrium occur with appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, and acute pancreatitis. A specific sign is a gradual increase in symptoms against a background of elevated temperature.
If pain or discomfort occurs, you should contact a antenatal clinic. It is important to avoid self-administration of medications until a diagnosis is made.
>
Therapy methods
For symptomatic treatment of colic, the doctor will prescribe an antispasmodic (safe during pregnancy) in the form of tablets or injections. Such therapy should be short to minimize the side effects of the drug.
The main treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of colic. If these are problems with the intestines, a diet and medications are prescribed to normalize the microflora or eliminate excess gases.
For kidney pathologies, antibacterial agents, herbal anti-inflammatory drugs, and surgical procedures (to remove stones) are selected.
Nutrition rules
With intestinal colic, a woman should give up gas-forming foods (legumes, sweets, brown bread, yeast baked goods) and “heavy” dishes (fatty, fried, smoked foods). To normalize peristalsis, she needs to drink a lot of water and fill her diet with fresh fruits and vegetables.
To avoid renal colic during pregnancy, it is necessary to reduce the amount of salt consumed. It is important to drink enough liquid (total volume about 2.5 liters). All foods that contribute to the formation of stones (sorrel, radish, radish, rich broths) should be excluded from the diet.
Drug treatment
During pregnancy, self-medication is unacceptable. A woman should take only those medications prescribed by her doctor. The specialist recommends the most gentle antibiotics, painkillers, and herbal remedies. Individually selects doses and timing of treatment. The patient’s task in position is to strictly follow the specialist’s instructions and coordinate the slightest deviations with him.
ethnoscience
Traditional recipes are often used to eliminate colic. Herbs with anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects are recommended (mint, lemon balm, chamomile, dill, fennel). However, during pregnancy, a woman should be especially careful.
Even infusions and decoctions can increase the risk of premature birth or lead to allergic reactions. Phytotherapeutic treatment methods can be used only with the permission of a doctor, in parallel with drug therapy.
Indications for surgical treatment
The operation is performed in emergency conditions that threaten the life of the mother and child:
- appendicitis;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- blocking of the urinary ducts with stones.
Surgery is highly undesirable during pregnancy. Doctors try in every possible way to avoid it. However, if a woman’s life is at stake, they take risks.