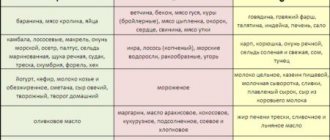
Incompatibility of the blood of the fetus and mother according to the Rh factor is one of the serious problems in obstetrics. Severe forms of hemolytic disease can even lead to life-threatening problems for a newborn baby. The pathological condition in 90% of cases occurs when the mother has Rh-negative blood and the child has positive blood. Less commonly, such reactions occur when there is incompatibility with other blood factors.
To prevent the development of such conditions, the administration of immunoglobulin after childbirth or termination of pregnancies at different stages is used. What kind of drug is this, how does it work and how effective is it?
How does immunoglobulin work after childbirth?
If a woman has Rh-negative blood, it means that there are no certain proteins on the surface of her red blood cells. According to statistics, about 15% of people on Earth have this, this is the absolute norm.
In the case when a baby developing in utero carries Rh-positive blood, its red blood cells have such proteins. This is how they differ from the mother's blood cells.
During pregnancy and childbirth, several milliliters of plasma and the baby's formed elements enter the woman's blood vessels. As a result, the mother’s body begins to actively respond to such foreign cells by forming antibodies. The latter subsequently penetrate into the fetus in utero and begin to destroy those same Rh-positive red blood cells with the development of anemia in the child.
The consequences can be so serious that intrauterine death of the baby is not ruled out.
We recommend reading the article about Rh conflict during pregnancy. From it you will learn about the signs of Rh incompatibility, detection methods and diagnostic methods, as well as treatment.
Immunoglobulin is a drug containing components that can actively bind the child’s Rh-positive red blood cells in the mother’s blood, if they enter here. Thus, if fetal red blood cells are circulating in a woman at the time of administration of the drug, they are destroyed without any consequences for the body.
But there are several conditions that must be met in order for such prevention to be effective. They are as follows:
- The administration of immunoglobulin is carried out in most cases in a non-pregnant state. This is the prevention of the development of hemolytic disease. According to some recommendations, the administration of immunoglobulin during pregnancy is indicated. But if a woman already has signs of Rh conflict during pregnancy, using the drug is pointless. In this case, it is no longer possible to prevent the disease, including for subsequent pregnancies.
- Immunoglobulin must be administered within 72 hours after birth, and the sooner this is done, the better. The fact is that during childbirth or termination of pregnancy, the maximum transfer of the child’s blood to the woman occurs. The quantity increases with various additional manipulations - curettage, manual separation of the placenta, etc.
As soon as antibodies to the baby’s red blood cells have already formed in the woman’s blood, the administration of immunoglobulin is pointless, since the chain reaction has already been started.
Rh factor: what kind of animal is this?
As everyone has known since time immemorial in school, a “rhesus” is such a monkey. It was she who was the first to discover a certain “factor” in her blood, which was named after her.
Those of our readers who had a solid A in biology at school and whose mother still has a certificate of honor from the meeting of young anatomy lovers on the mezzanine know that this “factor” is actually the proteins of the “Rhesus” system, located on the surface of red blood cells. Moreover, some people have these proteins on their red blood cells, while others have them completely absent.
The presence or absence of the Rh factor in human red blood cells determines whether they belong to the Rh positive or Rh negative group. It has been established that 86% of people of the Caucasian (“white”) race have a positive Rh factor, and 14% have a negative Rh factor.
Antigens of the Rh system are produced in the fetus, starting from 8-10 weeks of intrauterine development.
Who will need immunoglobulin after childbirth?
Immunoglobulin is administered to women if they have Rh-negative blood. The main indications for administration are as follows:
- After the first birth in Rh (-) women. Ideally, immediately after birth, the baby’s blood type and Rh are determined, and only in the case of Rh(+) is immunoglobulin administered to the mother.
- It is also advisable to administer the drug after the second birth. After the third, it is considered that its use is inappropriate, since immunization has already occurred in any case or, for some reason, it did not exist and will not happen again.
- After removal of an ectopic pregnancy.
- If during childbirth a woman had placental abruption.
- If the mother received a transfusion of Rh-positive blood or platelets.
- Immunoglobulin is also administered after miscarriages, non-developing pregnancies, premature births with an unsuccessful outcome.
- During pregnancy, this remedy is used if chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis is performed.
Watch the video about Rhesus conflict:
Immunoglobulin KEDRION Immunoro Kedrion – review
Are you a universal donor and are you always welcome at blood donation points? Do all gynecologists in paid and free clinics sigh in doom when collecting anamnesis? Congratulations, you have the First Negative blood type!
In general, in ordinary life this does not affect anything until pregnancy occurs, and from a partner with a positive blood type...
If the stars align this way, then my review of the Anti-D immunoglobulin drug KEDRION will be useful to you.
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
Human anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin, or anti-D immunoglobulin, is necessary during pregnancy if the mother’s blood type is negative and the father’s is positive. In this case, the child can obviously get both a negative and a positive blood type.
If the child is negative, no immunoglobulins are needed either during pregnancy or after. The mother's body will not react hostilely to the child and destroy his hematopoietic system.
If the child has the father’s Rh factor, then events can develop as follows:
- Hypoxia in the fetus + circulatory system disorders.
- Everything will be fine with the first pregnancy (since during the first pregnancy, Rh conflict is considered a rarity), but subsequent pregnancies will be too problematic for pregnancy due to hypoxia and disruption of the circulatory system (the body learns from its mistakes and begins to recognize the Rh difference much faster)
Everything seems simple... But how do you find out what blood type and Rh factor your child has during pregnancy? Problem…
So if you have a negative blood type, and your man has a positive one, you will have to get acquainted with immunoglobulin.
human plasma proteins (containing at least 90% immunoglobulins) 25-180 mg, incl. human immunoglobulin anti-Rhesus Rh0(D) 150 mcg (750 IU)
Excipients: glycine, sodium chloride.
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
Immunoglobulin is given in several cases:
- When terminating pregnancy in the early and late stages. Without diagnosis in the next pregnancy, the body quickly goes into Rh conflict mode.
- At 28 weeks of pregnancy with a negative antibody titer. This is the so-called “vaccination” of Rhesus conflict. The body reacts to the drug, produces a small amount of antibodies, and at a later stage this allows the body’s reaction to the Rh-positive child to be slowed down.
- After childbirth. Here there is already an option not to give immunoglobulin if the child was born with negative Rh, but if it is positive, then intramuscular immunoglobulin is necessary
Kedrion is one of the most budget options for anti-Dimmunoglobulin, its price varies from 3.5 to 4 thousand per dose. Most immunoglobulins for this purpose start at 5 thousand.
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
Unfortunately, because of this, buying Kedrion can be problematic. Both times I ordered it 2 weeks before the due date and just before giving birth I called and found out about the availability in pharmacies in the city (and both times I booked a pack, pharmacies often make appointments with just such drugs)
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
Immunoglobulin is poorly stored; it needs to be provided with a poor dry environment, i.e. fridge.
Although the instructions happily write that 25 degrees is enough - in all the pharmacies that I contacted they began to fanatically talk about storage conditions.
Their motivation is simple - as the temperature rises, the effectiveness of the drug decreases. I don’t know to what extent, but all that remains is to trust the doctors and pharmacists and pharmacists.
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
The shelf life is 3 years, but in order to avoid damage to the expensive drug and reduce its effectiveness, it is often advised to buy immunoglobulin on the day of placement.
Both times I needed immunoglobulin in hot weather (very hot! at +15 there is no need to jump), so I took a thermos, came to the pharmacy, bought the pre-ordered Kedrion and immediately went to the hospital to have it installed.
ONLY in a hospital setting! Even though during my pregnancy my husband improved his skills in giving injections, and I also injected myself with medicine, although not like a seamstress, but at a decent level - the main problem is not the injection, but a possible reaction to the drug.
Therefore, we come to the hospital, where the immunoglobulin is opened in front of us and injected intramuscularly into the upper outer quadrant of you-know-what.
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
The kit includes cedrion powder and a solution for mixing it; there are no syringes or needles. So if there is a need, you need to buy it yourself.
After this, you must be under the supervision of doctors for 30 minutes to an hour!!
Possible adverse reactions can be either local (if the injection site is not properly treated) or of an allergic type.
I was lucky, I didn’t have any reaction to Kedrion’s injection . The pregnant woman who took immunoglobulin with me was less fortunate - weakness, dizziness and vomiting. It is impossible to say for sure that there was a reaction to the drug, but still...
Anti-d immunoglobulin Kedrion
- How to understand whether it works or not?
I was given the so-called “vaccination” against Rh conflict. One of the MANDATORY conditions was the absence of antibodies in the blood, which was last checked 3 days before the date of immunoglobulin testing.
Next, you need to take this test again, but not qualitatively (there are/no antibodies), but quantitatively (if there is, then how much?)
Within a week, a small titer should appear (both times my tests showed 1/16, which is a normal reaction). The titer is checked twice; there should be no additional growth.
So Kedrion anti-D immunoglobulin works and works well.
- What tests are needed during pregnancy with a possible Rhesus conflict?
Even if everything is perfect according to the tests, during a complicated pregnancy (and for a Rh-negative mother this is considered a complication), additional monitoring is necessary. So you will be sent for Dopplerometry and CTG many times more often than normal pregnant women.
During the period when I started having problems with blood, which could also have been the result of a Rh conflict (but looking ahead, no) I was sent to check the state of the fetal blood flow once every 3 days until the results of a detailed coagulation analysis came back.
- How to get immunoglobulin for free?
In theory, pregnant women and those who gave birth should be provided with immunoglobulin according to compulsory medical insurance. And in some regions this happens without any problems, but alas, the county town of NSC is not one of them.
To get immunoglobulin, you need to write letters of happiness to the insurance company, starting from the very first weeks of pregnancy, you need to complain to the head of the housing complex at your place of registration, you need to pester and pester and pester, not forgetting to clarify once a week - will I have immunoglobulin? Why not? I’ll write a complaint!
And not only in the residential complex you need to get sick, but also in the maternity hospital where you plan to give birth. And also from 8 weeks.
And still, this will not protect you from running out of immunoglobulin. But it must be placed within a certain period of time (either during pregnancy or after childbirth, time is very limited) and when the delivery will take place, only Cthulhu knows...
So, judging that I was too lazy to knock on doorsteps and write complaints, I decided to pay and not worry about it any more.
- Bureaucratic and pharmacological nuances:
The drug is not only administered under the supervision of doctors; its administration must be recorded in the exchange card.
In my case, the date of introduction was written right on the cover, and the front side of the package was glued to the last page of numerous ultrasound scans.
In the maternity hospital, the presence of immunoglobulin given at 28 weeks in a Rh-negative mother is checked.
It is often advised to use the same brand of immunoglobulin at 28 weeks and after childbirth, but this is not a necessary condition.
Both of my children took my Rh factor and blood type from their father, i.e. They have 2 negative blood group. It was not necessary for me to be given immunoglobulin during pregnancy and I was not given it after the CS.
But! Guessing whether you will be lucky or not is an unaffordable luxury. If there is a need for a drug, then it should be given, and not play roulette with the health of the child and his brothers/sisters in the future.
At a relatively low price (others are more expensive and strong), it did not give me any side effects. The effect of the drug has been confirmed by laboratory tests, so I recommend anti-D immunoglobulin from Kedrion if you need its administration at 28 weeks.
Well, or as obstetricians always advise: “look for a husband with a negative blood type!” there won’t be any problems at all!”, only there are too many demands on men when choosing
Source: //irecommend.ru/content/antirezusnyi-immunoglobulin-na-28-nedele-beremennosti-privivka-ot-rezus-konflikta-pri-otrits
Is it necessary to administer anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin?
The introduction of immunoglobulin can really insure a woman against the development of subsequent Rh conflict with her unborn baby. But in order for prevention to be effective, the following conditions must be met:
- Administer the drug as indicated, including during pregnancy.
- The sooner after birth, the more effective. Most manufacturers indicate an acceptable time interval of 72 hours, but, for example, similar Russian drugs should be used up to 48.
- It is imperative to adjust the dose of administered immunoglobulin depending on the expected blood exchange between mother and child.
The standard dose is 200 - 300 mcg (this is about 1 - 1.5 ml), but after a cesarean section, manual separation of the placenta and many other manipulations, the amount must be increased by 1.5 - 2 times.
Otherwise, not all red blood cells in the mother’s blood will be bound, and an immune response will still develop to the remaining portion. As a result, the effectiveness of prevention is reduced to zero.
Complications
This injection is a drug that is administered intramuscularly. After use, complications and problems may arise such as:
- Allergy, even if such hypersensitivity has never been noticed before. If you notice a rash on your body, trouble breathing, swelling or other signs, notify your healthcare provider immediately. Quincke's edema, urticaria or anaphylactic shock are possible.
- Redness, pain, and swelling may appear at the injection site. Sometimes this place itches.
- Sometimes there is a deterioration in the general condition of the body (nausea, vomiting, increased body temperature).
- It is not excluded that HIV and hepatitis can be transmitted, despite the fact that careful selection of donors and multiple and different methods of testing the medication are carried out. Therefore, it is advised to do a follow-up examination for these infections (in about six months).
If you are interested in the questions: whether to inject this medicine or not, whether it will harm, then the answer is this: if you do not administer the medicine, then the outcome can be a hundred times worse and sadder! Whatever it is, it's up to you to decide!
Read also: How to improve bowel movements after childbirth while breastfeeding (BF)?
Rh conflict between mother and fetus is a rather serious condition that primarily threatens the health and sometimes the life of the baby. The choice of drugs to combat such conditions is not large enough, so prevention of development plays an important role. If you use the product according to strict recommendations and carefully follow all conditions, you can prevent the development of pathologies and abnormalities.
Reasons why doctors did not administer immunoglobulin after childbirth
Women are not always notified that they have been given immunoglobulin, since this is a common procedure after childbirth or other similar manipulations.
But sometimes the use of the drug is not intended. This is possible in the following situations:
- If this is the woman’s third and subsequent births. It is believed that such prevention should be carried out the last time after the second child.
- If the newborn baby also has Rh-negative blood. In this case, no conflict arises. But a similar reaction is excluded in subsequent pregnancies if the fetus already has a different blood type.
- If a woman has contraindications to the drug, for example, allergic reactions, etc.
- If the drug is not available at the hospital or clinic. In this case, the doctor must notify the woman and recommend purchasing, explaining all the possible consequences.
Certain security measures
Many women are interested in whether it is possible to have an abortion with a negative blood type and what are its consequences? In order to prevent serious negative consequences from having a negative Rh factor during an abortion, it is important to follow certain recommendations:
- The best time to terminate a pregnancy is considered to be before 6-7 weeks. In this case, this is due to the active formation of the circulatory system, therefore, the risk of antibody formation in the maternal body increases.
- If a negative Rh factor is detected, after termination of pregnancy it is necessary to administer the so-called anti-Rh immunoglobulin. It is produced on the basis of donor blood, and has the ability to stop the formation of antibodies.
It should be noted that the procedure for administering immunoglobulin should be carried out no later than several days after the abortion. When the patient has a negative blood group, otherwise its effectiveness will be lost.
Why is abortion dangerous in case of Rh conflict?
During the first pregnancy of a woman with negative Rh, doctors always insist on maintaining it. The reason for this attitude is simple: during the first pregnancy, the antibodies produced by the mother's immune system are relatively slow and large; they are not able to penetrate the placental barrier and harm the fetus.
But all subsequent pregnancies are at risk, since the “trained” immune system reacts much more aggressively, attacking the red blood cells of the fetus. During childbirth or abortion, a small amount of fetal blood can enter the mother's body, which leads to increased antibody production.
The consequence of Rh conflict can be anemia, hydrops of newborns, jaundice, and the likelihood of intrauterine fetal death and stillbirth increases.
Therefore, for women with negative Rh blood, the first abortion is contraindicated; doctors always strongly advise them to refuse and continue the pregnancy. After all, all subsequent ones can be much more complicated.