In the mid-18th century, an English doctor named John Langdon Down described the signs of a disease that was then called “Mongolism” because of the characteristic shape of the eyes. Subsequently, the pathology was named Down syndrome.
Down syndrome is one of the chromosomal abnormalities that are occasionally diagnosed in newborns. The disease is associated with changes in the chromosome set. These children have similar health problems, common facial features and body shapes.
The reasons for the development of pathology are still unknown. Children with Down syndrome are born into both poor and rich families; both in healthy and sick parents. The average life expectancy of a person with Down syndrome is 49 years.
Types of disease
Down syndrome occurs in several variants:
- Trisomy is a complete copy of chromosome 21. This variant of the disease occurs in 94% of children. Pathology is formed at the stage of formation of gametes (sex cells of the parents). In the 21st pair there are three chromosomes instead of the required two.
- Robertsonian translocation. It occurs when the long arm of chromosome 21 is displaced and attached to other chromosomes. Occurs in only 2-3% of children with the disease. The clinical picture is mild; children with this form develop almost on a par with ordinary children. The disease can be transmitted across generations of the same family.
- The mosaic form with a triple chromosome occurs in only 2% of children with pathology. Formed in the early stages of embryo development. The disorders affect only a part of the body's cells, so clinical changes are less pronounced.
With the mosaic form, the child has few differences from healthy children. This diagnosis is difficult to confirm. A man with a mosaic form of Down syndrome is capable of reproducing offspring. In other cases, infertility is usually registered.
Is it possible to do without collecting amniotic fluid?
For those who are afraid of amniocentesis, today there is a DOT test - a study of fetal DNA that is in the mother's bloodstream. This test is designed to detect several of the most common chromosomal diseases.
If the test determines that the fetus has an abnormality, it is usually suggested to confirm this result with an invasive procedure. If the test shows normal, the result is not rechecked.
We do not offer such tests, because they are not yet carried out in Belarus. If future parents want to undergo such a study, they themselves make a decision about this and contact a private center or laboratory.
Causes and risk factors
This syndrome occurs as a result of a random genetic mutation. Risk factors for developing pathology include:
- consanguineous marriage;
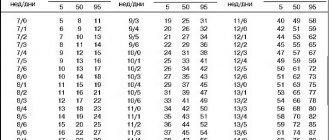
- late labor in a woman. After 35 years, the risk of having a sick child increases: 1:214. After 45 years, the probability is 1:19. For comparison: the risk of having a child with Down syndrome before the age of 35 does not exceed 1:1000;
- father's age (over 42 years).
Sick children are born with the same frequency both in third world countries and in prosperous economically developed countries. According to statistics, there is one case of birth of a child with Down syndrome in 700 births in the world. Thanks to the development of modern prenatal diagnostics, this figure has decreased to 1 in 1000.
It is impossible to become infected with Down syndrome. Its development is not affected by the area of residence, the course of pregnancy, modified foods or increased radiation. The disease is not inherited.
Termination of pregnancy after diagnosis
Undoubtedly, there is a risk of miscarriage, but not every expectant mother can intentionally kill a baby. Some women experience great fear of such children and cannot firmly understand the essence of the problem and its consequences. Only the woman decides to terminate a pregnancy; the doctor should not influence her decision in any way. The gynecologist is obliged to tell and explain: what kind of baby will be born externally, health problems, what difficulties in development and upbringing are possible.
If the tests you have completed have given a positive result, and you are not confident in your abilities, then termination of pregnancy after identifying Down syndrome is possible only up to 22 weeks. If the period is longer, it can lead to serious health problems.
How dangerous is chickenpox during pregnancy, what are the consequences for the fetus and for the mother?
How to give birth to a healthy baby? The answer to this question is here.
What are training contractions: .
Symptoms in a newborn
Immediately after the birth of a child, Down syndrome can be identified by external signs in 90% of cases. Children with trisomy are similar to each other, and they have practically no similarities with their parents. Characteristic facial features “down” and other anomalies are inherent in the extra chromosome:
- low weight - less than 3 kg and height up to 50 cm (at birth);
- flat face;
- brachycephaly (shortening of the skull);
- skin fold on the neck;
- the eyes are narrow, slanted, similar to Mongolian eyes;
- strabismus;
- flat bridge of the nose;
- Brushfield spots along the edge of the eye shell (more often found in light-eyed children), the size of the spots reaches up to 1.5 mm, in appearance they resemble beads;
- neck low, wide;
- the tongue is large and does not fit in the mouth;
- narrow, arched palate;
- mouth that won't close;
- asymmetrical ear shells, ear canals are narrowed;
- muscle weakness;
- joint hypermobility;
- shortening of fingers;
- fold under the big toe;
- transverse skin fold on the palms;
- dental anomalies;
- shortening of the nose;
- congenital heart defects;
- cataract;
- chest deformity.
As the child grows, a low level of intelligence, speech disorders, and mental disorders are revealed. Episyndrome may develop. Genetic analysis is required for an accurate diagnosis.
Ultrasound diagnostics
During pregnancy, ultrasound can be used to verify the health of the developing child.
An ultrasound to determine Down syndrome is performed at 12-14 weeks. Earlier screening is not advisable due to the high risk of diagnostic errors. Ultrasound is recommended for all pregnant women. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the less harm an abortion will cause.
When performing an ultrasound, the following signs are visible:
- absence of nasal bone (not visualized);
- TVP - thickness of the collar space - more than 3 mm.
These parameters are monitored during the first ultrasound screening. At this stage, you can terminate the pregnancy (up to 22 weeks). If a woman refuses an abortion, she is sent for a second ultrasound screening at 18-21 weeks. During this period, the condition of the fetus is assessed and possible malformations are identified:
- shortening of tubular bones;
- reduction of the iliac bones;
- reduction of the frontal lobe of the skull;
- abnormalities in the structure of the cerebellum;
- the size from the coccyx to the crown of the fetus is less than normal;
- increased echogenicity of the intestine;
- heart defects;
- one umbilical cord artery (instead of two normally).
A competent diagnosis based on ultrasound results can be made by a highly qualified doctor. The more of the listed symptoms are identified, the higher the risk of developing Down syndrome.
Ultrasound of the fetus at 12 weeks of pregnancy with Down syndrome
In addition to the enlarged nuchal region in trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), 60–70% of fetuses have no visible nasal bones. It is noticed that people with Down syndrome have a short nose. During embryogenesis, the nose in Down syndrome (nasal bones) is formed later than in fetuses with a normal karyotype. Also, from 15 to 21 weeks of pregnancy, there is an increased incidence of shortening of the nasal bones compared to the average values for this period of pregnancy in fetuses with Down syndrome.
In fetuses with Down syndrome, there is a shortening of the upper jaw, which results in smoothness of the contours of the face.
In fetuses with Down syndrome, Doppler measurements determine the pathological nature of the blood flow velocity curves in the ductus venosus. Assessment of the nature of blood flow in the ductus venosus is one of the mandatory screening parameters when performing fetal ultrasound at 12 weeks as part of prenatal screening in the first trimester. Reverse blood flow in the ductus venosus is considered pathological.
Biochemical screening
Prenatal screening - studies to identify genetic pathologies, including Down syndrome, in the fetus of pregnant women.
Examinations can be invasive or non-invasive.
Non-invasive examinations are safer for the child . Among them are biochemical screening (blood testing):
- double test - 10-14 weeks (hCG and PAPP-A);
- triple test - 16-18 weeks (hCG, AFP, estriol).
The doctor interprets the tests.
The PRISCA computer program, based on biochemical screening and ultrasound data, quite accurately calculates the degree of risk of having a child with Down syndrome and determines further pregnancy management tactics.
For any deviations from the norm, the pregnant woman is at risk. But there is no need to rush into an abortion. All tests only show the degree of risk, but cannot in any way be the basis for making a diagnosis. Every woman has the opportunity to get a more accurate picture by undergoing invasive examinations.
Invasive techniques are indicated if Down syndrome is suspected based on screening results. All of them are based on the study of tissue from the amniotic bladder. Amniocentesis, cordocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy - a geneticist gives directions for all these examinations.
- Amniocentesis is one of the safest invasive examinations. Prescribed from 10 to 21 weeks of pregnancy. Under ultrasound guidance, a puncture of the membranes is made and 10 ml of fluid is collected from the amniotic fluid. They contain all the chromosomes of the developing fetus. A detected extra chromosome will indicate Down syndrome in 99%.
- Cordocentesis is a study of umbilical cord blood. Prescribed from the 16th week. Under ultrasound guidance, a needle is inserted into the umbilical cord, where 5 ml of blood is taken. Based on the detection of three chromosomes in the 21st pair, a diagnosis of downism is made. The accuracy of the study is 98%-99%. Usually combined with amniocentesis.
- Chorionic villus sampling is an examination of placental tissue. Prescribed from 9 to 14 weeks. The puncture is done both through the abdominal wall and through the cervix using a flexible probe. If three chromosomes are found in the 21st pair in the test material, the probability of Down syndrome is 99%.
Examination using invasive methods is close to 100% accurate. Despite this, whether to have an abortion or not should be decided by parents in consultation with a geneticist. When making a decision, we must remember that abortion itself can deprive a woman of the opportunity to have children.
How else can you determine the risk of having a child with Down syndrome?
In addition to ultrasound signs, biochemical screening is used to determine the degree of risk in the first and second trimester. In this case, the blood of a pregnant woman is examined. The best results are obtained by combining ultrasonic and biochemical signs. If the combination of factors is threatening, a decision may be made to conduct invasive diagnostic techniques for Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. Invasive techniques involve obtaining particles of fetal skin or blood followed by genetic analysis. Such methods are 100% reliable. At the same time, even complete well-being during screening in the first and second trimester using ultrasound and biochemical markers cannot give an absolute guarantee of the absence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. The selection and determination of the sufficiency of diagnostic methods is carried out taking into account the age of the parents, family history and the presence of abnormalities during previous pregnancies.
We provide all types of ultrasound diagnostics:
3D and 4D ultrasound during pregnancy Fetometry data at various stages Ultrasound diagnosis of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities Assessment of the correct development of the fetus by ultrasound
Hydrotubation (echohydrotubation): examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes (ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy) Transvaginal Ovaries Uterus Mammary glands
Duplex scanning of cerebral vessels, neck vessels (duplex angioscanning of the main arteries of the head) veins of the lower extremities
Transrectal (trus): prostate gland Scrotum (testicles) Penile vessels
Appendicitis Abdominal cavity Gallbladder Stomach Intestines Bladder Soft tissues Pancreas Liver Kidneys Joints Thyroid gland Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart)
Varicose veins: Ultrasound diagnosis of varicose veins Hypertension: Ultrasound diagnosis of hypertension Thrombosis: Ultrasound diagnosis of vein thrombosis Ultrasound diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis for kidney stones with cholecystitis
Adviсe
Even if all diagnoses show signs of Down syndrome, do not rush to have an abortion, think about it! Surveys of parents who refused an abortion showed that more than 80% of married couples are glad that they left the child in the family.
Massage, exercise therapy and other procedures help the baby adapt to normal life. But the main role in this adaptation is played by the enormous, hourly and minute-by-minute emotional work of parenthood. A mother must devote her entire life to her child. If she is ready for this, the born baby will not be a punishment for her, but a joy.
Many children with mosaic Down syndrome are able to learn at school. They get along well with their peers, get an education and a specialty. Sunny child, and they are called that because of their kindness, simplicity and smile.
Read
Also:
- Dangers of fetal malposition
- Pregnancy calculator
- Signs of a tubal pregnancy disorder
- How to decipher an ultrasound during pregnancy, what is BPD