Norm of the result obtained
Upon completion of the necessary studies, clear boundaries of the norm were established, which are worth familiarizing yourself with, since medical institutions do not always give out deciphered data, and knowledge of at least an approximate CTG result is extremely necessary for women who are worried about the condition of their child.
If the patient can visit a specialist who can decipher CTG readings, it is better to take advantage of this chance: self-analysis of the test often becomes the reason for an erroneous conclusion
When independently analyzing the obtained indicators, you need to focus on the digital values of the norm:
- Basal rhythm: 110–160 beats per minute in a calm state for both the child and the mother. If the baby is active, the indicator can increase to 190.
- Accelerations: the corresponding “teeth” must appear at least twice in 15 minutes. The complete absence of accelerations indicates pathology.
- Decelerations: with proper development of the fetus, the indicator in question should not make itself known. The relative norm is considered to be insignificant depth and rare manifestation of decelerations on the cardiotocogram.
- Variability: ranges from 5 to 25 beats per minute.
- Fetal health indicator (FSI): up to one.
- Tocogram (uterine activity): a good indicator does not exceed 30 seconds.
Attempts to create a device for recording fetal heart tones - a kind of electrocardiogram for an unborn baby - led to the emergence of a cardiotocograph. Cardiotocography or CTG is the simultaneous recording of fetal heart rhythms and uterine contractions.
Table of contents:
- Fetal cardiotocography
- How is fetal CTG done?
- Rules for decoding CTG
- CTG assessment according to the Dawes-Redman criteria
- CTG assessment according to Fisher criteria
- What does CTG show?
- What to do if the CTG result is bad
- CTG (cardiotocography). Interpretation, interpretation and evaluation of CTG results in normal and pathological conditions
- Values and indicators of the CTG graph, interpretation and evaluation of results
- Basal rate (fetal heart rate)
- Low and high rhythm variability (heart rate range, oscillations)
- Accelerations and decelerations
- Norm of fetal movements per hour (why does the child not move on CTG?)
- Is it possible to see the tone of the uterus with CTG?
- What do the percentages on the CTG monitor mean?
- What do contractions (uterine contractions) look like on CTG?
- Will CTG show training (false) contractions?
- What does sinusoidal rhythm on CTG mean?
- What does STV (short-term variation) mean?
- CTG assessment by points (Fisher, Krebs scale)
- CTG assessment according to FIGO (FIGO)
- Dawes-Redman tests
- Why does the CTG say “criteria not met”?
- PSP (indicator of fetal condition) on CTG (initial and severe disturbances)
- What does a positive and negative non-stress test mean with CTG?
- What will CTG show if the child is sleeping?
- Is it possible to determine the approach of labor using CTG?
- Is it possible to determine the gender of a child using CTG?
- CTG values and indicators, interpretation and evaluation of results for various pathologies
- High, rapid fetal heart rate (tachycardia)
- Bradycardia
- Monotonous fetal heartbeat
- Signs of fetal hypoxia
- What will CTG show when the umbilical cord is entwined around the fetal neck?
- CTG for oligohydramnios
- Will CTG show leakage of amniotic fluid?
- Is CTG harmful (can it harm the mother or fetus)?
- Is it possible to buy (rent) a home CTG machine?
- Where (in which clinic, antenatal clinic) can CTG be done?
- In Moscow
- In St. Petersburg (SPb)
- In Ekaterinburg
- To Rostov-on-Don
- In Nizhniy Novgorod
- In Voronezh
- In Krasnodar
- In Novosibirsk
- In Tver
- In Volgograd
What does it mean if the doctor does not approve the CTG results?
The fact that the doctor did not like the results of cardiotocography does not mean a final determination of fetal hypoxia and pathology in principle. There are cases when young doctors without sufficient work experience incorrectly interpreted the information contained in the received graph, although everything was completely normal for the baby and his mother.
Therefore, you should not rush and immediately panic when you get a bad result. But you shouldn’t relax, as this may actually indicate a real pathology that requires immediate treatment and action on the part of medical professionals.
Most likely, if the results show alarming deviations from the norm, the doctor will ask you to go to the maternity hospital , where they will conduct regular CTG and be able to quickly react in a dangerous situation.
Informative indicators
When deciphering cardiotocography, the following rhythm indicators are taken into account:
- Basal (main) rhythm - it predominates on CTG. To evaluate it objectively, it is necessary to record for at least 20 minutes. We can say that the basal heart rate is an average value that reflects the fetal heart rate during the resting period.
- Variability (variability) is the dynamics of heart rate fluctuations relative to its average level (the difference between the main heart rate and rhythm fluctuations).
- Accelerations (acceleration of the heart rate) - this parameter is taken into account if within 10 seconds or more there are 15 beats more. On the graph they are represented by the tops facing up. As a rule, they appear during the baby’s movements, uterine contractions and functional tests. Normally, at least 2 accelerations of heart rate should occur in 10 minutes.
- Deceleration (slowing down the heart rate) - this parameter is taken into account in the same way as acceleration. On the graph these are the teeth looking down.
The duration of decelerations may vary:
- up to 30 seconds, followed by restoration of the fetal heartbeat;
- up to 60 seconds with high amplitude (up to 30–60 beats per minute);
- more than 60 seconds, with high vibration amplitude.
In addition, in conclusion there is always such a thing as signal loss. This happens when the sensors temporarily lose the sound of your baby's heartbeat. And also in the diagnostic process they talk about the reactivity index, which reflects the ability of the embryo to respond to irritating factors. In deciphering the results, the fetal reactivity index can be assigned a score ranging from 0 to 5 points.
The printout, which is handed to the pregnant woman, contains the following 8 parameters:
- Analysis time/signal loss.
- Basal heart rate.
- Accelerations.
- Decelerations.
- Variability.
- Sinusoidal rhythm/amplitude and oscillation frequency.
- STV.
- Frequency of movements.
During recording, a graph of two types of signal is displayed on the calibration tape
Condition of the expectant mother
40 obstetric weeks is the established standard. Due to various factors, labor may begin at 38 weeks or two weeks later, at 42. Such births are called urgent, i.e. they are completed on time.
Feel
As the size of the fetus increases, the volume of the uterus decreases. Before birth, the baby no longer has enough space for active movements. At this stage, the woman clearly feels the movement and tremors of the fetus and can monitor its activity.
The norm is 1–2 fetal movements per hour or 10–12 in 6 hours.
Calmness or increased activity may be signs of intrauterine hypoxia, when the umbilical cord wraps around the fetus and prevents it from breathing. The most correct decision would be to consult a doctor.
There is no need to be afraid that you might miss or miss the baby’s movements.
Panic is a very bad advisor. It is better to try to be calm and lovingly accept every movement of the baby, although sometimes it can be so expressive that it can cause discomfort or pain.
Stomach
A sagging belly of an expectant mother is one of the main signs that the baby is getting ready to be born. The fetus has already turned head down closer to the cervix and this increased pressure on the uterus.
At 40 weeks the belly is already too big. Due to the severity, problems with the musculoskeletal system may arise:
- pain in the hip joint;
- pulling and painful sensations in the lower back;
- swelling of the legs and poor circulation in them;
- softening the pelvic bones, relaxin is already working here - a hormone that is released before the birth itself;
- the appearance of tension in the muscles that support the hip joint - they stretch and prepare the body for childbirth.
Don't be afraid of these symptoms. Light physical activity, proper rest, walks, comfortable clothes and shoes will help relieve them.
In case of severe discomfort, it is better to consult a doctor.
Discharge
At 40 weeks of pregnancy, colorless discharge without an unpleasant odor is normal. The baby strives to come out, the pressure on the uterus increases, and because of this, amniotic fluid may begin to leak.
During this period, the mucous plug peels off. Its main function is to protect the fetus from harmful bacteria and infections.
The plug looks like one large clump of mucus the size of your thumb. There are visible veins or blood spots in it, and it can also come out in small parts. This process is individual for each woman.
The release of a plug is a healthy reaction of a woman’s body to the approaching birth.
You need to worry if the discharge has an unpleasant odor, a grayish or greenish tint, or if it is cheesy. This indicates the presence of infection in the woman’s body. To prevent infection of the fetus, you need to consult a doctor and begin treatment in accordance with his instructions.
Rules for decoding CTG
Of course, the evaluation and interpretation of cardiotocograms is carried out exclusively by the doctor. Self-evaluation of records is completely unacceptable, since in particularly complex cases even experienced doctors doubt the diagnosis for a long time.
As we have already mentioned, there are many evaluation criteria for deciphering CTG. I would like to note that domestic scientists - Savelyeva, Voskresensky, Gerasimovich and others - were also involved in the creation of such criteria. At the moment, two rating scales are widely used - Dawes-Redman and Fisher. Despite the variety of scales and tables, they all mainly use several basic cardiotocogram indicators:
- Fetal heart rate. Normally, this indicator fluctuates within beats per minute.
- The presence of special indicators of the curve itself - accelerations and decelerations. These are special surges and falls in the fetal cardiac activity, the presence of which can be used to predict the condition of the fetus with a high degree of probability.
- The frequency of oscillations, that is, how varied the rhythm curve is.
- The reaction of the child’s cardiac activity to movements and uterine contractions. This indicator is extremely valuable during childbirth.
- Uterine activity - the presence of contractions, their frequency, duration and strength.
The Dawes-Redman criteria are included in most CTG devices with the ability to automatically analyze cardiotocograms, that is, at the end of the recording, the cardiotocograph produces a column of numbers:
- Number of accelerations and decelerations.
- Fetal activity – fetal movements per hour.
- CTG recording time.
- The average fetal heart rate, as well as peak - its minimum and maximum values during the recording period.
- The total indicator of all these is the so-called STV – short-team variation or heart rate variability.
It is STV that is the criterion for assessing the condition of the fetus. It is important to understand that the Dawes-Redman scale is only relevant for assessing a pregnant woman, but not relevant during childbirth. Here is a gradation of variability values:
- For healthy fetuses, the boundaries of normal variability will be 6-9 ms.
- STV values of 5-3 ms are borderline and should definitely be assessed by doctors as suspicious.
- An STV of 2.6 to 3 ms indicates a high risk of fetal pathology and requires constant monitoring and fairly intensive treatment.
- An STV of less than 2.6 is assessed as preterminal, that is, the risk of fetal death in the next three days is about 80%.
- There is no upper limit of normal for STV in utero. This means that variability above 9 ms while maintaining other indicators (accelerations, basal rhythm, etc.) is normal.
Automatic evaluation of cardiotocograms necessarily takes into account the duration of pregnancy. That is why the interpretation of fetal CTG at 36 weeks of pregnancy will be slightly different from that at 28 weeks.
The Fisher scale is used for the so-called manual assessment of cardiotocograms. This scale is used during childbirth. There is a special table for evaluating each of the indicators in points: basal rhythm, the presence of accelerations and decelerations, amplitude and frequency of oscillations. The total points received are assessed as follows:
- The normal condition of the fetus is 8-10 points. Such numbers indicate a normal heart rate and adequate oxygen supply to the fetus.
- Questionable condition of the fetus – 5-7 points. This may indicate oxygen starvation of the fetus - hypoxia. Such indicators require close attention from a doctor. Additional studies and repeated CTG recordings within 24 hours are recommended.
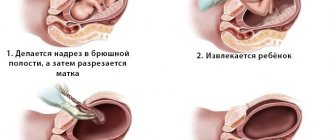
- Unsatisfactory condition of the fetus – 0-4 points. In this case, fetal hypoxia can become fatal, so active medical action is required, including urgent delivery via cesarean section or the application of a vacuum extractor.
Types of devices
Medical facilities have various options for assessing your baby's heartbeat. Most often, the doctor simply listens to the baby’s heart rhythm using an obstetric stethoscope, but if there is any doubt (or if there is evidence), it is necessary to use a special device. What types of CTG devices are there?
- CTG without automatic analysis
These outdated devices are generally quite rare in modern hospitals, but they can still be found in remote corners of our country. The main inconvenience of these devices is that the doctor must independently evaluate the fetal heartbeat graph. If the doctor has experience and masters this technique, then the effectiveness of these devices is no lower than that of new CTG devices.
- CTG with computer analysis
Modern cardiotocographs not only record the graph, but also independently process the data. The doctor only needs to read the finished result and decide on the need for treatment. This version of CTG is used most often in medicine.
The modern mobile era offers an excellent option for monitoring the baby using a special sensor attached to the skin of the abdomen and a smartphone connected to the Internet. Information about the fetal heartbeat in real time is transmitted to the web portal, processed and provided in the form of a ready-made report to the doctor. Unfortunately, online CTG is still rarely used.
Technique
The expectant mother should come to the CTG in a calm state of mind, because any worries and worries of a woman can affect the heartbeat of her baby. It is advisable to eat and go to the toilet first, because the examination lasts quite a long time - from half an hour to an hour, and sometimes more.
You should turn off your cell phone and sit comfortably in a position that will allow you to spend the next half hour in comfort. You can sit down, lie down on the couch, take a semi-recumbent position; in some cases, CTG can be performed even while standing, the main thing is that the expectant mother is comfortable.
A wide belt is put on top of it - a tensimetric sensor, which will determine, based on minor fluctuations in the volume of the expectant mother's abdomen, when a uterine contraction occurred or the baby moved. After this, the program is turned on and the study begins.
At this stage, a pregnant woman may have two questions: what do the percentages on the fetal monitor mean and what do the sounds heard during CTG indicate. Let us help you figure this out:
- Sounds during examination. The sound of the baby’s heartbeat, already familiar to the expectant mother, needs no explanation. Previously, ultrasound specialists probably already allowed the woman to listen to the beating of a small heart. During CTG, a woman, if the device is equipped with a speaker, will hear it constantly. Suddenly, the woman may hear a prolonged loud sound, similar to interference. This is how a child's movements can be heard. If the device suddenly starts beeping, this indicates a loss of signal (the baby has turned and moved significantly away from the ultrasonic sensor, the signal has been disrupted).
- Percentages on the screen. Percentages indicate the contractile activity of the uterus. The more actively the main female reproductive organ contracts, the more reasons the doctor has to hospitalize the woman. If the values approach 80-100%, we are talking about the beginning of contractions before childbirth. Indicators in the range of 20-50% should not frighten a woman - it is definitely too early for her to give birth.
How contractions appear on CTG
This study will definitely indicate the presence of contractions , since normally the uterus should respond to the active motor activity of the baby with its spasms. In addition, the uterus has the ability to spontaneously contract. On CTG, in response to contractions, a decrease in the number of baby’s heartbeats and deceleration will be visible, which occurs in rare cases.
The second curve (hysterogram) reflects the increase in the force of contraction of the myometrium (muscular layer of the uterus) during contractions. The higher it is, the stronger the contractions. Some women in labor do not feel contractions; CTG helps determine their strength and frequency.
Evaluation points
Doctors use this scale to evaluate CTG results. The essence of the procedure is that each indicator is awarded from 0 to 2 points. All values are added up and determine the information content of this diagnostic method, as well as the presence or absence of pathologies.
- 1-5 points – the condition of the fetus in the uterus is poor, it experiences a pronounced lack of oxygen.
- 6-7 points – mild hypoxia, borderline state.
- 8-10 points – the child’s body does not experience oxygen starvation and is in excellent condition.
Childbirth at 41 weeks: why there are no signs
Of course, if the 41st week comes to an end and labor does not begin, almost any pregnant woman will begin to get nervous and look for the reasons for what is happening. However, you need to understand that this is not yet the deadline and if the baby is born now, the pregnancy will not be considered post-term.
Even if you don’t notice any signs of impending labor, this is not yet a reason to worry: in some cases they are simply very mild, and in others they appear all together a few days before the birth. Rest assured, you will definitely not miss the onset of labor, as this will be indicated by intensifying contractions, occurring 5-6 times an hour. You can go to the maternity hospital when the interval between them is 7-10 minutes; However, this recommendation is only valid for those cases when not all the water has broken yet.
In general, the 41st week is practically no different from the 39th or 40th, except that the woman’s impatience increases, and with it comes panic due to the unknown of what is happening. Try to be positive, imagining how very soon you will see your child’s face, walk with a stroller and sing lullabies to him. Positive emotions help you cope with any difficulties.
Pregnancy Pregnancy calendar by trimester
What can a fetal CTG show during pregnancy?
Fetal movement (actography) is an equally important component when conducting an ultrasound examination. Often, a particular type of activity of the baby worries the expectant mother, however, some changes in actography during CTG with increasing gestational age are completely normal.
It is worth remembering that the fetus is in motion throughout the entire period of pregnancy, with the only exception being periods of dreaming. The baby's activity gradually increases, so at 32, 33, 34 and 35 weeks approximately 45–70 movements per hour can be observed. And in the period from 36 to 37 weeks, the norm is 60–85 movements per 1 hour.
Approaching his birthday, the child increases in size, which prevents him from leading an active lifestyle. By 39–40 weeks, the baby becomes more peaceful and serene.
As we have already found out, cardiotocography evaluates the heart rate of the unborn baby, its motor activity and uterine contractility. Based on this, we list the conditions that can be tracked and suspected using CTG.
- Fetal hypoxia – oxygen starvation. This situation occurs for a variety of reasons: placental insufficiency, increased uterine tone, inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity, high blood pressure and diseases of the maternal cardiovascular system, and much more. Cardiotocography will not show the cause of hypoxia, but will only establish the fact of its presence.
- Fetal heart rate abnormalities. For example, a constant increase in the fetal heart rate - tachycardia - may indicate fetal heart pathology, fetal anemia, Rh conflict and other alarming conditions.
- Threatening or beginning premature labor. In this case, recording uterine activity comes to the rescue. Frequent and regular contractions before 37 weeks of pregnancy may indicate a threat of premature birth.
- Anomalies of labor. CTG shows irregular, rare or weak contractions during labor, as well as the reaction of the labor process to the administration of drugs - oxytocin or prostaglandins.
This device has the following sensors:
- Ultrasound, which detects the movements of the fetal heart valves (cardiogram);
- Tensometric, determining the tone of the uterus (tocogram);
- In addition, modern cardiac monitors are equipped with a remote control with a button that must be pressed at the moment the fetus moves. This allows you to assess the nature of the baby’s movements (actogram).
example of a CTG tape: above - fetal heartbeat, below - uterine tone values
Cardiotocography (CTG) is a diagnostic method for assessing the condition of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth through the frequency of its heartbeat and its fluctuations at rest, activity, during contractions of the uterine muscles, and exposure to external stimuli.
CTG is prescribed, according to the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, starting from the 28th week of pregnancy.
In fact, doctors rarely prescribe this examination before the 32nd week, believing that until this time CTG is not very informative. In total, during the third trimester, during a normal pregnancy, the woman will have to undergo two CTG.
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe a CTG procedure as often as he sees fit, even daily.
Indications for additional monitoring of fetal heart rate through CTG analysis are:
- unfavorable result of previous CTG;
- suspected pathology of fetal development;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- a decrease in the baby’s physical activity noted by the woman;
- threat of premature birth;
- post-term pregnancy;
- the presence of diseases in a pregnant woman such as: diabetes, hypertension, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, etc.;
- late toxicosis;
- Rh conflict between the blood of the expectant mother and the fetus;
- early aging of the placenta noted on ultrasound;
- pathological course of previous pregnancies and childbirths;
- entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord detected during ultrasound.
But the information obtained with the help of CTG allows us to identify and reduce the risk of intrauterine suffering in the baby.
CTG is an auxiliary research method and is not mandatory. If the doctor believes that the pregnancy is proceeding completely normally, then he may not refer the expectant mother for CTG. But if a woman has any abnormalities, then cardiotocography is done regularly.
CTG is almost always prescribed for the following conditions:
- suspicion of intrauterine growth retardation;
- pathology of the placenta identified by ultrasound;
- threat of premature birth;
- scar on the uterus;
- gestosis;
- concomitant chronic diseases, for example, hypertension or diabetes;
- post-term pregnancy;
- change in the amount of amniotic fluid;
- decreased fetal activity;
- umbilical cord entanglement detected during ultrasound;
- abnormalities in the previous CTG.
The latter receives data on fetal heartbeats and uterine contractions of a pregnant woman, processes them and displays the result on tape in the form of graphs. How to prepare for CTG during pregnancy?
Requirements for the patient: remain calm while the cardiotocograph is operating, i.e. for approximately minutes. The medical worker and the equipment will do the rest.
First, the midwife or doctor performing the procedure uses a regular ear stethoscope to determine the area on the woman's abdomen in which the fetal heartbeat can be heard most clearly.
Based on the cardiac impulse signals, a graph is drawn showing changes in heart rate throughout the procedure.
At the same time, on the woman’s abdominal wall, just below the navel, in the area of the fundus of the uterus, a pressure sensor (strain gauge) is fixed, which transmits data on the tone of the myometrium (uterine muscles).
The position of the woman during fetal CTG: usually reclining, sitting or lying on her side in a horizontal position, as desired.
Additional vibrations are reflected in the recording of the curve, and the device produces false results.
If not a single movement is recorded, you will have to undergo the procedure another day. But this rarely happens, because the baby’s intrauterine sleep is very short and tremors will still be recorded at the beginning of the procedure or at the end.
In the normal course of pregnancy, they may not be carried out even once. If indicated, they can do it at least every day (in a hospital setting).
For the results of the study to be reliable, its duration must be minutes.
This procedure does not require special preparation. However, given the fact that it lasts quite a long time, you need to tune in to it, take a light snack with you: an apple, chocolate or a piece of bread, as well as a blanket or pillow. Do not forget to visit the toilet before going for a CTG - otherwise the examination time will seem like an eternity, and its results may be unreliable.
Usually, the study time is simply extended, waiting for the natural activity of the fetus. All attempts to wake the child artificially, for example, patting the stomach, are unacceptable.
Heart rate examination is necessary both in the first (cervical opening) and in the second (pushing) stages of labor. This is necessary in order to prevent acute intrauterine hypoxia, which threatens the life of the fetus and is an indication for emergency caesarean section.
It is for this reason that CTG recording must begin at the first signs of labor. During normal labor, it is enough to register a CTG every hour.
This study also shows:
- After the rupture of amniotic fluid;
- When performing epidural anesthesia during childbirth (after administration of the anesthetic).
Permanent CTG recording is necessary for conditions such as:
- Loss of umbilical cord loops;
example of indication for multiple pregnancy
Bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- Pelvic position of the fetus;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Two- and three-fold entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck;
- Signs of gestosis;
- Diabetes;
- Yellow or green amniotic fluid;
- Hemolytic disease of the fetus;
- Intrauterine growth retardation;
- Premature birth;
- Scar on the uterus after previous operations;
- With weak or excessively strong labor.
- When inducing labor with drugs, such as Oxytocin or prostaglandins.
However, it should be remembered that CTG during pregnancy and childbirth is not the same thing. Therefore, the interpretation of the results must be approached differently. The natural question is: why does this happen?
Research methodology
Most often, the examination is carried out at 32 - 34 weeks of pregnancy. CTG is performed in the pregnant woman's supine position with a small bolster under her right side (the optimal position is a slight turn to the left side). It is possible to perform CTG in a position lying on your side, or sitting, leaning back in a chair.
- First, the doctor uses a stethoscope to find the point on the abdomen where the baby's heart can best be heard.
- An ultrasound probe is placed on this site, and a probe is placed on the fundus of the uterus to assess muscle tone.
- To notice the baby's movements, the woman is given a special device with a button that she will press when she feels intrauterine movements.
- Recording time is 40-60 minutes.
When CTG is done, the study is carried out using sensors with a frequency of ultrasonic waves of 1.5-2 MHz, which is absolutely safe for the fetus even with prolonged exposure. Any modern device has the ability to assess the vital functions of two fetuses at the same time, which is used in women with twins.
Fetal health indicators
By FIGO
This value is calculated automatically. The following PSP options are distinguished:
- Less than 1 is normal. However, if the CTG value is from 0.8 to 1.0 during pregnancy, it is recommended to repeat it.
- From 1 to 2 – initial changes in the general condition of the fetus. Outpatient treatment and control cardiotocography after one week are recommended.
- From 2 to 3 – the child’s condition is serious. Urgent hospitalization and immediate initiation of treatment are required.
- More than 3 – the condition is extremely serious. The question of emergency management of childbirth is raised.
Evaluation of fetal cardiotocography
CTG results may not always be accurate - for this, certain conditions must be met, and the first of them is to conduct the study only during those hours when the child is most active (usually from 9 to 14 hours and from 19 to 24 hours).
“Bad” CTG: reasons why distorted research results may be obtained
- Carrying out CTG on an empty stomach or after a heavy lunch (it is better to carry out the procedure a couple of hours after breakfast or a light dinner);
- Before the procedure, you should not use certain drugs that distort CTG readings: glucose, magnesium, sedatives;
- interpretation of cardiotocography will be unreliable if the study is carried out under stress or after physical activity (for example, immediately after cleaning or walking up the stairs);
- You should also not conduct research after drinking alcohol or smoking;
- in a pregnant woman with excess body weight, CTG interpretation can also give distorted results (due to the fat layer, which prevents the sensor from “hearing” the baby’s heartbeat);
- sometimes with fetal CTG, the decoding gives the result of a heartbeat of 65-80 beats per minute; There is no need to panic: these are indicators of the woman’s heart rate, not the fetus, due to incorrect application of the sensor (just apply the sensor correctly and conduct the study again).
How to get the results of a “good” CTG:
- get some sleep and have a snack;
- After eating, move around, but before the test, rest so that your heart rate is restored;
- Go to the toilet in advance to feel calm during the 30 minutes of the study;
- do not smoke at least 2 hours before the procedure.
Is CTG a safe research method?
Before undergoing this procedure, many women are concerned with the question of whether CTG is harmless to the health of both the mother and the baby.
There are no contraindications for CTG; the method of its analysis is absolutely harmless to health. Thanks to this, such research can be carried out as often as the analysis requires. Even if he requires it every day.
CTG is used during pregnancy and childbirth. This allows you to monitor the well-being of the fetus during the birth process and monitor the contractions of the uterus. CTG studies help to carry out therapeutic measures right during childbirth. And often it is the CTG readings that are an indicator for changing the management of labor.
Cardiotocography analysis during childbirth is recommended for premature birth or delayed labor, fetal position abnormalities, and hypoxia.
Video about decelerations of their types and reasons for their occurrence
CTG and diet
For a young mother, it is extremely important to follow a diet throughout the entire period of bearing the baby. A balanced, proper diet without fried, spicy, smoked, or over-salted foods is a source of minerals and vitamins responsible for the growth and development of the baby
Often, when the mother is hungry, the child is overly active or, conversely, is in a state of sleep. Therefore, before the procedure, women are advised to have a light meal. You must have breakfast or lunch, depending on the time for which cardiotocography is scheduled. It is advisable to eat a moderate amount of food without overeating.
You will learn more about why this method of examining pregnant women, successfully used in obstetrics for more than a hundred years, is needed, and what it determines, as well as how to interpret its results, from the video: