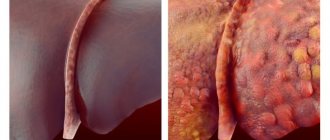
What does eczema look like?
The name of the disease refers to the Greek term ekzeo - to boil. This most accurately describes the external and internal nature of the health condition when symptoms are detected.
Acute signs of the disease create a feeling that the skin is “boiling”, this is expressed as follows:
- unbearable itching occurs;
- burning;
- the affected area becomes very red;
- small bubbles filled with liquid (serous exudate) appear in the lesion;
- locally, the skin undergoes pathomorphological changes: it thickens, cracks, becomes very dry, and flakes;
- papules are grouped and slightly resemble bubbles of boiling liquid, which quickly burst, leaving deep wounds - wells or pinpoint erosions;
- the disease proceeds in waves, so over time one can observe old “wells” and fresh vesicles in one focus;
- eczema is a disease characterized by long-term presence and frequent seasonal relapses;
- the disease appears in both children and adults;
- General health affects the likelihood of exacerbation and the frequency of recurrence.
The main difference between eczema and classical forms of allergic diseases, such as urticaria, is that the rash blisters contain serous fluid, and after they heal, the epithelium changes according to the principle of hyperkeratosis, while urticaria disappear without leaving any traces and contain virtually no fluid.
Which doctor should I contact?
Skin diseases are treated by a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist. To determine and eliminate the causes of eczema, a dermatologist may prescribe a consultation:
- phlebologist;
- endocrinologist;
- allergist;
- neurologist.
Causes of the disease
In modern medicine, eczema is classified as a group of diseases with polyethylological factors, that is, those ailments that arise due to a combination of unfavorable circumstances.
- Heredity. It is known that the risk of developing skin pathology is about 60% if both parents have a history of this disease, as well as bronchial asthma. If such a diagnosis is assigned to one of the parents, then the risk of eczema in the child will be from 20 to 30% probability.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. Nutritional disorders, as well as insufficient functioning of the biliary tract and liver, have a great influence on the development of skin pathology, manifested by the symptoms of eczema.
- Neurological disorders. Eczema can occur as a result of damage to peripheral nerve endings and vegetative-vascular disorder.
- Injuries. The disease can develop due to serious damage to the epidermis, for example, after a burn.
- Chemical substances. Statistically, people whose professional activities in any way involve interaction with various reagents and chemical compounds have a high risk of contracting this disease. Thus, eczema develops among employees of chemical laboratories, pharmacists, and also when working with pesticides and fertilizers.
- Metabolic disorders as a consequence of pathology of the endocrine system.
The pathogenesis of eczema involves disorders of an immunological nature. At the same time, the mechanism of development of the disease is somewhat different from the allergic and autoimmune processes we are accustomed to understanding.
Thus, in the chronic course of the disease, a shift in the ratio of immune cells is distinguished in the patient’s blood picture: a decrease in the number of T-lymphocytes and, conversely, an increase in the number of B-lymphocytes, as well as a violation of the ratio of immunoglobulins. Let us recall that in typical allergic reactions there is a significant increase in Ig E, which indicates the presence of antibodies to a certain factor.
With eczema, immunoglobulins G (markers of the chronic course of the process) also increase, and Ig M (determining the acute phase of the reaction) is reduced. Such indicators indicate precisely the atypical functioning of the body’s defense system and the ability to form pathological immunocomplexes, which make the body vulnerable to external infections and damage its own tissues.
Main types and forms of the disease
We will tell you about the most common forms of the disease, but do not forget that a rare disease occurs as described in medical textbooks, so if you have doubts, it is better to consult a doctor to reliably establish a diagnosis.
- Idiopathic (true eczema). Its main signs are: acute redness of the skin and significant swelling (erythema), small vesicles with liquid, and a wave-like flow.
- Diathesis. This is the name given to eczema, which develops in children at an early age. It can be provoked by both diaper dermatitis and skin infection by microbes. Often proceeds according to the principle of an allergic reaction. May affect the face and head, gluteal folds, and groin.
- Microbial eczema is formed when a damaged area of skin is infected with streptococci and staphylococci. Such inflammation can occur even if there are microcracks in the skin.
- Seborrheic. Selects areas of the body rich in sebaceous glands: face, scalp, space behind the ears, chest. In this form, the skin erythema is hidden under yellow, greasy scales.
- Dyshidrotic. It occurs on the arms and legs, and selects areas with a denser surface structure: palms, soles of the feet. Looks like deep small vesicles that tend to merge. Over time, the blisters burst and form ulcers, after healing of which the affected skin becomes keratinized, becomes drier and is susceptible to cracks.
Using natural homemade ointments
To treat hand skin lesions, you can prepare home remedies using natural ingredients.
From millet
Wash the cereal thoroughly several times and air dry. Using a blender or coffee grinder, grind it into flour. Melt pork or interior fat in a water bath. To 4 tbsp. fat add 4 tbsp. millet flour and mix thoroughly. The ointment must be applied 3 times a day to the skin of the hands. Use the remedy until complete recovery.
From fir oil
This product must be added to melted animal fat. Pork, chicken, badger or goose lard is suitable as a base. The ratio of ingredients is 1 part fir oil, 2 parts fat melted in a water bath. The ointment must be applied 2 times a day. Duration of therapy is up to 1 month.
Out of tar
Eczema on the hands, which can be cured forever with course procedures, quickly disappears when using ointment made from sea buckthorn berries and tar. In a blender, mix 70 g of fruits and 2 tbsp. birch tar.
Apply the ointment to the skin of your hands and leave for 30 minutes. After this, rinse off the product with warm water. The procedure must be repeated daily for 10 days. Then a break is taken for 1 month, and the course is repeated 8 more times.
From sour cream and vitriol
To prepare the ointment, mix thoroughly:
- 0.5 tsp sour cream;
- 2 g vitriol.
Every day before going to bed, apply the product to the skin of your hands. In the morning, rinse off the product with warm water and apply moisturizer. This ointment is suitable for treating all types of eczema.
From birch raw materials
An ointment based on birch leaves is suitable for any eczema. They must be washed in cold water and air dried. Place butter on a baking sheet in a 1 cm layer, then a thick layer of birch leaves. In total, you need to collect 3 layers of oil and 2 layers of leaves.
Cover the baking sheet with foil and place in the oven for 2 hours at minimum power. Then keep the mixture at room temperature for 2 hours. Then repeat heating and cooling again. Apply the prepared ointment to the skin 2 times a day for 1 month.
The fastest way to cure eczema
It is not for nothing that we paid such detailed attention to covering the pathogenesis and causes of the disease; this is necessary in order to clearly illustrate that eczema is not just an itchy wound and cracking skin - but a whole complex of disorders within the human body.
And where the disorder is systemic in nature, there is always a chronic form, associated pathologies and, accordingly, complex treatment.
Conventionally, the fastest way to cope with the disease and put it into remission includes the following recommendations:
- See a doctor as soon as possible.
- Do not experiment with self-medication, even if advice is given to you by a person who, according to him, has successfully overcome the symptoms.
- Prepare yourself for a long and persistent struggle.
- Follow the recommendations of your treating specialist.
- Follow a specially prescribed gentle diet.
- Conduct a full examination to identify hidden diseases.
- Treat concomitant pathologies as much as possible.
Since the disease is extremely complex and persistent, today there is no one magic remedy that could cure it. Working to normalize processes in the skin is, first of all, working on yourself, analyzing the shortcomings of your lifestyle and the dangers of your usual environment. Treatment of eczema depends not only on the prescription of the attending physician, but also on the patient himself.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease and its type, you must pass:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- skin applications to detect allergens;
- thorough visual inspection of the affected areas;
- bacteriological analysis.
Scraping to identify abnormalities in the epidermis of the skin
Based on the research results, a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed.
How is eczema treated: local treatments
In medical practice, hormonal drugs based on hydrocortisone are used to combat eczema. Depending on the form of the disease and complications, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Lokoid;
- Flucinar;
- Hydrocortisone ointment;
- Advantan;
- Akriderm GK;
- Triderm;
- Elokom;
- Belosalik.
Hormonal ointments are not recommended for long-term use, as they contribute to the development of systemic disorders, as well as the formation of trophic ulcers. Therefore, only a doctor prescribes a course of medications. In severe cases, therapy can be supplemented with a course of prednisolone in tablets or injections.
In an uncomplicated form of the disease, in order to eliminate dryness and speed up skin recovery, it is advisable to use non-hormonal ointments and creams:
- Bepanten;
- La Cree;
- Dermalex Atopic;
- Radevit;
- Skin Cap;
- Eplan.
These products are acceptable for use in the initial stages of the disease in children, are safe and have good reviews.
Recommendations
During treatment, you must strictly adhere to medical recommendations. You cannot independently adjust the frequency of using ointments and taking medications. Even when applying an ointment, the effect may be delayed - it is necessary to wait several days to adequately assess the therapeutic effect. Attempts to use ointments, especially those containing hormones, more often than prescribed by the doctor can lead to complications in the form of toxic systemic effects of these drugs.
During an exacerbation of eczema, you should not take water procedures: shower, bath. Before applying the ointment, clean the skin by blotting the eczematous lesions with a clean bandage; you can moisten it with a solution of tannin or furatsilin. Treatment of eczema lesions with aggressive antiseptics (alcohol, miramistin, potassium permanganate) is prohibited - it can cause skin burns.
Patients with eczema should not expose their skin to cold, heat, or strong wind. If eczema is localized on the face, you can cover your face with a mask when going outside.
Personal hygiene and adherence to a hypoallergenic diet can significantly reduce the frequency of exacerbations of eczema. Hypoallergenic, unscented soaps and detergents should be used for hygiene procedures.
Antihistamines
Allergy medications are prescribed for oral administration in the form of tablets or drops. In severe forms of the disease and large areas of damage, it is permissible to administer drugs by injection.
For eczema, antiallergic drugs of the second and third generation are prescribed, since they have a less pronounced hypnotic effect and do not have a pronounced effect on the activity of the central nervous system.
These may be the following drugs:
- Tavegil;
- Zodac/Zyrtec;
- Loratadine;
- Cetrin;
- Telfast;
- Erius;
- Allegra;
- Claritin.
Antihistamines can reduce vascular permeability, thereby preventing increased tissue swelling and helping to reduce itching.
Medicinal plants for external use
Eczema on the hands, which many herbs can help cure forever, requires preventive measures. Some plants are suitable for this.
Swamp duckweed
20 tsp fresh duckweed pour 1 liter of vodka. Leave the product in a dark place for 2 weeks. Take 15 drops. every day for 1 year.
Kalanchoe juice
This plant allows you to relieve the first signs of eczema on your hands. To use, Kalanchoe juice is squeezed out and slightly heated. It must be applied up to 6 times a day. The duration of the course is 3 months.
Coltsfoot
Chop fresh herbs and boil in milk for 5 minutes. Lubricate problem areas with the resulting mixture overnight and wrap with film. Duration of use: 10 days.
Valerian officinalis
This plant has a calming effect. The tincture from it must be taken orally, 30 drops. 3 times a day for 7 days.
Birch leaves and buds
Birch raw materials are best used in the form of hand baths. To prepare them, use 100 g of buds and 300 g of leaves. The raw material is poured with 500 ml of water and boiled for 10 minutes. Then let the mixture cool and put your hands in it for 20 minutes. After the procedure, it is necessary to air dry the skin. It is recommended to repeat such baths 3 times a day for 7 days.
Adjuvant therapy
Additional treatment is those activities that not only speed up the moment of recovery, but are also necessary to combat complications (the addition of fungi, viruses, microbes).
They are no less important than the main therapy:
- Immunocorrection - as prescribed by a doctor, measures are taken to normalize the functioning of the immune system. For this purpose, both special medications and a set of general health measures can be used. For persistent forms of the disease, plasmapheresis is acceptable.
- Vitamin therapy. It is part of immunocorrective treatment. Vitamins A, E, as well as vitamin complexes that have a general strengthening effect are used.
- Antibiotics and antimicrobial ointments are prescribed only if microbial flora is present. They should not be used for prevention, since immunity is reduced, and conditional pathogens may have time to develop resistance, which in the future will require the use of more powerful drugs of this group.
- Antifungal ointments are also prescribed if the presence of fungi in the affected area is clinically confirmed. A frequent companion to eczema is candidiasis and pityriasis.
- Physiotherapy: microcurrent effects, magnetic, UHF, electrophoresis.
- Strengthening the nervous system : often symptoms such as itching and pain contribute to increased irritability and the development of insomnia. Therefore, the use of over-the-counter sedatives is justified: tincture of valerian or motherwort, Novo-Passit, Afobazol.
- External anticoagulants - ointments and gels: heparin ointment, troxerutin, lyoton, etc. They are actively used for eczema of the lower leg to prevent the development of phlebitis.
- Spa treatment has a calming effect on the nervous system and helps normalize immune processes in the body. Recommended for prolonging the remission phase and almost always gives good results.
- A gentle diet. First of all, it allows you to regulate the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and exclude the penetration of food allergens, which aggravate the disease.
- Phytotherapy. The use of lotions and baths with infusions of medicinal herbs helps to significantly improve the condition of the skin and speed up regeneration. It is carried out in consultation with the attending physician (to avoid the development of allergic reactions and side effects), and is effective in treating children. For this purpose, the use of decoctions and infusions of chamomile, oak bark, bay leaf, and yarrow is indicated.
Dry and weeping eczema: how to treat
Treatment of different forms of the disease requires a different approach. Dry eczema is accompanied by pronounced dryness of the skin, which leads to the appearance of cracks in the lesion and infection of wounds. Therefore, the main emphasis in the treatment of this symptom is on maximum hydration and antibacterial treatment.
More often, this form of the disease occurs due to fungal infection, so the use of antifungal drugs is possible.
Weeping eczema develops due to a large number of serous papules, which, when opened, pour out their contents. The resulting wounds can be quite deep, and since the local protective reaction of the skin in this area is significantly impaired, the risk of contamination with microbes is very high.
Wet eczema in the acute phase of the disease does not heal for a long time, and the appearance of new vesicles aggravates the skin condition and increases the area of damage to the body.
Therefore, the treatment of this form is based on the following goals:
- reduce exudation - this requires the use of antihistamines, which reduce the release of plasma into the tissue;
- erosive formations in the granulation phase;
- prevent secondary infection.
For this purpose, all the methods described above can be used in various combinations. It is noteworthy that simultaneously a person can have both forms of the disease in different areas on the body.
Weeping eczema on the legs requires the use of drugs that strengthen venous blood flow. We will talk about the treatment features in more detail in one of the following publications.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are not the main ones - they are used as concomitant treatment to speed up recovery. Their main task is to reduce the risk of relapse of the disease. Physiotherapeutic techniques are quite varied.
Thalassotherapy. Salt baths, mud and applying algae to the skin - all this helps reduce inflammation on the skin and dries out the skin. The greatest effectiveness is observed with weeping eczema. The average course of thalassotherapy is 7-8 days.
Laser therapy. Irradiation of the skin with laser radiation stimulates the growth of healthy skin, reduces the frequency of exacerbations, and increases the duration of remission. The course requires from 7 to 14 procedures. Suitable for treating eczema on the face.
Therapeutic electrophoresis. Exposure to electric current with clearly defined parameters accelerates the absorption of medicinal substances. Electrophoresis with antihistamines accelerates the onset of the therapeutic effect and significantly prolongs it.
Magnetotherapy. Magnetic fields of a certain configuration, when exposed to foci of eczematous rashes, reduce the severity of skin itching and facilitate the healing of skin defects. Can be used for both weeping and dry eczema. Varicose eczema is a relative contraindication - you first need to find out if there are any blood clots in the veins that can break off.
UV therapy. Irradiation of the skin with ultraviolet rays should be carried out during a period of stable remission. The penetration depth of UV rays is 1 mm, which is sufficient to provide a local immunostimulating effect. Phototherapy is prescribed only after trial irradiation of a small area of skin to avoid the occurrence of photodermatosis.
Cryotherapy. Cooling skin areas with liquid nitrogen helps improve cell division, which leads to faster skin healing. Cryotherapy is prescribed in short courses of 4-7 procedures (1 procedure per day).
The use of physiotherapy is not recommended during an exacerbation - it can aggravate the course of the disease.
A set of physiotherapeutic procedures is selected individually for each patient by a physiotherapist. All concomitant diseases must be taken into account, and possible contraindications to each method must be identified. Do not think that physiotherapy is completely harmless to the body.