Medical Consultant ENT Diseases Pharyngitis in adults: symptoms, photos, effective treatment
Pharyngitis in adults is not always the result of infection and is not necessarily transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. External irritating factors play a major role in the occurrence, especially of the chronic form.
Inattention to one's own health during pharyngitis can result in quite serious problems that require long-term therapy. In order for the treatment of pharyngitis in adults to be effective, you need to know what it is, the symptoms and cause of sore throat.
- Acute and chronic pharyngitis, photo
Is pharyngitis dangerous in adults?
- Pharyngitis during pregnancy
Pharyngitis: what is it and what are its causes?
Pharyngitis is an inflammatory process in the pharynx, occurring acutely or chronically. Local signs of pharyngitis are detected when examining the posterior wall of the pharynx.
This is a rather unpleasant disease, the main symptom of which is a constant sore throat and the desire to cough, which can cause insomnia and discomfort when being in society (work, lectures in educational institutions, watching a movie in a cinema, etc.).
However, this is not the only annoying thing about pharyngitis. The disease can cause quite serious complications that spread to other organs and systems.
Pharyngitis is often associated with seasonal colds (acute respiratory infections, flu), but not only pathogenic microorganisms can cause this disease.
The main causes of pharyngitis in adults:
- infection - bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci), viruses (influenza, adenovirus), Candida fungus, chlamydia;
- childhood infections (in the absence of specific immunity in an adult) - whooping cough, scarlet fever, measles;
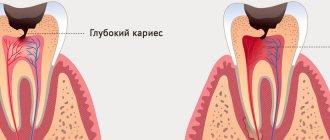
- inflammatory foci in adjacent tissues - sinusitis, caries, rhinitis (pharyngitis is provoked by frequent use of vasoconstrictor drops), tonsillitis and deviated nasal septum (difficulty in nasal breathing);
- temperature changes - general hypothermia, eating very cold/hot food;
- unhealthy habits - alcohol, alcohol;
- external influence - voice overexertion (singers, lecturers), inhalation of dust, smoky air, chemicals;
- Gastrointestinal diseases - hiatal hernia, reflux esophagitis;
- endocrine abnormalities - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, menopause;
- tonsillectomy - removal of the tonsils leads to the unhindered proliferation of bacteria on the pharyngeal mucosa;
- decreased immunity due to chronic infections, stress, vitamin deficiency.
Causes
The reasons why chronic pharyngitis occurs can be very different, namely:
- systematic damage to the pharynx;
- abuse of salty foods;
- consumption of hot food and alcohol;
- nasal congestion;
- chronic oral diseases and many others.
Pharyngitis is provoked by viruses, the causes can be bacterial and fungal, and the disease also develops against the background of a cold. That is why it is necessary to promptly diagnose and treat existing viral diseases in order to prevent the occurrence of complications in the form of acute pharyngitis. Depending on the cause, you can select the appropriate treatment method, so it is important to know how to cure chronic pharyngitis forever.
Acute and chronic pharyngitis, photo
Chronic and acute form, photo
There are acute and chronic forms of the pharynx disease. Acute pharyngitis in adults occurs several hours or days after exposure to a provoking factor (hypothermia, inhalation of irritants, etc.).
At the same time, bright signs of inflammation are found on the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx: redness, swelling, the appearance of lumpiness, plaque. The acute course has more pronounced symptoms and, with proper treatment, is easily eliminated without aggravating consequences (see photo).
With chronic pharyngitis, periodic exacerbations are diagnosed. This form is a consequence of improper treatment of acute pharyngitis or the result of prolonged exposure to irritants.
At the same time, more changes occur in the pharyngeal mucosa: atrophy, formation of granulomas. It is with chronic pharyngitis that complications are most often observed.
Is pharyngitis dangerous in adults?
Pharyngitis is not as harmless a disease as most people think. The disease is fraught with:
- chronicity of the process;
- conjunctivitis, otitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia;
- peritonsillar abscess (with streptococcal infection);
- rheumatism of the joints;
- glomerulornephritis.
With proper and timely treatment of the disease, complications are practically eliminated.
Complications of pharyngitis
A complication of the acute form of the disease is chronic inflammation of the pharynx, which over time leads to the development of a number of serious pathologies.
Streptococcal pharyngitis is complicated by the formation of a peritonsillar abscess, manifested by unilateral symptoms: soft tissue swelling, pain and erythema.
With pharyngitis, the infection spreads in a descending manner, which leads to the development of inflammation of the larynx, trachea and bronchi. In addition to laryngitis, tracheitis and bronchitis, articular rheumatism occurs in patients with prolonged streptococcal inflammation of the pharynx.
The main complication of pharyngitis is a general decrease in quality of life. For people whose professional activities involve the need to speak, this disease becomes a real problem. Long-term inflammation leads to a change in voice timbre.
- Local complications of pharyngitis include: sore throat, abscesses, otitis, phlegmon, inflammation of the salivary glands, cervical lymphadenitis.
- Common complications of pharyngitis: scarlet fever, rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, sepsis, false croup in children, shock, respiratory arrest.
Symptoms of pharyngitis in adults, photos
Photo of pharyngitis symptoms
With acute pharyngitis, a person notices the sudden appearance of a strong sore throat, sharp pain when swallowing or talking, and a painful cough without sputum discharge. The more a person coughs, the more irritated the inflamed mucous membrane becomes.
A characteristic symptom of pharyngitis in adults is “empty throat”: a person constantly makes swallowing movements due to the accumulation of mucus in the throat. Sore throat with pharyngitis can radiate to the ear, and there is a feeling of stuffiness in one/both ears.
In this case, a reddish tuberosity and small ulcerations appear on the posterior pharyngeal wall, which is easy to notice independently when examining the throat in a mirror.
symptoms of chronic pharyngitis, photos in adults
When local symptoms appear, general health often begins to suffer: the temperature rises to 37.5ºC (sometimes higher), and malaise appears. Submandibular lymph nodes often become enlarged.
In case of an infectious lesion, specific symptoms are recorded: difficulty breathing, skin rashes, intoxication.
The symptoms of chronic pharyngitis during exacerbations exactly repeat the clinical picture of the acute process. During the period of remission, dryness in the throat (feeling of a lump in the throat) and almost constant coughing come to the fore.
The general health of the chronic inflammation in the pharynx practically does not suffer.
Pharyngitis during pregnancy
Since the female body is more vulnerable during gestation, pharyngitis during this period quickly spreads to the larynx, bronchi and lungs. Treatment of these diseases in pregnant women is quite difficult due to the undesirable effects of antibiotics on the growing fetus.
Pharyngitis can cause fetal hypoxia, developmental delay and even the threat of miscarriage, especially with prolonged non-productive cough and uterine hypertonicity.
That is why the expectant mother should avoid crowded places during flu epidemics, carefully monitor her health and consult a doctor at the first manifestations of inflammation. Before medical consultation, a pregnant woman can take Faringosept.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pharyngitis includes an instrumental examination of the patient - pharyngoscopy, immunodiagnosis, microbiological examination of nasopharyngeal discharge, determination of streptococcal antigens in the blood.
When the first suspicion of inflammation of the pharynx appears, it is necessary to examine it. Examination of the pharynx is a simple procedure, often performed at home and does not require special skills or abilities. The patient must be brought to the light and the handle of a spoon pressed on the central part of the tongue. The depth of advancement of the spoon should be controlled so as not to provoke vomiting.
Patients have a red throat, the mucous membrane is injected and swollen. If the disease is accompanied by fever, you should consult a doctor, since the symptoms of pharyngitis are in many ways similar to the symptoms of a sore throat. Acute inflammation of the tonsils is a terrible pathology, often leading to severe complications.
Distinctive signs of sore throat in children are:
- Purulent plugs on the tonsils;
- Plaque in the form of yellow dots, islands, threads;
- Severe intoxication - lack of appetite, fever;
- Severe pain syndrome.
Differential diagnosis of pharyngitis is carried out with laryngitis and tonsillitis.
Inflammation of the pharynx and larynx
Pharyngitis is a disease with localization of the pathological process on the mucous membrane of the pharynx. It is manifested by local inflammatory signs and general symptoms of intoxication - fatigue, tiredness, decreased performance, headache. The pathology complicates the course of rhinitis and ARVI.
An inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the larynx and vocal cords of bacterial or viral origin is called laryngitis. Local symptoms of laryngitis: hoarseness, hoarseness, barking cough. Systemic signs include: fever, muscle and joint pain, malaise, weakness. In addition to infectious factors, the causes of laryngitis are: overstrain of the vocal cords, injuries of the larynx and their consequences.
Inflammation of the pharynx and larynx differ in the localization of the pathological process, etiology and pathogenesis. Treatment of laryngitis in most cases is carried out using antibiotics, and in the treatment of pharyngitis they are practically not used. Both pathologies are companions of ARVI and make themselves felt from the very beginning of the disease.
Inflammation of the pharynx and tonsils
Tonsillitis is an acute infectious and inflammatory pathology that affects the mucous membrane of the tonsils. Sore throat is caused by conditionally pathogenic bacteria of the droplet group of infections - streptococci and staphylococci, transmitted by airborne droplets from a sick person. In more rare cases, the disease is caused by viruses, fungi and even chlamydia. Sore throat complicates the course of respiratory infections.
Inflammation of the pharynx and tonsils manifests itself with similar clinical signs.
With pharyngitis - morning sore throat, hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane, burning and dryness, coughing, lump in the throat. General signs of intoxication are mild or completely absent.
With a sore throat , the sore throat is more intense,
radiating to the ears and worsening after lunch. The tonsils are covered with purulent plaque. Patients develop characteristic symptoms of intoxication - headache, fever, chills, muscle and joint pain, nausea, vomiting.
The therapeutic principles used for lesions of the pharynx and inflammation of the tonsils are significantly different. For acute tonsillitis, antibiotics are prescribed, and for chronic tonsillitis, surgery is prescribed. For pharyngitis, antiseptic solutions for rinsing, aerosols, inhalations, and drinking plenty of fluids are usually used.
Treatment of pharyngitis in adults
An antibiotic for pharyngitis is most often inappropriate, since 70% of cases of the disease are provoked by a viral attack. You shouldn't rely on advertised cough drops either.
Some of them (for example, Travisil, with sage, licorice) consist of medicinal herbs, others (Strepsils, Faringosept) contain an antiseptic.
Both of them act only as a symptomatic remedy to reduce pain, and at best only prevent the spread of infection, but do not cure it.
Complex treatment of pharyngitis in adults involves:
Diet
Exclusion of hot/cold foods, spicy and sour foods, alcohol, carbonated drinks. The menu consists of cereals, vegetable purees, soups.
Warm milk with honey and butter (for 1 tbsp milk, 1 tbsp of each component), warm tea with raspberry jam have a softening effect.
Regular events
During periods of high fever, stay in bed. Silence mode - temporarily minimize talking, stop shouting and singing.
Hot foot baths are great. Avoid even passive smoking. During the heating season, to solve the problem with air humidification, ventilation is necessary.
Gargling and inhalation
For rinsing and inhalation, use Chlorhexidine, Iodinol, decoction of calendula, chamomile, propolis tincture, essential oils, soda solution (1 tsp per glass of water). If you have pharyngitis, you should gargle every 3-4 hours, starting immediately from the onset of the disease.
Oral sprays Ingalipt (containing sulfanilamide and essential oils), Hexasprey, Tantum Verde (containing an NSAID), Bioparox (containing an antibiotic) are effective.
Immunomodulators and vitamins
With pharyngitis, the need for vit is increased. C. Herbal immunomodulators (eleutherococcus, Schisandra chinensis) are also used. Lizobact and other drugs with interferons are effective.
Etiotropic therapy
Depending on the causative infection, antiviral drugs are prescribed (effective in the first 3 days), antibiotics (for a combination of pharyngitis and sore throat), and antifungal agents.
Symptomatic treatment of pharyngitis
It is acceptable to take antihistamines (reduce swelling, use a sedative effect for insomnia), and cough suppressants with plantain.
Treatment methods
All purulent diseases of the oropharynx must undergo complex therapy. To begin with, the patient is provided with:
- Diet with the exclusion of irritating foods. If you have a sore throat, you should not consume coarse, poorly cooked food, spicy, over-salted, smoked, or cold foods.
- Abundant drinking regime. If you take healthy drinks in large quantities, intoxication will noticeably decrease. Hot teas, decoctions, and soda are not allowed for pharyngitis.
- Bed rest. In the absence of unnecessary energy expenditure, the body will cope with the infection faster. If it is impossible to stay in bed all the time, you should at least limit your movements and exclude active activities, for example, sports. And, of course, if you have purulent pharyngitis, you should not visit the workplace.
- Ventilate the room as often as possible. In a dry room, the throat dries up, all the painful symptoms of the disease intensify, and the person begins to feel even worse.
Drug treatment for purulent pharyngitis is prescribed by a doctor. In most cases, you cannot do without taking antibiotics that will help eliminate the cause of the disease - a bacterial infection. From the group of penicillins, the drugs Augmentin, Ampiox, Amoxiclav are suitable for a patient with purulent pharyngitis; if you are allergic to penicillins, choose a medicine from the group of macrolides - Sumamed, Clarithromycin. Cephalosporins are rarely prescribed for this type of ENT disease, mainly when severe complications occur.
Other methods of treating purulent pharyngitis are aimed at eliminating cough, dry throat, swelling, inflammation, temperature, and also to enhance the fight against infection:
- anti-inflammatory, antipyretic drugs - Paracetamol, Nurofen, Nimesil;
- Antitussives - Libexin, Sinekod, which in case of a wet cough should be replaced with mucolytics and expectorants - Doctor Mom, Gedelix, Ambrobene;
- anti-inflammatory drugs for cough - Erespal, Bronchomax, Inspiron;
- sprays for disinfecting the pharynx - Yox, Ingalipt, Hexoral, Stopangin;
- local tablets to alleviate painful sensations in the throat - Decathylene, Septolete, Faringosept, Agisept, Trachisan;
- preparations in rinse solutions - Furacilin, Hexoral, Yox, Stomatodin, Miramistin, Rivanol, Chlorophyllipt, as well as infusions of medicinal herbs (sage, chamomile, eucalyptus);
- inhalation with a nebulizer with mineral water, saline, antibiotics (as prescribed by a doctor and only at temperatures below 38 degrees);
- lubricating the throat with emollients based on oils or glycerin (for example, Chlorophyllipt).
We must not forget about the side effects that treatment of pharyngitis with antibiotics can cause. Read about how to restore the body's microflora in the following article.
To reduce symptoms such as sore throat, sore throat, itching, irritation, etc., inhalations for pharyngitis through a nebulizer are used.
In rare cases, with pharyngitis, it is necessary to remove accumulations of pus surgically. This is usually required for complications of the disease in the form of abscesses, or when large follicles with pus form. The doctor removes the pus with a syringe or scalpel under local anesthesia, and then prescribes a course of local and systemic antibiotic therapy.
Folk remedies
Usually, antibacterial treatment of this pathology is recommended to be supplemented with traditional methods, even by conservative doctors. Below are recipes for drugs that can be used in the treatment of purulent pharyngitis:
- Brew a spoonful of mint and coltsfoot in 300 ml of boiling water, leave until the infusion cools. Drink 100 ml three times a day.
- Pour a glass of boiling water over a spoonful of a mixture of equal parts of mint, yarrow, petals and rose hips. Let it brew, take with honey, dividing into 2 doses.
- Add 3 drops of eucalyptus and thyme oil to 100 ml of warm water, then gargle 4-5 times a day.
- Take 2 buds of cloves, chew in the throat for 5 minutes, repeat the treatment 3-4 times a day.
- Mix a teaspoon of grated horseradish, chopped garlic and a tablespoon of honey, pour everything with a glass of warm water. After an hour, use the rinse, after filtering it. Read more about the treatment of pharyngitis with folk remedies in adults
Treatment in children, pregnant and lactating mothers
In children, treatment of the disease is carried out with the appointment of a pediatrician or otolaryngologist, more often at home. Sometimes, if the course of the disease is severe, and it is also complicated by bronchitis, laryngitis, or tonsillitis, hospitalization may be required. The child is always prescribed plenty of warm drinks, alkaline, salt rinses, and irrigating the pharynx with herbal infusions. Age-appropriate sprays should also be used for irrigation, but any drug in this group should be used no earlier than 2 years of age. In the treatment of children against purulent pharyngitis, antibiotics are always used - Augmentin, Flemoklav, Sumamed. Depending on the severity of the process, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs are prescribed, and antihistamine tablets or drops are prescribed to prevent swelling.
In pregnant women, any purulent disease can lead to unpredictable consequences, and therefore antibiotics are introduced into the course of therapy at the earliest stage of this type of pharyngitis. Now there are many medications that do not harm the baby, and the expectant mother should not worry about their pathogenic effects. It is also necessary to frequently rinse the throat with a solution of salt and soda, sea water, herbal infusions, and approved solutions from the pharmacy. Read more about how to treat chronic pharyngitis in pregnant women
Antitussive drugs are prohibited during pregnancy, like many other medications, but usually antibiotics, rinsing and rinsing the throat are sufficient for a complete cure. In a similar way, purulent pharyngitis is treated in nursing mothers, who may have to temporarily reduce lactation by expressing milk, but after completing the course of medication (3-7 days), you can return to full breastfeeding.
Basic information about the symptoms and treatment of pharyngitis
- Bacterial pharyngitis is characterized by the presence of purulent foci on the back wall of the pharynx (yellowish-green plaque, bad breath).
- With fungal pharyngitis, ulcers with a white coating are found in the throat. Taking antibiotics only worsens the clinical picture.
- Pharyngitis is distinguished from tonsillitis by a large area of inflammation.
- If your throat is constantly dry, you should rule out diabetes mellitus and thyroid pathology.
- Thinning and “glazing” of the mucosa indicates chronicity of pharyngitis and the development of mucosal atrophy.
- Home treatment is permissible only if the disease is mild and there is no severe intoxication. Lack of effect within 2-3 days or worsening symptoms require consultation with an ENT doctor.
- The main factor in successful treatment is the elimination of irritating effects (diet, air hygiene, elimination of gastrointestinal pathology, treatment of caries).
- Antimicrobial, antiviral treatment is prescribed only by a qualified specialist.
- Treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults is most effective with a combination of drug therapy, physiotherapy (medicinal electrophoresis, ultraviolet radiation), and immunostimulation.