Harm caused by radiation therapy for cancer treatment
Radiation therapy for cancer causes damage to nerve endings (this manifests as numbness and pain). Radiation in the head and neck area can harm the tonsils and cause ulcers in the throat and mouth. Radiation to the stomach or pelvis can harm the intestinal tract. Radiation also limits restorative functions in the treatment of breast cancer,
and can cause significant damage to the heart, lungs and other nearby organs.
But radiologists consider these side effects to be minor compared to the benefits of using radiation therapy to treat cancer. But they are wrong, and this theory itself is fundamentally wrong.
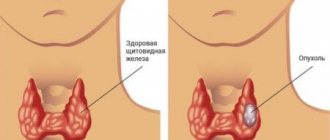
Radiation therapy creates more cancer
While in the past researchers believed that radiation could actually kill cancer cells , modern researchers have discovered that radiation, on the contrary, promotes the growth of cancer.
A recent study from UCLA's Johnsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found that radiation causes breast cancer cells to form more tumors. In addition, the likelihood of malignant neoplasms in the breast was about 30 times higher. That is, in fact, radiation promotes the development of tumors instead of killing them, and it leads to the fact that the cancer grows with even greater force.
Another report showed that radiation therapy transforms cancer cells into treatment-resistant cancer stem cells (CSCs), even though it kills some cancer cells inside the tumor. It would seem that radiation therapy hits cancer cells and can help shrink tumors, but this is only a short-term effect before the tumors grow again with even greater force.
Another study found that these cancer stem cells are the reason why traditional treatments fail. In fact, awareness of the very existence of RKS dates back to around 1910, although the term was not used then. Along with chemotherapy, numerous researchers have discovered that radiation does not kill all cancer cells inside a tumor.
Cancer stem cells remain.
Additionally, radiation actually turns normal cells into cancer cells, thereby creating therapy-resistant cells that can produce more cancerous tumors
.
When might anticancer radiation therapy be useful?
Radiation therapy may be useful in palliative care. For example, it is often used as a method of pain control. But the theory that radiation therapy cures has long been questioned.
Besides the obvious questions such as “does radiation therapy harm nearby organs?” (yes, it does), or “will I suffer from overwork?” (with a high degree of probability - yes), and “does it contribute to lymphostasis?” (contributes), there are several other important questions that you need to ask your doctor before you agree to undergo treatment.
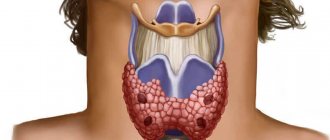
Classification and radiation dose
Radiotherapy is classified according to the type of radiation and the method of delivering it to the tumor tissue.
Exposure to radiation leads to the gradual destruction of tumor tissue. Decay products enter the bloodstream and cause intoxication. To remove it, as well as to minimize the negative impact of the procedures, you need to eat right.
Nutrition during radiation therapy should be carried out in accordance with the principles of healthy eating. The patient should drink up to 2 liters of liquid (compotes, juices, fruit drinks) per day. Food is consumed in small portions, up to 6 times a day. The basis of the diet should be protein foods and dishes rich in pectin.
The negative consequences of radiation directly depend on the dose of ionizing radiation entering the human body. Therefore, at the stage of preparation for therapy, accurate dose calculation is important. When determining an individual treatment plan, a variety of factors are assessed:
- size and type of education;
- precise placement;
- the patient’s condition based on the results of additional studies;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- previous irradiations.
Examinations before radiation therapy
Taking into account the indicators, medical specialists determine the total dose of radiation for the full course and for each session, their duration and number, breaks between them, etc. A properly calculated dose helps achieve maximum treatment effectiveness with minimal unwanted side effects.
Tolerance to radiation therapy varies greatly among patients. Some patients experience side effects exclusively during the treatment period, while others develop side effects some time after it. It happens that negative phenomena are completely absent.
Radiation reactions and damage
Typically, the severity of side effects depends on the duration of radiation and its dose. The location of the cancer, its stage, the patient’s condition, and individual tolerance to the procedure also have an impact.
The general effects of radiotherapy are presented in the following table.
| Organs and systems | Consequences |
| Leather | Soreness, swelling of varying degrees of severity, increased sensitivity, dryness, the appearance of bursting blisters, weeping of the affected area, and when an infection occurs, ulcers form. In complicated cases, non-healing ulcers, atrophy, and thinning of the skin form |
| Respiratory system | Shortness of breath, nonproductive cough, pneumonia, difficulty breathing |
| Mucous membranes | Damage to the epithelium of the digestive tract, genitourinary system (during irradiation of the peritoneum and pelvis). There is a disruption in the functioning of these organs |
| ENT organs | Stomatitis, laryngitis, dryness, pain and difficulty swallowing, swelling |
| General state | Chronic fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbance, restlessness, anxiety, hair loss |
| Digestive system | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, development of colitis, esophagitis, colitis, rectitis, in severe cases, development of fistulas |
| Circulatory system | Bone marrow dysfunction, reduction of red blood cells, leukocytes in the blood, anemia |
| Female reproductive system | Manifestations of menopause. Menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea, vaginal narrowing and dryness, sweating, infertility |
| Male reproductive system | Erectile dysfunction, acute pain during ejaculation (with irritation of the urethra), decreased sperm count |
| Urological system | Cystitis |
| Skeletal system | Bone necrosis, inflammation of the periosteum, perichondritis, problems with joints and muscles |
Radiation reactions
The most common negative effect of radiation is hypersensitivity reactions on the skin, similar to a burn. They usually appear two weeks after the start of therapy and heal a month after the cessation of radiation exposure. There are three degrees of damage to the epidermis:
- first - slight redness;
- the second – redness, peeling, possible swelling;
- third – significant redness with weeping peeling, severe swelling.
Radiation damage
Respiratory effects occur with chest irradiation and usually occur within three months of therapy. Disturbances in the circulatory system occur when radiation is exposed to a large area of the body.
A common side effect of radiation therapy is fatigue. General weakness persists for a long time and does not go away after sleep and rest. In some cases it is a consequence of anemia.
Radiation reaction
Long-term consequences of radiotherapy include:
- fibrosis (replacement of affected connective tissue);
- dry skin and mucous membranes (eyes, mouth);
- oncology (development of secondary formations);
- skin pigmentation;
- hair loss;
- death (with concomitant cardiovascular pathology);
- decreased cognitive function.
Local radiation reactions
The occurrence of serious consequences is quite rare and is associated with prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation on the body or concomitant diseases. Usually the manifestations are moderate and disappear over time. The benefits of treatment significantly outweigh the risk of undesirable consequences.
During and after treatment, the body needs help to rehabilitate. The oncologist prescribes a set of drugs and measures to stabilize the patient’s condition and restore the body’s strength.
For minor skin reactions, hygiene and moisturizing the damaged area with cream is recommended. For severe lesions, hormonal ointment is used. Radiation wounds serve as “entry gates” for infection, so antiseptic treatment with a bandage should be carried out regularly. Clothing should be comfortable and loose, and avoid rubbing the affected areas.
Don't forget about a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to observe a daily routine, work and rest, perform feasible physical exercises, take walks in the fresh air, gradually increasing the distance.
Nutrition is of great importance; your doctor can recommend a list of foods you want to eat.
The menu should be high in calories and high in protein. At the same time, fried, fatty, smoked foods, and alcohol are excluded. It is advisable to include foods rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and plant fiber in your diet. In case of nausea and vomiting, antiemetic drugs are prescribed, in some cases they are taken some time before the start of treatment.
To get rid of the effects of radiation, physiotherapy (electric and phonophoresis, magnetic therapy) is used; inhalations and special gymnastics are used for respiratory disorders. To improve the general condition and get rid of chronic fatigue, massage sessions are prescribed.
— I have prostate adenoma. I prepared questions before the meeting. Here I have it written down. Nutrition? A tan? Bathhouse? State of health, tone? Medicines? What vitamins should you take?
- Let's start with nutrition. During treatment, it is better to eat heavily. And this applies to everyone. Whatever treatment you receive, surgical, chemotherapy or radiation, you need to receive fats, proteins and carbohydrates in excess. Try not to even fast.
To the doctor? Be sure to constantly go to the doctor. As a rule, leaving our hospital, many believe that the disease has been cured and “I’m off and running.” So, if you fall out of the dynamic observation of an oncologist at your place of residence or with us here, then troubles will immediately begin. And all relapses that are detected in the early period are also subject to treatment.
About the bathhouse. The bath is a physiotherapeutic effect, so it obviously increases the risk of recurrence of the disease that we are trying to fight together. And it is better to avoid sunbathing.
— Do families need separate dishes and cutlery?
“I repeat that for yourself and for those around you, you are absolutely safe people who do not require isolation. You are no different from the rest. It’s just that at this moment you need treatment.
— And when the doctor says that you can choose either surgery and radiation therapy, or without surgery, but more intense radiation. Which is better to choose? And how can the patient understand what is best?
— Yes, there are diseases when radiation therapy and surgery are equivalent and equally replaceable. And if for some reason it is impossible to perform surgical intervention due to the general condition of the patient, then we go for radiation therapy.
Sometimes there are situations when, on the contrary, radiation therapy cannot be carried out for reasons of the patient’s general condition, and we are forced to perform surgery. Everything is individual. There is no such thing as just a strict standard approach. We always weigh the benefits and harms of treatment on the scales. If the harm is greater, then we will carry out, for example, chemotherapy to delay the radiation intervention and then carry out radiation a little later.
— Can the same organ be irradiated a second time? What if there was a relapse in him?
- Sometimes yes. But this is very individual. This is quite a risky undertaking.
— Tell me, doctor, if I am undergoing radiation therapy, can I undergo a CT scan, ultrasound, MRI or bone check at the same time? Or does it interfere with one another?
— You just named completely different examination methods. MRI can be done despite radiation therapy. Computed tomography, if the area is small, can be combined with sessions. And if you need to examine two or more areas, then it is better to skip the CT scan, because the radiation dose will be too high.
In the case of bone scintigraphy, a bone test, you will be injected with a radiopharmaceutical, and for some time you are unsafe for others, so it is better to wait so as not to expose others to the effect, and yourself to additional exposure.
Therefore, when you have any examinations planned or want to carry them out while undergoing radiation treatment, you must agree with your doctor.
What to do if you decide not to accept adjuvant radiation therapy for cancer
The very thought of radiation therapy causes fear in many people. And this is true, since research shows that, instead of killing cancer cells, radiation, on the contrary, promotes their growth and spread. What remains to be done? Fortunately, there are many natural substances that specifically target cancer cells, reducing the likelihood of relapse and metastasis, without harming healthy cells. We have discussed many of them here on The Truth About Cancer. Vitamin C, vitamin D, and modified citrus pectin are just a few examples of cancer-fighting substances.
Vitamin C
Often compared to a Trojan horse that penetrates and kills cancer cells, it has been used for decades to fight cancer.
Physicians use it in high doses as part of conventional and holistic treatments to enhance effectiveness. The good news is that new research shows that vitamin C suppresses cancer growth and metastasis by curbing cancer stem cells that arise from chronic stress. Cancer stem cells are not like just cancer cells.
They make it possible for cancer to move and grow in any other place in the body.
That chronic stress contributes to the development of cancer
, has long been a theory, but recent research has shown exactly how it works. Chronic stress not only suppresses the immune system, but the resulting adrenaline (epinephrine) has been shown to trigger the development of breast cancer by stimulating cancer stem cells into action.
Vitamin D
Known as the "anti-cancer hormone" (in fact, it is a hormone). It primes the immune system so that it kills cancer cells, including tumor suppressor genes, and generally has a strong anti-cancer effect. It is important to note that the cancer cell turns off the process of apoptosis (i.e. programmed cell death) by producing an anti-apoptotic protein called Bcl-2). Vitamin D has been found to reduce Bcl-2 production. Vitamin D also reduces the production of cyclooxygenases (eng: COX-2) as well as the enzyme aromatase, which leads to an increase in estrogen.
Modified Citrus Pectin
(MCP) causes cancer cell death (apoptosis) and prevents circulating tumor cells from becoming trapped inside the walls of blood vessels and subsequently forming tumors. More specifically, research shows that MCP may help reduce the expression of the protein Galectin-3, which promotes cancer spread and metastasis. Cancer uses Galectin-3 to shut down the immune system so that it can no longer recognize and eliminate life-threatening cancer cells—a hallmark of cancer. MPC reduces the immune and inflammatory response associated with cancer and helps remove carcinogenic metals from the body.
Warning: This information is not medical advice and should not be taken as medical advice. Always discuss all medical questions with your healthcare provider.
Please share this information with your friends and family. This could save someone's life!
Links to referenced studies:
- Stem Cells, PubMed
- Radiation treatment generates therapy-resistant cancer stem cells from less aggressive breast cancer cells, Printz, C (2012)
- Biological consequences of radiation-induced DNA damage: relevance to radiotherapy, Pub Med.
- Mechanisms of injury to normal tissue after radiotherapy: a review, Pub Med.
- Why high-dose vitamin C kills cancer cells
- Mouse study reveals how chronic stress promotes cancer, identifies vitamin C as therapy
- Stress hormones promote breast cancer metastasis
Author:
Elyn Jacobs
Source:
The Truth About Cancer
Translation:
MedAlternative.info
Materials on the topic:
- Radiation (radio) therapy for cancer
- “Cut, poison, burn” - traditional oncological methods (or listen to the audio version)
- 13 Questions You Need to Ask Your Oncologist Before Saying “YES” to Chemotherapy
- “The truth about cancer. Search for treatment methods." All films of the project
- The book “Diagnosis of cancer: to be treated or to live? An alternative view of oncology"
- The diagnosis is cancer. What to do?
- 25 Foods That Kill Cancer Stem Cells Better Than Radiation and Chemotherapy
- The truth about the oncology industry. Mike Adams (video)
Attention! The information provided is not an officially recognized method of treatment and is for general educational and informational purposes only. The views expressed herein do not necessarily reflect those of the authors or staff of MedAlternativa.info. This information cannot replace the advice and prescription of doctors. The authors of MedAlternativa.info are not responsible for the possible negative consequences of using any drugs or using the procedures described in the article/video. The question of the possibility of applying the described means or methods to their individual problems should be decided by readers/viewers themselves after consultation with their doctor.
We recommend reading our book:
Diagnosis of cancer: to be treated or to live? An alternative view of oncology To quickly get into the topic of alternative medicine, as well as find out the whole truth about cancer and traditional oncology, we recommend reading the book “Diagnosis of Cancer: Treat or Live” for free on our website.
An alternative view of oncology" Read for free
We spread truth and knowledge. If you find our work useful and are ready to provide financial assistance, then you can transfer any amount feasible for you. This will help spread truthful information about cancer and other diseases and could save lives. Participate in this important matter of helping people! Support the project
Contraindications to therapy
Each treatment method has its own specific contraindications. Radiation therapy is no exception. It may be prohibited for the patient for the following reasons:
- Tumor disintegration;
- Bleeding from a tumor;
- Suppuration of the neoplasm;
- Tumor growth into the organs of the reproductive system;
- Presence of septic diseases;
- Distant metastases present in the body;
- Severe physical exhaustion of the body;
- The patient is feeling unwell;
- Intoxication of the body;
- Active tuberculosis;
- Blood diseases such as: leukopenia and thrombocytopenia;
- Presence of anemia. It is expressed in a pathologically low level of hemoglobin in the blood;
- Impaired blood supply;
- Kidney dysfunction;
- Liver dysfunction;
- Myocardial infarction that occurred within the last year.
If a patient has at least one of the listed phenomena, then radiotherapy will be prohibited or limited.