Treatment for atrial fibrillation depends primarily on the form of the disease and requires a person to change their lifestyle, diet, take certain medications, and in some cases, undergo certain procedures or even surgery.
Without a doubt, AF is a condition that needs to be carefully monitored. Fortunately, there are a number of options available today to manage AFib, and for many people, there are medications and other treatment options that can help reduce the risks associated with the condition. To understand what AF is (causes and symptoms of the disease), you can read this material - Atrial fibrillation: causes, symptoms, treatment.
Once you understand the causes and symptoms of atrial fibrillation, you probably want to know what can be done to correct or at least control your condition. The answer to this question usually depends on the type of atrial fibrillation, how the condition affects your daily life, and how much AF increases your risk of stroke or other serious complications. Your doctor will likely strongly encourage you to make some lifestyle changes, and depending on your situation, he may also recommend medications, medical procedures, or surgery.
Why is fibrillation dangerous?
When contractions are chaotic, blood stays in the atria longer. This leads to the formation of blood clots.
Large blood vessels emerge from the heart, carrying blood to the brain, lungs and all internal organs.
- The resulting blood clots in the right atrium travel through the large pulmonary trunk to the lungs and lead to pulmonary embolism.
- If blood clots form in the left atrium, then with the blood flow through the vessels of the aortic arch they enter the brain. This leads to the development of a stroke.
- In patients with atrial fibrillation, the risk of developing a cerebral stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident) is 6 times higher than without rhythm disturbances.
Blood clot formation in the left atrium leads to stroke
Contraindications for stopping attacks of atrial fibrillation
In the following conditions, stopping attacks is not recommended:
- Tachy-bradysystolic syndrome.
- Frequent attacks of atrial fibrillation, in which electrocardioversion or the introduction of antiarrhythmic drugs into a vein is indicated. Due to the fact that in such patients it is impossible to maintain sinus rhythm for a long period, it is not advisable to stop an attack of arrhythmia.
- Severe heart failure in chronic form and observed enlargement of the left ventricle.
- An absolute contraindication is a history of thromboembolism and the presence of a blood clot in the atria.
Causes of pathology
The reasons are usually divided into two large groups:
- Heartfelt.
- Non-hearty.
Rarely, with a genetic predisposition and abnormal development of the conduction system of the heart, this pathology can be an independent disease. In 99% of cases, atrial fibrillation is not an independent disease or symptom, but occurs against the background of an underlying pathology.
Heart reasons
The table shows how often cardiac pathology occurs in patients with AF:
| Heart reasons | How often are patients with AF diagnosed with heart problems? |
| Valvular heart defects | 30% |
| Coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension | 20% |
| Cardiomyopathy – congenital or acquired damage to the heart muscle | 10% |
| Condition after cardiac surgery | 70% |
Among all the defects, atrial fibrillation is most often detected with mitral or multivalve heart defects. The mitral valve is the valve that connects the left atrium and the left ventricle. Multivalve defects are damage to several valves: mitral and (or) aortic and (or) tricuspid.
Mitral heart disease
Combinations of diseases can also be the cause. For example, heart defects can be combined with coronary heart disease (coronary disease, angina) and arterial hypertension (high blood pressure).
The condition after cardiac surgery can cause atrial fibrillation, because after surgery the following may occur:
- Changes in intracardiac hemodynamics (for example, there was a bad valve - a good one was implanted, which began to work correctly).
- Electrolyte imbalance (potassium, magnesium, sodium, calcium). Electrolyte balance ensures the electrical stability of heart cells
- Inflammation (due to stitches on the heart).
In this case, doctors’ recommendations depend on heart surgery and rhythm disturbances. If there were no such problems before the operation, then the arrhythmia will “go away” during general treatment.
Non-cardiac causes
| Non-cardiac causes | How often does it occur? |
| Obesity | 25% of patients |
| Diabetes | 20% of patients |
| Hyperthyroidism | 10% of patients |
| Adrenal tumors | 10% of patients |
Alcohol consumption may influence the risk of atrial fibrillation. A study conducted by American scientists in 2004 showed that when the dose of alcohol increases to more than 36 grams per day, the risk of developing atrial fibrillation increases by 34%. It is also interesting that doses of alcohol below this figure do not affect the development of AF.
Vegetovascular dystonia is a complex of functional disorders of the nervous system. With this disease, paroxysmal arrhythmia often occurs (a description of the types of arrhythmia is in the next block).
Causes of development and risk factors
- AMI (impaired conductivity and excitability of the myocardium).
- Arterial hypertension (LA and LV overload).
- Chronic heart failure (impaired myocardial structure, contractile function and conductivity).
- Cardiosclerosis (replacement of myocardial cells with connective tissue).
- Myocarditis (structural disorder due to inflammation of the myocardium).
- Rheumatic diseases with damage to the valves.
- SU dysfunction (tachy-brady syndrome).
- Diseases of the thyroid gland with manifestations of thyrotoxicosis.
- Drug or other intoxication.
- Overdose of digitalis preparations (cardiac glycosides) in the treatment of heart failure.
- Acute alcohol intoxication or chronic alcoholism.
- Uncontrolled treatment with diuretics.
- Overdose of sympathomimetics.
- Hypokalemia of any origin.
- Stress and psycho-emotional stress.
Age-related organic changes.
With age, the structure of the atrial myocardium undergoes changes. The development of small focal atrial cardiosclerosis can cause fibrillation in old age.
Classification and symptoms of AF
There are many principles for classifying AF. The most convenient and generally accepted classification is based on the duration of atrial fibrillation.
| Form of AF | Duration | Outcome or treatment recommendations |
| Newly diagnosed or emerging | 10–15 minutes | Spontaneous restoration of sinus rhythm is possible, meaning treatment may not be required |
| Paroxysmal form* (see explanations at the bottom of the table) | 3 minutes – 7 days, more often 1−2 days | |
| Persistent | More than 7 days | Treatment can restore sinus rhythm |
| Long-term persistent | More than one year | |
| Permanent form of atrial fibrillation | Years, measures to restore rhythm are ineffective | Treatment is aimed at controlling the rhythm frequency |
* Paroxysms are attacks that can occur and stop spontaneously (that is, on their own). The frequency of attacks varies from person to person.
Characteristic symptoms
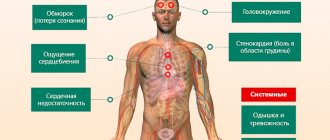
All types of fibrillation have similar symptoms. When atrial fibrillation occurs against the background of an underlying disease, patients most often present the following complaints:
- Palpitations (frequent rhythm, but in the bradysystolic form the heart rate, on the contrary, is low - less than 60 beats per minute).
- Interruptions (“freezing” of the heart and then a rhythm follows, which can be frequent or rare). Frequent rhythm - more than 80 beats per minute, rare - less than 65 beats per minute).
- Shortness of breath (rapid and difficult breathing).
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
If atrial fibrillation exists for a long time, then swelling in the legs develops in the evening.
Complications
The long course of atrial fibrillation provokes the following consequences:
- Severe cardiomyopathy with symptoms of heart failure, developing against the background of chronic atrial fibrillation.
- Thromboembolism, the cause of which lies in ineffective atrial contractions. Blood clots can be in the kidneys, lungs, spleen, brain vessels, peripheral vessels of the extremities.
- Hemodynamic disturbances, as a result of which heart failure develops or progresses, reduces the quality of life and performance of the individual.
Quite a high mortality rate among individuals with atrial fibrillation due to the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation. The tachysystolic form of atrial flutter is especially dangerous, so it is advisable to follow the advice of specialists on taking medications and other preventive measures. Comprehensive measures will help prevent new attacks and slow down the transition of the disease to a chronic form, in which there is a high risk of serious consequences.
Diagnostics
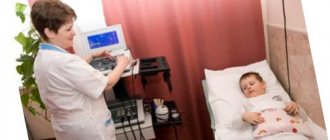
Diagnosing atrial fibrillation is not difficult. The diagnosis is made on the basis of an ECG. To clarify the frequency of attacks and combinations with other rhythm disturbances, special Holter monitoring is performed (ECG monitoring throughout the day).
Heartbeat on an electrocardiogram. Click on photo to enlarge
Atrial fibrillation is diagnosed using an ECG.
Development
The functioning of the heart muscle is influenced by many factors, not all of which have a positive effect. The main cause of heart palpitations is IHD (coronary heart disease). Patients with this diagnosis suffer from a lack of oxygen in the blood, as blood clots or plaques form in the arteries leading to the myocardium. The atria are the first to react to this; they begin to contract chaotically. The ventricles suffer from this. Coronary disease usually affects older people. It is completely impossible to get rid of this disease.
Not only ischemic heart disease can cause pathological changes in heart rhythm. There are a number of risk factors. It is extremely important to know which diseases can lead to permanent atrial fibrillation. Among the most common causes are the following diagnoses:
- arterial hypertension;
- oncological pathologies of the myocardium;
- valve defects (congenital and acquired);
- inflammation of the heart muscle;
- heart failure;
- cardiomyopathies of various types.
Medical practice knows of cases where atrial fibrillation occurred in young people without adequate reasons. Most often it manifests itself in stressful situations for the body. In this case, there is no need to worry, since the disease is not capable of causing irreparable harm to health. However, people with this form of the disease need to visit a cardiologist regularly every six months.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause and/or preventing complications. In some cases, it is possible to restore sinus rhythm, that is, to cure fibrillation, but it also happens that the rhythm cannot be restored - in this case, it is important to normalize and maintain heart function and prevent the development of complications.
To successfully treat AF, you need to: eliminate the cause that caused the rhythm disturbances, know the size of the heart and the duration of the flicker.
When choosing a particular treatment method, the goal is first determined (depending on the specific condition of the patient). This is very important, since tactics and a set of measures will depend on it.
| Treatment Goals | What treatment measures do doctors recommend (all approaches are discussed in this section below) |
| Restoration of sinus rhythm | Medicines Electropulse therapy Radiofrequency ablation |
| Prevention of rhythm disturbances, that is, maintaining sinus rhythm | |
| Maintaining heart rate if rhythm cannot be restored | |
| Prevention of thromboembolism |
Initially, doctors prescribe drug treatment, and if ineffective, electropulse therapy.
When drug therapy and electropulse therapy do not help, doctors recommend radiofrequency ablation (special treatment using radio waves).
Drug treatment
If the rhythm can be restored, then doctors will make every effort to do so.
Medicines that are used to treat AF are presented in the table. These recommendations are generally accepted for stopping rhythm disturbances such as atrial fibrillation.
| Drugs that affect heart function and rhythm | |
| Slow calcium channel blockers | Reduce HR (heart rate) |
| Beta blockers | |
| Cardiac glycosides | The good thing about this drug is that by reducing heart rate, it improves the strength of contractions |
| Antiarrhythmics such as amiodarone | Used to restore rhythm. Use with caution in case of thyroid dysfunction |
| Potassium and magnesium preparations | By eliminating the imbalance, the heart rate is reduced. When administered intravenously, they can restore the rhythm |
| Sodium channel blockers | Effective for restoring rhythm at the very beginning of AF |
Electropulse therapy
Sometimes treatment with medications (intravenous or tablets) becomes ineffective and the rhythm cannot be restored. In such a situation, electropulse therapy is performed - this is a method of influencing the heart muscle with a discharge of electric current.
Electropulse therapy
There are external and internal methods:
- The external one is carried out through the skin and chest. This method is sometimes called cardioversion. Atrial fibrillation is cured in 90% of cases if treatment is started in a timely manner. In cardiac surgery hospitals, cardioversion is very effective and is often used for paroxysmal arrhythmia.
- Internal. A thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the heart cavity through large veins in the neck or in the collarbone area. An electrode is passed through this tube (similar to a wire). The procedure takes place in the operating room, where, under X-ray control, the doctor can visually assess on monitors how to correctly orient and install the electrode.
Next, using special equipment shown in the figure, a discharge is applied and looked at the screen. On the screen, the doctor can determine the nature of the rhythm (sinus rhythm has been restored or not). Persistent atrial fibrillation is the most common case in which doctors use this technique.
Radiofrequency ablation
When all methods are ineffective, and atrial fibrillation significantly worsens the patient’s life, it is recommended to eliminate the lesion (which sets the heart’s abnormal rhythm) that is responsible for the increased frequency of contractions - radiofrequency ablation (RFA) - treatment using radio waves.
Radiofrequency ablation
After the lesion is eliminated, the rhythm may be rare. Therefore, RFA can be combined with the implantation of an artificial pacemaker - a pacemaker (a small electrode into the heart cavity). The rhythm of the heart will be set through an electrode by a pacemaker, which is installed under the skin in the collarbone area.
How effective is this method? If RFA was performed on a patient with paroxysmal AF, then within a year sinus rhythm is maintained in 64–86% (data from 2012). If there was a persistent form, then atrial fibrillation returns in half of the cases.
Why is it not always possible to restore sinus rhythm?
The main reason when it is not possible to restore sinus rhythm is the size of the heart and left atrium.
If, according to ultrasound of the heart, the size of the left atrium is determined to be up to 5.2 cm, then in 95% restoration of sinus rhythm is possible. Arrhythmologists and cardiologists report this in their publications.
When the left atrium is larger than 6 cm, restoration of sinus rhythm is impossible.
An ultrasound of the heart shows that the size of the left atrium is more than 6 cm
Why is this happening? When this part of the heart is stretched, some irreversible changes occur in it: fibrosis, degeneration of myocardial fibers. Such a myocardium (the muscular layer of the heart) is not only unable to maintain sinus rhythm for seconds, but, according to cardiologists, it should not do so.
Peculiarities
Pathological processes in the heart can affect both the entire organ and its individual parts. However, negative consequences affect the body as a whole. Atrial fibrillation is a disease characterized by impaired functioning of the ventricles. Normal functioning is hampered by factors such as improper blood circulation, insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood, and thinned myocardial walls. Due to the irregular rapid beating of the atria, frequent contractions of the ventricles appear. Long-term absence of therapy leads to rapid wear and tear of the heart muscle and can result in a heart attack.
Atrial fibrillation is included in a more complex classification, where it is one of the forms of supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. That is why the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination to identify additional concomitant or underlying ailments. It is extremely important to make a diagnosis in time to avoid irreversible processes. Dealing with a permanent form of atrial fibrillation is not easy, but it is possible. The main thing is to find a competent doctor and follow all his recommendations.
Atrial fibrillation is characterized by a high frequency of myocardial contraction. This disease is said to occur when more than 400 beats per minute occur. This speed is dangerous for human life and can cause necrosis of cardiac tissue. The chronic form is considered to be rapid heartbeat that lasts more than a week. Throughout this time, the patient feels tired and weak, and shortness of breath appears. If the contraction frequency is slightly lower (up to 350 beats per minute), then we are talking about a pathology such as flutter of the myocardial chambers.
Uncoordinated chaotic beats of the ventricles and atria are not only a consequence of disruption of the heart muscle. They can warn of disruptions in the nervous system or improper functioning of the brain. Patients with a permanent form of atrial fibrillation should be under the supervision of a cardiologist, since the risk of sudden death in the presence of such a pathology increases by 2 times.