The human body is not able to function properly without vitamins.
A person of any age will feel a lack or excess of vitamins in their own health. A deficiency of vitamins in the body can lead to a constant feeling of hunger and obesity. This happens due to poor nutrition, because along with a decrease in calories, the supply of the required amount of vitamins also decreases. This means that in order to get them, the body will begin to require more and more food.
In this article, we will pay special attention to B vitamins, which are essential for health.
On health record
The role of B vitamins is difficult to overestimate, since they are involved in many processes in our body. Each B vitamin performs its own vital mission for humans. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the main elements of group B.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
The first discovered element from group B. Despite the fact that the intestinal microflora synthesizes this element, the body requires its replenishment daily.
Thiamine function:
- Improves metabolism: produces energy, helps absorb proteins;
- Helps the nervous system function properly, produces a special substance that is responsible for brain function, improves the tone of the heart, stomach and intestinal muscles;
- Participates in the copying of genes transmitted to cells during division.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
This yellow-orange substance can be synthesized in the intestines. His role is also irreplaceable:
- Promotes the synthesis of nerve cells, supporting the functioning of brain neurotransmitters;
- Helps to mature red blood cells and absorb iron;
- Acts as a regulator in the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- Is an eye protector from ultraviolet exposure;
- Helps form skin and mucous membranes.
Vitamin B3 - niacin
Presented in the form of a white powder, soluble in water. Niacin is more tolerant of heat, ultraviolet light, alkaline substances and air. It is produced by the body due to amino acid conversion.
Function in the body:
- Helps synthesize enzymes, absorb proteins, fats and carbohydrates, release energy and even improves cholesterol metabolism;
- Participates in the production of various hormones;
- Eliminates problems at the genetic level that result from the influence of viruses and drugs on cells.
Vitamin B5 - pantothenic acid
Like its classmates, it is soluble in water. Produced in the intestinal environment with the help of symbiotic bacteria. If B5 is heated in an acid-base environment, it will collapse.
The role of pantothene:
- Helps release food energy;
- Regulates the functioning of the central nervous system by producing a special enzyme for this – acetylcholine.
- Protects the immune system, helps synthesize antibodies and heal wounds;
- Promotes the effective functioning of the adrenal glands, helps to produce a special hormone responsible for the response to stress.
- Forms healthy red blood cells and helps synthesize hemoglobin.
Vitamin B6 - pyridoxine
Consists of a whole group of water-soluble compounds. They are resistant to high temperatures and oxygen, but almost do not tolerate light. They can be synthesized by symbiotic microorganisms in the human intestine, but they are easily harmed by antibiotics.
The role of pyridoxine:
- Supports almost all metabolic processes of the body, controlling the activity of sixty enzymes;
- It is a synthesizer of special fat-containing elements that regulate the activity of the heart and blood vessels.
- Stimulates cell division and promotes the formation of antibodies, thereby supporting the health of the immune system;
- Supports stable functioning of the central nervous system;
- Helps form genetic material, absorbs vitamin B12.
Vitamin B7 - biotin
It is soluble in water, contains sulfur in its composition, and does not lose strength under the influence of high temperatures. Produced by symbiotic bacteria that live in the intestinal environment.
Functions of vitamin B7:
- Triggers digestive enzymes;
- Is an accomplice in metabolic processes;
- Helps fight diabetes;
- Improves skin condition.
Vitamin B9 - folic acid
Water-soluble element of bright yellow color. The form of the vitamin is quite stable. Synthesized by healthy intestinal microflora.
Functions of folic acid:
- Needed for the formation of RNA, DNA;
- Participates in protein metabolism;
- It is a synthesizer of healthy red and white blood cells.
Vitamin B 10 – para-aminobenzoic acid, PABA
This vitamin-like white substance, unlike its vitamin counterparts, dissolves in alcohol and essential liquids. The element is chemically stable and can withstand boiling in an acid-base environment.
The functions of the B 10 are very diverse:
- responsible for normal pigmentation of nail plates and hair;
- stabilizes the growth of beneficial intestinal microflora;
- is the main material that helps produce vitamin B10 for the intestines;
- promotes the production of protein and red blood cells; normalizes the functioning of the thyroid gland; improves digestive processes;
- helps increase breast milk production;
- helps to absorb certain vitamins; is a means of helping to prevent the formation of blood clots;
- supports healthy sexual function in men.
Vitamin B12 -cyanocobalamin
This is a bright red element. It is resistant to elevated temperatures. If it is exposed to oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, alkaline and acidic environments, it loses its properties. Most of the vitamin cyanocobalamin is found in the liver, some is produced by the intestines.
B12 functions:
- Releases food energy;
- Indispensable for rapid cell division;
- Forms a protective nerve sheath.
- Boosts immunity by helping red blood cells mature.
- Reduces cholesterol in the blood and helps the liver work.
Beneficial properties of B vitamins
There are many opinions regarding the benefits of various B vitamins. Thiamine is thought to help support the condition of people with Alzheimer's disease, a disease that is also associated with low levels of pyridoxine and cobalamin. High doses of niacin, as prescribed by a doctor, lower cholesterol and balance lipoproteins. Some evidence suggests that niacin may prevent adolescent diabetes (insulin-dependent type 1) in children at risk by maintaining pancreatic insulin excretion for longer than normal. Niacin is also used to relieve intermittent claudication and osteoarthritis, although using high doses for the latter can lead to liver problems. The frequency of migraines can be significantly reduced and the severity reduced through the use of supplemental riboflavin. Pyridoxine is used therapeutically to reduce the risk of heart disease, to relieve nausea during pregnancy, and to relieve symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. When combined with magnesium, pyridoxine may have some positive effects on the behavior of children with autism. Supplementation with cobalamins has been shown to improve male fertility. Depression, dementia and intellectual disabilities are often associated with deficiencies of both cobalamin and folic acid. Folic acid may reduce the likelihood of cervical or colon cancer in certain risk groups[7].
B vitamins play a key role in the processes of DNA formation, being responsible for the speed of certain processes. Severe deficiency of B vitamins can lead to failures in the formation of new cells and their uncontrolled growth, which, in turn, can cause cancer.
B vitamins, among other substances (such as vitamins C, D, E, omega-3, fats, coenzyme Q10, lipoic acid), are very important for heart health. Particularly noteworthy is the role played by folic acid, B6 and B12 in lowering homocysteine levels. Although it has not been officially confirmed by medicine, many studies have observed high levels of homocysteine in fat deposits on the endothelium (the thin layer of cells that line the inside of blood vessels), as well as in blood clots and heart disease.
Psychiatrists are also increasingly turning to B vitamins as a treatment. Together with vitamin C, they help support an effective adrenal response to stress. Multiple studies show that up to 30 percent of patients hospitalized with depression are deficient in B12. Several epidemiological studies have reported an association between low blood levels of folate, vitamins B6 and B12, and a higher prevalence of depressive symptoms. B-vitamin deficiency is also associated with anxiety disorders and, especially, obsessive-compulsive disorder. Many doctors begin treating OCD with therapeutic doses of the vitamin inositol.
Finally, one cannot fail to note the effect of the level of B vitamins on the amount of energy and vitality. Deficiency often leads to chronic fatigue, increased fatigue and drowsiness[11].
Each B vitamin is either a cofactor (usually a coenzyme) for key metabolic processes or a precursor necessary for their performance. These vitamins are water-soluble, meaning they are not stored in the fatty tissues of the body, but are excreted in the urine. Absorption of B vitamins occurs in the digestive tract and, as a rule, requires the presence of certain substances (proteins) in the body that allow the vitamins to be absorbed.
Interaction with other elements
All processes in the body are interconnected, so some substances can increase the effectiveness of B vitamins, and some can reduce it.
Fats and proteins reduce the body's need for vitamin B1, while carbohydrates, on the contrary, increase it. Raw seafood (fish and shellfish) contain an enzyme (thiaminase) that breaks down thiamine in the body. Therefore, people who eat large amounts of these foods may experience symptoms of vitamin B1 deficiency. In addition, thiamine interacts with magnesium; without it, B1 cannot turn into its biologically active form. Riboflavin should not be taken with calcium, which reduces its absorption. Niacin works in tandem with zinc to provide higher levels of antioxidants and zinc in the liver. Copper increases the body's need for vitamin B5. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is recommended to be used with magnesium; among the positive effects of this combination is relief of the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. The combination of pyridoxine and thiamine, as well as pyridoxine and vitamin B9, is undesirable. It is not advisable to consume folic acid with zinc, as well as vitamin B12, since they mutually increase the body's need for each other. Cobalamin (B12) should not be taken with vitamin C, especially when taking thiamine and copper simultaneously[12].
The best combinations of foods for the absorption of B vitamins:
- 1 Pumpkin pudding with chia seeds. Ingredients: milk, pumpkin puree, chia seeds, maple syrup, sunflower seeds, almonds, fresh blueberries. Contains thiamine, biotin, proteins, fiber and many other beneficial substances.
- 2 Salad with quinoa and kale. Ingredients: quinoa, fresh kale, red cabbage, carrots, dill, boiled eggs, rice vinegar, extra virgin olive oil, ground black pepper. Contains riboflavin, biotin, folic acid and cobalamin.
- 3 Gluten-free quinoa and broccoli salad. Ingredients: fresh broccoli, quinoa, cucumber, cherry tomatoes, pumpkin seeds, sea salt, black pepper, Dijon mustard, vinegar, extra virgin olive oil, maple syrup. Contains thiamine and riboflavin.
- 4 Gluten-free stuffed peppers with quinoa. Ingredients: quinoa, green bell peppers, canned lentils, fresh spinach, feta cheese, frozen corn kernels, salt, black pepper. Contains thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, folic acid, pantothenic acid and cobalamin.
In the absence of medical contraindications, diseases, or ethical preferences, B vitamins are best obtained from food. These vitamins are widely distributed in many foods and it is not difficult to choose a diet that would replenish the supply of vitamins and suit everyone's taste. The exception is vitamin B12, which can only be obtained from animal products and is therefore difficult to obtain in its natural form for vegans. In this case, under the supervision of a doctor, synthetic vitamins are prescribed. No matter what, uncontrolled intake of synthetic vitamins can not only bring no benefit, but also cause harm. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor before taking any vitamins.
Application in official medicine
Due to the fact that each B vitamin has its own functions, one or another vitamin is prescribed by a doctor depending on the immediate indications.
Vitamin B complex is prescribed primarily in cases of obvious deficiency, insufficient absorption, or when the diet is limited. I also often recommend taking these vitamins to older people, as well as to people who drink alcohol or smoke. Folic acid is often prescribed in preparation for or during pregnancy, as it promotes the proper development of the fetus. In addition, it is recommended to take B complex vitamins in the form of medications in the following cases:
- to accelerate wound healing;
- with stomatitis;
- to improve the physical fitness of athletes;
- under stress;
- for anxiety conditions;
- as part of complex therapy for vitiligo;
- to relieve symptoms of premenstrual syndrome;
- for hyperactivity and attention deficit disorder[1];
- for relief of acute pain syndrome[13].
Currently, B vitamins can be purchased in pharmacies both individually and as a complex. Most often, multivitamins come in tablet form. As a rule, such vitamins are taken in courses, on average for one month. Separately, B vitamins can be found in the form of injections (intravenous and intramuscular) - they are prescribed to improve and speed up the absorption of substances - and capsules.
The use of B vitamins in folk medicine
Traditional doctors, as in traditional medicine, recognize the importance of vitamins B complex in the processes of energy production, general health of the body, as well as the health of skin, hair and nails. Ointments containing B vitamins (especially B6) are recommended for eczema. Rubs with vitamins B1, B2 and B6 are used for arthritis. There are also folk recipes for treating anemia using foods containing high amounts of vitamin B12. An extract from calf liver, which contains a lot of vitamins, and the amount of fat and cholesterol is minimal, is considered especially useful[14].
Latest Scientific Research on B Vitamins
- Scientists from the University of Adelaide, Australia, have found that taking vitamin B6 can help people remember their dreams. The study, published online, included 100 participants in Australia who took a high-vitamin B supplement before bed for five consecutive days. Vitamin B6 had no effect on dream vividness, bizarreness, or color, among other aspects. Some participants took a placebo drug, while the rest took 240 mg of vitamin B6 immediately before bed. Many subjects who previously rarely remembered their dreams admitted that after taking the vitamin it was easier for them to remember what they dreamed. However, study leaders caution that long-term use of such doses of pyridoxine should be under the supervision of a physician.[15]
- A recent report published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society examines a case of misdiagnosis due to the use of a biotin supplement known as vitamin B7. The patient took 5000 mcg of biotin daily, which led to flawed clinical trials, unnecessary radiography, tests and almost resulted in a complex invasive procedure, which is prescribed for hypercoagulability. This is because doctors suspected the patient had hypercortisolemia or a testosterone-producing tumor. As it turned out, the primary symptoms were caused by excessive consumption of biotin, which is traditionally considered a vitamin that improves the condition of skin, hair and nails[16].
- A review article published in the Journal of the American Institute of Cardiology hypothesizes that taking vitamin supplements has no benefit in preventing or treating heart disease. The researchers found that data on the four most commonly used supplements—multivitamins, vitamin D, calcium, and vitamin C—showed no benefit in preventing cardiovascular disease, heart attack, or stroke, and there were no changes in mortality rates from all of the above. . The only exceptions were folic acid and multivitamins B, in which folic acid was an ingredient. Vitamin B9 has been shown to reduce the risk of stroke. At the same time, niacin (vitamin B3) and antioxidants have been associated with an increased risk of mortality from heart disease[17].
The use of B vitamins in cosmetology
We can say without a doubt that B vitamins are vital for the beauty and health of hair, skin and nails. That is why there are many recipes for masks, decoctions, lotions - both with natural ingredients and with the addition of pharmacy vitamins.
Hair masks containing B vitamins are most often positioned as strengthening, restoring and improving pigmentation. The most beneficial and commonly used natural foods that contain vitamins are raw egg and aloe vera juice. Various oils, honey and herbal infusions are added to them. This produces a mixture of substances necessary for hair (vitamins B, A and E), which has antiseptic, antioxidant and conditioning properties. Such compositions, for example, are a mixture of egg yolk, burdock oil, honey and aloe juice. In addition, you can safely use pharmacy B vitamins in ampoules, adding them to vegetable oil and mixing with decoctions, for example, chamomile or nettle. The most effective pharmaceutical vitamins for hair are vitamins B1, B3, B6 and B12.
B vitamins are essential for the beauty and health of the skin. They have restorative and antioxidant properties. In addition, in combination with other components, they provide additional benefits as an anti-aging, protective, moisturizing and antibacterial agent. Products used in face masks are egg, banana, spinach, almonds, oatmeal, avocado.
- An effective recipe against acne is a mask containing a pinch of sea salt, a pinch of turmeric, a teaspoon of honey, natural yogurt and half a mashed banana.
- For oily skin, we recommend a mask with 1 teaspoon of aloe vera juice, 1 teaspoon of chamomile infusion, half a teaspoon of lemon or apple cider vinegar, half a mashed banana and 1 teaspoon of starch.
- A homemade scrub can be made with 1 teaspoon honey, 1 teaspoon oatmeal, a pinch of salt, a pinch of brown sugar, 1 teaspoon avocado or almond oil, and 1 teaspoon kiwi, pineapple, or papaya puree.
- For aging skin, an antioxidant mask with 1 teaspoon argan oil, 1 teaspoon honey, guava puree, 1 teaspoon sunflower oil and 1 teaspoon ground almonds may be suitable.
Biotin, vitamins B6 and B12 are very important for healthy nails. It is recommended to use almond and avocado oil to strengthen the nail plate.
Do not forget that beauty comes first from the inside, and the most important thing is to ensure access to all vitamins and minerals from food. A healthy body, which contains enough necessary substances, looks beautiful and well-groomed.
The use of B vitamins in animal husbandry
Just like for human health, B vitamins are vital for animals. They ensure the normal functioning of the nervous and immune systems, growth and development, energy production, metabolism in cells and organs, as well as healthy appetite and digestion of the animal. All vitamins of the group are irreplaceably important, so it is necessary to ensure access of the entire complex to the body. As a rule, industrial animal feeds are artificially fortified with vitamins and minerals. Particular attention should be paid to the presence of thiamine in the feed, since it is more susceptible to destruction[18].
Use of B vitamins in crop production
There are several vitamins that act as plant biostimulants, but the most popular are B1, B2, B3 and B6 due to their positive effects on plant metabolism. Many microorganisms produce B-vitamins as natural byproducts, but yeast extracts contain the highest concentrations. B-vitamins work at the cellular level and are commonly found as additives in cloning gels and cloning solutions, mineral brine, and most commercial plant biostimulants.
One of the best uses for B vitamins is to help plants recover after transplanting. When a plant is transplanted, the microscopic root hairs are often damaged, making it difficult for the plant to receive enough water and minerals. Adding B-vitamins to irrigation water gives plants the boost they need. B-vitamins are also beneficial when transplanting from soil to hydroponics. To do this, before transplanting, the plant is immersed in water enriched with B vitamins[19].
Interesting facts about B vitamins
- Royal jelly contains a fairly complete complex of B vitamins to the point that it can be taken in the same way as dietary supplements.
- Thiamine deficiency usually occurs in countries where white rice is the staple food. In Western countries, it is most often caused by excessive alcohol consumption or a very unbalanced diet.
- Excessive consumption of raw egg whites, such as by bodybuilders, can interfere with biotin absorption and cause biotin deficiency.
- Research shows that people with low folic acid levels are more likely to experience hearing loss after age 50.
Dangerous properties of B vitamins, their contraindications and warnings
A deficiency of each of the vitamins of the complex manifests itself in the form of certain symptoms; in each individual case they may differ. And only a doctor, after conducting special studies, will be able to tell whether you have a deficiency of a particular vitamin. However, there are the most common symptoms of B vitamin deficiency, including:
- nervous disorders;
- visual disturbances, conjunctivitis;
- inflammation of the tongue, skin, lips;
- dermatitis;
- anemia;
- depression, anxiety, increased fatigue;
- confusion;
- hair loss;
- sleep disturbance;
- slow wound healing[20].
In many cases, large doses of water-soluble vitamins can be taken without side effects because excess amounts are easily eliminated from the body. However, if you take more than 500 mg of niacin daily, you may develop liver inflammation. Niacin can also cause difficulty controlling blood sugar levels in diabetics and can also increase uric acid levels, which can make gout worse. In addition, excess niacin increases the secretion of gastric juice and lowers blood pressure. However, the form of niacin known as inositol hexaniacinate generally does not cause these effects.
High doses of pyridoxine can cause liver inflammation or permanent nerve damage.
High doses of vitamin B2 can cause urine color to change; this is a normal side effect and does not pose a risk to the body.
In general, B vitamins are not toxic, and no severe side effects have been reported when the daily intake is exceeded. However, any vitamin preparations should be taken with caution and consult with your doctor about contraindications and interactions with other medications[7].
Editor of the “Nutrients” section Lyudmila Malakhova, © Food+
Discuss
Daily norm
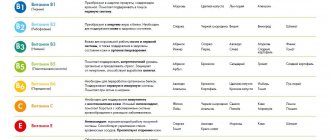
Based on the considered role of B vitamins, we can conclude that these substances support the stable functioning of the body. Throughout his life, if a person wants to remain healthy, he must ensure a sufficient supply of the vitamins discussed. A table containing data on the required daily intake of vitamin B in the diet from birth to old age will help with this.
It is important to note that the body, under the toxic effects of heavy metals, nicotine and alcohol, needs to increase the norm of vitamin B1 to 5 mg. This also applies to cases where a person has been exposed to stress for a long time.
If you have an incorrect diet, when carbohydrates predominate in the food and alcohol is often consumed, it is also better to increase the dose of vitamin B1. On the contrary, it is necessary to reduce the norm of this element if you are a fan of fatty or protein foods.
It is always necessary to meet the daily requirement of vitamin B, because its deficiency, as well as its excess, in the diet entails problems in the functioning of important organs.
Vitamin B1
Thiamine is found in many foods and can be produced independently in the intestines. If a person includes a large amount of carbohydrates in his menu, does not watch his diet, or periodically drinks alcohol and loves coffee, he simply needs vitamin B1.
Why does the body need this valuable element? Its deficiency immediately manifests itself in the form of lethargy, gradually developing into chronic fatigue. Thiamine plays an important role in almost all metabolic processes. It promotes the proper absorption of amino acids, lipids and proteins, thereby providing all cells of the body with adequate nutrition and filling it with energy.
Its deficiency is acutely manifested in the form of disruption of the heart and gastrointestinal tract. Protein compounds are less easily absorbed by the body, resulting in poor breakdown of amino acids and carbohydrates. All this clearly manifests itself externally, and doctors attribute the following to the main reasons for the presence of such a deficiency:
- a monotonous menu in which the amount of carbohydrates significantly exceeds the content of proteins and fats;
- consumption of large quantities of easily digestible carbohydrates, including baked goods made from processed flour;
- abuse of products with thiaminase, alcohol, coffee.
In food
It is possible to replenish your supply of B vitamins with certain foods. Knowing the daily requirement of a certain vitamin and the foods that contain it, it is not difficult to improve your health, and at the same time eat deliciously. The second table contains food products for each considered category of elements in group B.
IMPORTANT: By subjecting food to heat treatment, boiling, and refining, we force B vitamins to lose their beneficial properties or be completely destroyed. And under the influence of alcohol, coffee, tobacco, citric acid, citric acid and products containing them, thiamine almost completely loses its ability to be absorbed into the body.
Vitamin B3
Nicotinic acid helps in proper absorption of nutrients. It plays an important role in cholesterol metabolism and carbohydrate metabolism. In case of sleep disturbances, irritability, lethargy and bad mood, a mandatory intake of vitamin B is indicated. Why the body needs niacin becomes clear when the first signs of its deficiency appear, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- memory impairment;
- excessive dry skin;
- muscle weakness;
- fatigue;
- pale skin.
Vegetarians have to consume additional vitamin PP in the form of biological supplements. Every medical professional knows why the body needs this element. Its long-term deficiency leads to the development of severe, almost irreversible consequences in the form of serious disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, digestive organs and skin lesions. In some cases, pellagra may develop, and in the absence of proper treatment, mental disorders cannot be ruled out.
Shortage
But more often than not, what we eat now is not beneficial to our health. People living in big cities suffer from vitamin deficiency. Mired in the bustle of offices, in eternal problems, they live on the run and, as a rule, eat food that is not entirely healthy on the run. And then suddenly they notice that not everything is going smoothly with their health.
B vitamins are insidious due to their long silence about their deficiency. This group does not have the habit of “making reserves” in the body and you always need to be on guard with them. A lack of vitamins can manifest itself in various ailments.
A person especially needs vitamins during extreme physical exertion, stress, and during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
It is very important to provide children with vitamins, thereby protecting them from infections and negative environmental influences.
Elderly people, whose impaired metabolic process leads to vitamin deficiency or hypovitaminosis, should not forget about vitamins. Due to age-related cellular changes, absorption and utilization disorders, they cause vitamin deficiency even when all daily norms are met.
Victims of preset beauty standards—dieters—are also at risk.
In addition, many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract interfere with proper digestion, and, as a result, the full absorption of vitamins, even from foods rich in them.
It is possible to prevent a lack of B vitamins if you carefully monitor the alarm signals that the body sends. Each representative of this group has special calls.
Vitamin B1 deficiency
Dietary monotony, preference for eating wholemeal bread, abuse of refined carbohydrate-rich, sweet foods, and alcohol are the reasons for the lack of vitamin B1 in the body. Following this, a harmless disease called beriberi may develop, which has the following symptoms:
- the appearance of neurasthenicity, migraine, dulling of memory, development of peripheral polyneuritis and even paralysis;
- the presence of heart pain, shortness of breath, heart rhythm disturbances, swelling of certain parts of the body;
- the presence of constipation (constipation), nausea, pain in the gastrointestinal area.
Thiamine deficiency causes malfunctions in the following components of the body:
- Central nervous system: impaired coordination, brain function, the appearance of depression, irritability, a feeling of lethargy, decreased memory, exhaustion and muscle weakness appear, burning and “cottoniness” of the limbs, decreased pain threshold;
- Gastrointestinal tract: a person suffers from diarrhea and constipation, loses weight, the liver increases in size;
- SHF: the presence of shortness of breath with weak physical activity, swelling of the extremities, tachycardia, decreased systolic pressure, and, as a consequence, acute vascular and heart failure.
Riboflavin deficiency manifests itself if:
- The lips and oral cavity become inflamed, the tongue becomes red and swollen, the corners of the mouth ulcerate and crack;
- Dermatitis rashes on the skin begin;
- The cornea of the eye and the mucous membrane of the eyelids become inflamed, lacrimation, burning, photophobia are noted, and with the onset of twilight, vision decreases;
- Loss of appetite, decreases vitality, and headaches.
If a person has gastritis, a diseased intestine or liver, eye and skin diseases, or anemia, it is imperative to increase the level of vitamin B2. Its excess does not threaten toxic manifestations, since the gastrointestinal mucosa is not able to absorb dangerous amounts of the vitamin.
Lack of niacin
A person is deficient in vitamin B3 if he feels tired and weak, suffers from insomnia and poor memory. Such people, as a rule, have perverted taste, a painful tongue, dry skin, pale cheeks, lips and hands.
Chronic malnutrition and a monotonous diet can cause a lack of nicotinic acid and lead to the appearance of pellagra. With this pathology, the gastrointestinal tract, skin, and central nervous system are severely affected, and mental disorders can begin.
Diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, ulcers, cholecystitis, gastritis, rheumatism are accompanied by a lack of vitamin B3.
You should be careful with excessive doses of nicotinic acid, since in addition to facial redness and vasodilation, liver damage can be caused.
B5 deficiency
Fortunately, it occurs infrequently and is accompanied by weakness, poor sleep, disrupted metabolic processes, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, blood vessels and nervous system.
Lack of vitamin B6
Has a negative effect on the central nervous system. Polyneuritis, drowsiness and irritability may begin. The skin and mucous membranes are often damaged, and childhood anemia is noted. In adults, neuritis, dermatitis and digestive disorders begin.
Those at risk for these diseases and symptoms include:
- bottle-fed children;
- people treated with antibiotics for a long time;
- pregnant women, especially those suffering from toxicosis;
- fans of hormonal contraceptives;
- persons with unhealthy liver, patients with atherosclerosis and polyarthritis.
You need to be interested in vitamin B6 wisely: in large doses it is toxic and causes nervous disorders.
Biotin deficiency
If a person frequently eats raw eggs, this may interfere with the absorption of vitamin B7, resulting in the following unpleasant symptoms:
- The skin will become inflamed, the skin will begin to peel, and it will turn gray;
- Nails will become brittle and hair weak;
- Skin sensitivity will worsen;
- There may be nausea;
- Anemia and cholesterolemia will begin to appear.
Vitamin B9 deficiency
Deficiency of vitamin B9 is also dangerous, leading to gastrointestinal diseases (which can be recognized by the following symptoms) and hematopoietic diseases. A lack of folic acid is very dangerous for fertile women. It leads to fetal deformities and mental disorders of newborns.
Excess B9 can cause toxic effects, primarily in epilepsy. It is not recommended to take folacin for a long time.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Available if a person has a decreased appetite, suffers from stomach pain, constipation, and weakness. Also included in this group are patients with stomach and intestinal problems. As a result of a severe lack of this vitamin, pernicious anemia and mental disorders begin to develop.
An excess of vitamin has no toxic effects on the body.
IMPORTANT: The insidiousness of vitamin B deficiency is that the need for one of its elements disrupts the entire integrity of this team in the body. Acting in combination, elements of group B are indispensable individually. Each has its own mission, each is responsible for important processes of the body.
Vitamin B2
Riboflavin is responsible for the quality condition of hair, skin, nails, the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and reproductive organs; thanks to its presence, the required number of red blood cells is produced, the microflora is normalized and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is improved.
With improper storage, excessive heat treatment and freezing and thawing of food, almost all vitamin B2 is destroyed. Why does the body need riboflavin? Its daily requirement is only two milligrams, and insufficient consumption of this element over a long period of time leads to the development of the following symptoms:
- the appearance of cracks in the corners of the mouth and swelling of the tongue;
- constant fatigue, decreased performance, and in children, stunted growth;
- pain and burning in the eyes, blurred vision;
- loss of appetite, headaches;
- Dermatitis appears on the face, neck and chest.
Riboflavin is required by the body every day, and it should be consumed with natural fresh foods, which must be included in the mandatory menu. The most properly absorbed vitamin B2 is found in cottage cheese, cheeses, yoghurts and milk; there is a lot of it in liver, eggs, fish, beef and pork. Add leafy greens, grains, tomatoes and cabbage to your diet.
Medicines containing B vitamins
An attentive eye will notice even unobtrusive signs of B-vitamin deficiency. After this, you need to get involved in the fight against hypovitaminosis.
Of course, it will be most useful to get a source of B group from certain foods, but this is not the fastest and most convenient way. Besides, where can we now find products that would retain all the vitamins after going through the stage of modern methods of growing, storing and cooking?
Fortunately, pharmacology provides a great opportunity to enrich the body with these missing elements. In any pharmacy it is not difficult to buy the entire complex of B vitamins, which take into account a variety of indications for use.
The most popular drug names are presented in the table below.
More detailed information about these vitamin complexes is indicated in the instructions for them.
There are also now many different complexes, including vitamin B-group, for pregnant women. Vitrum Prenatal, Materna, Pregnavit, Elevit Prenatal and other similar drugs will help expectant mothers consume the required amount of these beneficial elements during the day.
For children, a range of B-vitamins is provided in tablets, syrups and drops: Adivit, Alphabet – Our Baby, Multi-Tabs, Pikovit and many others.
But, always keep in mind that even if you know all your diseases and symptoms, you should not self-medicate. The doctor will give more precise instructions on the use of the vitamin complex and, if necessary, prescribe tests to detect allergies to vitamins.
Vitamin B5
Panthenol is necessary for energy production. It promotes the proper breakdown of proteins and carbohydrates, participates in the biosynthesis of antibodies and neurotransmitters, thanks to it the correct formation of the adrenal hormone and high-quality tissue regeneration occur. This vitamin B is produced in small quantities in the intestines and is found in a wide variety of foods. Why the body needs panthenol can be understood if we consider the symptoms of its deficiency in the body. The doctor will definitely prescribe calcium pantothenate if the patient has the following complaints:
- identifying various metabolic disorders;
- frequent nervous excitability and poor sleep;
- fatigue that persists for a long time;
- lethargy, depression, pain in muscles and lower extremities.
To make up for the lack of energy and not resort to treatment with medications, it is enough to replenish your diet with meat, liver, offal, eggs and fish. Be sure to include a small amount of dairy and fermented milk products, fruits, herbs, nuts and legumes in your daily menu.
Overdose of vitamin PP (B3)
An overdose of vitamin B3 is extremely dangerous, although it is well excreted in the urine. If the daily dose is 1 gram, headaches, tinnitus, and increased sweating may occur. A dose of 3 grams is even more dangerous and can cause jaundice and other liver diseases. An overdose is very dangerous if you have asthma, since the vitamin promotes the release of histamine.
An overdose can even trigger gout, as niacin increases the concentration of uric acid.
Why should you give preference to vitamin complexes?
In many cases, you have to make a decision: use individual vitamins or choose vitamin complexes? To maintain optimal health, you need to purchase supplements that contain several valuable components.
Even food products contain several vitamins at the same time. That is, the human body receives a full set of valuable substances, as if “in bulk.” And if nature provides for this, then the level of vitamins should be artificially maintained in a similar way.
As for water-soluble compounds, they are also recommended to be used in combination. Pharmacists today offer various vitamin supplements, which include several B vitamins at once. This will allow you to get rid of hypovitaminosis, working “in different directions.” Vitamin complexes have an ideal dosage, they are convenient to take, and instructions for use are provided with each drug.
List of foods rich in vitamin E
Microelement E is an activator of the reproductive functions of living organisms, so its presence in the diet is mandatory. It helps to increase the body's protective functions, improve the reproductive and endocrine systems, and slows down the aging process.
To replenish your daily dose, you need to know which foods contain vitamin E.
Foods rich in vitamin E:
- Vegetables and fruits: carrots, potatoes, cucumbers, radishes, apples;
- Legumes: beans and peas;
- Almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, pistachios, cashews and peanuts;
- Meat: beef;
- Fish (pike perch, salmon, eel, mackerel);
- Spinach, sorrel;
- Barley, oatmeal, wheat;
- Prunes, dried apricots;
- Rose hip;
- Sea buckthorn.
If you regularly include component E in your diet, your body will be saturated with useful substances. It will begin to affect muscle activation, help improve the immune system and slow down the aging process.
Contraindications to the use of vitamin PP (B3)
First of all, additional administration of nicotinic acid is not recommended under the age of 2 years, unless it concerns the treatment of a specific disease. Contraindications also include:
- hemorrhage;
- exacerbation of ulcers;
- glaucoma;
- gout;
- low pressure.
Long-term, and even more so uncontrolled, intake of vitamin B3 can cause the development of arrhythmia. A person may experience periodic hot flashes in the face and upper torso, manifested by redness. Dizziness and diarrhea may occur.
If it is necessary to use vitamin PP for a long time and in large quantities, the diet should be adjusted towards the consumption of cottage cheese, and the use of lipotropic agents. Treatment with drugs containing this substance should be carried out against the background of constant monitoring of the condition of the liver.
Signs of vitamin PP (B3) deficiency
The most characteristic signs of vitamin PP deficiency include:
- frequent dizziness;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- problems with the digestive tract;
- all kinds of wounds and ulcers in the oral cavity;
- muscle weakness.
The deficiency also affects fatigue, the person becomes irritable, and often becomes depressed. He suffers from headaches and even insomnia. In extreme cases, if steps are not taken to correct the deficiency, dementia and even pellagra can develop.
Vitamin B7
This vitamin B is of great importance in the regulation of metabolic processes. Let us consider why this element is needed in the body using the example of its obvious deficiency, which is manifested by the following striking symptoms:
- the appearance of severe seborrhea, significant deterioration in appearance, fragility and greasiness of hair, itching of the scalp;
- nervous system disorders, persistent depression, sleep disturbances, periodic outbursts of aggression;
- complete indifference to food, fatigue, lethargy;
- significant increase in blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Such symptoms can be easily eliminated with a properly balanced diet. Why is vitamin B7 needed in the body and what does it contain?
Biotin helps lift your mood, promote proper energy production and improve overall functioning. There is a lot of it in bananas, brewer's yeast, nuts, green peas and rice. The mandatory diet should include meat, fish, liver and eggs.
Vitamin B6
Pyridoxine is mostly produced by the body independently. A common cause of hypovitaminosis is treatment including antibiotic therapy. Vitamin B6 is destroyed for the most part under the influence of sunlight and during the heat treatment of foods. Why does the body need this water-soluble element?
It is responsible for regulating most metabolic processes, allowing cells to properly absorb all useful substances. Its daily intake in the correct quantities helps normalize cardiac activity and blood pressure levels. Pyridoxine strengthens the immune system, improves mood, participating in the production of serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine. Vitamin B6 makes the skin more elastic and nails strong, and is responsible for a person’s emotional state, mental and physical performance.