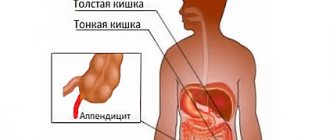
Appendicitis during pregnancy is the most common pathology in the field of surgery. A characteristic feature of the disease is that bearing a child is often the root cause of inflammation. This is explained by an increase in the size of the uterus and the growth of the fetus, which leads to displacement of the internal organs and the appendix in particular.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
- Prevention
The causes of this disorder in pregnant women are practically no different from the predisposing factors of this disease in other people.
Specific clinical manifestations of inflammation of the cecal appendage, for example, pain in the right iliac region, nausea and vomiting, as well as an increase in body temperature, are often mistaken by patients for pregnancy.
Diagnosis requires an integrated approach, and treatment consists of surgery. The danger of such a disease is that it develops quite quickly and in a few days can lead to serious consequences that are dangerous both for the life of the expectant mother and for the unborn baby.
Etiology
In gastroenterology, there are several theories regarding the formation of appendicitis in pregnant women. Mechanical – based on the fact that the development of the inflammatory process occurs against the background of blockage of the lumen of the appendix. The cause of obstruction may be:
- fecal stones;
- hyperplasia;
- helminthic infestations;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the appendix;
- malignant or benign neoplasms;
- foreign objects, for example, grape seeds, sunflower seed husks, a small button, etc.;
- atypical location of the appendix;
- parasites.
All of the above factors lead to the fact that a large amount of mucus begins to accumulate in the cavity of the appendage, which entails the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Infectious theory - defines appendicitis as a secondary disease, which, in most cases, can develop against the background of the following disorders:
- typhoid fever;
- amoebiosis;
- tuberculosis;
- yersiniosis.
The vascular theory of inflammation is less common among clinicians. She claims that a disease such as vasculitis very often leads to the development of such an illness.
The last theory, endocrine, suggests the occurrence of appendicitis against the background of increased production of the hormone serotonin, which can become a source of inflammation in the appendage of the cecum.
It is these reasons that make up the group of fundamental factors in the formation of the disease. It is worth noting that the likelihood of inflammation in pregnant women is several times higher than in other women. This disease often worries expectant mothers in the first trimester, but occurs at any stage.
In addition, there are several specific factors that can cause the development of such a pathology in a pregnant woman. These include:
- tendency to constipation. It is no secret that one of the manifestations of pregnancy is bowel dysfunction;
- a decrease in the immune system, which occurs against the background of changes in hormonal levels;
- poor nutrition or irregular diet;
- changes in blood composition, which can lead to the formation of blood clots that can block the lumen of the appendage;
- an increase in the size of the uterus and active growth of the fetus. In this case, tension, compression and bending of the appendix occurs, which disrupts its blood supply.
Can there be appendicitis during pregnancy?
Expectant mothers are at risk for the following causes of the disease:
- The uterus, which is constantly increasing in size, puts pressure on the abdominal organs, displacing them from their usual place. In this condition, blood flow is disrupted, which causes an inflammatory process to develop in the appendix.
- Hormonal changes in a woman’s body lead to disruption of the digestive process, causing constipation. Hardened stool is difficult to move through the intestines and can clog the appendix, causing inflammation in it.
Classification
Depending on the nature of the course and expression of symptoms, several forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute appendicitis in pregnant women - the pathological process goes through several stages. The period of transition of the disease from the simplest to the most complicated degree is three days. At the same time, there is an increase in the intensity of symptoms;
- Chronic appendicitis is rare for the average person, but is more common among the fairer sex during pregnancy. Characterized by a predominance of pain and nausea.
The acute course of the inflammatory process is divided into several types:
- catarrhal - in this case, there is an increase in the size of the appendage and its swelling. From the emergence of a simple form to the development of destructive ones, six to twelve hours pass;
- destructive.
Classification of acute appendicitis
Destructive forms of appendicitis are divided into:
- phlegmonous - in this case, purulent contents penetrate through all layers of the appendix;
- gangrenous – characterized by necrosis of the walls of the appendage;
- perforative - characterized by rupture of the appendix and the development of perforation, i.e., a hole in the wall of the appendix. It is at this stage that complications develop that threaten the lives of not only the mother, but also the child.
Often appendicitis during pregnancy takes a chronic course, which is also divided into several forms:
- residual or residual - an acute attack goes away on its own;
- recurrent – expressed in alternating periods of exacerbation and remission;
- primary chronic – characterized by a slow course without exacerbations.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestation of such a disease may differ slightly depending on at what stage of pregnancy the disease begins to manifest itself.
In the first trimester and the beginning of the second, the external manifestations of inflammation of the appendix will be almost the same as in non-pregnant women. The main features are:
- pain syndrome, which at first does not have a clear localization, after which it moves to the navel area and over time is localized in the right iliac zone;
- nausea with single or double vomiting;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- increased heart rate;
- the appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- dry mouth.
Significant deterioration of the condition occurs when the disease passes into destructive forms. In such cases, the symptoms of appendicitis during pregnancy will be as follows:
- increased manifestation of pain;
- signs of intoxication of the body;
- decreased or complete loss of appetite;
- increased vomiting;
- pallor of the skin with the appearance of an unhealthy blush on the cheeks;
- temperature rise to 39 degrees.
In the second half of pregnancy, due to the enlargement of the uterus and fetus, the location of the appendix changes. This reduces the likelihood of complications such as peritonitis, but there is a risk that the inflammatory process may spread to the uterus or fetus.
The main clinical manifestations of appendicitis in late pregnancy are:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- increased signs of intoxication;
- severe pain in the right hypochondrium;
- frequent urge to urinate.
The longer the pregnancy, the more difficult it is to diagnose such a disease.
Features of surgical intervention
The most important question for patients in such a situation is: how will they operate (open access or laparoscopically)? And what to do with pregnancy?
Before the 20th week of pregnancy, a woman can be operated on using a laparoscopic technique. However, at a later date it is very problematic to do this, since the large uterus prevents full access of instruments to the appendix.
Thus, in the second half of gestation it is preferable to use the open method.
The issue of pregnancy and its further “fate” must be approached individually:
- If acute appendicitis occurs before the 37th week, then it is necessary to maintain the pregnancy.
- If an attack of appendicitis occurs after the 37th week, the woman can be delivered by cesarean section.
Diagnostics
Establishing a correct diagnosis during the period of bearing a child is difficult due to several factors, for example, displacement of the appendix, which entails the manifestation of uncharacteristic symptoms, or the chronic course of such a disease, which may have an asymptomatic course.
Primary diagnosis includes:
- detailed interview with the patient;
- the doctor’s examination of the patient’s medical history and life history;
- performing a physical examination with mandatory palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity and measuring temperature;
- gynecological examination - the hallmark of such a disease is that such an examination brings pain.
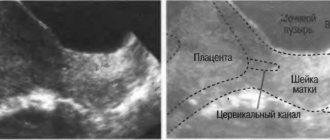
Diagnosis of appendicitis during pregnancy
This will enable the clinician to establish the causes of inflammation, and, based on the first time of manifestation and severity of signs of appendicitis, to determine the form of the disease.
Laboratory tests consist of:
- clinical blood test - which will show an increased level of leukocytes and ESR;
- general urinalysis - it will contain red blood cells and leukocytes. Which indicate the occurrence of a pathological process, because normally they should not be in the urine;
- blood biochemistry – aimed at identifying complications and acute phase indicators;
- microscopic examination of feces.
During the period of bearing a child, women are prohibited from performing almost all instrumental diagnostic measures. Permitted ones include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - indicates an increase in the volume of the appendix;
- Diagnostic laparoscopy is the most informative method of establishing the correct diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis of appendicitis in pregnant women is carried out with:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- threat of miscarriage;
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum or stomach;
- cystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- urolithiasis;
- intestinal colic;
- intestinal obstruction;
- gestosis;
- housing and communal services;
- oncological process;
- torsion of ovarian cyst;
- gynecological diseases.
In addition, you may need to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Treatment
The manifestation of symptoms of appendicitis is an indication for surgical intervention, especially in pregnant women.
An attack of appendicitis often begins at home, and it is necessary to call an ambulance. While waiting for doctors, some patients try to independently reduce the manifestations of the clinical picture and often use prohibited methods, namely:
- apply a heating pad to the location of pain;
- massage the stomach;
- take painkillers, which makes diagnosing the disease even more difficult;
- give enemas;
- drink laxatives;
- eat;
- Traditional medicine recipes are used.
Before the doctors arrive, you need to take a horizontal position, which will reduce pain, and drink cool drinks, but not carbonated ones.
There are several ways to perform surgery to remove an inflamed appendix - appendectomy:
- classic - through a large incision on the stomach;
- laparoscopic - through several small punctures on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
The second method is more preferable for pregnant women.
Laparoscopic appendectomy during pregnancy
In the postoperative period it is shown:
- follow a diet - the rules of which coincide with the diet of other patients;
- take medications to prevent premature labor and complications. Antispasmodics and antibiotics are prescribed;
- physiotherapy.
How is appendicitis treated during pregnancy - can a pregnant woman have surgery for appendicitis?
The only way to cure appendicitis is to remove it. For pregnant women, the same method is used - laparoscopy or open intervention . Even before the operation, the woman is given antibiotic therapy, which helps to minimize the occurrence of postoperative complications and diseases.
During pregnancy, the most gentle operations are performed - therefore, if possible, then laparoscopy is used, since patients tolerate it more easily, there are fewer complications, and this is very important during gestation.
It is also possible to perform epidural anesthesia during such an operation, so less harm is done to the baby.
When the appendix is located in an inconvenient place, or the clinic does not have the necessary equipment, the appendix is removed as usual, performing a classic operation. The incision is made along the anterior abdominal wall at different levels - this depends on the stage of pregnancy.
Complications
In cases of ignoring symptoms, chronic appendicitis and refusal of surgical treatment, there is a high probability of developing the following complications:
- miscarriage;
- peritonitis;
- spread of the inflammatory process;
- anemia;
- trauma to the uterus with surgical instruments;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- premature birth of a baby;
- placental abruption;
- internal hemorrhages.
Sometimes intrauterine fetal death can occur, but this occurs in only 1% of all cases of diagnosing appendicitis in pregnant women.