Rest angina is characterized by sudden pain attacks in the sternum, appearing in the absence of provoking factors. The attack develops at rest, often occurring during a night's rest. The pain in this case is pronounced, characterized by longer duration, shortness of breath, and a feeling of insufficient inspiration. Accompanied by disorders of the nervous and autonomic system, panic. Fear of death. It is a form of coronary heart disease.
Features of the disease
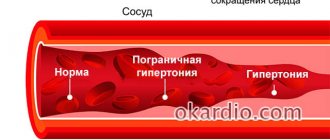
Angina at rest is a clinical form of IHD (coronary heart disease), one of the manifestations of coronary pathology. Other names: postural, decubital angina. It is characterized by attacks of pain and a feeling of chest compression without connection with physical activity, at rest.
In medical practice, angina at rest is classified as an unstable form of the disease, very dangerous and ending in serious consequences. Anginal pain can be of significant severity and duration, accompanied by fear of death and reminiscent of an incipient myocardial infarction.
The disease most often occurs in men after 55 years of age, and is registered less frequently at a young age.
Angina: classification and consequences
Main types of angina
With the advent of new technologies in the medical field, many diseases that were previously considered incurable have become a thing of the past and no longer bother people. But, unfortunately, some diseases, despite everything, were able to persist, and continue to burden the lives of many of us. One of these ailments is angina pectoris, the classification and treatment of which has long been no secret to modern scientists and doctors.
Angina is a heart disease manifested by sharp pain in the chest, often radiating to the neck, shoulder blades, left arm, and solar plexus. The pain lasts for 10-15 minutes, and the cause of the pain is physical activity and emotional stress.
Classification of pathology
The disease belongs to the fourth functional class. There are several separate varieties of it. Here is their description:
- Prinzmetal's angina. The attacks occur cyclically, follow each other, the time interval between them can be any. They usually occur in a series of 2 to 5 at the same time, usually in the morning. The duration of attacks is up to 30 minutes, and they are almost always accompanied by severe arrhythmia. The cause is a sudden spasm of the coronary arteries.
- Post-infarction angina. Begins 14 days or less after myocardial infarction.
Among the cases of angina at rest, spontaneous angina is distinguished, which can occur when changing body position or at night, during sleep. Based on the type of course, there are two forms of the disease:
- Acute - the previous attack was recorded no later than 48 hours ago.
- Subacute - attacks have been observed over the past month.
Young patients often have Prinzmetal angina, which does not carry a high risk of myocardial infarction. Its danger lies elsewhere - the disease provokes severe types of arrhythmia.
First aid and attack relief
Nitroglycerin for relieving angina attacks
The very first rule of providing first aid to a patient with a heart attack is to sit or lay him down and give a nitroglycerin tablet or any other drug under the tongue that can relieve vasoconstriction. Most often, patients are prescribed nitroglycerin, which is taken only sublingually. If, after a few minutes after the patient has taken the tablet, he does not feel relief, then you can repeat the dose and give him another tablet under the tongue. Usually the attack does not last longer than fifteen minutes, if even after 15 minutes the pathological process is not stopped by a nitroglycerin tablet, then you need to immediately call an ambulance. Since this may indicate that a person has developed a myocardial infarction, which already threatens with more serious consequences and even death.
Causes
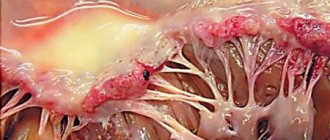
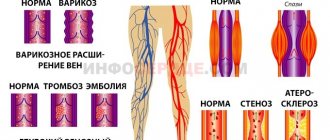
The main cause of rest angina is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. If during angina pectoris cholesterol plaques block a small part of the arteries, this form always implies a more advanced state of the arteries. The size of the plaques is significant, they cause oxygen starvation of the myocardium, its reserves are depleted. Therefore, pain can occur quite often.
As a rule, the disease affects most of the coronary arteries. In addition to atherosclerotic plaques or along with them, the cause of attacks can be:
- vasospasms - associated with a malfunction of the vascular endothelium;
- vascular thrombosis - caused by blood thickening or the movement of blood clots from other arteries and veins (usually from the lower extremities).
Occasionally, the disease develops against the background of other severe heart diseases - cardiosclerosis, cardiomyopathy, congenital and acquired heart defects. For many patients, the problem arises in the early post-infarction period. The following factors accelerate the transition from exertional angina to resting angina:
- diabetes;
- arrhythmias;
- anemia;
- past infections - including myocarditis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- physical inactivity;
- high blood density;
- stress.
The first signs in men and women
The most significant symptom of angina is pain. Duration: from 1-15 minutes (2-5 minutes).
Nature of the pain syndrome: paroxysmal discomfort or pressing, squeezing, deep dull pain; an attack can be described as tightness, heaviness, lack of air.
Localization and irradiation:
- The most typical location is behind the sternum or along the left edge of the sternum.
- irradiation to the neck, lower jaw, teeth, interscapular space, less often to the elbow or wrist joints, mastoid processes.
In addition to pain, symptoms may also include so-called angina equivalents. These include:
- shortness of breath - a feeling of difficulty breathing both when inhaling and exhaling. Shortness of breath occurs due to impaired relaxation of the heart
- severe and sudden fatigue during exercise is a consequence of insufficient oxygen supply to the muscles due to reduced contractility of the heart.
| Signs | |
| Among women | Signs of cardiac angina in women
Women may also experience the following symptoms:
|
| In men | A typical angina attack is often accompanied by the following characteristic symptoms:
|
Symptoms
An attack of the disease usually occurs for no apparent reason, but the person is already familiar with its manifestations. By the time the pathology develops, most patients have been living with coronary artery disease for many years, manifested by exertional angina. But after a heart attack, against the background of other cardiac problems, an attack of severe pain may occur for the first time. This usually provokes panic, fear of death, and the person is afraid to move.
Additional signs:
- severe pallor;
- cold sweat;
- weakness;
- fatigue.
Before an attack, patients almost always experience an increase in blood pressure, both systolic and diastolic. The heartbeat becomes rapid and tachycardia occurs. Typically, manifestations are noted when a person takes a horizontal position, after rest or in the morning, upon awakening. This is due to an increase in venous blood flow in the supine position.
Often the patient wakes up from a feeling of sharp compression in the chest, combined with a lack of air (suffocation). If the onset of an attack occurs during sleep, the person may have nightmares, running quickly, or lifting heavy objects. The cause is a change in the tone of the vagus nerve and the release of special substances - catecholamines.
The pain is localized in the chest, arm or under the shoulder blade, radiating to the jaw. The attack lasts up to 5 – 15 minutes (more with Prinzmetal’s angina). For relief, you have to take up to 3 - 4 tablets of Nitroglycerin.
Main manifestations of the disease in males
If this pathological process in women most often occurs in old age and even old age, then angina pectoris in young men is quite common and common. Young men under thirty years of age are often affected by the disease. This may be due to the fact that it is at this age that men are most exposed to physical activity, play sports more diligently, which can also provoke psycho-emotional overstimulation, which often leads to an attack. The most basic and most striking manifestation of the disease is pain in the chest area, and this pain occurs spontaneously and abruptly. Sometimes pain can spread beyond the sternum to the area of the shoulder blades, forearms, neck, and in some cases, a man may complain of pain in the jaw.
The second most important manifestation of angina in men is a change in the condition of the epigastric region. The patient may feel a sharp pain in the abdomen, nausea, heartburn, and sometimes vomiting. In addition, droplets of cold sweat can be observed on a person’s forehead during an attack; some experience increased sweating throughout the body. There is a pronounced feeling of suffering on the face; the patient may feel numbness in the upper extremities and tingling in the fingertips. Also, during this pathological condition, the pulse quickens, but closer to its end, the pulse returns to normal.
A common occurrence is increased blood pressure with angina pectoris in men; this manifestation will indicate that the disease has developed as a result of excessive physical strain. Due to the fact that the disease occurs in representatives of the stronger half at a fairly early age, doctors recommend listening with particular care to the work of the cardiovascular system. Especially if a young man or a mature man plays sports or his professional activity involves performing a large amount of physical activity, then he should definitely pay attention to periodic pain in the chest area. It is these pain sensations that may indicate the development of angina, which can lead to more serious consequences, such as myocardial infarction or coronary insufficiency.
In order to be able to recognize this pathology, react in a timely manner and undergo the necessary examinations, it is necessary to know all the symptoms of angina pectoris in men, which can appear at any age. The most important thing is that if you are aware and prepared, you will be able to provide timely help to yourself or another person who may be suffering from this disease.
Diagnostics
Typically, diagnostic measures are carried out in a hospital, as they require a serious approach. An ECG reveals the presence of severe stenosis of the coronary arteries, various types of arrhythmia, and conduction disturbances (heart block). In the post-infarction form of the disease, there are most often signs of cardiosclerosis.
The patient is required to undergo echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) and daily ECG monitoring. These types of instrumental studies help to clarify the degree of vascular damage, myocardial function, and detect concomitant diseases.
The diagnostic complex includes the following methods:
- blood biochemistry and lipid profile - to assess the state of lipid metabolism, coagulation, glucose, kidney and liver tests;
- stress tests - to determine the class of the disease (they do not always allow you to determine angina at rest, therefore they are not considered decisive).
The modern examination method is cardiac CT or CT coronary angiography. Often the procedure replaces invasive research (angiography), but is no less informative. A PET scan may be recommended before surgery.
To differentiate cardiac pain from damage to the stomach, esophagus, pleura and intercostal nerves, other instrumental techniques may be prescribed.
Angina is not a sentence, but a signal
The first symptoms of angina pectoris are subtle and pass quickly. That's why people rarely pay attention to them. But you should be more attentive to the signals that the body gives in case of problems. You may need to radically reconsider your lifestyle and diet. Many people do not like to visit doctors, but this is not a solution to the problem, but postponing it for later. And this approach only leads to dire consequences. The appearance of angina is a serious signal to take care of your own health.
Treatment of angina
The treatment algorithm is selected depending on the cause of the disease, concomitant pathologies and severity. Many patients are recommended to undergo surgery; if it is not possible, they take medications.
Therapeutic method
Changing your lifestyle will help slow down the progression of the pathology. It is important to completely give up bad habits and eat right. Animal fats in the diet make up no more than 25 - 30%, cholesterol - up to 300 mg.
The menu must include vegetables and grains in large quantities, the diet should be enriched with bran and fiber. Salt intake is severely limited. For obesity, the diet is selected individually. Be sure to perform a complex of exercise therapy, which will help improve blood supply to the heart.
Medicines
Planned therapy is usually carried out at home; in case of exacerbation, angina pectoris should be treated in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Drugs to reduce blood clots (Aspirin, Clopidogrel). Thin the blood, reduce the risk of heart attack.
- Beta blockers (Betalok, Bisoprolol). Reduces the heart's need for oxygen.
- Statins (Crestor, Simvastatin). Reduces the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
- Antihypertensive drugs (Valz, Enalapril). Bring blood pressure back to normal.
- Nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Trinitrolong). They dilate arteries and relieve acute pain.
Surgery
Almost all patients with angina at rest have indications for surgery. To widen the arteries, stents are inserted into them or inflated with balloons (stenting, balloon angioplasty).
In some cases, only CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting) helps - removing the vessel affected by plaques and creating alternative blood circulation routes.
First aid for pathology
People with resting angina have a very high risk of developing a heart attack, so loved ones should be attentive to attacks that occur. If pain occurs, take one Nitroglycerin tablet every 3 minutes (maximum amount - 5 pieces), which will help restore blood flow. It is better to start taking it at the very beginning of the attack. If there is no improvement within 10 minutes, you should call an ambulance.
Other first aid measures:
- loosen tight clothes;
- open the window for air flow;
- put the person down, don’t let him lie down.
Modern nitrates in sprays (Nitrosprey, Nitromac) work much faster than Nitroglycerin. It's better to buy them in advance and keep them on hand.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made in a hospital setting, since a diagnosis cannot be made using a routine examination. Before determining a patient for hospitalization, he is examined and sounds are listened to.
In the hospital, the examination consists of:
- General examination of blood and urine. This allows you to find out if there are concomitant diseases.
- Biochemical blood test. During which they determine the amount of glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides and other compounds in the blood. Information is necessary to determine the cause of angina.
- Electrocardiography. They determine the state of the ST segment, whether there are any disturbances in heart rhythm and conduction.
- Load tests. The patient should exercise on an exercise bike or treadmill. These methods are rarely used, since their information content is not high.
- 24-hour ECG monitoring. It is necessary to identify foci of ischemia.
- Echocardiography. With its help, concomitant pathologies and myocardial contractility are determined.
- Coronary angiography. The procedure allows you to examine the arteries that supply the heart.
- Two-photon emission tomography to determine the location of the ischemic focus.
At the initial stages of the development of the pathological process, differential diagnosis is carried out so as not to confuse angina with pleurisy, ulcers or cancer.
Disease prognosis and prevention
The prognosis is always more serious than with angina pectoris, which is associated with multiple lesions of the coronary arteries. The likelihood of developing a myocardial infarction and death is quite high, but timely treatment reduces it.
To prevent pathology, it is important to prevent obesity and eat right, practice moderate physical activity and exercise therapy. We must forget about smoking forever and give up alcohol.
All diseases should be treated in time and risk factors that can cause resting angina should be eliminated. If you have a hereditary condition, it is worth strengthening the blood vessels in advance and increasing their elasticity with the help of special medications.
Therapy
Angina at rest involves treatment in a hospital setting. To eliminate the problem, therapeutic and medicinal methods are combined. The patient may not be hospitalized, but only on the condition that his condition will be constantly monitored.
The patient must immediately make adjustments to their usual lifestyle. It is important to avoid bad habits and adhere to the principles of proper nutrition. You also need to ensure yourself an optimal level of physical activity.
During the treatment process, it is desirable to reduce the consumption of animals and saturated fats, foods containing cholesterol, focus on fruits, vegetables, cereals, and reduce salt intake.
If a person is overweight, this problem should be solved. Shock diets should be abandoned. Sports and a healthy diet are good for improving your well-being.
Drug therapy primarily consists of the use of Nitroglycerin. With its help you can eliminate severe pain in the heart. At one time you need to take 0.5 mg. Relief occurs within five minutes.
If the duration of the attack is more than ten minutes, you need to use analgesics, since such a clinical picture may indicate the development of myocardial infarction.
Angina is eliminated using:
- ,Antihypertensive drugs if a person suffers from high blood pressure in the arteries.
- Beta blockers. Under their influence, the need of the heart muscle for oxygen decreases and the frequency of contractions decreases.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. If the initial stage of development of heart failure is observed. Anticoagulants to avoid blockage of blood vessels by a blood clot.
They may also resort to diuretics and immunomodulatory drugs.
Surgical treatment is resorted to if severe heart damage is observed. Elimination of the problem is carried out using:
- Coronary angioplasty. In this case, a metal stent is installed on the affected vessel, thereby improving blood flow through the artery.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery. Using biological material, they create a bypass for blood movement to the heart muscle.
This type of angina leads to severe conditions that cause serious damage to the heart, causing the organ to malfunction. Only transplantation of a healthy organ can save a patient’s life in this situation.