Induction of labor, in what cases is it necessary, risks, types of procedure
Every expectant mother is closely monitored by obstetricians and gynecologists during the prenatal period in order to avoid risks to her health and the life of the baby.
In the practice of specialists, there are many cases of premature birth, or timely (at 39-40 weeks), but with the uterus unprepared for this process. To ensure the safety of the child and mother, it is necessary for her to be fully matured by the time contractions begin. A pregnant woman herself cannot determine this; only specialists can assess the situation through a gynecological examination.
If the uterus does not open in a timely manner to allow the fetus to pass through the birth canal, and the moment of delivery is already close, obstetricians resort to stimulation methods.
Possible problems
From about 37 weeks, a woman’s body begins to actively prepare for the upcoming birth. Many pregnant women by this time, experiencing fear of the upcoming event, fall into panic.
Stress, nervous tension, and insufficient psychological readiness often lead to the fact that the production of hormones necessary for the beginning of the opening is inhibited, which is why the body is forced to delay the date of birth.
Many women wonder: what to do if the cervix does not open? First of all, don't be nervous. Secondly, you need to listen to the doctor and follow all his recommendations.
Often, cervical dilatation does not occur with severe polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
- With polyhydramnios, the uterus stretches too much, which significantly reduces its natural contractility and leads to weakness in labor as a whole.
- With oligohydramnios, the amniotic sac cannot exert the necessary pressure on the cervix for its proper full dilatation, and this also causes weakness in labor.
Also, problems with disclosure also occur in women over 35 years of age. In this case, difficulties are associated with a decrease in the elasticity of the tissues of the cervix and vagina.
In addition, difficulties during childbirth due to the fact that the cervix does not open often occur in women with various diseases of the endocrine system, for example, obesity or diabetes, as well as diseases of the genitals.
It often happens that when visiting a doctor before giving birth, a woman hears that the cervix is not yet ready and does not have the required maturity, although the day of birth is already close. This problem is serious in cases where the pregnancy is already full term and exceeds 40 weeks, since during this period the placenta can no longer perform the necessary functions of providing the fetus with nutrition and oxygen, resulting in pregnancy loss.
Stimulation of labor and the onset of dilatation can be carried out using both medicinal and non-medicinal methods.
At the same time, medicinal stimulation using tablets and drugs to dilate the cervix is carried out only in a hospital setting, since such actions can cause rapid labor.
Drug stimulation may include:
- the introduction of special drugs into the cervical canal, which allows you to achieve the desired result in just a few hours;
- insertion of kelp sticks into the cervical canal. Absorbing moisture, seaweed sticks begin to swell, opening the neck mechanically in 4-5 hours. But, in addition, the rods contain endogenous prostaglandins, which stimulate the ripening of the cervix in a biochemical way;
- amniotomy is also a stimulation method and involves puncturing the amniotic sac. After this procedure, the anterior waters are released, and the baby's descending head begins to put additional pressure on the cervix, forcing it to stretch.
To non-drug methods
This includes not only conducting a cleansing enema, which smoothes the posterior uterine wall and causing its contraction, but also sexual intercourse, as well as physical activity.
But you should not use such methods yourself, since the risk of other complications will be very high.
Dilatation of the cervix is the first stage of the birth of a baby, the correctness of which determines the entire birth process, its speed and the occurrence of possible complications.
You should not try to speed up labor on your own and influence the cervix to open it, if this is necessary - you need to entrust such actions to a doctor. It is important to properly tune in to childbirth emotionally and be psychologically prepared for this process, then everything will go much easier and faster.
What is stimulation
Stimulation in the work of obstetricians and gynecologists involves inducing labor using artificial methods for medical reasons, or activating labor directly during the natural process in order to intensify pushing and contractions.
The optimal time for the birth of a baby is 40 weeks of the mother's pregnancy. During this period, examinations by doctors become more frequent to exclude the development of pathologies and risks. The child’s life support is monitored using an ultrasound examination, which makes it clear what condition the fetus is in, how it is located, and size indicators.
Artificial induction of labor is recommended when the baby is small in size or very large (weighs more than 4.5 kilograms). If this does not happen, he will gain weight, which will complicate natural delivery.
Most often, indications for such actions arise in expectant mothers suffering from chronic diseases, with a complicated pregnancy, or the development of pathologies.
Indications and contraindications for labor induction
Induction is considered appropriate when the risk of induction is lower than the risk of prolonging the pregnancy, and there are no contraindications to natural childbirth. Doctors induce labor if there is evidence for it. They can be general, as well as only on the part of the woman or the fetus.
The first includes a gestational age of 41 weeks with obvious signs of postmaturity; severe polyhydramnios; rupture of amniotic fluid with absence of labor; preparatory period with irregular and painful contractions.
On the maternal side, indications for the use of stimulation are severe forms of gestosis, preeclampsia, and diabetes mellitus. It can also be other progressive ailments that threaten a woman’s life. On the part of the fetus, indications for induction are severe malformations, intrauterine growth retardation, hemolytic disease and antenatal death.
A relative indication for labor induction is a presumably large fetus or multiple pregnancy at 37-38 weeks.
There are also contraindications for induction, including a scar on the uterus, a woman’s narrow pelvis, abnormal position of the fetus, complete placenta previa, primary acute disease of genital herpes, the presence of a cervical myomatous node, and severe illnesses of the expectant mother.
The question of the possibility of inducing labor is always considered by obstetricians on an individual basis.
When is stimulation applied?
Stimulation by medical workers in the maternity hospital is used to ensure that a woman’s uterus opens to allow the fetus to come out as quickly as possible, since it is no longer safe for the child to be in the womb and the pregnancy is coming to an end.
This event is implemented by specialists both planned and unscheduled.
As planned
Planning to artificially induce labor occurs if the child has problems with intrauterine development during pregnancy, there are pathologies, or the mother has a painful condition. If a woman is seen by a doctor regularly, this procedure can be planned based on the medical indications for its use.
In case of irregular visits to the gynecologist, but there are reasons for planning stimulation, the woman in labor risks both her health and the life of the child.
Unscheduled
More often in the practice of obstetricians, unplanned artificial delivery occurs. It is used in the following cases:
- if labor does not begin within the prescribed period (the 41st week of pregnancy has begun);
- the woman’s water has broken, but the uterus is not dilated, and the birth process does not begin more than 24 hours after this moment;
- contractions have begun, and the baby cannot leave the womb due to incomplete dilatation of the uterus.
Typically, problematic issues arise with women in labor who do not feel that the baby is ready to come out at 40-41 weeks. This means that the degree of maturity of the cervix has not yet reached the desired state for the natural process.
This difficult moment is dangerous because there are no indications for labor yet, but the condition of the placenta should be assessed, since it may stop performing its functions - delivering nutrients, providing oxygen to the baby’s blood circulation. If this happens, and the internal organs are not yet ready for birth, unscheduled stimulation will be mandatory to save the baby’s life.
Gel for stimulating labor and during childbirth: who needs it?
If the period in which you and your gynecologist were expecting a newborn is already far behind you, and the baby has not yet been born, the doctor will most likely start talking about inducing labor. And when asked how this will happen, you may be offered a gel to induce labor as one of the options. In addition, the doctor can use the same gel not before contractions, but directly during childbirth.
In this article we will explain how the stimulation gel is used and what exactly happens during its use before labor and during childbirth.
Required conditions for stimulation
Stimulation is carried out by specialists if certain conditions are met for this procedure. They are:
- mature state of the cervix;
- necessary and optimal duration of contractions;
- sufficient strength of contractions.
If the dynamics of these indicators are weak, we can talk about possible difficulties during childbirth, since the woman actually does not have enough strength to push the fetus through the birth canal.
Cervical dilatation
This organ of the reproductive system of the expectant mother is responsible for a successful and safe delivery, since the entire process depends on how timely its maturation occurs and the timing of dilation.
In the practice of obstetricians and gynecologists, it is generally accepted that preparation for the rejection of a baby begins around the 32nd week. The uterus begins to soften, this lasts until the 38th week. After which, the fetus descends down the abdomen, it additionally puts pressure on it, naturally stimulating it to open. During this entire period, the expectant mother must be observed by a doctor, who will diagnose how close the onset of labor is in terms of the degree of dilatation.
If the doctor tells a woman that the dilatation is 1 finger, you can think about and evaluate the anticipation of childbirth based on your own feelings. But this state of affairs only signals physiological readiness; subsequent opening begins during contractions.
The optimal state of readiness is considered to be the moment when the cervix has dilated by 3-4 centimeters. Many doctors, when observing pregnant women, rely not on centimeters, but on the size of their fingers.
What week can you start stimulation?
Typically, this measure is resorted to at 40 weeks of pregnancy, since this period is optimal for bearing a child.
Nowadays, the natural process of childbirth is encouraged, excluding the influence of drugs on the condition of the mother and baby. It is not used before 42 weeks, if the woman does not have swelling, the amniotic fluid is light according to ultrasound radiation, and she feels normal.
Stimulation is sometimes used before the specified period, but only for medical reasons, in case of a threat to the life of the fetus or the expectant mother.
Contraindications to the use of stimulation gel
In what cases does the doctor prefer to refuse to use the gel to induce labor?
First of all, if there are certain risks to the health of the mother and fetus:
- development of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) in the fetus;
- development of aspiration syndrome (if there is a risk of the gel getting into the fetal respiratory tract).
The following conditions are contraindications for administering the gel:
- narrow pelvis (anatomical narrowing of the pelvis) in a pregnant woman, namely, a discrepancy between the size of the fetal head and the parameters of the pelvis: this phenomenon is observed in approximately 3% of women;
- if the position of the fetus in the uterus is not normal;
- for cardiac disorders in the fetus;
- if the use of the main components of the gel is dangerous to the health of the expectant mother.
Of course, the doctor will be aware of all these points in advance. Therefore, by the beginning of labor, the obstetrician-gynecologist will already know whether it is possible to use the gel to induce labor in your case.
- Expert
- Latest articles
- Feedback
About the expert: +MAMA
We are the friendliest site for moms and your babies. Questions and answers, unique articles from doctors and writers - we have it all 
- Oligohydramnios during pregnancy -
- A newborn's eye is festering -
- When does the fontanelle close in newborns?
- Nutrition after childbirth -
- Headache during pregnancy -
- How to lose weight after childbirth -
- Second screening during pregnancy -
- Precursors of childbirth in multiparous women -
- How long do newborns sleep?
- How to remove belly fat after childbirth -
See all
Is it safe to induce contractions without dilating the cervix?
Activities that involve stimulation are aimed at opening the cervix, so inducing contractions helps a woman go through the labor process faster than would happen naturally. They are used for medical reasons, if the pregnant woman requires it and the child does not push herself out of the womb.
Inducing contractions if the uterus has not yet opened has its own risks, since this is a surgical intervention in the natural process of birth, but without these actions when it is immature, there is another threat - harm to the fetus or the woman in labor.
How is cervical maturity assessed?
Starting from 38 weeks of pregnancy, during an examination with a gynecologist at a antenatal clinic or in a maternity hospital, the doctor conducts a vaginal examination to assess the condition of the cervix. It is also mandatory to examine the cervix before childbirth, as well as during labor. This is necessary to understand how quickly the process of maturation occurs.
There are four main parameters, by assessing which an obstetrician-gynecologist can conclude that the cervix is ready for childbirth. Its maturity is determined by a special Bishop scale, according to which each of the parameters is assessed on a three-point system (from 0 to 2 points). If this scale is rated 5, then we can talk about readiness for natural childbirth.
Is it possible to induce labor at home?
Many women, when approaching the 40th week, worry that there are no signs of labor in their condition.
Having consulted a doctor, they receive a recommendation to go to an inpatient department to carry out this process in artificial mode. Some women in labor prefer the option of inducing labor without the use of drugs that can have a negative impact on health - at home using light physical activity, food, and other procedures (bathing, massage).
Gymnastics
Moderate physical activity for a pregnant woman under the supervision of a doctor is a good method of inducing contractions, since movements can provoke dilatation of the uterus, which will start the process of natural delivery. Activities that are not contraindicated for women in labor include:
- walking outside (fresh air combined with movement has a beneficial effect on fetal development);
- cleaning at home (you can wash the floor not with a mop, but by hand, squatting);
- if a woman does not live on the 1st floor, climb to the required floor using the stairs in a sideways position;
- yoga has a good effect on the stimulation process by balancing breathing;
- charging in light mode using squats.
A light or moderate load on the body is encouraged; if a pregnant woman overdoes it with exercise, the birth process may be difficult and muscle tension will be present.
Foods that provoke contractions
Nutrition for an expectant mother is one of the important aspects of the well-being and harmonious development of the baby.
She must understand that the products she consumes are beneficial and do not cause harm. The following are considered products that can trigger labor:
- spicy food (it stimulates the intestines, as a result of which the uterus begins to contract and open). You need to be careful with this method and consult a gynecologist about its use (in most cases, women do not tolerate spicy food, as it causes heartburn and unpleasant taste sensations);
- tea that contains raspberry leaves or ginger pulp (not everyone can use it, it is not recommended for women in labor with special features in the structure of the pelvis, as there is a risk of rapid labor);
- pineapple pulp (it contains bromelain, which softens the uterus and prepares it for opening);
- products containing fiber (for example, seaweed) have a relaxing effect.
At home, you cannot use medications to speed up labor; such procedures are carried out only by obstetricians in a hospital setting.
Gel for intimate hygiene
In the practice of doctors, a procedure for introducing a specialized gel into the vagina is often used.
The woman in labor is seated on a gynecological chair, the vagina is filled with gel using a syringe, after which she is left lying down for 30 minutes to prevent leakage of the drug. The volume of medication that can be administered at one time does not exceed 5 mg.
Within 4-5 hours she feels mild cramping pain that spreads and gains strength. If this does not happen, the procedure can be repeated 6 hours after the first attempt. After repeated administration, there is a high probability of accelerating the process, since the concentration of stimulating substances in the body increases.
Ways to prepare the cervix for childbirth
The problem of a rational approach to pre-induction preparation of the cervix is one of the most complex and pressing in modern obstetrics. The readiness of a woman’s body for childbirth is determined by a number of signs, the appearance of which indicates the possibility of spontaneous onset of labor in the near future or allows one to count on a positive effect from the use of labor inducers [1,4,9,12]. Timely and correct assessment of the state of readiness (“maturity”) of the cervix for childbirth is of great importance in determining the prognosis of the course of the upcoming labor and especially in clarifying the indications and timing for induction of labor. This is primarily due to the fact that the condition of the cervix is a reliable indicator of the readiness of a pregnant woman’s body for childbirth. If the degree of maturity of the cervix is poorly or insufficiently expressed, spontaneous onset of labor in the near future is unlikely. On the other hand, with premature rupture of water and an immature cervix at the beginning and middle of the first stage of labor, pathological deviations in the contractile activity of the uterus may be observed, which manifest themselves in hypertonicity of the lower segment, in the absence of synergism of contractions of all parts of the uterus, etc. In this state, spontaneously beginning labor takes on a pathological (protracted) course associated with the development of discoordinated labor, its weakness, etc. According to the literature [3,5,13], with an immature or insufficiently mature cervix, labor in 57.2% of cases is accompanied by premature rupture of water, in 44.2% - by anomalies of labor, and as a result, in 16.3% of cases it is carried out surgical interventions. The presence of an immature cervix before timely birth is 16.5% in primiparous women, and 3.5% in multiparous women [2,6,8]. However, with concomitant somatic diseases, these indicators increase. For example, with class II obesity during full-term pregnancy, an immature cervix occurs in 15.4% of cases, with class III obesity – in 30.4%. In addition, in case of extragenital pathology (hypertension, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, etc.) and complicated pregnancy (preeclampsia, postmaturity, chronic fetal hypoxia, immune-conflicted pregnancy, etc.), there is often a need for early delivery. In such cases, before induction of labor, it is necessary to prepare the cervix for labor [2,4,7,11]. Back in 1960, studies were conducted that showed that all changes in the cervix during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period can be explained by connective tissue transformations. The cervix is a heterogeneous organ consisting of fibroconnective tissue, smooth muscle fibers, epithelium of blood vessels and crypts that penetrate deeply into the stromal tissue. The upper part of the cervix contains more smooth muscle fibers, and in its vaginal part fibrous tissue predominates. The extracellular basis of the fibrous connective tissue of the cervix is made up of collagen fibers and elastin, separated by a ground substance. Collagen gives the fabric stability, and elastin provides its elasticity. During pregnancy, muscle tissue is gradually replaced by connective tissue, “young” collagen fibers are formed, which are highly hydrophilic and flexible, which ensures cervical resistance and the uterus plays the role of a fetal receptacle. By the time of delivery, the concentration of collagen decreases and its physicochemical properties change. Degradation (partial resorption) of collagen is the main sign of a ripening cervix. In 1978, increased amounts of partially degraded collagen were found in biopsies taken from the cervix before and immediately after delivery, whereas it was low in biopsies obtained from non-pregnant fertile women. The process of collagen degradation is caused by the surface-concentric cleavage of molecules from the core fibers in combination with the destruction of some of them. Partial resorption of collagen fibers, changes in the concentration of glycoprotein and glycosaminoglycan begin in the vaginal part of the cervix, spreading gradually from the external pharynx to the internal pharynx. This observation made it possible to put forward the concept of the connective tissue “nucleus” of the cervix, the presence of which explains why, in the process of “maturation,” the area of the internal pharynx softens and opens last. By childbirth, a system of branched lacunae located in the thickness of the tissue of the cervix reaches extraordinary development. An increase in cervical volume was detected due to the deposition of arterial blood in them. This creates a dilatation effect that exerts a force on the internal structure of the cervix and provides “additional stretching” of the cylindrical part of the lower segment of the uterus. The moderate effect of post-stretching is one of the mechanisms of cervical ripening. Changes in the microvasculature of the cervix are used by many researchers to assess its maturity. These structural and biochemical changes are the basis for the appearance of clinical signs of cervical maturity [1,2,10]. Palpation determination of the condition of the cervix is not only a reliable method of assessing a pregnant woman’s readiness for childbirth, but also the simplest. For the first time in 1942, De Snoo proposed calling the cervix “ripe for childbirth” when loosening, shortening and gaping of the cervical canal is detected in it by palpation. Later, they also began to take into account the location of the cervix relative to the wire axis of the small pelvis and the location of the presenting part of the fetus. In our country, methods for assessing the “maturity” of the cervix during vaginal examination were developed by M.V. Fedorova (1969), A.P. Golubev (1972), G.G. Khechinashvili (1974), etc. Quite often in Russia the M.S. scheme is used. Burnhill (1962) modified by E.A. Chernukha. With this technique, during vaginal examination, the consistency of the cervix, its length, its location in relation to the pelvic axis and the patency of the cervical canal are determined. Each sign is scored from 0 to 2 points. With a total score of 0–2 points, the cervix should be considered immature, 3–4 points – insufficiently mature, 5–8 points – mature. However, the E.N. scale is most widely used abroad. Bishop (1964), where, in addition to the above characteristics, the location of the presenting part of the fetus is taken into account. Each sign is scored from 0 to 2 points. With a score of 0–4 points, the cervix is considered immature, 5 points – insufficiently mature, more than 5 – mature [2, 4, 6]. In connection with the above, methods of preparing the cervix for childbirth when its maturity is insufficiently expressed and the need for rapid delivery are becoming relevant. Despite the availability of various methods for preparing the cervix for childbirth, research in this area continues. If an “immature” cervix is determined at 39 weeks, then the following measures can be taken to prepare the cervix for childbirth: • non-drug methods; • instrumental (methods of acupuncture, massage, intranasal electrical stimulation, acupuncture, electrical stimulation of the nipples of the mammary glands, etc.); • local use of prostaglandins; • introduction of kelp; • prescription of antispasmodics. Non-medicinal methods of preparing the cervix for childbirth after 36 weeks include regular sexual activity without a condom. Sperm softens the cervix, preparing it for childbirth. This is why a condom is necessary during pregnancy itself. Many doctors believe that sex is the best way to prepare the cervix for childbirth. From 34 weeks you can take evening primrose oil in capsules - 1 per day, from 36 weeks - 2, from 39 - 3 capsules per day. Drink a collection of herbs to prepare the cervix for childbirth: rose hips (chopped) – 1 tbsp. – St. John's wort herb – 2 tsp. – dried herb – 1 tbsp. – hawthorn fruits (chopped) – 1 tsp. – motherwort herb – 1 tbsp. – birch buds – 1 tsp. – horsetail herb – 1 tbsp. – lingonberry leaves 2 tbsp. – strawberry fruits or leaves – 1 tsp. Pour 1 liter of boiling water. Boil for 30 seconds. Leave for 10–15 minutes. Strain and drink 100 ml hot 3 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals for 35 days. 10 days break and again 35 days. Those. 80 days before the expected date of birth. It is also recommended to prepare salads seasoned with vegetable oil, brew and drink raspberry leaves, tea from raspberry leaves - 1 tsp. per glass of boiling water. At 36 weeks, 1 cup per day, at 37 – 2, from 38 to 3, from 40 – 4 cups per day. After 40 weeks, you can drink sage and use tampons with sage (it is advisable to consult your doctor about this). The development of medicinal methods of preparation for childbirth is based on the fact that the main factors in the development of labor are hormonal factors: maternal (oxytocin, prostaglandins), placental (estrogens and progesterone) and fetal hormones of the adrenal cortex and posterior pituitary gland, which change the metabolism of steroids at the level of the placenta. hormones (decreased progesterone production and increased estrogen levels). PGs are local hormones and are synthesized in many tissues: seminal vesicles, uterus, brain, platelets, myocardium, endocrine glands. The most important physiological effect of PGs is their ability to cause smooth muscle contraction. The initial purpose of using PG was to soften and smooth the cervix, i.e. its maturation, which makes it easier to induce labor. If this could be achieved, the usual method of inducing labor could begin. Later, initiated cervical ripening began to be perceived as the actual induction of timely labor, without separating these processes. The indication for prescribing PG is an “immature” cervix. Moreover, they are most often used when the degree of “maturity” of the cervix according to Bishop is 0–4 points. Various routes of administration of prostaglandins have been proposed. The initially used intravenous route of PG administration is effective. However, it has been revealed that this method of administration requires relatively large doses, since prostaglandins are quickly inactivated in the lungs and, in addition, side effects often occur (in particular, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pallor of the skin, muscle tremors, etc. ). The desire to avoid such nonspecific (systemic) complications led to the creation of dosage forms for topical use. Gels and vaginal suppositories are the most commonly used dosage forms of PG for topical use. Less commonly used are tablets, cervical caps, and vaginal rings. Experience with the use of the gel has shown a longer duration of action of the drug and a significant reduction in the frequency of side effects. Typically, local administration of one dose of PG is performed the day before the planned induction of labor. Thus, most studies have attempted to speed up the process of cervical ripening (which physiologically can last several days) and accommodate it within 18–24 hours. It should be noted that quite often a significant proportion of patients develop labor without further treatment and with intact membranes. In the majority of those pregnant women who failed to induce labor, there is a significant improvement in the degree of “readiness” of the cervix, and after the administration of oxytocin, the time interval between the induction of labor and the birth of the child is significantly reduced. Local use of prostaglandins involves the following routes of administration: extraamnial, intravaginal and intracervical. In recent years, it is the local use of GHGs that has become most widespread. However, in most clinics the extra-amnial method is not used due to the large number of complications (premature rupture of water, placental abruption, myometrial hypertonicity, etc.). In obstetric practice, the most commonly used PG is PGE2 (dinoprostone), less often PGE1 (misoprostol), which is almost exclusively used for intravaginal administration. Rarely used nowadays PGF2
α due to higher therapeutic doses, which lead to an increased incidence of side effects and reduce effectiveness. The effectiveness of a single use of PG depends on the dose, route of administration (intravaginal, intracervical or extra-amnial) and the pharmaceutical form of the drug (tablets, suppositories, gels). With repeated use of PG, the effectiveness of cervical ripening increases significantly. For example, with daily administration of vaginal suppositories with 0.1 mg of enzaprost (PGF2 α), cervical ripening is observed in 92.2% of women in labor. In this case, the authors use a very different interval between procedures (as a rule, it is a 4-6 hour interval). Large intervals (1–2 days) are used in outpatient practice. The doses used in practical medicine and the frequency of their administration are selected so that with maximum efficiency there is a minimum number of side effects. In general, uterine hypertonicity is the most common complication: from 0.8% to 1.6–3.6%. Frequent cramping pains in the lower abdomen and lower back occur much more often (up to 38%), which do not affect the health of the mother and fetus and do not require medical intervention. There are contraindications for prescribing PG: bronchial asthma, active phase of ulcerative colitis, glaucoma, sickle cell anemia, tuberculosis, bleeding disorders, fibroids and uterine malformations. Considering the above, we can conclude that prostaglandins have the following advantages: 1) PG is a highly effective agent for cervical ripening; 2) cause not only ripening of the cervix, but also induction of labor; 3) when used correctly, they rarely cause side effects; 4) relatively easy to use (especially vaginal forms of drugs that can be administered independently on an outpatient basis). Along with the noted advantages, the use of PG has its disadvantages: 1) the presence of a fairly large list of contraindications for use; 2) with an individual overdose, side effects are possible in both the mother and the fetus; 3) special equipment is needed to diagnose the main complications; 4) relatively high price of one procedure. A mixed method of preparing the cervix includes the use of natural and artificial kelp. Natural kelp is seaweed that is found in the northern and Far Eastern seas. In obstetrics and gynecology, two types of kelp are used: Laminaria digitata (digitate) and Laminaria japonica (Japanese). The main active principle of kelp is polysaccharides (mainly sodium, calcium and magnesium salts of alginic acids). Alginic acids are polyuronides in chemical structure and are linear polymers. Thanks to polysaccharides, dried kelp is able to quickly absorb water from the environment, increasing in size. In addition to these polysaccharides, kelp contains proteins, amino acids, mannitol, microelements (including iodine), and vitamins. Sticks 6–7 cm long and 2–3 mm in diameter are made from specially processed kelp. A strong silk thread is passed through the stick, through which the used dilator is removed. Due to its hygroscopicity, already 3–4 hours after entering the liquid, kelp swells in diameter, reaching a maximum expansion of 3–5 times after 24 hours, and its consistency turns from dense to much softer and resembles rubber. An important positive feature is that, expanding the cervical canal to 9–12 mm, the kelp after swelling remains unchanged in length. Laminaria acts on the cervix not only by applying radial force, but also by removing water from the cervical stroma. As mentioned above, the cervix is formed mainly of fibrous connective tissue. Dense muscle constitutes little more than 15% of the cervical mass and is not concentrated into muscle. Most cervical tissue consists of long, complex proteoglycan molecules stretched across hyaluronic acid cores. The side chains of the hyaluronic acid core are loaded, and due to the fact that the load is uneven, the molecule curls into a long spiral. Inside the spiral molecules are water molecules. The process of cervical dilatation appears to involve the extraction of water molecules from coils of helical molecules. The disadvantages of using kelp are the acute pain that rarely accompanies their administration, as well as moderate, spastic pain when the sticks are in the cervical canal. Possible displacement of the sticks in the vagina, pinching of the swollen kelp in the cervix. Thus, an analysis of the literature data made it possible to determine the following positive aspects of using kelp to prepare the cervix for childbirth: a fairly high efficiency of cervical ripening, a low incidence of complications and side effects, a relatively low cost of kelp sticks, the presence of a complex of biologically active substances that have a beneficial effect on mucous membrane. At the same time, kelp has the following disadvantages: an indefinite number of sticks are required for sufficient expansion of the cervical canal (from 2-3 to 10-12), it takes a fairly long time to obtain a clinical effect (up to 16-24 hours or more), there is a risk of infectious complications, as well as allergic reactions [2,3,6]. In most cases, according to the literature, to prepare the cervix for childbirth, you can limit yourself to prescribing antispasmodics from 38 weeks of pregnancy. One of the most commonly prescribed is hyoscine butyl bromide. Hyoscine butyl bromide is a selective blocker of m-cholinergic receptors; m-anticholinergic, antispasmodic. Reduces the tone of the smooth muscles of internal organs, reduces their contractile activity, and causes a decrease in the secretion of exocrine glands. Hyoscine butyl bromide is a semi-synthetic derivative of hyoscyamine, an alkaloid found in belladonna, henbane, datura, and scopolia; quaternary ammonium compound. One of the main indications for the use of this drug in obstetric practice is the preparation of the cervix for childbirth during full-term pregnancy, as well as its antispasmodic effect to accelerate the dilatation of the cervix during childbirth. The main characteristic of hyoscine butyl bromide is the ability to cause local muscle relaxation due to the effect on smooth muscle m-cholinergic receptors (intracellular calcium current is suppressed) in combination with poor absorption into the systemic circulation. Taking into account the selectivity of hyoscine butyl bromide (impact only on the m-cholinergic receptors of spasmodic muscles) and its low bioavailability, international practice has experience of its use in cases of late dilatation of the uterine pharynx during childbirth. It is noted that in some cases its effect exceeds the effect of drotaverine and papaverine. Many years of clinical experience has been accumulated in the use of hyoscine butyl bromide in obstetrics, reflected in the Cochrane Library database. In 1952, the results of its clinical use in obstetrics practice in Germany were described. It has been established that the use of hyoscine butyl bromide to prepare the cervix for childbirth has a beneficial effect on its course and outcome. In 2005, results were obtained indicating the high effectiveness of hyoscine butyl bromide in shortening the duration of the first stage of labor (dilatation period) in women who received hyoscine butyl bromide suppositories during the active phase of labor, compared with those women in labor who were not prescribed hyoscine butyl bromide. The duration of the first stage of labor in the first group was 123.86±68.89 minutes, in the second group – 368.05±133.0 minutes (p<0.05) [1,2,5,13]. Thus, the experience we have accumulated and data from domestic and foreign literature indicate that the administration of the m-cholinergic receptor-selective antispasmodic hyoscine butylbromide in the form of rectal suppositories, which has a good range of effectiveness and tolerability, is a highly effective means for preparing the cervix for childbirth at full term. pregnancy, as well as to accelerate the dilatation of the cervix during childbirth.
References 1. Abramchenko V.V., Abramyan R.A. Induction of labor and its regulation by prostaglandins. Guide for doctors, Elbi: St. Petersburg, 2005, 288c. 2. Glagoleva E.A. Preparation of the cervix for childbirth (comparative effectiveness of the use of dinoprostone, Dilapan and natural kelp): Abstract. diss. Ph.D. honey. Sciences, M., 2000.– 27 p. 3. Gutikov L.V., Liskovi V.A. The use of kelp to prepare the cervix for childbirth with mild preeclampsia. // Obstetrics and gynecology. – 2006. – No. 5. – P. 47–49. 4. Kuzminykh T.I., Ailamazyan E.K. Preparing pregnant women for childbirth. Methodological manual, Publishing House N-L, St. Petersburg, 2007, 36 p. 5. Sidorova I.S., Makarov I.O., Edogova A.B. and others. The effectiveness of induction of labor using vaginal gel Prostin E2. // Bulletin of the Russian Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. – 2000. – No. 2. – P. 33–35. 6. Sinchikhin S.P., Mamiev O.B., Ogul L.A. and others. Comparative assessment of the effectiveness of various methods of preparing the cervix for childbirth. // Problems of reproduction. – 2009. – No. 4. – P. 12–17. 7. Allen R, O'Brien BM. Uses of misoprostol in obstetrics and gynecology. Rev Obstet Gynecol. 2009, 2(3):159–68. 8. Chammas MF, Nguyen TM, Vasavada RA et al. Sequential use of Preepidil and extra–amniotic saline infusion for the induction of labor in NULLiparous women with very low Bishop scores. J Matern Fetal Med. 2001, 10(3):193–6. 9. Church S, Van Meter A, Whitfield R. Dinoprostone compared with misoprostol for cervical ripening for induction of labor at term. J Midwifery Women's Health. 2009, 54(5):405–11. 10. Denoual-Ziad C, Hors Y, Delande I et al. Comparative efficacy of vaginal insert and dinoprostone gel for cervical ripening at term in current practice. Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2005, 34(1 Pt 1):62–8. 11. Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Fazzio M, Volpe A. Elective cervical ripening in women beyond the 290th day of pregnancy: a randomized trial comparing 2 dinoprostone preparations. J Reprod Med. 2007, 52(10):945–9. 12. Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Verocchi G, Volpe A. Comparison of two preparations of dinoprostone for pre-induction of labor in NULLiparous women with very unfavorable cervical condition: a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005, 119(2):189–93. 13. Vollebregt A, van't Hof DB, Exalto N. Prepidil compared to Propess for cervical ripening. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2002, 104(2):116–9. Gift for newborn children
Types of stimulation
Gynecologists in their practice use stimulation measures, both without surgery and with its use. If previous actions - gymnastics, yoga, consumption of foods that influence the induction of contractions - do not help, specialists resort to more serious methods of stimulation.
Amniotomy
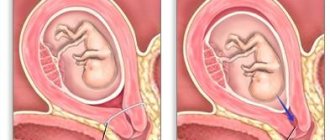
This event refers to the rupture of the membranes, which keeps the amniotic fluid from coming out.
It can be pierced or cut with special tools. After which, fluid pours out of the uterus. It is carried out only for certain medical indications, taking into account the fact that there is no risk to the fetus and mother. It is prescribed by an obstetrician; it is simply not performed at the request of women in labor without the presence of conditions.
The event is subject to the following conditions:
- the fetus lies head first;
- bearing 1 child;
- period of at least 38 weeks;
- the baby's weight is no more than 3 kilograms;
- the birth canal is ready for delivery;
- pelvic size is normal;
- There are no scars on the uterus after operations.
If these conditions are not met, then there is no indication for the procedure.
Oxytocin injections or drips
Inducing contractions is practiced using the hormone oxytocin, which is administered to the patient by injection or IV.
It is responsible for muscle contraction and starting the lactation process. After 30 weeks of pregnancy, its natural content in the body increases. In situations where there are deviations from the norm, the hormone is not produced in an amount effective to initiate labor, so it must be administered artificially. When the contents enter the bloodstream, the activity of the uterus increases within 5 minutes. One injection is effective for up to 3 hours.
Prostaglandins
One of the current and safe ways to stimulate labor is the use of substances containing prostaglandins. Exactly the same components are produced by the female body when the process of delivery proceeds as planned without deviations. After their use, the concentration of substances occurs near the uterus, they soften it, force the muscles to contract, causing contractions.
The contents are administered only in a hospital setting by an obstetrician through the cervical canal. According to practice, the effect begins after 4-6 hours from the moment the gel is introduced into the woman’s body.
Medical reviews on induction of labor
Many people care about a doctor's assessment of a particular medicine. Almost all experts have a positive attitude towards the use of stimulating gels. Although side effects are noted.
Vertical childbirth: advantages and 8 contraindications
Disadvantages of using the drug:
- Hypertonicity of the uterus;
- In some cases, headaches and chills;
- The patients complained of nausea and gastrointestinal disorders;
- Disorders of the circulatory system.
And yet, experts often use stimulant gels, considering them the safest means.
Feedback from pregnant women is mostly positive. They note a rapid inducing effect and rarely suffer from adverse reactions.
The gel affects women in labor differently. Some noted a quick effect and quick birth, while others used additional drugs to open the uterus and induce the process.
Expectant mothers are interested in: how painful is it to insert gel into the uterine canal? According to most women, the procedure is painless. In medical practice, analogues of Prepidil and Prostin are used.
Name of drugs to induce labor:
- "Prostenon";
- "Prostenongel";
- "Cerviprost";
- "Vazaprostan."
To facilitate childbirth, with vaginal dryness and after birth injuries, “Gynodek” gel and suppositories are used. They help restore the perineum and have an antibacterial and antiviral effect.
How long does it take for labor to begin after stimulation?
The duration of action of stimulating procedures depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body, the amount of active content, and the mechanism of the event. The birth process begins in different ways:
- if the expectant mother independently tries to induce contractions with the help of physical activity, nutrition, gels, the onset of labor depends on the body, the degree of impact, may occur in a few hours, or the result will not be achieved and surgical intervention will have to be used;
- when stimulated by injections and droppers, the release of hormones into the blood provokes contractions within 5 minutes;
- the method of introducing prostaglandins through the cervical canal gives results on average in 4-6 hours;
- in case of amniotomy, the effect is observed within 3-4 hours.
Medication methods can be considered more effective methods, since the action of drugs and hormones quickly stimulates delivery.
The cervix is not ready for childbirth, what to do?
Basically, before giving birth, the doctor examines the cervix and tells you whether it is ready or not. At the time of the 40th week, the cervix should measure 2 cm, be not only soft, but also elastic, and the pharynx area should allow the transverse finger to pass through. At the time of birth, the cervix descends towards the center of the vagina.
Do not worry if the doctor did not give positive news about the maturity of the uterus; there are many methods that will help achieve the desired result.
Basically, doctors prescribe massage, medications, and sometimes acupuncture to expectant mothers, each approach is focused on the characteristics of the body. It is very important to remember that all procedures should be carried out exclusively as prescribed by the doctor leading your pregnancy and under the supervision of staff.
There are some folk methods that affect the preparation of the uterus for childbirth. One of the most popular is sexual intercourse in the last stage of pregnancy. It has been scientifically proven that during orgasm, the muscles of a woman’s uterus are toned.
Why do an enema before childbirth?
But in this case, you need to be extremely careful, since such actions can lead to premature contractions and childbirth. Many doctors claim that male sperm, as well as evening primrose oil, can help an unprepared uterus. The latter is a medicine and can only be taken on the recommendation of a specialist. If the doctor did not allow you to take it, then equip your diet with fish and vegetable oil, this will be an excellent replacement for any drug.
Risks to mother and fetus
Many women try to induce contractions naturally because they believe that medical intervention can harm the baby.
In most situations, the procedure goes without difficulty, because without it, the woman’s situation may worsen, leading to a caesarean section. When implementing incentives, the following risks are noted:
- infection of the fetus (as a result of surgery, an infection may occur that has a negative effect on the baby);
- oxygen starvation of the child;
- requires the administration of painkillers with the risk of effects on the fetus;
- the occurrence of complications during childbirth (placental abruption, uterine rupture).
Natural birth is preferable, since this method is a natural process that does not involve the introduction of drugs or instruments into the uterus.
How does labor proceed when stimulated?
In the case of stimulation, the process of delivery differs from natural. Firstly, a woman experiences more pain and needs medications that can relieve pain. Secondly, failure to dilate the uterus on time suggests difficulties with the birth of a child, and thirdly, there are risks of infection.
Mothers who gave birth this way are observed longer in the maternity hospital until their condition is completely restored. In this case, obstetricians are more attentive to patients, since they have a greater risk of negative consequences, but with correctly applied procedures and professional management of pregnancy, they are minimized.
Restoration of the body
After the birth of a baby with artificial stimulation, the body’s recovery occurs as usual.
All vital systems return to normal within 3 days. Hormonal levels are fully restored only after the baby has finished breastfeeding. If oxyotocin was used, the mother may feel pain in the form of abdominal cramps during lactation. Menstruation can be restored within 1 to 1.5 months, depending on the characteristics of the body. The uterus shrinks and returns to its prenatal state within 6 weeks.
The birth process, especially with stimulation, requires special attention from obstetricians, whose main task is to maintain the health of the child and mother. If indicated, a woman must fully follow the recommendations of specialists so that her birth takes place without difficulties and critical problems leading to irreversible consequences.
What happens to the cervix before childbirth
The cervix begins to prepare for the birth of a child from 32 to 34 weeks of pregnancy. First, its edges soften, leaving a dense area of tissue along the cervical canal. Closer to childbirth, the uterus more often comes to tone, due to which its lower segment softens and becomes thinner. The upper myometrium, on the contrary, becomes denser.
Due to this, the fetus begins to gradually descend and put its weight on the neck, provoking its further opening.
Dilatation of the cervix before childbirth does not occur equally in women who give birth for the first time and in multiparous women. In the first, it begins with the opening of the internal pharynx.
In the latter, the process of opening the internal and external pharynx occurs simultaneously, since by the end of pregnancy their external pharynx usually already allows one finger through. As it opens, the neck thus becomes shorter. A couple of days before the onset of labor itself, the process of its maturation accelerates significantly. Gradually it completely smoothes out and easily lets through 2 fingers or more.
Based on the Bishop scale above, on the eve of childbirth the cervix should meet certain parameters.
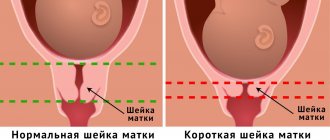
A soft cervix is ideal for childbirth. Her softness is evidenced by the fact that she freely passes 2 or more fingers of the doctor. During this period, a woman may notice the release of the mucus plug. This is one of the harbingers of the upcoming birth, indicating the imminent onset of contractions. As for the length of the cervix, during pregnancy a length of 3 cm is considered normal.
In this case, both ends of the cervical canal must be closed. Closer to childbirth, it shortens. The length of the cervix before childbirth should not exceed 1 cm, gradually smoothing out completely.
As for its location, it was tilted back throughout the entire pregnancy. This further helps keep the fetus inside. Gradually, due to the softening of the lower segment of the uterus, it begins to unfold forward. When the time comes for childbirth, it should be located exactly in the center of the small pelvis.