Examination by a gynecologist during pregnancy: what is important to know
One type of examination during pregnancy is a gynecological examination.
However, we have all heard that a gynecological examination can cause miscarriage or premature birth, and pregnant women often worry about this. Is a gynecological examination necessary during pregnancy? In general, a gynecological examination should be carried out only upon registration and at the end of pregnancy (after 36 weeks), but if there are complaints, for example, spotting, then at any stage.
An examination before childbirth is important; it is necessary to assess the condition of the cervix, its softness, and the degree of opening.
However, not in all cases, an examination by a gynecologist can bring clarity; sometimes an ultrasound can be much more informative, for example, to exclude a frozen pregnancy or determine the length of the cervix.
Previously, an examination was practically the only way to determine the presence of pregnancy, but now, when there are tests for hCG and ultrasound, this is no longer so relevant. Remember that you can refuse the examination, as it has its own risks, such as: infection, cervical stimulation and premature birth, premature rupture of the membranes.
Of course, with a properly performed gynecological examination and if there is no additional threat of interruption, for example, bleeding, this is a safe manipulation. But if there are no indications, but the doctor just wanted it that way, or you doubt the doctor’s qualifications, then it’s better to refuse.
What are the dangers of examining “with passion”?
When separated, the lower part of the amniotic membranes is “peeled off” from the cervix and walls of the uterus. Both the insertion of the finger and the manipulation cause painful sensations, then the lower abdomen may “ache,” blood may be released, and the mucous plug, which protects the cervix and the uterus itself from infection, may come off. Normally, this is considered a harbinger of labor, but with stripping it is a consequence of manipulation. What else could it be?
- Cervical injury if dilatation is assessed incorrectly or the doctor performs the procedure incorrectly.
- Bleeding due to early and too rapid detachment of membranes, expansion of the cervical canal.
- The introduction of infection from the vagina or its subsequent independent penetration, since the plug comes away and there is nothing left to protect the amniotic sac and the child from bacteria.
- The outpouring of water may begin without the birth itself, which is dangerous due to the anhydrous period, and subsequent stimulation during labor, and infection of the fetus.
- Moreover, if desired, you can deliberately open the bladder or administer a drug to locally stimulate the onset of labor, and do this unnoticed by the woman.
Stripping is not noted in the medical record. Inspection - yes, but the actual manipulation of the membranes and neck - no. This is an unofficial, although popular, method of inducing labor, and it will not be noted in the documents. This means that in case of complications, it will be impossible to find the culprit.
Despite the impressive list of disadvantages and possible complications, stripping is considered the gentlest and most natural method for stimulating the birth process. For example, if the pregnancy has been delayed and the cervix is already open, or labor has begun, but is going slowly, and you need to speed it up a little. Therefore, it is worth resorting to in a situation where stimulation is definitely needed. But this must be done consciously.
Is it possible to watch a pregnant woman on a chair?
This question interests many, since women are often afraid of harming their child. Indeed, an incorrect examination on the chair can provoke bleeding and even pregnancy failure, but this happens very rarely, usually when there are already predisposing factors and the doctor is very careless during the examination.
An examination in a chair is not advisable if there is placenta previa, as this may cause bleeding. It is worth knowing that a woman can refuse a gynecological examination and any other manipulation; this right is provided for by law.
In a normal pregnancy, the pregnant woman is examined in a chair only during registration. After 36 weeks, the doctor can see the pregnant woman to assess the condition of the cervix before giving birth. At any stage, an examination is possible if there is a risk of premature birth, bleeding, or symptoms of infection.
Separately, it is necessary to say about colposcopy during pregnancy. Unfortunately, sometimes a pregnant woman is simply forced to do this examination, although it is done even in non-pregnant women according to indications.
If the cytological smear is normal, then colposcopy is not needed, especially since there may be changes in the cervix associated with pregnancy, which will go away on their own after childbirth. Why should mommy undergo an unpleasant procedure in vain, and even have unnecessary worries in case of a dubious result?
No one has the right to force, as this is contrary to the Constitution, they can offer you, you have the right to agree or refuse. If they offer colposcopy, let them first justify its necessity during pregnancy.
Discharge during pregnancy after examination.
After examination by a gynecologist, there should normally be no discharge. If bloody discharge appeared after the examination, then the doctor performed the examination roughly, possibly inserted instruments into the cervix and damaged the vessels.
The cervix softens during pregnancy and is easily injured; minor damage to the vaginal walls by a gynecological speculum is also possible. Usually such discharge is scanty and stops within 24 hours.
If the discharge continues longer or gets worse, and is also accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, then perhaps the problem is not the examination, but there is another problem, for example, placenta previa. In this case, you need to consult a doctor, possibly perform an ultrasound.
Is it possible to take a smear during pregnancy?
When registering for pregnancy, it is necessary to take a smear for flora and a smear for cytology. The first can be taken from the vagina, the second - only from the cervix.
Inserting instruments into the cervix can cause a miscarriage, so a smear for cytology is taken only from the surface of the cervix. If you took a cytological smear less than a year before pregnancy and everything was normal, then you don’t have to take it. You have the right to know which swabs will be taken and where they will be taken and you can refuse them.
A smear test for flora must be taken upon registration, as well as at any time if there are complaints, for example, itching or curdled discharge. It is safe to take a flora smear during pregnancy; it is taken with a disposable brush, which is included in the gynecological kit. Such a smear can be taken even without the use of mirrors.
Many doctors try not to look at the pregnant woman in the chair one more time. If your doctor insists on an examination, you have the right to know why it is needed, what information the examination will provide to the doctor, and whether it can be replaced by another research method, for example, ultrasound.
Sometimes examination, colposcopy and smears during pregnancy are carried out only because it is necessary, for example, upon admission to the gynecological department or to fulfill plans that still exist in our medical institutions. Remember: you have the right to refuse an examination, especially if there is no objective evidence for it.
How the cervix changes before childbirth
The uterus is the main organ necessary for pregnancy. It consists of a bottom, body and neck. The latter looks like a tube connecting the uterus to the vagina. The successful course of pregnancy and natural childbirth directly depends on its condition. The cervix changes significantly before childbirth, although for the woman herself these changes are practically unnoticeable, since this process is not accompanied by any special symptoms. What happens in the prenatal period and why is special attention paid to the cervix?
What can cause early miscarriage?
No one is immune from miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy. Many women go through this. Typically, an interruption occurs before 12 weeks and often goes unnoticed. Many people are still unaware of their situation, and the bleeding that occurs is perceived as a disruption in the menstrual cycle.
It is important to understand the cause of fetal loss. If you eliminate the provoking factor, you can take appropriate measures and avoid recurrence of the problem.
Nervous experiences negatively affect women's health. Many people experience menstrual irregularities and spontaneous uterine bleeding due to stress. And taking sedatives definitely does not benefit the fetus.
Lifestyle
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of sleep, poor nutrition can terminate a pregnancy. If conception is unplanned, the woman does not have time to reconsider her habits. Her lifestyle causes irreparable damage to the fetus.
Previous abortions
Medical abortion causes serious hormonal changes. The body needs a lot of time to recover. And curettage and vacuum aspiration can damage the walls of the uterus. Infections are often associated with injuries. And after the wounds heal, scars may remain that interfere with the normal attachment of the fertilized egg.
Genetic disorders
A common cause of early miscarriage is genetic abnormalities of the fetus. These are not hereditary diseases, but the consequences of the fusion of pathologically altered germ cells. The resulting embryo cannot develop normally and dies. This can happen even in completely healthy parents. It's just that some of their genetic material has mutated for various reasons. There is a high probability of success in the next attempt at conception, because sperm is renewed approximately once every 2 months. And the set of eggs in women is laid during intrauterine development.
Mother's age
Women who become pregnant after 40 find it more difficult to carry a child to term than younger women. Their body wears out, the quality of the eggs decreases. Middle-aged ladies should be even more careful about their health. And if fertilization is unplanned, there is a high risk of losing the child before the woman finds out about her situation.
Hormonal disorders
Androgens reduce the production of female sex hormones. And a lack of progesterone is detrimental to pregnancy. This hormone helps implantation of the fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus, suppresses the contractility of the reproductive organ, and prevents the onset of menstruation.
Infectious diseases
Sexually transmitted infections often cause early miscarriage. They have a detrimental effect on the organs of the reproductive system and the embryo. Pathogenic microorganisms destroy the membrane of the fertilized egg, making it unviable. And systemic inflammatory pathologies provoke intoxication and weakening of vitality. The body in this state is not able to bear a child, and gets rid of it so as not to waste resources.
Rhesus conflict
If future parents have different Rh factors, and the child inherits the father’s Rh factor, the mother’s body perceives it as a foreign body and gets rid of it. The death of the embryo occurs in the first two months. This is a normal reaction of the immune system, which can be combated if you are aware of the possible risks in advance.
Medications
Many medications can terminate a pregnancy or cause fetal abnormalities, which also leads to the death of the embryo. So, antibiotics provoke various mutations. Aspirin and other blood thinners cause bleeding. Antitumor drugs interfere with the normal formation of fetal tissue. Hormonal medications can create progesterone deficiency. Homeopathic remedies and some herbs increase the tone of the uterus. These include parsley, St. John's wort, bay leaf, etc.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of early miscarriage can easily be confused with normal periods. The first stage of spontaneous abortion is called threatened miscarriage. It is characterized by cramps in the lower abdomen and nagging pain in the lower back. In this case, there are no allocations.
An incipient miscarriage is accompanied by spotting or heavy bleeding due to detachment of the endometrium or fertilized egg. The greater the blood loss, the more difficult it is to save the fetus. But even a couple of drops can be dangerous. Therefore, at the first alarming symptoms, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
The next stage is called miscarriage in progress. It is accompanied by sharp pain in the abdomen and lower back, severe blood loss. In this case, the situation cannot be corrected, because the embryo has already separated from the endometrium and passed into the cervical canal. The released fertilized egg can be seen in the discharge. It is a light clot or film.
After the incident, you need to contact a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination and necessary tests. You may need to cleanse your uterus. If there is something left in it, there is a high risk of developing inflammation.
If the cervix is not ready for childbirth
A soft, shortened cervix, which is located in the center and slightly open, indicates the approach of labor. However, it also happens that the due date has already approached, but the maturity of the cervix has not yet occurred.
An immature cervix can lead to complications during labor, so if it is not ripe by the expected date of birth, the doctor may decide to induce stimulation.
Pregnancy after 40 weeks is post-term and dangerous for the baby. At this point, the placenta ceases to fully perform its functions. Therefore, if the cervix does not mature by this time, then its stimulation is mandatory.
In addition to postterm pregnancy, indications for stimulation are:
- The mother has a disease in which further pregnancy threatens her health.
- Development of hypoxia in the fetus.
- Large fetus or multiple pregnancy.
- The cessation or weakening of contractions during labor.
- Premature placental abruption.
In all other cases, the question of the need for stimulation is decided individually. There are various methods to prepare the cervix for childbirth.
Medical methods include the following:
- Kelp sticks. Kelp is seaweed. They are placed along the entire length of the cervical canal, where they swell with moisture and begin to mechanically expand it. Laminaria also secrete endogenous prostaglandins, which are involved in the process of cervical ripening.
- Synthetic prostaglandin. These can be suppositories or gels that are injected into the cervical canal, or intravenous injections. Synthetic preparations can soften the cervix faster than kelp, thereby bringing the moment of birth closer.
- Amniotomy. Piercing the amniotic sac provokes the release of anterior waters, as a result of which the fetus drops lower and puts more pressure on the cervix, thereby stimulating its opening.
There are other, non-medical methods to prepare the body for natural childbirth. Unlike the first ones, they can be used at home, but subject to full-term pregnancy, satisfactory health of the woman and baby, and only after consultation with a doctor. Otherwise, such stimulation can be dangerous. Non-medical stimulation methods include:
- Sex. Orgasm causes the uterus to contract, causing the cervix to open. In addition, semen contains a significant amount of prostaglandins, so unprotected sexual contact makes sense. This method is only suitable if the woman’s mucus plug has not come off, otherwise the risk of infection increases.
- Cleansing enema. This procedure causes the uterus to contract. After an enema, the mucus plug usually begins to come off, and the cervix gradually opens.
- Physical exercise. These include walking up stairs, washing floors, long walks, etc.
How to avoid miscarriage?
Early termination of pregnancy rarely leaves serious consequences. If the cause is identified and eliminated, the next pregnancy will most likely pass without complications.
The main aspect in the success of bearing a child is planning the conception. If fertilization is expected, the woman is attentive to her health, registers with a gynecologist on time and takes the necessary preventive measures.
Future dads also need to prepare for conception. They should give up bad habits. It is useful to drink antioxidants. They have a beneficial effect on sperm quality and reduce the risk of gene mutations.
Expectant parents should have their blood tested. If it turns out that they have a different Rh factor, the loss of the child can be avoided. The doctor will prescribe medications that reduce the risk of rejection of the fertilized egg.
It is important to promptly treat chronic and infectious diseases. When diagnosing pathologies during pregnancy, self-medication is prohibited. Even folk remedies cannot be used without a doctor’s prescription. When going to the hospital, even with a common cold, it is important to tell the doctor that you are pregnant.
After an abortion, you must follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist. Of course, you need to give up alcohol, drugs and cigarettes. Ideally, this should be done a couple of years before the planned pregnancy. It is recommended to avoid stress if possible.
At the first signs of early miscarriage, you should seek medical help. The doctor will prescribe hemostatic agents and drugs with progesterone. This will help maintain the pregnancy.
possible consequences of examinations on the chair
- Like
- I do not like
rodi_doma July 24, 2011
Please Login
or
Register
to see this Hidden Content
In short, the disadvantages of chairside examinations include: - Discomfort for the pregnant woman during the examination - May increase the risk of infections - May cause premature labor due to cervical stimulation - May increase the risk of premature water breaking
sisters who have the time and desire. It's a good job to translate. We find the material bit by bit, after all.
- Like
- I do not like
Santia July 24, 2011
here is a translation of the material about inspections))))
Are vaginal exams really necessary during pregnancy?
I know few women who would be happy after having an examination during pregnancy. Regarding this, I have also met few women who would be happy to undergo an examination without being pregnant, but what is the purpose behind performing a vaginal examination during pregnancy? But if this happens on the initiative of the patient, i.e. What exactly is the woman asking for an examination, what is her reasoning? On the other hand, if the doctor or midwife insists, then what are they looking for and why? Of course, it is easier to be the person performing this function, but it is not always so easy to be the recipient, and during pregnancy, this very event can cause both emotional and physical discomfort to the woman. Conducting a vaginal examination is more like invading the most private of all our possessions. ourselves. However, let's look at this from a medical point of view.
Advantages of VO during pregnancy • Cervical (related to the cervix) abnormalities can be found, such as early dilation and effacement, so that appropriate changes can be made to care for the woman, including bed rest, hospitalization, drugs that reduce labor, etc. . • improvements may be seen from examination to examination, giving the woman the satisfaction of knowing that the pregnancy is coming to an end and the support of a midwife or doctor • the cervix can be stimulated without the need for medical intervention • may provide a high level of comfort for the midwife or doctor, which will allow them to feel good about the beneficial continuation of the pregnancy
Disadvantages of VO during pregnancy • performing an examination does not guarantee that labor will begin • vaginal examinations can be very uncomfortable during pregnancy • the risk of infection may increase • preterm labor may occur due to cervical stimulation • the risk of premature rupture of the membrane may increase • there may be presents a false picture of the duration of the remainder of pregnancy
Making a Choice There are genuine reasons to check a woman's cervix to ensure a safe pregnancy, but like many of the "interventions" offered during pregnancy, it is important for every woman to be aware of the potential harms of such a decision before agreeing. How can reasoning about the need to “know what is happening” be called anything other than pure curiosity? Who exactly is referred for examination? Consider the following situations: • Was the woman frightened by the stories about the “big baby”? • did the woman have a premature birth or a miscarriage, and therefore she is not sure that she will be able to carry and give birth to a healthy child? • is she tired of pregnancy and wants to overcome it? • Is she trying to avoid medical intervention or a caesarean section? • did the doctor make her think that there was some problem with the baby and should she continue the pregnancy? • Does the woman want immediate gratification and want to hold her baby NOW? • Is the woman trying to avoid the possibility of an argument or quarrel with her caregiver? • does the woman have problems with “self-control”? There are valid reasons for performing a vaginal examination during pregnancy, but if a woman is having a good pregnancy, what is the reason? A huge number of studies show that natural pregnancy with the least amount of intervention is much better. Do women consider vaginal examinations an “intervention,” a “common practice,” or a “necessity”? Ask three women and you'll probably get three different answers. However, everyone must make their decision individually. Did she actually weigh the pros and cons before going for the exam? Does she know of any alternatives to vaginal exams, such as NST (NON Stress Test), BPP (Biophysical Profile), baby beat count tracking, high level sonograms, or any other less intrusive suggestions? Does she know that the examination itself can bring internal discomfort associated with muscle spasms and bleeding? Post edited by Santia: July 24, 2011 - 19:32
Procedures to prepare for the day of birth
Homebody Neighbor
- Examination by the attending or duty doctor, and, if necessary, by the head of the department.
- CTG recording - fetal heartbeat.
- Cleansing enema and shower.
- Transfer to an observational or physiological maternity ward.
If a woman is planning a caesarean section, the procedure is the same. A light dinner is allowed the night before; in the morning you can only drink a little clean water.
Also, the pregnant woman must collect all her things if she was previously in the pathology department. Some can be taken with you to the delivery room, the other will need to be put in a storage room.
We suggest you read: How to get pregnant with twins 100 percent the first time
In the delivery room
The maternity room includes an examination room (usually several), prenatal wards where women are during contractions, as well as the maternity rooms (halls) themselves - they contain special chairs, a table for treating a newborn, as well as equipment and tools that may be needed during childbirth, everything is sterile, and consumables are disposable (diapers, etc.).
The delivery room also includes an operating room, where, if necessary, a woman can be sent urgently during childbirth.
After admission to the delivery room, the woman is assigned to one of the prenatal wards, where she will be monitored (including video), and CTG monitoring of the fetal condition is carried out. The doctor, who is in charge of the delivery room at this time, clarifies the woman’s complaints and medical history, studies the birth chart and, if necessary, conducts an examination in a gynecological chair.
If childbirth proceeds without complications, then the frequency of vaginal examinations is as follows:
- every four hours during labor;
- after the rupture of amniotic fluid;
- if complications are suspected.
The woman is in the prenatal ward throughout the contractions; she is also allowed to move along the corridor and take a shower (as a method of pain relief).
With the beginning of the pushing period, the issue of transfer to the delivery room itself is decided. Here the woman lies down on a chair, the doctor monitors the condition of the fetus by heart rate (listened to with a stethoscope or CTG monitor).
After the birth of the child, the birth canal is examined for rupture. If necessary, the doctor performs suturing, as well as additional manipulations. For another two hours, the woman is under close supervision of medical personnel for timely detection of complications. After which the postpartum woman is transferred to a ward with the baby.
If an emergency or planned caesarean section is performed, then immediately after the operation the woman is transferred to the intensive care unit for observation - for at least two hours, most often for 12-24 hours. After this, she is also transferred to the postpartum ward.
Can a gynecologist's examination cause a miscarriage?
Maybe. At 29 weeks I went to the doctor and she decided to examine me - the result was premature birth. I told her to pray, if something happened to the child she would not live. Thank God and the other doctors, we stayed until 31 weeks and everything was fine with the baby, but what I experienced was terrible. She's still hiding from me. Probably it all depends on experience. Based on this, I think it can.
After examining the gynecologist and her intervention, I took a smear, I had a stomach ache and smear for a long time, I had to lie down, when I told her about it, she was very surprised, like it shouldn’t, I say I myself know that it shouldn’t, but they did it sloppily, and Once I almost died altogether, I was in the hospital, again after their intervention, despite the fact that I asked the nurse through the nurse to come to me, but no one was there, and then she was also surprised, but I didn’t know anything. Thanks to prayers, she survived and the child was preserved. Therefore, after this I don’t trust anyone and say that anything can happen.
Examination by a gynecologist if there is a threat of miscarriage.
Unfortunately, it happens that a desired pregnancy is unexpectedly terminated. If this process occurs on its own, we are talking about a miscarriage or spontaneous abortion.
A miscarriage can happen when a woman has not even shown visible signs of pregnancy, and maybe at such a time when the pregnant woman feels the fetus moving.
REASONS FOR THREATENED MISCORREAGE.
There may be various reasons:
— The pregnant woman suffered a nervous breakdown, experienced stress — Genetic disorders occurred during the development of the fetus, which caused its death — If the pregnant woman has problems with the endocrine system
— When a pregnant woman becomes infected with certain viruses and bacteria that are transmitted through sexual contact
— Different Rh factors in mother and child
— Bad habits that a woman abused before pregnancy.
FIRST SIGNS OF THREATENED MISCORREAL.
Usually a woman feels pain in the lower abdomen, as if menstruation is about to begin. In this condition, the uterus contracts greatly. In the future, the pain becomes more severe and bloody discharge from the vagina may appear. The discharge may simply be smeared or be more abundant, as during menstruation. These are the first symptoms of a miscarriage.
If the fertilized egg separates from the uterine wall, a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. In this situation, the pregnancy is terminated. Bleeding may increase, accompanied by blood clots. The fertilized egg can leave the uterine cavity naturally and the spotting will gradually stop. This situation most often occurs during pregnancy up to 12 weeks.
If the egg does not come out completely, the discharge becomes stronger and larger in volume, which can cause serious complications due to large blood loss.
If any of the listed signs of a threatened miscarriage appear at any stage, the pregnant woman must immediately attend an examination by a gynecologist.
An examination by a gynecologist in such a situation is of paramount importance. When examining a pregnant woman in a gynecological chair, a doctor can easily determine whether a miscarriage has begun. At the same time, the gynecologist checks the state of uterine tone, how tightly the cervix is closed, and what vaginal discharge is.
To determine whether the pregnant woman’s condition is safe for the child, the gynecologist will refer her for an ultrasound.
Based on the results of the examination, the gynecologist decides on the advisability of continuing the pregnancy with the obligatory stay of the pregnant woman in the hospital.
Medical examination at 39 weeks of gestation
At this stage, the expectant mother, as a rule, does not undergo any special examinations. The necessary tests and examinations may be prescribed if any abnormalities or abnormalities were observed in the pregnant woman or fetus during pregnancy.
An examination in a hospital or an additional ultrasound at the 39th week of pregnancy is prescribed for those women who will have a caesarean section. In such a case, the expectant mother is recommended to discuss all the nuances of the operation, since each maternity hospital has its own rules for the use of anesthesia and management of the postpartum period.
Examination on the chair, miscarriage
Can a gynecologist provoke a miscarriage after an early examination in the chair? Do I have the right to refuse an examination in a chair?
Maybe only if something is already wrong there
I don't think they will provoke me. I had a threat, they looked at me every week from 6 weeks to 12 in the hospital. Everything is fine.
You can give up everything. Getting examined is your right, not your obligation. In general, you don’t have to go to the residential complex at all if you want. But it’s better, of course, to go and get tested according to Order 50 of the Ministry of Health
Indications
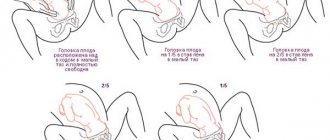
Before the embryo appears, the cervix softens. This happens from 32 weeks. When opening, the fruit moves outward, stretching the throat. If the birth is not the first, the process happens faster. By the end of pregnancy, the organ is open to several fingers. During the examination on the chair before childbirth, the location and length of the organ is determined.
The readiness of the cervix is assessed according to four parameters. Maturity is judged using the Bishop scale and a three-point system. A score of 5 indicates readiness for natural childbirth. One of the parameters is consistency. Hardness is zero, average density is 1 point, softness is 2 points.
When determining the length, pay attention to the smoothness of the neck. If it is no more than 1 cm, on the scale the indicator means 2 points, about two centimeters - 1 point, over 2 cm - zero points. The last result indicates unpreparedness for childbirth.
The location can be in three options: tilted back, forward and in the middle. The patency of the cervical canal is determined. To measure, use your fingers, passing them beyond the outer and inner pharynx.
The gynecologist examines the condition of the amniotic sac, whether there are any ruptures, tension, and how much the organ is filled with water. Determine how open the passage is. In the normal course of pregnancy, it is 10–12 cm. If, during examination, the doctor sets the limit to 5 points, the cervix is soft and ready, labor may begin.
Refusal to be examined by a gynecologist
A gynecological examination during pregnancy is one of the most informative ways to monitor a woman’s health status. Despite this, many pregnant women try to avoid it, fearing that the doctor’s manipulations could provoke a miscarriage.
Indeed, sometimes after an examination on the chair bleeding may begin - “daub”. Let’s make a reservation right away that in official medicine there is no such term as “spotting”, but it is this word that most accurately defines the nature of vaginal discharge: more than a few drops, but less than during menstruation (i.e. spotting discharge, staining the lower underwear). The color of the discharge can vary from light beige to dark red or brown. There are several reasons why spotting may appear after a pregnancy examination :
- During the period of bearing a child, the uterus is intensively supplied with blood, and if a woman also has weakened vascular walls, and this is a common occurrence during pregnancy, microtraumas are understandable.
- During the examination, swabs will be taken for analysis. A special instrument is used to collect material from the cervix, vaginal walls and urethra, which can also injure the delicate surface of the organs and cause minor bleeding.
- After a two-handed examination, used to assess the condition of the cervix, patency of the external pharynx, etc., pain and minor bleeding often occur. This is explained by increased blood supply to the pelvic organs and changes in the muscular and ligamentous apparatus of the uterus.
- Sometimes blood during pregnancy after examination signals an incipient miscarriage. It is extremely rare that this happens due to inept or rude actions of the doctor, much more often the reasons for the miscarriage are completely different, and the examination only aggravates them.
Many women are interested in the question: will they be registered as pregnant without a gynecological examination? And is it possible to avoid this unpleasant procedure during pregnancy?
An examination in a gynecological chair is usually carried out at the first consultation regarding pregnancy, at 20-22 weeks and at 35 weeks. According to indications - more often.
During the first examination, the doctor determines the approximate period and also takes the necessary biomaterial for analysis. However, at the moment there is a good trend - a conscious approach to planning the appearance of offspring. Therefore, a woman often comes to a consultation with the results of an ultrasound, a blood test for hCG, and pre-tested tests for sexually transmitted infections. In the case of such a “prepared” patient, registration without examination . But it will not be possible to avoid it at all: even if all the smears were “clean”, hormonal changes gradually reduce the activity of leukocytes and local cellular immunity, as a result of which the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms can occur, which are not so harmless for the unborn baby. In addition, there are a number of alarming symptoms that are not always detectable by an all-seeing ultrasound sensor, but are obvious upon palpation.
Many antenatal clinics practice a “gentle” method of collecting biological material, which does not use mirrors. In case of a complicated medical history, threat of miscarriage or premature birth, a gynecological examination is carried out very carefully. Sometimes a pregnant woman is examined not on a chair, but on a special examination couch.
As you can see, the main purpose of a gynecological examination is to take smears. This is done not at the whim of the supervising doctor and not with the aim of harming the patient, but for the early detection and treatment of infections that lead to disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus or premature birth.
Of course, you can ignore the examination by a gynecologist, citing the law, according to which you have every right to refuse any medical interventions. But before you make such a decision, weigh the pros and cons. Do you really want your child to be born in the observation department of the maternity hospital (and this will happen if not all health information is collected in the exchange card)? And this is far from the worst option. It is much worse to unknowingly, out of good intentions, cause harm to the health of a little person.
How is cervical maturity assessed?
Starting from 38 weeks of pregnancy, during an examination with a gynecologist at a antenatal clinic or in a maternity hospital, the doctor conducts a vaginal examination to assess the condition of the cervix. It is also mandatory to examine the cervix before childbirth, as well as during labor. This is necessary to understand how quickly the process of maturation occurs.
There are four main parameters, by assessing which an obstetrician-gynecologist can conclude that the cervix is ready for childbirth. Its maturity is determined by a special Bishop scale, according to which each of the parameters is assessed on a three-point system (from 0 to 2 points). If this scale is rated 5, then we can talk about readiness for natural childbirth.
- The first parameter that the gynecologist evaluates during a vaginal examination is consistency. The maximum number of points is 2 for a soft neck; if it is softened, but a little denser near the internal pharynx, then its condition is assessed as 1 point; a hard cervix is not ready for childbirth and is scored 0 points.
- The second important parameter is length. On the Bishop scale, a smoothed neck, the length of which does not exceed 1 cm, is scored 2 points. A neck 1–2 cm long receives 1 point. If the length is more than 2 cm, then it is not ready for childbirth and is scored 0 points.
- The third parameter that matters is location. The Bishop score suggests a score of 0 for a cervix that is deviated posteriorly; 1 point for anterior deviation and 2 points for midline position.
- The fourth important parameter is the patency of the cervical canal. It is usually measured by the number of fingers that can pass beyond the outer and inner pharynx. If the external pharynx is closed or allows only the tip of the finger to pass through, the neck is considered not ready (0 points). If the outer pharynx has opened, but the internal pharynx remains closed, then this is scored 1 point. If the channel freely passes 2 fingers through the internal os, then 2 points are given.