Prolapse of the genital organs is a pathology that can often be encountered even in young women. Difficult childbirth, trauma and many other reasons can lead to a similar condition. The initial stages of genital prolapse are not an obstacle to pregnancy, and young women with such problems are often planning to expand their family. Can pathology affect pregnancy and childbirth? What to do, how and when to solve the problem?
Causes of uterine prolapse
The initial stages of prolapse (genital prolapse) are asymptomatic. A woman often does not pay attention to minor displacements of the cervix or vaginal walls. Therefore, most people come for medical help when they already have obvious symptoms and discomfort, or the occurrence of concomitant diseases.
Pathology can develop even in young girls, between the ages of 25 and 30. But obvious symptoms of the disease, when serious surgical treatment or some conservative measures are necessary, appear after 45 - 50 years and older. It all depends on the triggering factors, lifestyle, etc.
We recommend reading the article about planning pregnancy. From it you will learn about general recommendations, visits to doctors, and examinations for men.
And here is more information about the possibility of getting pregnant with one fallopian tube.
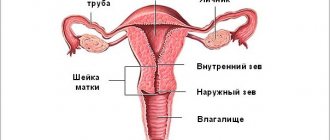
A little about the anatomy of the female reproductive organs
Normally, the uterus is “suspended” in the pelvic cavity with the help of ligaments and muscles. They are attached to its lateral surfaces, in the cervical area, holding the organ in a certain position.
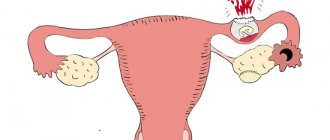
When the anatomy of this musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the uterus is disrupted, prolapse occurs - a displacement relative to other pelvic organs.
Over time, it moves so far from its physiological position that the cervix and even the body itself can be easily found at the entrance to the vagina or even outside.
Features of connective tissue in a girl
It is rare to hear the diagnosis of “connective tissue dysplasia”, although the number of girls suffering from this pathology is quite large. This is a kind of hereditary trait. As a rule, girls with such properties are tall, have long and fragile bones, “pianist” fingers, they are very flexible, etc.
The connective tissue that forms ligaments, including their ligaments, is excessively stretchable. The slightest deviation is an injury. The same applies to the ligaments of the uterus. Even with minor provoking factors, their excessive stretching occurs, and as a result, the uterus prolapses.
Injuries during childbirth
Most often, the main provoking factor for the development of prolapse is traumatic childbirth. This can be assumed in the following situations:
- if a large child was born (more than 4 kg);
- if there were complications such as ruptures of the perineum and vagina (especially 3-4 degrees);
- in case of long labor (more than 10 - 12 hours);
- if additional operations were used - vacuum extraction, application of obstetric forceps, etc.
Not all injuries can always be diagnosed on time. Even with extensive ruptures of the perineum and vagina, the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus may not be damaged.
Many women believe that episiotomy (dissection of the perineum with the threat of spontaneous rupture) always subsequently leads to prolapse of the genital organs. However, this is not quite true. If, during suturing, all tissues are carefully compared, and subsequently the sutures heal well, no long-term unpleasant results should be expected.
But if a woman did not properly care for the wound, began to sit down earlier than expected, or did not take care of her stool, then even a well-made seam can come apart. As a result, after 5 - 10 years this will contribute to hair loss.
Excessive physical activity
Due to their work or household work (for example, in a rural lifestyle), women have to perform difficult physical work, lift weights, etc. This leads to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity. Under such pressure, the uterus and appendages begin to descend, stretching its ligamentous apparatus.
Exactly the same situations can be simulated in the gym by lifting large loads, barbells, etc. Therefore, you need to practice with an instructor so as not to harm yourself.
Overweight
If extra pounds are deposited in the abdominal area, additional pressure is created in the abdominal cavity. Moreover, it is not temporary, but permanent. This also provokes prolapse. Even in a young, overweight woman, signs of prolapse can be found, which progress over time.
Hormonal disorders
Lack of estrogen leads to loss of elasticity of tissues, including the ligamentous apparatus. Therefore, during menopause, genital prolapse begins to progress rapidly. Also at risk are women who have had one or both ovaries removed.
Causes and manifestations of the disease
Uterine prolapse can be caused by the following factors:
- muscle injuries in the pelvic area;
- multiple natural births;
- numerous ruptures of the perineum (they are especially dangerous if the sutures are applied incorrectly);
- congenital malformations of the internal genital organs;
- neurological disorders that affect the innervation of organs in the pelvic area.
Concomitant reasons for the development of uterine prolapse are middle and old age of a woman, chronic constipation and frequent carrying of heavy objects. Complicated labor (eg, breech position, use of a vacuum) can also cause the cervix to weaken and prolapse.
Symptoms of uterine prolapse can be different - it all depends on the stage of the disease (there are 4 stages in total). At the first stage, the entire uterus or only its cervix descends, but the descended part is not visible from the vagina even with significant muscle tension. In the second stage of development of the disease, the uterus drops lower, which is why it can be seen from the vagina when a woman pushes. During the third and fourth stages, the uterus may partially or completely fall out of the vagina.
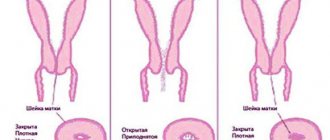
Degrees of uterine prolapse
Depending on the extent to which the uterus has shifted relative to other pelvic organs, several degrees of prolapse are distinguished. The classification takes into account changes in the position of the vaginal walls, body of the face and cervix.
The following stages of progression of the disease are distinguished:
| Degrees of uterine prolapse | Symptoms |
| 1st degree | All symptoms can be detected only when the woman strains strongly. In this case, there is some prolapse of the vaginal walls, and the cervix moves along its axis, but remains inside. |
| 2nd degree | In this case, without any tension, the woman can feel the protruding vaginal mucosa during palpation. Since all organs are closely connected anatomically to each other, the bladder and rectum descend after them, a vesicocele and rectocele occur, respectively. The cervix also moves, but is visible from the genital slit only when straining. |
| 3rd degree | It is characterized by the fact that a foreign body is constantly felt in the perineal area. This is a part of the cervix that no longer goes inside the vagina on its own in a calm state. |
| 4th degree | Complete prolapse of the uterus. It can be moved inward, but at the slightest tension it appears outside again. |
How to avoid complications?
Many women with a similar pathology wonder whether it is possible to become pregnant with uterine prolapse and not encounter serious complications. Modern medicine really allows us to avoid most of the negative consequences. To do this, the patient will have to:
- Consult a gynecologist.
- Strengthen the muscles of the perineum.
- Complete the prescribed course of treatment.
Consulting a doctor will help you choose the right direction in preparing the body. He will examine the patient, tell you how to get pregnant with this disease and not encounter the most dangerous complications of uterine prolapse. The gynecologist will prescribe the necessary examination. Their minimum volume will include the following activities.
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for glucose levels;
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for the content of female sex hormones;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
After this examination, the doctor will determine the degree of uterine prolapse. If this pathology is not very pronounced, then the specialist will tell you about exercises to strengthen the muscles of the perineum. The most commonly used is the Kegel complex. It allows you to almost completely restore the position of the uterus within a few months. Unfortunately, such exercises are effective only in mild cases of the disease.
In order to ensure the normal position of the body and cervix during pregnancy, women with severe prolapse of these organs undergo surgery. It involves fixation of the uterus to surrounding tissues. Thus, a possible miscarriage or termination of pregnancy becomes much less likely outcomes after conceiving a child.
With any prolapse of the uterus, various types of inflammatory and infectious processes pose a significantly greater danger to pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to carry out specific treatment for this pathology even before the baby is conceived. Otherwise, not only may a miscarriage or termination of pregnancy occur, but there may also be a need for a complex surgical intervention - a hysterectomy. After such treatment, a woman will no longer be able to become pregnant.
Among other things, the doctor may well prescribe replacement therapy to a woman in cases where prolapse of the uterine organ leads to a decrease in the production of female sex hormones.
All recommendations of specialists for this pathology must be followed. If you do exactly as gynecologists advise, then the likelihood of having a healthy baby will significantly increase, and the risk of developing serious complications will sharply decrease.
It is characterized by the incorrect location (displacement) of the female organ responsible for the full bearing of the child. This is why the disease complicates the process of pregnancy and childbirth.
Uterine prolapse is diagnosed during a gynecological examination and ultrasound. Possible causes of the disease may be:
- congenital defects in the structure of the internal genital organs;
- inflammation, adhesions, tumors;
- weak pelvic floor muscles.
Problems a woman may face
Prolapse of the genitals in the early stages brings practically no worries to the woman, in addition to psychological discomfort. As the pathology progresses, especially if provoking factors persist, the symptoms will worsen. The main ones include the following:
- Periodic, especially after physical exertion, aching pain in the lower abdomen, sacrum and lower back.
- Impaired urination in the form of frequent urge, incontinence, and even uncontrollable urge. A woman may notice that when she coughs, sneezes, or mildly strains, she cannot hold her urine.
- Impaired defecation - prolapse provokes constipation, as the normal evacuation of feces is disrupted.
- There may also be discomfort during intimate relationships. Sometimes they are possible only after realignment of the neck and body.
- A woman may complain of recurrent thrush, constant inflammation in the vagina. This is due to the fact that the genital gap does not close, and it is very easy for pathogenic bacteria to penetrate inside, causing an inflammatory process.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the perineal area.
Four degrees of uterine prolapse
Prevention
Uterine prolapse is one of the diseases that is much easier to prevent than to treat. Considering the consequences of the disease, its prevention should be carried out from a young age, that is, long before childbirth. Girls need to engage in light sports and strengthen their abdominal muscles. Kegel exercises (relaxation and tension of intimate muscles) are considered useful. They not only help keep the uterus in good shape, but also reduce the likelihood of ruptures during childbirth.
Other ways to prevent uterine prolapse include:
- adequate management of the birth process;
- compliance with the protective regime after childbirth;
- timely treatment of all inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- performing exercises for correct posture;
- moderate constant physical activity.
Women are not recommended to lift weights weighing more than 10 kg, as this significantly affects the stretching of the muscles in the pelvic area and can cause a weakening of their normal tone. It is important to monitor your diet - the body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals. Particular attention should be paid to preventive measures in the first year after childbirth, during menopause and in case of hormonal disorders.
When is pregnancy banned?
Genital prolapse of the first and second degrees will not affect the pregnancy process in any way. And if a woman still feels some discomfort in the first trimester, then after 12 weeks all symptoms will gradually go away. This is due to the growth of the uterus.
There are no direct contraindications for pregnancy due to genital prolapse. Most often, during childbearing years there is no 4th degree of pathology, when the uterus is completely outside the genital slit. If this is the case, you must first undergo a full examination and establish the cause. In this situation, a new pregnancy can worsen the situation so much that it puts the woman’s health at real risk.
The issue of delivery is decided individually. For example, if genital prolapse occurs as a result of extensive ruptures of the vagina and perineum, then a cesarean section should be performed in the future.
This is due to the fact that scars form at the site of old tears. And even with the slightest stress (for example, in the case of repeated natural childbirth), injuries can lead to large blood loss and a threat to the woman’s life.
Watch the video about uterine prolapse:
Symptoms of uterine prolapse during pregnancy
All clinical manifestations of prolapse during pregnancy do not differ from those in the normal state. But, as a rule, as the period increases, the body of the uterus rises, and the symptoms are minimized. Most often, a woman encounters the following:
- she may detect a cervix that protrudes from the genital slit, especially if she is sitting in a squatting position;
- frequent urination and constipation;
- in the early stages, nagging pain in the lower abdomen due to uterine prolapse can be interpreted as a threat of miscarriage and vice versa.
If the uterus has prolapsed in the early stages: complications that you may encounter
Many women believe that prolapse can cause detachment (hematomas), leading to pregnancy failure and other pathologies. In fact, there are no direct connections. Prolapse indirectly affects the pregnancy process due to the following reasons:
- With prolapse, women more often suffer from inflammatory processes in the vagina, cervix and uterine cavity. And the infection can provoke pathology of fetal development, threat, etc.
- When the genitals prolapse, it is easy to injure the genitals, including during intimate relationships. Therefore, it is important for women to protect themselves from stress, both physical and psycho-emotional.
Prolapse of the uterus during pregnancy and the rules of behavior for the mother in this case
Women who have prolapse of any degree should plan their pregnancy. Only in this case will it be as successful as possible. The main recommendations are as follows:
- It is better to undergo an examination on the eve of pregnancy for possible sexually transmitted infections and, if necessary, a full course of treatment.
- Carrying heavy objects, prolonged vertical position of the body, and violent sexual intercourse should be avoided.
- As the period increases, you can additionally wear a unloading belt, which can partially relieve the load from the pelvic floor.
- Together with your doctor, you need to choose the most optimal method of delivery. In the case of a natural birth, you should listen as carefully as possible to all the instructions of the doctor and midwife and try to follow everything correctly to prevent serious ruptures.
- Unloading pessaries and circular sutures on the cervix are necessary only when there is a threat of interruption and shortening of the cervical canal. This has nothing to do with genital prolapse.
What should a woman do?
When a woman is diagnosed with prolapse during pregnancy, she is asked to insert a special uterine ring, which will reduce the pressure of the constantly gaining weight of the fetus on the cervical area, and thereby prevent premature dilatation of the cervix.
However, a woman must understand that this device cannot guarantee a positive course and favorable outcome of pregnancy.
It is also recommended that a woman wear a special bandage , and if the displacement of the uterus is pronounced, then bed rest is preferable .
If a woman’s hormonal background undergoes changes, special hormonal suppositories may be prescribed.
In most cases, a pregnant woman spends almost the entire period of bearing a baby in a hospital setting, but if the doctor allows her to stay at home, she must adhere to the following rules:
- do not carry heavy objects;
- avoid prolonged vertical position of the body;
- in later stages it is necessary to wear a bandage;
- thoroughly and accurately carry out all doctor’s orders;
- When prescribed, perform Kegel exercises.