Cervical rupture: causes
The consequence of insufficient dilatation of the cervix is its rupture during pushing. A woman begins to push at a time when the cervix has not yet fully dilated, and it may not withstand the tension and rupture.
Often this injury occurs due to a combination of several factors:
- decreased tissue elasticity in primiparous women after 30 years of age;
- decreased tissue elasticity for other reasons (adhesions and scars, previous abortions, inflammatory processes);
- rapid labor (the cervix simply does not have time to open to an acceptable size);
- anomalies of labor, in which the process of dilation of the cervix is disrupted;
- large child;
- breech birth;
- surgical delivery with forceps or vacuum extraction of the fetus;
- improper provision of obstetric care.
When two or more factors coincide, the risk of cervical rupture increases significantly.
Causes of uterine rupture during childbirth
The most common causes of uterine ruptures during childbirth are the following:
- Large fruit (fruit weight more than 4000 g);
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Polyhydramnios;
- Anatomical features of the structure of the uterus, for example, with bicornuate organ;
- The presence of scars on the uterus after previous cesarean sections, previous operations, or long-term surgical abortions;
- Narrow pelvis of a woman;
- Incorrect position of the fetus in the uterus, presentation;
- Titanic contractions of the uterus as a result of hyperstimulation by oxytocin.
Signs of threatened uterine rupture during childbirth. Symptoms and diagnosis of uterine rupture after childbirth
An obstetrician-gynecologist is constantly with the woman in the delivery room, which is necessary in order to notice threatening conditions in time and provide immediate assistance. Signs of impending uterine rupture include the following:
- Excessive and incessant contractions of the uterus;
- Sharp pain on palpation in the area of the lower third of the organ;
- The uterus takes on the shape of an hourglass, its upper and lower segments are located obliquely from each other;
- Ichor is secreted from the genital tract;
- When examining the genital organs, the doctor notes their swelling.
If the threatening rupture is caused by thinning of the walls of the uterus in the area of the lower segment of the organ, then the woman will experience a weakening of labor.
Symptoms of uterine rupture during childbirth are:
- The woman behaves restlessly, clutches her stomach with her hands, complains of piercing pain;
- Blood pressure readings drop sharply;
- The skin of a woman in labor is pale, cold sweat appears, the pupils dilate, the pulse becomes thread-like;
- Shortness of breath and loss of consciousness appear.
Consequences of uterine rupture during childbirth
Almost always, after a uterine rupture during childbirth, a woman has her uterus removed, so she will no longer be able to have children. The serious consequences of this complication are massive hemorrhages in the abdominal cavity, painful shock, acute vascular and heart failure in women. If a woman in labor does not undergo emergency surgery in a timely manner, she and her child may die.
Rupture of the uterine scar after surgical delivery
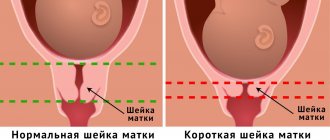
They always try to admit a woman who has undergone surgical delivery to the maternity hospital in advance, approximately 1-2 weeks before the expected date of birth. Throughout pregnancy, doctors pay close attention to the scar on the uterus. Immediately before giving birth, the patient is once again sent for an ultrasound to control the condition of the scar - its stretching, thickness, and surrounding tissues. If the scar is incompetent, then the woman undergoes a repeat cesarean section, and the operation is scheduled a week earlier before the expected due date. Such measures are due to the danger of uterine tissue diverging along the old scar during contractions or pushing, so obstetricians prefer not to take risks.
If, however, the scar ruptures during pregnancy or during childbirth, then the woman undergoes emergency surgery. When tissue ruptures, the pregnant woman feels piercing pain in the abdomen, loss of consciousness is possible, and blood pressure levels drop. If assistance is not provided, the expectant mother may die from painful shock and blood loss, and the child from acute hypoxia.
Rehabilitation period after uterine rupture
In the rehabilitation period after a uterine rupture during childbirth, a woman is prescribed strict bed rest on the first day. Afterwards, she can get out of bed with the help of medical personnel to prevent the development of adhesive disease.
Since with this complication a woman loses a lot of blood, for a speedy recovery she is prescribed antianemic drugs, drugs that prevent the formation of clots, and vitamins. During the recovery period, it is strictly forbidden to lift weights and be sexually active.
Irina Levchenko, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mirmam.pro
Degree of cervical rupture
During labor, the cervix is greatly stretched, the edges of its external pharynx become very thin, and small tears occur, which do not necessarily bleed, remaining unnoticed. If heavy bleeding begins, then this is a clinical sign of deep ruptures of the cervix.
Photos of cervical rupture show that most often ruptures occur on the left side, sometimes reaching the vaginal vault.
There are three degrees of cervical rupture:
- 1st degree cervical rupture (the length of the rupture is no more than 2 cm);
- 2nd degree cervical rupture (the length of the rupture is more than 2 cm, but does not reach the fornix);
- 3rd degree cervical rupture (the ruptures reach the fornix, extend to it and to the upper parts of the vagina).
Types by method of occurrence
This pathology is divided into types according to the method of its formation. This is important, because it is the correctly identified type of rupture that will help quickly provide help. Based on the type of occurrence, they are divided into two groups.
- Spontaneous. These are the ruptures that occur during the natural birth process and are caused by:
- Age of the woman in labor (over 30);
- A large number of abortions;
- Presence of scars on the neck;
- Large fruit;
- Unskilled midwifery care;
- Breech presentation;
- Narrow pelvis of a woman in labor;
- Long labor;
- Inelastic neck.
- Forced ruptures occur due to external interference during labor. They consist of mechanical injury to the cervix.
- Using forceps to pull out the baby and vacuum;
- Removing the child from the pelvic area.
If a woman has several symptoms at the same time, then the risk of rupture is quite high.
Cervical rupture: consequences
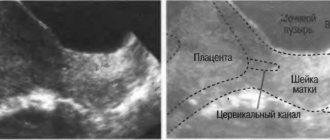
Cervical ruptures are diagnosed only after the birth of the child and placenta. Doctors look for bleeding to determine whether it is a natural consequence of childbirth or a sign of injury. In Russia, in maternity hospitals, it is customary to examine every woman for the presence of pathologies on the cervix using mirrors. If ruptures are detected, they are sutured with special absorbable threads (catgut). Such sutures do not require care, but it is advisable to refrain from intimate relations for two months after childbirth.
Problems occur if for some reason a cervical rupture was not detected or the stitches were placed incorrectly. In this case, the vagina and uterus may become inflamed, and a postpartum ulcer develops. Subsequent pregnancy and childbirth may be too much for the damaged uterus to bear, leading to miscarriages and premature birth.
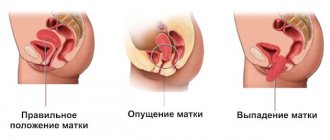
The gap has not yet been sutured; its edges heal spontaneously, which leads to the occurrence of ectropion (eversion of the cervix). Ectropion requires regular monitoring by a gynecologist, as it can cause chronic inflammation of the cervical canal, erosion of the cervix, and in some cases provoke an oncological process.
Types by type of complication
Another classification of such cervical pathology is to sort by type of complication. There are two types of such breaks.
- Complicated. This group leads to complications not only on the cervix itself, but also on nearby organs. There are several types of severe ruptures:
- The divergence of tissue reaches the vagina and captures its vaults;
- The tissues diverge, touching the inside of the vagina;
- The rupture goes all the way to the cervical canal and reaches the opening of the uterus;
- The tissue discrepancy is so great that it affects the peritoneum and the fat layer around the uterus.
- Uncomplicated ruptures are classified into grades 1 and 2. Read about the degrees of tissue divergence in the next subheading.
Cervical rupture: treatment
If a cervical rupture is diagnosed, it is immediately sutured. To do this, using bullet forceps, the cervix is brought closer to the vaginal opening and retracted in the direction opposite to the rupture. Separate interrupted sutures are applied from the upper corner of the rupture, starting slightly above it through all layers of the cervical wall, without suturing its mucosa.
Suturing of a cervical rupture is necessarily carried out under anesthesia: either intravenous or inhalational, administered through the respiratory tract.
Symptoms of a rupture
There are several degrees of cervical rupture, on which the manifestation of certain symptoms depends:
- First degree - a gap of no more than two centimeters on one or both sides,
- Second degree - a gap of more than two centimeters, which does not reach the vaginal vault by more than 1 cm,
- The third degree is considered complicated when the rupture reaches the vaginal vault and can extend onto it.
Symptoms of cervical ruptures:
- tears up to one centimeter are asymptomatic,
- cold sweat, excessive sweating,
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes,
- spotting with blood clots, which depend on the depth and size of the rupture.
To diagnose the presence of tears, doctors can use several methods:
- presence and nature of bleeding,
- studying the history of past births and the course of pregnancy,
- examination of a woman by a doctor, palpation of the tone of her uterus, shape and size,
- measuring the pulse and blood pressure of a pregnant woman, feeling her abdomen,
- examination of the cervix in the mirrors on the gynecological chair for the presence of ruptures,
- For third-degree ruptures, manual examination of the cervix is necessary.
Top
Prevention
Due to the fact that the woman in labor plays the main role in the process of childbirth, it is her adequate behavior, willingness to follow the advice of the doctor and midwife, and proper breathing during pushing that are the most important prevention of cervical ruptures.
Today, antispasmodic drugs are often used during childbirth to promote dilatation of the cervix. In addition, to prevent ruptures, various types of pain relief are used, thanks to which the woman calmly endures contractions and waits for the start of pushing, without starting to push prematurely.
In rare cases, when the doctor suspects possible strangulation of the cervix, as well as the occurrence of ruptures, he may perform a surgical dissection during childbirth. This is an advisable preventive measure, since it is easier to suture and treat an incised wound than a torn one with uneven edges. Generally, cutting or cutting the cervix is a safer method of quickly delivering a woman in the event of predicted problems with the cervix.
Take care of yourself and give birth easily and without ruptures!
Treatment of rupture
After making a diagnosis of cervical rupture, treatment begins immediately.
- Lacerations are usually repaired using self-absorbable sutures (catgut).
- Stitching of cervical ruptures must be carried out under inhalation or intravenous anesthesia.
- If the rupture is very complicated and extends to the fatty tissue around the uterus and the presence of a hematoma is observed, stitching is performed with opening of the abdominal cavity under anesthesia.
After stitches are applied, you cannot have sexual relations with a man earlier than two months later.
To prevent possible ruptures during childbirth, you should definitely follow the preventive instructions:
- It is necessary to be attentive and listen to everything the midwife says, especially when it comes to pushing. She will see for herself and tell you when you need to push, and you shouldn’t do it before the allotted time.
- Proper breathing during childbirth will help a woman reduce pain and concentrate on the birth process.
- It is possible to use antispasmodic drugs that promote normal dilatation of the cervix.
- Pain relief can be used to prevent a woman from pushing prematurely without a doctor's instructions.
- If pregnancy is planned, you should prepare for it - cure all chronic diseases, do vaginal gymnastics and take a course of vitamins.
- Eat foods that are recommended for pregnant women, especially those high in fiber.
- Eat well and rest.
If the doctor sees that ruptures cannot be avoided, you can resort to surgical dissection during childbirth. It is easier to stitch up and treat such a wound than a torn one with uneven edges. After suturing, you must regularly visit a gynecologist. This will prevent possible inflammatory processes and avoid unpleasant complications.
Top
Is it painful to stitch up tears after childbirth?
Much depends on individual tolerance, as well as the affected area. Some women require anesthesia for the procedure.
If the cervix is ruptured, then most often no pain medication is used. In other cases, the degree of rupture is assessed.
How do you sew it up?
First, the perineal muscles are sutured using absorbable suture material. Sutures made of non-shrinkable material are placed on the skin. When the incision is straight, the specialist applies a cosmetic suture. The thread runs in a zigzag pattern, appearing outside at the beginning or end of the cut. This results in a thinner scar. A technique is often used when tissue and skin are sewn together with one thread, using absorbable material.
Is anesthesia used?
The choice of anesthesia - local or internal - directly depends on the degree of damage. It may not be used at all if the tissue of the cervix, which is insensitive after childbirth, is sutured.
To apply sutures in the vagina, a local anesthetic (Novocaine, Lidocaine) or general (short-term intravenous anesthesia) is required. The perineum is sutured under Novocaine or Lidocaine. In some cases, pain medication may not be used, because some physiological mechanisms provide protection from pain during childbirth.
Diagnostics
The obstetrician-gynecologist leading the pregnancy collects medical history data.
If the patient has had any inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, abortions, or surgical interventions on the reproductive organ in the past, the pregnancy will be monitored more closely.
At each visit to the gynecologist, a pregnant woman undergoes an external obstetric examination and monitors indicators such as heartbeat and blood pressure.
If necessary, additional ultrasound is prescribed.
Types of postpartum injuries
Trauma to the birth canal can be divided into:
- Microtraumas that inevitably appear as the baby passes through the birth canal - in the absence of more severe injuries, they recover on their own within a few weeks after birth.
- Ruptures of the perineum and vaginal walls - depending on the severity of the damage, can be small, affecting only the skin of the perineum with the mucous membranes of the vagina, or more serious, in which damage occurs to the muscles of the perineum and even the sphincter and rectum.
- Uterine ruptures are the most dangerous injuries received during childbirth, which can even lead to death of both mother and child, and are rare.
- Episiotomy - surgical incisions in the perineum and posterior vaginal wall to avoid arbitrary ruptures in the mother and possible injuries to the child during childbirth.