Causes of uterine duplication
It is reliably known that abnormalities in the formation of the uterus are associated with distortion of the mechanisms of normal development of the embryo.
Apparently, undesirable changes in environmental conditions (nutrition, gas exchange, etc.) in which the fetus is formed occur due to the negative impact of unfavorable factors on the pregnant woman’s body. Incorrect development of the embryo can be caused by:
- infections suffered by a pregnant woman, especially in the early stages, when the development of the uterus in the embryo occurs;
- improper nutrition of a pregnant woman, when the embryo lacks the nutrients necessary for normal formation;
- taking teratogenic (that is, capable of harming the fetus) medications;
- endocrine disorders (ovarian dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- severe stress;
- severe toxicosis, manifesting already at the beginning of pregnancy;
— intoxication (nicotine, occupational hazards, alcohol, drugs, radiation).
The hereditary factor plays a significant role in the occurrence of uterine duplication, so pregnancy in women in whose families there have already been cases of abnormal fetal development deserves special attention.
The close connection of the embryonic rudiments of the genital organs with the rudiments of the kidneys and urinary tract explains the often occurring joint anomalies in the development of these systems, when the fetus simultaneously has a duplication of the uterus and a duplication of the kidney.
Reasons for bifurcation
The anomaly is based on the consequences of teratogenic factors that acted on the fetus during its intrauterine development. The most dangerous are the first months of pregnancy (from 8 to 16 weeks), when the formation of human internal organs occurs.
Why a bicornuate uterus is formed - reasons:
- Intoxication of the fetus with alcohol, nicotine, chemicals, drugs;
- Stressful situations experienced by the expectant mother;
- Diseases of the endocrine system in a pregnant woman (diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies) or a history of heart disease;
- Vitamin deficiency in the fetus;
- Early or late toxicosis of pregnancy;
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Infectious diseases (measles, rubella, syphilis, influenza, toxoplasmosis) suffered during pregnancy.
Similar reasons cause uterine doubling, since the walls of the Müllerian ducts do not dissolve due to the influence of teratogenic factors, or are subject to incomplete destruction.
Symptoms and signs of uterine duplication
Duplication of the uterus is a pathological division of it into two parts. This pathology has many anatomical variants, which are classified into several groups:
1. Complete duplication of the uterus, which we will discuss in detail in the next chapter. There are two independent anatomical structures, that is, in fact, two uteruses. Duplication of the uterus and vagina is considered absolute duplication, when each half has its own cervix and its own vagina.
2. Incomplete duplication of the uterus. The uterus is partially divided in two by a septum, the resulting halves resemble horns, which is why the term “bicornuate uterus” is used. This anomaly is considered the most common (62%) occurring. Both horns have one cervix and a single vaginal cavity. In this case, the degree of development of each half of the uterus may be unequal. In addition to symmetrical development, there are options when among two there is one atretic (non-developing) uterine horn or one closed but functioning horn.
The most common anatomical variant is the saddle uterus, so named due to its external resemblance to a saddle. With this developmental anomaly, the septum in the uterine cavity is present only in the area of the uterine fundus, and otherwise bicornus is not expressed. A saddle-shaped depression forms in the fundus of the uterus.
A double uterus with an open lumen is asymptomatic until the arrival of the first menstruation. Incomplete duplication of the uterus may not provoke active complaints. They appear only if the outflow of menstrual blood is disrupted. Most often, severe pain similar to labor contractions is provoked by a bicornuate uterus with a functioning closed horn, when the accumulated blood cannot be evacuated from the confined space, accumulates and overstretches the accessory horn, that is, a hematometra is actually formed.
Contrary to the common misconception among patients, infertility is not a frequent concomitant of uterine doubling, since this defect is not associated with ovarian dysfunction and does not affect ovulation and fertilization. A fertilized egg can be successfully implanted in one of the halves of the uterus, but its further fate depends on the conditions under which the placenta and the fetus itself will form.
The diagnostic search for uterine duplication includes a gynecological examination, ultrasound scanning, metrosalpingography and hysteroscopy.
Palpation of the uterus often provides information about the irregular shape of the organ, but a more detailed study of the pathology is only possible with the help of instrumental diagnostic manipulations. Typical variants of uterine duplication are clearly visualized during ultrasound scanning. At the same time, the structure of the kidneys is studied to exclude the presence of symmetrical developmental pathology.
If uterine duplication is associated with the presence of severe clinical symptoms and also requires surgical correction, a more detailed examination is necessary: hysteroscopy and hysterosalpingography. They allow you to examine the inner surface of the uterus, determine the type of duplication, as well as introduce a contrast agent and take a series of x-rays to detail the information received.
Atypical forms of uterine duplication are rare; MRI is preferable for their diagnosis.
Abnormalities of the reproductive organs
Pathologies in the development of the uterine cavity are formed at the stage of embryonic growth of the fetus, when gender differences begin to emerge. The body of a pregnant woman is exposed to negative factors that provoke various anomalies in the anatomical structure of the child. These factors include:
- bad habits of a pregnant woman;
- influence of harmful production conditions;
- viral infections;
- taking certain pharmacological drugs;
There are many variations of defects:
- doubling of the uterine cavity with one vagina;
- bicornus;
- saddle;
- presence of a partition inside.
Such pathologies are detected during the first examination by a gynecologist. For a detailed study, ultrasound scanning and other medical procedures are prescribed.
Complete and incomplete duplication of the uterus and cervix
Duplication of the uterus and cervix is diagnosed very rarely. This is explained by high-quality medical care, which helps prevent the occurrence of negative effects on the fetus, which is the dominant cause of bifurcation. If there is no fusion or improper fusion of the embryonic ducts, the cavity is divided.
Intrauterine embryonic development represents a gradual process of formation of cells and tissues from which internal organs are formed. The appearance of the uterine cavity in female embryos occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy. Initially, this organ is divided by a septum, which is reduced over time.
Doubling can manifest itself in different ways, based on the process of its formation. A septum is sometimes fixed in the uterine cavity, which divides it into two sections. With the isolated development of these sections, complete duplication of the vagina, cervix and cavity from which the fallopian tube with the ovary departs is diagnosed. Both reproductive organs can be separated by the rectum and bladder or touch each other.
There are cases when, with complete doubling, one part of the uterus progresses, while the other stops developing.
In the case of incomplete doubling of the organ, the septum is located only in the upper part, the lower part represents a single space.
Uterine anomalies may not manifest themselves in any way, especially with a bicornuate and saddle-shaped uterus. The main symptom indicating doubling is infertility. Delayed menstruation in girls may also indicate pathology.
Septum in the uterine body
An intrauterine septum is an anomaly in which the cavity is divided into two parts. A distinction is made between complete and incomplete septum. In the first case, the pathological formation passes through the entire uterine cavity, starting from the bottom and ending with the cervix. Occasionally, the inclusion is observed to extend beyond the cervix, into the vaginal area. The length of an incomplete septum does not exceed 4 cm. Such formations can also be transverse and have different thicknesses.
Often, along with the malformation of the uterus and cervix, doubling of the kidneys is diagnosed.
Women with this defect have problems conceiving and frequent miscarriages. Differential diagnosis of a septum in the uterus is difficult and requires the use of modern diagnostic methods.
Complete duplication of the uterus
A complete duplication of the uterus is considered complete if it is divided into two independently functioning sections (horns), each of them has its own cervix and is anatomically connected to only one ovary located on the same side. More often, complete duplication of the uterus is combined with the presence of a single vaginal cavity, but sometimes other anatomical options are diagnosed: vagina with a septum or complete duplication of the vaginal cavity.
Symmetrically developed complete duplication of the uterus and vagina, which is sometimes called absolute, rarely bothers patients. More often, pathology is diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound scan.
There is also unequal development of duplicate organs, when one half is fully developed, and the second is underdeveloped, or remains in its infancy (complete or partial aplasia). In situations where there is partial aplasia of one of the vaginas, menstrual blood gradually accumulates in a confined space, and 3-6 months after the start of menstrual function, it provokes severe pain that cannot be corrected with medication.
Sometimes a fistula-type opening is formed in the septum between the two vaginal cavities, and the menstrual blood is partially thrown into the functioning vagina and evacuated in the usual way, while the remaining blood continues to accumulate in the closed cavity of the second vagina. In this situation, patients show signs of secondary infection - moderate pain and purulent leucorrhoea.
Step-by-step diagnosis of pathology
The doctor can assume that the patient has a complete or partial duplication of the uterus even before the diagnosis begins - based on typical complaints of abnormal bleeding, recurrent miscarriages, infertility or algomenorrhea. To clarify the diagnosis, the following activities are carried out:
Examination by a gynecologist.
It can reveal vaginal septums, doubling of the cervix and vagina, and deformation of the fundus of the reproductive organ.
Abdominal and intravaginal ultrasound.
Evaluates the condition of the pelvic organs and urinary system; if the uterine cavity is slightly deformed, the study may be unreliable.
X-ray examination.
Determines the contour of the organ, but is unable to classify the anomaly.
Hysterosalpingography with contrast agent.
Defines the contours of the uterine cavity.
Hysteroscopy.
An endoscopic examination evaluates the contours of the uterine cavity, the presence of septa in it, the structure of the endometrium, and the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Laparoscopy.
A therapeutic and diagnostic study determines the condition of the reproductive organ, its structure, and possible defects of the anatomical structure.
MRI, CT.
The study determines with a high degree of accuracy malformations of the uterus, its structure, and the anatomical structure of nearby organs.
Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor clarifies the functionality of the organ, the possibility of correcting the identified pathology using surgical methods, and determines whether it is possible to become pregnant with a doubling uterus or with a bicornuate uterus.
A woman’s two uteruses are not a myth, but a reality
In gynecology, the diagnosis of two uteruses is not news. Doctors have long encountered cases where a woman with a double uterus carried a pregnancy to term normally and gave birth to healthy children.
Of course, it is worth emphasizing that organ doubling is a rather rare phenomenon. According to statistics, it occurs in one in 50 million.
This pathology begins in the womb. The most common reasons are: smoking, alcohol and taking illegal medications that should not be taken during pregnancy.
The first thing that happens is that the uterus forms very slowly, the normal development of the Müllerian ducts is delayed, so their complete fusion does not occur. This is what leads to the appearance of as many as two uteruses.
Sometimes in such situations it happens that a woman has two vaginas and two cervixes. When two genital organs and one of the two uteruses are completely undeveloped, it is called rudimentary.
Considering that uterine duplication is a gynecological pathology, it often does not manifest itself in any way. A woman learns about the deviation already during pregnancy or before planning, when she is preparing for conception and then undergoes all the necessary examinations and tests.
Also, doubling may not have any effect on the menstrual cycle, the ability to conceive and bear a child without problems.
A real-life incident: a woman did not know about her pathology, became pregnant and carried twins. During childbirth, it became known that she had a doubling and the children were in different wombs.
Doubling may not manifest itself with obvious characteristic symptoms, especially if it is incomplete. It happens that all the patient’s complaints are infertility and miscarriage.
Anomalies can be diagnosed during the first gynecological examination, but their characteristics can only be obtained through instrumental examination. Two examinations can accurately establish the pathology: hysterosalpingography and ultrasound examination of the genital organs.
An important question for many women: is it necessary to eliminate the problem through surgery? No, not all cases require surgical correction of the uterus. As a rule, if the duplication of the uterus is incomplete, it is harmless and does not interfere with fertilization.
We can talk about the need to solve the problem in another way, more radically, if a woman has pronounced characteristic symptoms.
A double uterus has various anatomical nuances, so the method of elimination is selected individually.
Consequences and complications
Duplication of the uterus often complicates the functioning of the remaining genital organs and causes a deterioration in overall health. The outflow of menstrual blood is often disrupted, and the discharge accumulates in a confined space. The patient experiences severe pain, which increases and is not eliminated by conventional painkillers.
Sometimes a fistula tract forms in the vaginal septum. In this case, menstrual blood is excreted, but in small quantities. Over time, a secondary infection occurs, and discharge mixed with pus appears.
Also read: Signs of sore throat
Complications of pregnancy with a double uterus occur very often, so its management consists of timely diagnosis of disorders and prevention of increased uterine tone during gestation. Pregnancy in such patients is managed as pathological, while taking antispasmodics (No-spa) and tocolytics that prevent an increase in uterine tone (Partusisten).
With abnormalities in the structure of the organ, the incidence of placental insufficiency is high, which causes fetal hypoxia and sometimes developmental delay. To avoid negative consequences for the fetus, hypoxia should be prevented by taking antiplatelet agents (Curantil, Trental) and metabolic drugs (Actovegin, Troxevasin).
Classification and reasons
Duplication of the uterus has its own classification, which was identified solely on the basis of abnormal development.
Doubling classification:
- complete or insufficient development (one-horned uterus without a horn of a rudimentary type, underdeveloped);
- problems with the canals (one-horned with a vestigial horn);
- incomplete fusion of ducts (double and bicornuate);
- partial reabsorption of the septum (arcuate and septal).
It has been proven that such a pathology is an abnormal formation associated with problems in the embryonic development of the fetus. Unfavorable changes occur in the environmental conditions in which the fetus develops, for example, nutrition, gas exchange and other harmful factors that adversely affect the pregnant woman’s body.
Improper development of the embryo can be caused by the following factors:
- infections during pregnancy in the early stages, at this stage the formation of the uterus in the fetus occurs;
- unbalanced, unhealthy diet, when the embryo does not receive enough minerals, vitamins and enzymes necessary for normal development;
- taking teratogenic drugs;
- problems with the endocrine system - diabetes, imbalance in ovarian function, hypothyroidism;
- excessive stress, depression and psycho-emotional stress;
- severe toxicosis, which began from the very first days of pregnancy;
- intoxication of the body.
Genetics, that is, heredity, is also important. Therefore, if organ doubling has already been observed in a related family, it is necessary to plan a pregnancy and first obtain specialist advice.
Close connection between the rudiments of the genital organs together with the urinary tract and kidneys. Therefore, the fetus may often exhibit not only a doubling of the uterus, but also a doubling of the kidneys.
Characteristic symptoms and diagnosis
The manifestation of pathology depends on its characteristics, classification and intensity, as well as on the individual characteristics of each woman’s body.
Let's look at the most common reasons that will help identify the problem:
- A woman may feel fullness in the lower abdomen. This symptom can appear in girls during puberty and disappear after 3 months.
- Vaginal discharge in the middle of the cycle is not too profuse, brown spotting, sometimes with such symptoms it reveals a fistulous tract in the septum that overlaps the two vaginas.
- Systematic bloody discharge and leucorrhoea mixed with pus is detected with a fistula or secondary infection; pyometra and pyosalpinx can occur against the background of sexually transmitted infections.
- Women who have given birth experience weak labor activity, bleeding after labor and incoordination. Sometimes you can find out about two uteruses after childbirth.
- Suspicion or confirmed diagnosis – infertility.
- Impossibility of pregnancy and spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle, not always.
- Pain in the lower abdomen of a cramping nature.
In order to establish or confirm the diagnosis, the specialist must order a complete examination of all reproductive organs.
List of diagnostic measures:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and kidneys;
- MRI of the abdominal cavity and kidneys;
- gynecological examinations, together with retoabdominal;
- laparoscopy;
- hysteroscopy;
- colcoscopy;
- compiling a medical history and studying test results.
Important! An experienced obstetrician-gynecologist will be able to identify the abnormality during a routine examination in the chair.
Diagnostics
To diagnose this pathology in women, a specialist prescribes a complete diagnosis of the genital organs. To do this you need to undergo the following studies:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- Laparoscopy;
- MRI of the pelvis;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Hysteroscopy;
- Colcoscopy;
- MRI of the kidneys;
- Gynecological examination, including retoabdominal;
- Compilation and study of anamnesis (medical history).
This is important to know! An experienced specialist can determine complete duplication of the uterus during a routine gynecological examination.
Ultrasound image of a double uterus
For a more detailed study, vaginoscopy is often used, thanks to which in women with this pathology, bulging of the lateral vaginal wall can be easily identified.
Rectoabdominal examination sometimes causes an increase in the amount of uterine discharge with pus. Despite this, this method of research determines hematocolpos, hematometra, which are expressed in the form of a fixed tumor-like formation with a tight-elastic consistency.
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs provides complete information about the shape and size of the two uteruses, and also shows the size of the hematocolpos and hematometers.
As stated earlier, doubling is related to the kidneys. Therefore, for an accurate diagnosis, ultrasound of the kidneys is mandatory.
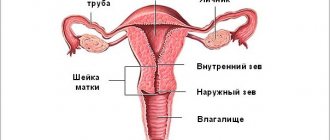
Normal structure of the uterus and vagina
Its structure changes with age. In girls it is small and cyclic changes do not occur in the endometrium. During adolescence and beyond, it increases and the endometrial layer begins to perform its function.
During menopause, it decreases again, and its aging is observed.
Duplication of the uterus and other malformations of the organ
There are a number of anomalies when there are partitions inside the organ or vagina, for example, septum or double vagina, unicornuate, bicornuate, double and saddle uterus. Some of these anomalies do not pose a danger, others interfere with motherhood, causing infertility or miscarriage.
Uterus during pregnancy
Pregnancy makes any expectant mother beautiful and amazing.
However, during this process a number of not very pleasant issues may arise that require resolution. The main organ involved during pregnancy is the uterus. Its location is the small pelvis, then the organ is located between the rectum and the bladder. The pear-shaped upper part is the body of the uterus. Its lower part, the cervix, is connected to the vagina. The fallopian tubes, which extend from the sides of the uterus, join the ovaries. The uterus is capable of changing position, moving back or forward, depending on the fullness of the intestine or bladder. When a woman is pregnant, she rises.
With age-related changes, the uterine structure also changes. In girls, the uterus is small and there are no cyclic changes in the endometrium. In adolescents and older, during the reproductive phase, the uterus increases in size and the endometrium functions. When menopause occurs, the organ ages and its size decreases.
Causes of the anomaly
Duplication of the uterus and other defects of the female genitourinary organs occur in no more than 1% of women (0.3-0.9%). The reproductive and urinary system is formed in utero from one embryonic germ, which can cause the formation of several types of defects (a double uterus is often combined with a double kidney or other types of congenital pathology of the urinary system). Abnormal intrauterine development of the genitourinary organs in a girl occurs against the background of the following causative factors:
- genetic disorders;
- complicated pregnancy in the mother (threat of miscarriage, gestosis, malnutrition, intrauterine infection);
- long-term use of toxic medications during pregnancy;
- occupational hazard in a pregnant woman;
- severe diseases of internal organs in the expectant mother.
It is often impossible to accurately identify the main cause that led to the occurrence of intrauterine pathology in a girl. Therefore, in all cases when a girl or woman is found to have congenital anomalies in the reproductive system, it is necessary to conduct a full examination to identify malformations of neighboring organs. It is optimal to use the MRI method for this, with which you can obtain maximum useful information about all genitourinary organs.
Pathological structure of the uterus: from bicornuate to doubling
A bicornuate uterus is a developmental anomaly. Normally, the uterus looks like a pear, but with an abnormal structure, its cavity splits, forming peculiar “horns”. Cleavage can be conditional or complete, in which the connection of the cavities occurs only near the neck. Moreover, with severe pathology, there may be two cervixes - one for each uterus, and a septum in the vagina.
There are two possible options for doubling the uterus: as in our heroines, when both organs are fully developed, or only one uterus is developed, and the second is rudimentary and defective. The frequency of diagnosis of bicornuate uterus anomalies is quite high, in almost every hundredth woman, but cases of full doubling are much less common.
This developmental pathology occurs as early as 10-14 weeks of intrauterine development under the influence of unfavorable factors, and may be accompanied by duplication of the organs of the urinary system, for example, the kidneys or ureter. There may be no symptoms at all; sometimes the pathology of doubling is manifested by dysmenorrhea, pain, and menstrual irregularities. Most often, women first learn about the pathology when they are examined before pregnancy or due to difficulties with conception. Thus, gestation in a rudimentary uterus proceeds as an ectopic pregnancy with spontaneous termination.
An abnormality of the uterus can also cause problems with gestation in the fully developed part, since the placenta and fetus may not have enough space; during childbirth there are higher risks of labor weakness, transverse presentation, placental abruption and uterine bleeding. For this reason, a bicornuate uterus is an indication for surgical delivery.
If there are problems with conception and pregnancy (more than 3 spontaneous abortions in a row), surgical treatment and restoration of the normal shape of the organ are recommended. In the absence of symptoms and complications, a bicornuate uterus requires only observation; therapy is not needed. But pregnancy must proceed under stricter control, and, as examples from patients show, issues of contraception must also be approached more carefully.
Uterus doubling options
Malformation of the uterus is almost always combined with pathology of the cervix and vagina. There are several possible types of congenital uterine anomalies.
Variant of malformation Description
| Full doubling | 2 uteruses and 2 vaginas are completely separated and separated from each other |
| Incomplete doubling | 2 isolated parts of the reproductive organs (uterus and vagina) in a certain area are connected by a fibromuscular septum |
| Complete doubling with one vagina | 2 uteruses, 2 cervixes and 1 vagina |
| Double organ with one cervix and vagina | 2 uteruses, but the cervix and vagina are presented in 1 version |
| Duplication of the uterus with a rudimentary horn | One half of the organ looks normal, and the second is underdeveloped and is represented by a defective cavity |
| Two-horned | The uterine cavity is deformed in the upper part, partially dividing the organ into 2 halves |
| Saddle | The fundus of the uterus is moderately deformed without dividing the organ into 2 parts |
| Internal partition | A thin fibrous septum inside the uterus separates the organ completely or partially |
It is not always the case that a young woman experiences typical symptoms and manifestations, so a congenital defect in the reproductive system is discovered by chance at the stage of preconception preparation or during an examination for infertility. The asymptomatic course of the disease is especially common with erased and unexpressed variants of doubling (bicornuate, saddle-shaped). It is much worse if the anomaly of the genital organs is combined with a delay in the outflow of menstrual blood: in this case, typical symptoms will become the basis for an accurate diagnosis.
Detection rate
Among the total number of intrauterine malformations, uterine pathologies account for about 4% of cases. In girls with gynecological pathologies, more than 6.5% are structural defects of the uterus and vagina, and over the past five years there has been a significant increase in this figure. Anomalies of the urogenital organs are in fourth place among all human developmental defects.
Also read: Epidural injection during childbirth
Among organ structural disorders, complete duplication is diagnosed in 20% of cases. Less commonly, two uteruses are diagnosed in a woman with one vagina. The saddle uterus has a heart-shaped shape with flattening in the fundus and accounts for 23% of the total number of structural defects of the organ.
Symptoms of congenital pathology
Manifestations of congenital pathology depend on the form of uterine duplication. There are 2 groups of defects possible:
No retention of menstrual blood in the uterine cavity
The vast majority of congenital anomalies of the uterus are represented by defects in which a woman has normal periods. With a regular cycle, women who do not have an intimate life will not have any symptoms or unpleasant manifestations of congenital pathology. With the onset of sexual activity, problems may arise associated with the act of love, which happens with a double vagina against the background of complete doubling. The main symptoms occur in women who want to give birth to a baby. With uterine abnormalities without menstrual problems, the following manifestations are possible:
- threat of miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy;
- spontaneous abortion in the early stages;
- late miscarriages;
- habitual miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- infertility.
In all cases of prematurity or in the absence of a desired pregnancy, it is necessary to do a full examination, starting with safe and highly informative examination methods (ultrasound and MRI).
Duplication of the uterus is an unpleasant malformation of organs
Defects with delayed blood outflow
The lack of communication between one part of the uterus and the cervix and vagina is the reason for the retention of menstrual blood and the appearance of the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain associated with menstrual periods;
- detection of a tumor-like formation gradually increasing in size in the lower abdomen.
Typically, such symptoms occur when the uterus is doubled with a functioning rudimentary horn. If the underdeveloped area of the double organ communicates with the cervix, then the following problems are possible:
- bleeding before and after menstruation;
- heavy periods;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Any types of defects can lead to the formation of genital endometriosis with typical symptoms.
Duplication of the uterus and pregnancy
Pregnancy and features of its course
The fear of some women to become pregnant with a similar diagnosis of a double uterus is understandable. Although this pathology does not exclude the possibility of having children, it can cause complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Women with a similar diagnosis may encounter the following complications while carrying a child:
- premature birth;
- miscarriage;
- weak labor activity;
- atypical location of the fetus;
- lochiometry (accumulation of postpartum discharge in the uterine cavity);
- heavy postpartum bleeding.
As a rule, only one organ has the ability to conceive; the second is considered rudimentary, i.e. "non-working" If conception has occurred, the zygote is fixed in one of the uteruses, after which it develops in it. Interestingly, the second organ can begin to grow synchronously with the first. This process usually stops at 4-5 months of pregnancy, and further intrauterine development of the fetus occurs directly in the first uterus.
If the doubling does not pose any threat to the woman's health and does not affect her reproductive functions, no treatment is required. If pregnancy with such a diagnosis is accompanied by miscarriages or early delivery, the woman needs medical help. In this case, it is recommended to conduct an x-ray examination. It will help identify the nature of the pathology, and also give the doctor the necessary information to prescribe subsequent therapy. Sometimes medication and physiotherapeutic treatment are ineffective, and the woman continues to have miscarriages. In this case, surgical intervention is performed to remove one of the uteruses (usually a rudimentary one).
If there has been a miscarriage, urgent curettage of both uteruses is necessary.
In very rare cases, pregnancy and gestation occur in both reproductive organs. In these cases, childbirth usually does not occur simultaneously. Having given birth to one baby, a few months later a woman “comes for the second,” which is born from another uterus.
Pregnancy in a double uterus
Important! Regardless of whether pregnancy proceeds easily or with complications, a double uterus and pregnancy require constant medical supervision.
Duplication of the uterus and pregnancy
The desired conception against the background of complete doubling of the reproductive organ is quite possible. Pregnancy begins on the side where the egg is released from the ovary. The beginning of pregnancy may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- menstrual-like reaction during pregnancy (a woman experiences scanty bleeding on the days of her expected period);
- brown discharge in the first months of pregnancy (rejection of the endometrium from the part of the uterus where there is no fertilized egg);
- nagging pain in the abdomen.
All these manifestations are similar to typical symptoms of a threatened miscarriage, so the doctor will prescribe maintenance treatment or refer you to the hospital. If no serious problems arise in the first stages of fetal development, then the woman, with constant monitoring and treatment, carries the fetus to term and gives birth to a healthy baby.
In difficult cases of infertility associated with uterine duplication, IVF is performed. After a full examination, including MRI, the fertilized “in vitro” egg is implanted in that part of the future fetal sac where conditions for gestation are most optimal.
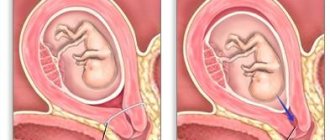
Fetal development with incomplete duplication of the uterus
Conception and pregnancy - fetal development abnormalities and possible complications
If a woman has a bicornuate uterus, natural conception and pregnancy may occur with complications. Reasons for the negative impact of pathology on childbearing:
- Reduced volume of the uterine cavity;
- Inferiority of the walls of the organ in the area of bifurcation;
- Increased intensity of myometrial contractions;
- Pathologies of the innervation and blood supply of the reproductive organ, leading to fetal malformations;
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- Impaired implantation of the fertilized egg.
If pregnancy continues during the first trimester, the walls of the uterus stretch, which provokes their functional inferiority, causing the following complications:
- Placental abruption;
- Premature birth;
- Hypoxia and fetal death;
- Frozen pregnancy;
- Fetal hypotrophy caused by placental insufficiency;
- Uterine bleeding;
- Breech presentation.
Despite the high risk, the birth of a full-term healthy child is quite possible even in the presence of anatomical defects of the reproductive organ. With increasing fetal hypoxia and a high risk of placental abruption, emergency delivery by cesarean section is resorted to.
Natural childbirth with a double and bicornuate uterus is quite possible, although it is accompanied by trauma to the birth canal and suturing. After childbirth, the patient needs careful medical supervision due to the high risk of hematometra formation and decreased contractility of the uterus.
Diagnosis of uterine duplication
The main methods for identifying various types of abnormal structure of the reproductive system are the following studies:
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- hysteroscopy;
- MRI;
- laparoscopy.
At the first stage of the examination, preference is given to non-traumatic methods - ultrasound and MRI. The doctor can easily detect a saddle-shaped and bicornuate uterus with an ultrasound scan. Endoscopic techniques are optimal when combining diagnosis and treatment.
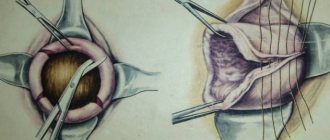
Visual examination of the inner surface of the uterus (hysteroscopy) allows you to detect the septum and immediately remove the developmental anomaly. External examination of the uterus during laparoscopy is combined with an operation to remove a non-functioning part of the organ in the presence of a rudimentary horn.
What will a tomography show when the uterus is doubled?
Treatment of pathology: basic methods of surgical intervention
Anatomical inferiority of the uterus can only be corrected surgically. Indications for surgical intervention:
- Pathologies of pregnancy;
- Infertility;
- Habitual miscarriages;
- Accumulation of blood in the isolated cavity of one of the horns.
The purpose of the operation is to create a full-fledged functional uterine cavity, allowing you to bear and give birth to a healthy child.
Surgical methods:
Laparotomy Strassmann operation.
Includes dissection of the bottom of the organ, excision of the septum, and stitching of the membranes.
Metroplasty.
Removal of the rudimentary horn, partial removal of the uterine wall with displacement of the intervention area into the sagittal plane and the formation of a new fundus of the organ.
Hysterectomy.
It is carried out in the presence of a second rudimentary uterus by extirpating it.
Hymenoplasty.
It is performed for atresia of the hymen and to eliminate the accumulation of blood in the vagina (hematocolpos).
Laser minimally invasive intervention.
Reduces the risk of complications and traumatism of the operation.
After surgical treatment, the patient is fitted with an intrauterine device for 4-6 months.