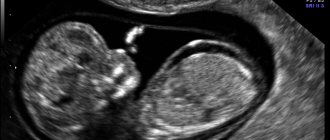
Intrauterine growth restriction, or IUGR, is a pathological process in which the weight and size of the fetus does not correspond to the norm according to the gestational age. Diagnosis of the size and weight of the fetus is carried out during an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman. The obtained data are compared with generally accepted standards. Depending on how much the child’s development does not meet standards, the severity of intrauterine growth retardation is determined.
Consequences of FGR
Fetal growth restriction syndrome is a condition that can have serious consequences.
The greater the severity of FGR, the more dangerous the consequences can be. Dangers are associated both with complications during the birth period (asphyxia, hypoxia) and in the neonatal period (difficulties in adapting to extrauterine life). Also, according to statistics, children born weighing less than 2500 grams are more likely to suffer from the following diseases:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hypofunction or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, etc.);
- lung diseases;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- decreased immunity, frequent respiratory diseases;
- neurological diseases.
In addition, in children with low birth weight, the following is observed with increased frequency:
- delayed speech development;
- hyperactivity disorder and attention deficit disorder;
- delayed psychomotor development.
Complications during pregnancy
As a rule, children who experienced IUGR in utero require more careful care after birth. In height and weight, such children usually catch up with their peers by one and a half to two years, although due to reduced immunity levels they get sick more often than other children. In addition, such children sometimes have problems with concentration and perseverance. However, medical rehabilitation helps young children overcome all difficulties and have full health in adulthood.
Babies born with intrauterine growth retardation naturally develop a little more slowly. But by the age of one and a half to two years they catch up with their peers. These children may also have problems concentrating.
But as with the diagnosis of IUGR, most babies are born premature, with a critically low weight. As a rule, problems arise with nutrition and the functioning of the digestive system, nervous and cardiovascular systems. Separate statistics include children with mental retardation and various genetic disorders, for example, Down syndrome.
Complications during pregnancy with intrauterine growth retardation include miscarriage and frozen fetus. Sometimes intrauterine developmental delay can lead to fetal death if attention is not promptly paid and appropriate measures are not taken.
What is the danger
Inappropriate fetal development is considered a serious pathology. In most cases, it affects the physical parameters of the newborn. The baby is born with low weight. However, the main danger of FGR is that if the problem is ignored, the fetus develops pathologies that are expressed in congenital diseases or lead to intrauterine death.
IUGR is most dangerous at the beginning of pregnancy. During this period, the formation of all organs and systems occurs. Developmental disorders can have irreversible consequences and affect the further course of pregnancy. Most children with IUGR are born prematurely. READ ALSO: Ginipral: instructions for use during pregnancy
The risk of complications during childbirth increases. Babies suffer from hypoxia and asphyxia. After birth, children adapt to the external environment for a long time and slowly gain weight. Low birth weight newborns are more likely to suffer from jaundice. As children grow up, they often get sick and have an increased risk of developing the following pathologies:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- overweight;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- anemia.
Problems of the placenta in the genesis of IUGR, the course of pregnancy
A common cause for the development of IUGR is problems in the structure and functioning of the uterus and placenta. So, this includes uterine defects (bicornuate, saddle-shaped, with septa), fibroids and other tumors, defects in the structure of the placenta and umbilical cord, its presentation (complete or partial), infarctions in the thickness of the placenta, calcifications or detachments with the formation of hematomas and bleeding. Threats of abortion, the development of anemia and Rh conflict, incompatibility by blood group or other factors also have an impact.
Important
Whatever the initial causes of IUGR, they all ultimately lead to disruption of the delivery of oxygen and nutrition through the placenta, which causes the baby to suffer.
Physiology of fetal development in the womb
For nine long months, the baby grows and gains strength, preparing to be born. All this time he “lives” in his mother’s stomach, existing at the expense of the resources of her body.
Until birth, the fetal respiratory system does not function. For the first time, the baby’s lungs “work” during the first breath - immediately after birth. Until this point, the fetus is supplied with oxygen through the placenta. Oxygen from the mother's blood enters the fetal blood through the placental villi. Carbon dioxide enters the mother's blood from the fetus's blood through the placenta.
An adult needs to inhale to saturate the cells and tissues of the body with oxygen. The oxygen contained in the inhaled air will fill the lungs and through the walls of the smallest element of the respiratory system - the alveoli - will penetrate into a small blood vessel, a capillary. In the bloodstream, oxygen molecules are “captured” by the carrier, hemoglobin, and deliver the source of power to every cell of the body.
The baby receives oxygen in a “ready-to-use” form - dissolved in the blood. Inhalation and exhalation, as well as gas exchange at the level of the lungs, are carried out by the mother. The placenta is responsible for the quality and speed of gas exchange between mother and baby. The fetus grows and develops very quickly, its metabolism is intense, which means the need for oxygen is always high.
The functions of fetal digestion during intrauterine development are also replaced by the placenta. It is through the placenta (as through customs) that nutrients for the baby are delivered from the mother’s body. The placenta produces enzymes that break down nutrients. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the mother's blood are captured by the villi of the placenta, undergo enzymatic processing and are delivered to the fetus in a state suitable for absorption by the body. Some products of the breakdown of proteins and carbohydrates (amino acids, glucose), as well as inorganic salts and water penetrate the placenta by diffusion. Vitamins and microelements necessary for the development and functioning of the baby's growing body pass from mother to fetus through the placenta.
Thus, the development of the fetus is completely dependent on the nutrients supplied by the mother. The expectant mother's breakfast, lunch and dinner are processed in her digestive tract; substances useful for the body's functioning - proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins - are absorbed into the bloodstream and delivered to the placenta through the bloodstream. The placenta completes digestion and sends a “healthy menu” to the baby. It turns out that the placenta is ultimately responsible for the supply and quality of nutrition.
How is IUGR formed?
Throughout pregnancy, the baby feeds on glucose, vitamins and other elements, “breathes” oxygen dissolved in the blood due to the uninterrupted supply of these substances from the mother’s body by the placenta. The placenta is a unique organ that appears only during pregnancy in order to communicate between mother and baby in both directions. It filters dangerous compounds that can reach the fetus, removes metabolic products, delivers oxygen from the mother’s red blood cells and all the substances necessary for growth, without mixing fetal and maternal blood with each other.
If for some reason the placenta cannot fully cope with its functions, a special pathology is formed - FPI (fetoplacental insufficiency). It gradually forms a state when the fetus receives smaller and smaller volumes of oxygen, and also “starves” due to a lack of amino acids, carbohydrate and fat molecules. This leads to a slowdown in his growth rates and weight gain.
Important
If the fetus lags behind the standards regulated by ultrasound results, specialists identify its malnutrition and the presence of IUGR. This term does not mean that it is a disease; rather, it is a complication of pregnancy that occurs under the influence of various negative factors affecting the structure and function of the placenta.
Causes of fetal growth retardation
In the first half of pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, all the nutrients and oxygen entering the baby’s body are used to “build” the organs and systems of the fetus. After the 20th week, intensive fetal growth and weight gain begin. Doctors who monitor the intrauterine development of a small person know the criteria for the rate and proportion of weight gain and height of the baby at each stage of pregnancy.
If there is insufficient oxygen supply through the placenta, the fetus experiences hypoxia - oxygen starvation. Hypoxia inhibits the intrauterine development of the fetus and can even cause its death. Conditions that interfere with the delivery of oxygen to the fetus often at the same time cause a delay in the excretion of carbon dioxide through the placenta. As a result, intrauterine asphyxia occurs (impaired respiratory function of the fetus), in which the baby suffers from a lack of oxygen and excess carbon dioxide in the body. If the cause of asphyxia is not eliminated, the fetus may die.
Impaired fetal gas exchange can occur with a number of maternal diseases, as well as with various changes in the placenta and umbilical cord. Insufficient oxygen delivery to the fetus can be a consequence of anemia (a condition characterized by a lack of hemoglobin - the main oxygen carrier), heart defects, pneumonia, febrile conditions (flu, ARVI with high fever), toxicosis and other diseases of the expectant mother.
Oxygen starvation of the fetus is caused by changes in the placenta that reduce the area of gas exchange between the mother and baby - the so-called respiratory surface of the placenta. Such changes include hemorrhages in the placental tissue, “white infarcts” - areas of dead placental tissue. Hemorrhages and infarctions in the placenta often form during severe gestosis of pregnancy (these complications are often manifested by the appearance of edema and increased blood pressure), diseases of the mother’s kidneys and cardiovascular system.
Fetal gas exchange is disrupted when the placenta is prematurely separated from the uterine wall. The larger the size of the detached area of the placenta, the worse the fetal gas exchange conditions become.
A disruption in the delivery of oxygen to the fetus and the removal of carbon dioxide from its body occurs when blood circulation in the vessels of the umbilical cord is impaired.
Similar disorders occur when the true umbilical cord knot is tightened, with prolonged compression of the umbilical cord section between parts of the fetus and the wall of the uterus.
Any disruption of blood flow in the maternal vessels, placental circulatory network or umbilical cord veins, along with gas exchange, disrupts the supply of nutrients. The baby, limited in oxygen and nutrition, begins to lag behind in development; The longer the “interruptions” in food supply and gas exchange, the more pronounced the lag in the baby’s growth and development.
Most drugs are administered intravenously by drip at a certain time interval.
Rational nutrition during pregnancy is also of great importance - not only for the health of the expectant mother, but also for the growth of the baby. Monotonous or insufficient nutrition can cause delayed or impaired fetal development. The presence of vitamins in a pregnant woman’s diet is no less important for the proportional height and weight of the baby. A lack of vitamins and minerals in the expectant mother's menu can cause growth retardation and the development of intrauterine anomalies.
A major role in the development of fetal malnutrition is played by the impact of unfavorable occupational (harmful production), social (poor living conditions, malnutrition) and environmental factors, as well as smoking, drug addiction and alcohol abuse.
However, the main and most common cause of insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus is fetoplacental insufficiency. This is the name of the pathological condition of pregnancy, characterized by a violation of the speed and level of blood flow in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system. As a result of deterioration of blood circulation in the placenta, both gas exchange and nutrient metabolism suffer, which means that the baby experiences a systematic lack of vital products that ensure its normal development. It is placental insufficiency that most often leads to a condition called fetal growth restriction syndrome.
The concept of IUGR: terms, definitions
In articles on obstetrics, various terms flash, essentially reflecting approximately the same conditions associated with deviations from the normal development of the fetus inside a woman’s uterus. Doctors use the concepts of “fetal hypotrophy”, or “intrauterine growth retardation”, “small height and weight for gestational age”, “fetal retardation”, and many other terms. According to the international classification (ICD-10), such concepts are included in the general category of pregnancy pathologies (P05), and they are combined under a single term - “slow growth and fetal nutritional deficiency.”
Such a frightening, incomprehensible term IUGR will imply problems and pathologies of the fetus associated with the negative influence of external and internal factors, which leads to a reduced supply of oxygen molecules and nutritional components necessary for growth to the baby . A similar diagnosis is made when, according to ultrasound or at birth, the child’s body weight by the time of pregnancy is reduced by 10% or more. In addition, a similar diagnosis will be given to those babies who are immature for their gestational age (in other words, they look at a shorter gestational age, with a deviation of at least two weeks or more).
Assessment of the condition of the fetus and criteria for its development
There are signs by which the attending doctor and even the expectant mother herself may suspect a deterioration in the baby’s condition due to a disruption in the supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Fetal movements characterize its condition. The mother may suspect a deterioration in the fetus’s condition if there is a significant, persistent decrease in the number and strength of movements. Normally, the frequency of fetal movements at 32 weeks of pregnancy is 90-100 per 12 hours, then it gradually decreases and by the end of pregnancy it is reduced to 40-50 movements per 12 hours. The critical frequency for suspecting a deterioration in the well-being of the fetus due to hypoxia is considered to be 10-20 movements in 12 hours. The nature of the baby's movements: long or short, single or multiple, weak or strong - will also help the doctor determine changes in the condition of the fetus. Mom can determine a change in the nature of movements without counting: she will simply notice that movements appear much less frequently or, conversely, more often.
It is advisable to count movements at the same time of day for an hour (in the morning from 8 to 9 o’clock, from 9 to 10, etc.). A sharp increase or decrease in fetal movements, and even more so a complete absence of movements during the observation process, may indicate an unfavorable state of the baby’s health.
Another criterion for the growth and development of the fetus is the increase in the size of the uterus. Each stage of pregnancy corresponds to a certain height of the uterine fundus; As pregnancy progresses, abdominal circumference increases. Both of these indicators are recorded at every doctor’s appointment.
The lack of dynamic growth of the uterus indicates a pathological condition of the fetus (this is especially important in 26-36 weeks of pregnancy)
Diagnosis of FGR
The diagnosis of FGR is made by a doctor based on the results of comprehensive studies, which include:
— external obstetric examination (external measurement of parameters such as abdominal circumference and uterine fundus height);
- ultrasonography. A study called ultrasound fetometry will determine the shape as well as the extent of FGR, as well as identify some possible causes.
More accurate diagnosis is possible with dynamic fetometry, with a difference of 2 weeks;
- Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound). Scanning blood flow and determining its disorders;
— cardiotocography (CTG) – determination of the reaction of the child’s heart contractions in response to stimuli.
It is worth noting that with true FGR, Doppler and CTG readings will have deviations from the norm (the severity depends on the severity of FGR), but with so-called constitutional malnutrition (due to the peculiarities of the baby’s constitution) there will be no deviations.
Classification and degrees of development
FGR is classified depending on the ratio of physiological parameters of the fetus. The following forms of IUGR are distinguished:
- Symmetrical. At the same time, a proportional discrepancy between all fetal indicators and the gestational period is noted. This pathology occurs in 10–30% of detected cases. Most often it develops due to genetic abnormalities and the influence of external factors in the first half of pregnancy.
- Asymmetrical. In this case, it is noted that only some parts of the child’s body are reduced in size. With asymmetrical IUGR, a small body size is most often detected with normal head parameters. The asymmetrical form is often diagnosed after 30 weeks of pregnancy. The main reason for deviations during this period is fetoplacental insufficiency.
- Mixed. It is the most unfavorable type of pathology. A slight discrepancy in the sizes of all parameters is revealed against the background of a pronounced decrease in abdominal volume.
The degree of development of IUGR is determined by how many weeks the fetus lags behind in development. There are 3 degrees of deviations:
- 1st degree. Less than 2 weeks behind the norm.
- 2nd degree. The fetus lags behind in development by 2–4 weeks.
- 3rd degree. Deviations of more than 4 weeks.
At what week does IUGR become obvious?
Signs of intrauterine growth retardation are almost invisible in the first trimester. Usually at 24-26 weeks the doctor can already assume the presence of a lag. Usually at this time the symmetrical form is diagnosed. Whether this is good or bad must be assessed on a case-by-case basis. In this case, there is a delay in the growth of all indicators.
That is, the circumference of the head and abdomen and the length of the femur lag behind. But their proportionality relative to each other remains. If a lag in size is diagnosed for up to 2 weeks, then a diagnosis of “1st degree intrauterine growth retardation” is made. The main thing at this stage is to identify the cause and begin correction in time.
Treatment of FGR
Treatment for FGR is prescribed by a doctor based on the severity of FGR and the reasons that caused it. Most often, treatment for FGR includes:
— treatment of chronic diseases of a pregnant woman and treatment of infections, correction of hemostasiogram;
- treatment aimed at normalizing the uteroplacental blood flow system. To do this, the doctor prescribes drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow (Actovegin, Kurantil), and also have a relaxing effect on the muscles of the uterus (Ginipral, No-Spa).
During treatment, it is mandatory to monitor the baby’s condition in order to assess the effectiveness of the therapy:
- ultrasound examination (fetometry). It is carried out every 7–14 days to take measurements and assess the baby’s growth rate;
- Doppler examination. Performed every three to five days to monitor uteroplacental blood flow;
— cardiotocography. It is carried out every other day or daily to assess the state of the child’s cardiovascular system.
To assess the effectiveness of therapy, data from all three diagnostic methods in combination are required.
Based on these results, the doctor makes a decision about continuing the pregnancy or the need for urgent delivery, as well as about the method of delivery itself (naturally or surgically).
What should the expectant mother do to increase the effectiveness of treatment?
- try not to worry, as emotional tension and stress only harm the baby;
- eat well, rest, sleep;
- be more outdoors;
- Follow doctors’ recommendations for taking medications and diagnostic procedures.
Instrumental methods for assessing SZRP
Often, extended monitoring of the dynamics of the fetal condition is required; here, doctors are helped by high-precision instrumental techniques.
- Diagnosis of placental insufficiency and the condition of the fetus makes it possible to identify fetal growth restriction syndrome and determine its forms and severity, as well as to assess the condition of the umbilical cord as a criterion of intrauterine fetal suffering (both a skinny umbilical cord with a diameter of less than 15 mm at 28–41 weeks of pregnancy and a hypertwisted ):
- cardiotocography is carried out from the 28th obstetric week and allows you to assess the indicators of fetal cardiac activity by recording fetal movements and the number of uterine contractions in a calm state and with a stimulus (sharp sound, administered oxytocin) determines possible tachycardia, slowdown or spontaneous increase in heart rate;
The cardiotocograph has ultrasound (detecting the movement of the fetal heart valves) and strain gauge (detecting uterine contractions) sensors - Cardiointervalography after 32 weeks is a 60-minute method of computer registration of the fetal heart rhythm and variations of this rhythm, determining how cardio intervals are distributed (time intervals during the work of the fetal heart);
- Doppler study of blood flow in the umbilical cord artery and uterine arteries is a safe and highly informative way to assess the functional abilities of blood flow, establish the size and location of blood vessels, the speed and characteristics of blood movement through them at the time of heart contraction and relaxation;
Doppler is one of the ultrasound methods, the data of which is presented in the form of curves that characterize the speed of blood movement through the vessels and chambers of the heart. - Three-dimensional ultrasound is more accurate than two-dimensional ultrasound, especially for oligohydramnios or abnormal fetal positions in the uterus (weight error less than 7% versus 21% for two-dimensional ultrasound).
- Ultrasound placentography, in addition to determining the location of the placenta, allows you to assess its structure and size, namely:
- abnormalities of placental maturation: premature maturation (II stage of maturity up to 32 weeks and III stage of placental maturity up to 36 weeks);
- delayed maturation.
- cystic formations on the fetal side of the placenta due to hemorrhages, softening, infarctions and other changes;
- thickness of the placenta:
- up to 20 mm in the third trimester of pregnancy - a child’s place with insufficient weight at normal sizes, inherent in gestational changes, the threat of miscarriage and FGR, is considered thin;
- up to 50 mm or more - thick in case of blood diseases and diabetes.
Video: ultrasound diagnostics doctor N. Sergeeva about the features of Doppler sonography
More on the topic: Intrauterine growth restriction
Moderate oligohydramnios 20 weeks
I was at the next ultrasound, the diagnostician left moderate oligohydramnios and 9 cm, the period was 20-21 weeks. The gynecologist scolded her and said that oligohydramnios was developing due to the fact that she had not taken the antibiotics prescribed for her for 10 days, but only 5!! And that according to the tests, leukocytes are still elevated, which, in her opinion, indicates an inflammatory process in the body. Although the ENT specialist said that the tests were perfect and there were no infections. Blood is normal. Dopplerometry showed the baby is ok. Now I can see from the table that my iage is within the limits...
Doppler-FPN
Intrauterine growth retardation. Using a type of ultrasound - Doppler study - you can obtain information about the speed and direction of blood movement through the vessels of the umbilical cord and large arteries of the fetus.
The only artery in the umbilical cord - has anyone encountered this?
Intrauterine growth retardation. Using a type of ultrasound - Doppler study - you can obtain information about the speed and direction of blood movement through the vessels of the umbilical cord and large arteries of the fetus.
Cancellation of Dufston (Utrozhestan) - opinion of the audience
Intrauterine growth retardation. During pregnancy, it is better to resolutely stop smoking and drinking alcohol, contact with toxic substances and radiation sources - especially in the early stages of pregnancy...
about the formation of the placenta
Intrauterine growth retardation. During pregnancy, it is better to resolutely stop smoking and drinking alcohol, contact with toxic substances and radiation sources - especially in the early stages of pregnancy...
I'm with you again
True, the ultrasound showed hypertrophy of the placenta and IUGR stage 1, and a small fetus. The local doctors sent me to a day hospital. Intrauterine growth retardation.
fetal hypertrophy
malnutrition is... there is no such diagnosis, hypertrophy... malnutrition (intrauterine growth retardation) is diagnosed based on a combination of signs, one of which is a low abdominal volume compared to other ultrasound measurements... malnutrition...
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Hypoxia inhibits the intrauterine development of the fetus and can even cause its death. Intrauterine growth retardation. A large arsenal of medications is used to treat fetal malnutrition.
I've been smoking for 28 weeks:(((((
Intrauterine growth retardation. During pregnancy, it is better to resolutely give up smoking, drinking alcohol, and contact with toxic substances. Frozen pregnancy: signs and causes.
Hypotrophy of the placenta
Intrauterine growth retardation. Nutrition and breathing of the fetus are provided by a temporary (“provisional”) organ - the placenta, which supplies the fetus with the necessary pregnancies)...
Diagnosis: “oligohydramnios”
Intrauterine growth retardation. True, the ultrasound showed hypertrophy of the placenta and IUGR stage 1, and a small fetus. The local doctors sent me to a day hospital.
Lifestyle
Psychologists note another reason. Intrauterine growth retardation can be a consequence of a woman's nervous tension. A difficult financial situation, poor family relationships, work that does not bring material satisfaction - all this also affects the baby. Difficult working conditions also have a negative impact.
The last risk factor in this group is bad habits. Intrauterine growth restriction syndrome is directly related to lifestyle. If alcohol enters the body, not to mention drugs, then it is not surprising that the child lags behind in development.
Forecast and possible deviations
With proper and timely treatment, taking into account all clinical recommendations, experts give favorable prognoses. However, the consequences of the pathology depend on the form and degree of its development and concomitant diseases of the expectant mother. With asymmetrical FGR of the 1st degree and the absence of serious abnormalities in the mother, the child is born healthy and on time.
However, 2nd and 3rd degree intrauterine disorders can affect the child’s health. In case of severe developmental delay (for example, with an asymmetric form of the 3rd degree or a mixed form), the following deviations are detected in the newborn:
- Disruption of the central nervous system. Manifestations of the pathology are different: increased excitability, mental retardation, delayed development of basic reflexes.
- Muscle weakness.
- Underdevelopment of internal organs.
- Low immunity.
- Congenital anemia.
However, most deviations are successfully eliminated in the first years of the baby’s life. The child needs more careful care. Some disorders are treated through physiotherapeutic methods, sometimes it is necessary to use medications. To prevent developmental delays, experts recommend:
- diagnose possible pathologies of future parents at the stage of pregnancy planning;
- register with the antenatal clinic in the first weeks of gestation;
- keep a schedule for visiting your doctor;
- do not refuse screening examinations;
- take tests in a timely manner.
>FGR 1st degree during pregnancy
What to do
VZRP cannot be ignored. After identifying the pathology and finding out the possible causes of its occurrence, the woman is prescribed treatment. When choosing the direction of therapy, the degree of FGR is taken into account. The main method of treatment is the use of medications. The following types of medications are recommended for therapy:
- Improving blood flow in the placenta. For this purpose, droppers with Actovegin are used.
- Blood thinners (Curantil, Trental, Aspirin). Thinned blood moves faster through the vessels, which speeds up the delivery of oxygen to the fetus.
- Relieving spasms of blood vessels and uterus. When spasms occur, the blood vessels are compressed, so blood flow in the placenta is disrupted and the fetus does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Have a relaxing effect: Magnesia, Ginipral.
- Vasodilators (Theophylline).
The woman is also prescribed medications that reduce nervous tension and vitamin complexes. During treatment, it is recommended to go to the hospital. During the subsequent months of pregnancy, the expectant mother should eat a varied diet, often walk in the fresh air, refrain from physical overexertion and get plenty of rest.
During therapy, the condition of the fetus is constantly monitored. For this, additional ultrasound and cardiotocogram are performed. If the child’s condition worsens, doctors decide on urgent delivery by cesarean section.
Actions of doctors in the presence of IUGR
If, according to all studies, developmental delay is identified, both general routine measures and nutritious nutrition, as well as drug support, are necessary. This leads to the enrichment of the placenta and uterus with oxygen, which helps the fetus receive enough nutrients for development and growth, and weight gain.
Important
With a mild degree of fetoplacental insufficiency, the woman is treated at home, under the supervision of a doctor at the antenatal clinic; severe degrees of IUGR require hospital treatment.
Today, there is a group of drugs that increase blood flow in the vessels of the fetoplacental complex, increase the fetus’s resistance to hypoxia and eliminate IUGR . The most basic treatment is to eliminate the cause that leads to developmental delay and fetal suffering. The earlier the problem is identified and treatment is started, the better the prognosis for the baby.
They use drugs that reduce the tone of the uterus and eliminate vasospasm, reduce blood viscosity and saturate the blood with oxygen, as well as vitamins, iron and minerals necessary for the full functioning of the mother’s body. The choice of drugs always remains with the doctor, based on the clinical situation, tolerability of a particular treatment and the severity of FPN.
Monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment is carried out every 2 weeks according to ultrasound and fetal cardiotocography; when the causes that led to IUGR are eliminated, usually the growth and weight gain of the fetus quickly return to normal.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician
8, total, today
( 185 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
42 weeks of pregnancy: what are the dangers of post-term pregnancy?
Weakness of labor: why is stimulation needed?