Such a delicate problem as urinary retention is not uncommon. Usually it is not life-threatening, but can become chronic. It is worth taking this pathology seriously, undergoing examination and adhering to the treatment regimen. Typical symptoms include tension and pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by very weak and insufficient urine output. If left untreated, complications may develop.
Diagnosis begins with a survey and physical examination - often this is sufficient. Treatment depends on the causes of the pathology. In most cases, installing a urinary catheter is sufficient to immediately alleviate the patient’s condition. In more severe cases, long-term therapy or even surgery may be required.
Urinary retention is a common problem affecting both men and women. In 99% of cases, its occurrence is due to the complicated course of a disease. According to statistics, the pathology is most often observed in older men, which is associated with prostate dysfunction. Although the symptom can accompany a variety of urological diseases.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a urologist.
- Initial consultation – 2,700
- Repeated consultation – 1,800
Make an appointment
Causes
Ischuria (this is the medical term used by specialists to describe problems with urination) is not a separate disease, but a symptom indicating other pathologies of the urinary, immune, nervous or endocrine system. It is important to distinguish ischuria from anuria (complete absence of urine).
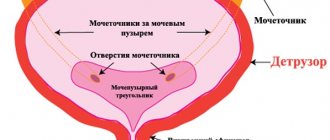
With ischuria, the fluid is filtered through the kidneys, enters the bladder, but is not excreted. When a significant amount of urine accumulates, a characteristic clinical picture appears.
The main causes of urinary retention:
- Impaired urethral patency. Due to the blockage of the urethra, the normal outflow of urine does not occur. Impaired patency may be associated with tumors, edema, stones and blood entering the urethra.
- Decreased contractility of the bladder. Refers to functional disorders. Most often it occurs against the background of muscular dystrophy or due to a violation of innervation.
- Psychosomatics. Stress and nervous tension can cause bladder dysfunction.
- Taking certain medications. Most often, urinary retention is provoked by sleeping pills and medications belonging to the group of narcotics.
- In men, a separate cause is identified as prostatitis and other prostate diseases.
- Other diseases of the genitourinary system.
Diagnostics
If the patient does not feel the urge to urinate, the doctor will first refer him to a general urine test, if the patient can pass it. With anuria, the patient is not able to give urine for analysis, so he is referred for anamnesis collection. Also, to confirm the fact that the patient has no urine, they are sent for an ultrasound examination. Also, in case of such pathology, computed tomography is prescribed.
Classification
First of all, urinary retention is classified as complete and incomplete (more common when it lasts for a long time). The first option is characterized by the absolute absence of urine outflow. The second is incomplete emptying.
In addition, there are several variants of pathology depending on the course and clinical picture:
- Acute urinary retention. Characterized by a sharp and sudden development. Caused, as a rule, by mechanical reasons, it occurs against the background of obstruction of the urethra. Often accompanied by the passage of stones or sand from the kidneys. May be complete or incomplete. In the second case, the release of liquid occurs only under tension.
- With a long course, a chronic form develops. Occurs against the background of a primary disease. In men it is often caused by prostate diseases, in women – by tumors of the genitourinary system. The full form is rare.
- There is another form of ischuria, which is called paradoxical. This term well describes the main symptoms: with the constant release of a small volume of fluid, the bladder remains full.
The forms of ishuria are not static; they can transform into one another. Thus, acute delay in the absence of proper treatment can lead to the development of chronic pathology.
Emergency care for acute ischuria
If a woman exhibits symptoms of an acute form of ischuria, then emergency medical care is indicated . In such cases, catheterization is performed in a hospital setting. Insertion of a flexible catheter through the urethra allows urine to be drained from a congested hollow organ. In some situations, when this treatment option is not suitable, the woman is given a special drainage that is thinner.
Before medical workers arrive, you must do the following:
- provide the patient with peace, lay her on the bed;
- give sweet tea in small quantities;
- to relieve pain when urinating, you need to take a warm bath with the addition of manganese solution;
- To relieve spasms, give No-Shpu.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the form of the pathology.
Manifestations of acute urinary retention:
- abrupt start
- often occurs against the background of exacerbation of the underlying disease
- may be accompanied by severe pain if it is caused by a kidney stone passing
- may be accompanied by dull pain if associated with prostatitis
- tension and discomfort in the lower abdomen
- discomfort increases over time
- symptoms quickly subside after fluid outflow is restored and the bladder is emptied
Typical signs of chronic delay:
- gradual development, symptoms increase over several weeks or months
- the first manifestations are a decrease in the amount of urine excreted per day, increased urge to go to the toilet
- alternating waxing and waning of symptoms
If chronic retention is complete, long-term catheterization will be required. In the case of an acute form, a single complete emptying of the bladder and restoration of urethral patency is sufficient. If there is complete retention, catheterization does not help restore normal urination; additional therapy is required.
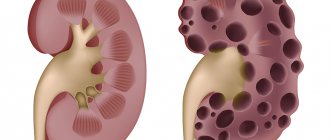
It is necessary to contact a urologist immediately after the onset of symptoms. Otherwise, complications begin to develop. Fluid stagnation provokes the proliferation of bacteria and the development of inflammatory diseases: cystitis and pyelonephritis. And excess fluid pressure disrupts the functioning of the entire excretory system. Chronic urinary retention can lead to the formation of stones due to the precipitation of salts contained in the urine.
Emergency care for acute ischuria
If a woman exhibits symptoms of an acute form of ischuria, then emergency medical care is indicated . In such cases, catheterization is performed in a hospital setting. Insertion of a flexible catheter through the urethra allows urine to be drained from a congested hollow organ. In some situations, when this treatment option is not suitable, the woman is given a special drainage that is thinner.
Before medical workers arrive, you must do the following:
- provide the patient with peace, lay her on the bed;
- give sweet tea in small quantities;
- to relieve pain when urinating, you need to take a warm bath with the addition of manganese solution;
- To relieve spasms, give No-Shpu.
Our doctors
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Survey
This pathology is difficult to confuse with something, so the diagnosis is simple. First you need to contact a urologist for an examination. Instrumental studies are required to establish the cause of the development of ischuria and to select treatment tactics for the chronic form.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound. They examine not only the bladder, but also the kidneys, and in men, also the prostate. The study allows you to quickly establish a diagnosis. Ultrasound can identify foci of inflammation and find tumors.
- If a psychosomatic or neurological nature of the pathology is suspected, an examination by a neurologist and psychotherapist is prescribed.
- If ischuria develops against the background of chronic kidney disease, then consultation with a nephrologist is required.
- Endoscopic examination - cystoscopy - is used to identify the source of blockage in the urinary tract.
- X-ray with a contrast agent - excretory urography (performed for chronic ischuria).
Possible complications
If urine is difficult to pass and treatment is not carried out, other problems may occur when urinating.
Among the main negative consequences are:
- the appearance of blood impurities in urine;
- inflammation of the bladder or kidneys;
- acute renal failure.
To avoid these problems, you need to go to the doctor immediately after the appearance of alarming signs indicating a disruption in the normal process of urine excretion.
Treatment
It is carried out in two stages: first, a catheter is installed to evacuate urine and alleviate the patient’s condition, and then therapy is prescribed to eliminate the cause and consequences of ischuria.
Catheterization is the installation of a catheter through the urethra. There are conditions that are contraindications to this procedure: tumors and other neoplasms, phimotic changes, strictures. In such cases, surgical intervention is required - cystostomy. This is the formation of urine outflow directly from the bladder through a tube that is discharged onto the stomach.
Treatment depends on the disease that caused the development of ischuria. When stones accumulate, therapy consists of crushing and removing stones. If there are pathological changes in tissues, surgery is necessary. Functional disorders require a comprehensive approach and are most often treated with the help of a neurologist. Stress-induced ischuria disappears after taking medications to relieve nervous tension, and drug-induced ischuria disappears after discontinuation of the drug that caused the delay.
This pathology is treatable. The main thing is to see a doctor in time and start treatment. Even chronic ischuria can be easily corrected, provided that the underlying disease is correctly identified.
You can undergo a full examination and choose an effective treatment regimen at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. Attentive and qualified doctors, the use of the latest medical advances and innovative methods and modern equipment are the key to good health for many years.
Possible pathologies
The full process of urination is influenced by many different factors. Among the main reasons that a woman does not pass urine are:
- Infectious diseases of the urinary system. They are accompanied by severe inflammation, which provokes swelling and closure of the sphincter (cystitis, urethritis).
- Urethrocele or cystocele is the formation of protruding areas of the urethra or bladder. This occurs due to decreased muscle tone.
- Spinal cord injury. It provokes a weakening of nerve impulses transmitted by the bladder.
- Injuries of the pelvic organs. They lead to changes in the lumen of the urinary tract due to the formation of scars on their walls. Similar injuries can occur during difficult childbirth, surgery or accidents.
- Urolithiasis disease. After the developing stones reach impressive sizes, they block the urinary tract. The blockage causes urine to not flow.
- Formation of tumors in the organs of the urinary system.
- Prolapse of the uterus.
- Diabetes. The disease provokes disturbances in the chain of transmission of nerve impulses, which is why urine does not pass away.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system that lead to oxygen starvation of tissues.
The full outflow of urine may stop due to prolonged stress or mental overstrain. Therefore, the first thing to start therapy with is restoring mental balance and normalizing the balance between work and rest.