A woman's pregnancy normally lasts 270-290 days, or 40 weeks, or 9 months.
What happens during this period in the female body? How does the fetus develop over the weeks? What do we know about the miracle of birth? In this article we will look at fetal development in the first trimester. All embryogenesis is divided into 3 periods: initial (1-2 weeks of development), germinal (embryonic) (3-8 weeks) and fetal, lasting from the 9th week of intrauterine development until the birth of the child. In the initial period, the organism is called a conceptus, in the embryonic period - an embryo, and in the fetal period - a fetus.
When does pregnancy begin?
We are used to thinking that pregnancy begins immediately after fertilization, male and female sex gametes unite, which carry a single set of chromosomes, a zygote is formed, and then simply cell division follows, but not everything is so simple. The union of the sperm and the egg occurs in the fallopian tube, after which the zygote moves into the uterus, and in parallel with this, cell division occurs (although the first period, starting from 15 minutes and up to 32 hours, may not change anything). The zygote divides asynchronously, i.e. an even or odd total number of cells is formed, and on the 3-4th day a morula is formed - 8-12 large cells that are tightly connected to each other. Externally, the morula is similar to the mulberry fruit, which is where it got its name.
Sperm and egg
During normal development, before entering the uterus, the morula becomes a blastula, or vesicle (there is already an internal cavity and an outer layer of cells). The blastula enters the uterus on the 6th-7th day, by which time it consists of 107 cells. All nutritional reserves are used up, as the need for energy and oxygen constantly increases, and therefore the vesicle attaches to the lining of the uterus - the process of implantation. Now the fertilized egg is completely dependent on the mother’s body, the walls of the blastula grow in the uterine mucosa, and many small blood vessels are formed that feed the small organism. The baby's body will be formed from the embryonic nodule, and from the outer layer - the placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic sac.
And only now the pregnancy actually began, when the fertilized egg was implanted into the wall of the uterus and became a conceptus.
How is pregnancy calculated?
Doctors use two methods for calculating gestational age: obstetric and embryonic. The first option is most often used. The first day of pregnancy is the beginning of menstruation.
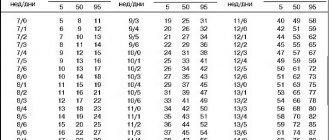
Normal intrauterine development of the fetus lasts about 40 weeks. In this case, an error of 14 days or less is allowed. If the birth of the baby occurred much earlier, then we can talk about premature birth. The onset of contractions and opening of the cervical canal in the first half of pregnancy leads to miscarriage. The period of development of a child in the womb can be determined using manual examination or ultrasound diagnostics. Moreover, the second method is more reliable and reliable.
1st week
The first week begins with fertilization, continues with cleavage, and ends with implantation of the embryo. After insemination (introduction of ejaculate into the woman’s genital tract) and fertilization (fusion of sperm and egg), the egg quickly completes its development from a second-order oocyte, a zygote is formed, and asynchronous, uneven, complete cell division begins. This stage is called fragmentation, since the number of cells increases, but they do not grow, and even lose some weight due to the use of energy. As a result of division, cells are formed of different sizes, small ones remain outside, and large ones accumulate inside. When there is already such a division into trophoblast (external small cells) and embryoblast (large dark internal ones), the embryo is called a morula - day 3 of embryogenesis.
Scheme of embryo development to the blastocyst stage
On the 4th day, the cells of the outer layer of the embryo secrete a special secretion, a cavity is formed inside and the embryoblast moves to one of the poles of the morula - this is how a blastocyst is formed.
The uterus is preparing to welcome the embryo, the mucous membrane swells, nutrients for the embryo are released (glycoproteins, glycogen, lipids), i.e. the embryo switches to the second type of nutrition - no longer at the expense of its own internal resources, but the secretions of the uterine glands.
This is followed by implantation, which is characterized by the stages of adhesion, or sticking, to the mucous wall of the uterus, and invasion - the introduction of the embryo into the mucous membrane. By releasing special enzymes, the embryo gradually destroys the walls of the mucous membrane, then attaches to the epithelium, the connective wall, and finally reaches the vessels. The implantation process ends, the mucous membrane grows around the embryo, a dense network of small blood vessels is formed and the embryo switches to a hemotrophic type of nutrition, i.e., the mother’s blood.
Implantation completed - day 8
Periods of intrauterine development
Pregnancy is a physiological process in a woman’s body that begins with the fertilization of an egg by a sperm and ends with the birth of a child. The gestation period lasts 9 calendar (36 weeks) or 10 obstetric months (40 weeks or 280 days). You should know that the obstetric month lasts 28 days.
The intrauterine development of a child takes place in 3 periods:
- the period of the fertilized egg - from the moment of fusion of the egg and sperm (conception) until the moment of implantation into the endometrium of the uterus, lasts 3-10 days;
- embryonic period - begins from the moment of implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium of the uterus, lasts 8 weeks, at this stage the formation of all organs and systems of the unborn child occurs, the embryo is usually called an embryo;
- fetal period - begins from the 9th week and ends with the moment of birth, at this stage the embryo grows and gains mass, organs and systems are improved, the body is prepared for life outside the womb, the embryo is usually called a fetus.
At each week of pregnancy, changes naturally occur in the body of the fetus, which contain the laws of evolution. The individual characteristics of the fetus depend on the genetic code that the child receives from the chromosome set of the reproductive cell of the father (sperm) and mother (egg).
3rd week
During the 3rd week, the second phase of gastrulation takes place, the result of which is the appearance of the middle (third) germ layer - mesoderm. After this, differentiation of the germ layers begins, and the rudiments of all organs of the human body and the main functional systems are formed.
The ectoderm gives rise to:
- skin;
- dentin of teeth;
- lining epithelium of the nose, eyes, ears;
- nails and hair;
- nervous system;
- bones of the skull;
- outer membranes of the eyes.
Mesoderm differentiation begins on the 20th day, resulting in the formation of:
- chord (future spine);
- skin dermis;
- muscles of the skeleton, tongue, cheeks, lips, facial muscles, but also muscles of the pharynx, soft palate, part of the esophagus, vagina, anal rectum;
- bones;
- blood;
- cartilage;
- lymph;
- kidneys;
- vessels;
- heart;
- gonads.
Endoderm gives rise to:
- light;
- epithelium of the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Starting from the 20th day, the embryo is detached from the auxiliary extra-embryonic organs, which is very important for further development, because the embryo acquires its own spatial orientation. Now we can select the front end, where the head will be in the future, and the rear end, where the pelvis and lower limbs will be in the future.
Third trimester
This period is characterized by strong growth of the baby. All organs and systems are already formed and function as they should. The norms of fetal development in the third trimester are as follows:
- week 27: 34 centimeters and 900 grams;
- week 28: 34.5 centimeters and 1050 grams;
- week 29: 36 centimeters and 1150 grams;
- week 30: 40 centimeters and 1300 grams;
- week 31: 41 centimeters and 1550 grams;
- week 32: 42 centimeters and 1700 grams;
- week 33: 43 centimeters and 1950 grams;
- week 34: 44 centimeters and 2200 grams;
- week 35: 45 centimeters and 2.5 kilograms;
- week 36: 46 centimeters and 2.6 kilograms;
- week 37: 49 centimeters and 3 kilograms;
- week 38: 49.5 centimeters and 3.03 kilograms;
- week 39: 50 centimeters and 3.2 kilograms;
- week 40: 53 centimeters and 3.5 kilograms.
4th week
At the fourth week, the embryo is already floating calmly in the amniotic fluid. It is visually very similar to the embryos of other mammals, as it has a tail and gills. From the 23rd day, the heart begins to contract, but the formation of internal organs still continues. Thus, the primary kidney develops from the preference, the rudiments of all parts of the brain are visible in the form of vesicles, and the rudiments of the lungs, duodenum and liver appear. Small tubercles are visible on the sides of the body - these are the future arms and legs of the child. The mouth, eyes, and inner ear are already developing. The thymus is formed.
Let's summarize. In one month, the embryo grows to 8 mm, weighs about 3 g, but at the same time the rudiments of most systems and organs have already been formed, which will continue to develop. The location of the head and limbs is already visible, and bilateral symmetry of the body is developed.
Life at 4 weeks
Fourth month
By day it is 22 – 25 days. Now the rudiments of the brain, pancreas, lungs, and liver are being formed. The basis appears for the formation of arms and legs in the future. At this stage, the neural tube has already formed and the nervous system is formed from it. Folic acid is still extremely important.
85 – 91 days
Now all the internal organs in the fetal body are fully formed. The child begins to have overactive skeletal growth, and if there is not enough calcium in the mother’s body, it’s time to replenish it.
92 – 98 days
Eyebrows and eyelashes appear on the face of the unborn child. The baby can make facial movements for the first time.
You can already hear the heartbeat if you use an obstetric stethoscope.
99 – 105 days
Now is the time for gender formation. Meanwhile, the pancreas is already coping with the production of insulin.
106 – 112 days
The fingers and nails on them are already formed. If you look at the baby using an ultrasound machine, you can see how the child sucks his finger. By the way, at this stage of development the baby can already distinguish smells and tastes.
During this period, the formation of the rudiments of the brain, pancreas, lungs and liver takes place. A basis appears for the formation of the upper and lower extremities. The nervous system is being formed. During this period, taking folic acid is important.
Thanks to the placenta, the baby receives everything it needs from the mother’s body, and also removes harmful substances and waste products.
The first reflexes appear: sucking and swallowing. Sometimes during an ultrasound it can be seen that the baby is sucking his thumb.
The baby begins active movements, while the mother practically does not feel them. The skin is covered with fluff - lanugo, which has a protective function. Hair on the head, eyelashes and eyebrows begin to grow.
The baby secretes urine into the amniotic fluid every 40 minutes. The fluid in which the embryo resides is frequently renewed, thanks to which it remains sterile and has an unchanged chemical composition.
5th week
The complexity, differentiation and development of the cardiovascular system continues, and its conduction system develops. If you take an electrocardiogram at this stage, it will be very similar to an adult ECG. The main endocrine organs are formed. Now the liver is already working, but for now it is responsible for hematopoiesis. From the internal organs, the kidney and lungs are formed, the intestines and nervous system are actively formed. The fins are replaced by the rudiments of arms and legs, which are formed from previously appeared tubercles.
Third month
A pregnant woman needs to be especially careful in the second week, because during this period the embryo is strengthening on the wall of the uterus.
Miscarriage can occur for the following reasons:
- exposure to chemicals on a woman’s body;
- excessive physical activity;
- deep vessels;
- uterine tone.
In the absence of these factors, the embryo is safely fixed in the area where the vessels are located, which are responsible for nutrition and development.
From the 9th to the 21st day, the placenta, umbilical cord, and neural tube begin to form, which will later pass into the baby’s nervous system.
From the eighteenth to the twenty-first day, the cardiovascular system develops. The baby's heart begins to work. This may be considered when performing the first ultrasound examination. It allows you to exclude possible miscarriage.
The baby floats in the amniotic fluid and can even push off from the walls. Has long arms and a large head, takes on a human appearance.
Eyes wide open. The iris is forming. The endocrine gland begins to work. The heart is already pumping blood through the vessels and can reproduce 150 beats per minute.
The fetus clenches and unclenches its hands and makes its first movements.
The second and immediately third weeks, which include days 9 to 21, are the period of active formation of the placenta, umbilical cord, and neural tube. As for the latter, it is where the nervous system begins.
Each stage is important in its own way, but it is in the second and third weeks that the foundation of the future organism is laid. This is why drinking folic acid is so important. It helps in the formation of all major organs.
And the most important thing at this stage is that the heart begins to beat.
57 – 63 days
From the third month of pregnancy, reflex movements appear. The cartilages of the larynx and ears are noticeably formed. The adrenal glands even produce hormones. The brain continues its active growth.
The heart is capable of producing 150 beats per minute, and it is already pumping blood through the vessels.
At this stage, there are only red blood cells in the blood, but no leukocytes yet, so the fetus’s body is protected from infections by the mother’s body. This is the so-called passive immunity.
The fingers can already clench because the joints are formed. The fetus makes its first movements.
64 – 70 days
It's time for the ponytail to disappear. The buttocks are actively developing.
The respiratory system is almost formed and is even ready to work independently.
Movements are no longer chaotic, but react to external stimuli. The mother will not feel this yet, because the size of the fetus reaches a maximum of 40 mm, but if you press on the areas of the uterus, the fetus will bend an arm or leg. Can turn his head.
71 – 77 days
Now the eyes are not only formed, but the iris has already been drawn. This means that the baby already has a certain eye color.
At this stage, the expectant mother may experience slight discomfort, for example, weakness, pressure, nausea. This is due to the development of hormones.
78 – 84 days
Remember when we said that there are no leukocytes in fetal cells yet? Now they appear and are able to protect the body of the unborn baby. The body parts are already formed and clearly visible.
8th week
By the end of the 8th week, lymph nodes appear and differentiation of the gonads is completed. The embryo already looks like a human baby, the tail disappears, but the buttocks appear, facial features are formed (and this process will last until the moment of birth), lips are visible, the vessels of the lungs and the ventricles of the heart appear. The length of the body during this period is 4 cm, and the weight is 5 g. The neck is already developing, and the head from cylindrical takes on a round shape, on which we see the nose and outer ear. The limbs are clearly distinguished, the fingers and all other parts are clearly visible. At the end of the second month, muscle tissue actively begins to develop, and by the end of the week the muscles are capable of contracting.
At the end of the second month, all internal organs have already been formed, and the cerebral hemispheres actively continue to develop (the cortex is being formed). Starting from the 50th day of embryo development, its brain activity can be recorded in the form of impulses, which is the main indicator of life.
THE GERMINAL PERIOD ENDS AND THE FRUITAL PERIOD BEGINS.
During the third month of pregnancy, organs continue to form in the fetus, some of which are already functioning. The face is becoming clearer and the placenta is forming.
Is it worth doing an ultrasound at this time?
Having learned about their situation, every girl wants to look at her baby, but many of them are afraid to carry out this procedure at such an early stage. According to experts, such fears are just prejudices. Experts recommend screening in the first trimester, starting at 4 or 4.5 weeks of pregnancy. A study at this stage is carried out to determine the viability of the embryo, as well as to exclude various pathologies. What does an embryo look like at 4 weeks? An ultrasound examination at this stage of pregnancy reveals a yolk sac, a fertilized egg, with a diameter of no more than five millimeters, which is covered with a luminous layer - the chorion.
Usually the embryo at 4 weeks is not visualized, but an experienced specialist will be able to determine its presence or absence, as well as see the contours of the back, abdomen, head and still unformed limbs in the form of gill arches and a tail.
Week 12
From the 12th week, leukocytes, or white blood cells, begin to appear in the blood. Hemoglobin is already in the blood, but in small quantities; its level increases significantly closer to childbirth. The fetal skeleton ossifies. Fingers (with the beginnings of “prints”) on the arms and legs are clearly visible, and nails begin to form. The external genital organs, which are still poorly distinguishable, are being formed, so it is not yet possible to distinguish a boy from a girl. The vocal apparatus appears, but the child will be able to produce sounds only after birth. Weight up to 25 g, and height up to 9 cm.
In the third month of development, the fetus makes its first body movements, but they are not yet sensitive to the woman, especially if she is pregnant with her first child.
Key words: beginning of pregnancy, fetal development, childbirth, conception of a child, first trimester, trimesters of pregnancy, gestational age, pregnancy by week, pregnancy fetus, pregnancy photo
Ideas for mothers and babies
Back in 1965, Swedish photographer Lennart Nilsson was the first to photograph the stages of embryo development using a powerful macro lens. And since then, as it turned out, nothing new has been invented yet. Nilsson's photographs are ingenious - he placed a microscopic macro camera lens and an illuminator on the tip of a cystoscope tube (a device used to examine the bladder) and shot a unique 40-week long “report” of how a new life is born and develops.
Lennart Nilsson was born in 1922 on August 24 and is still alive, which is good news. In 2006, he released his latest book, Life. It will still be interesting to understand his books and photographs, but that will be ahead.
Now let's look at the stages of fetal development week by week. After all, pregnant women always want to know how the life emerging in them develops. What the future man sees, hears, feels.
7-8 hours passed...
The sperm practically digs into the egg.
Until eight weeks, the fetus is called an embryo.
1 Week
For the birth of a new life in the female body, ovulation occurs. At the same time, the temperature rises, the amount of vaginal mucus increases, and there may be slight pain in the ovarian area. Hormones are active in the body, causing a desire for intimacy. The fertilization of the egg by the sperm occurs.
2 week
The fertilized egg divides. The child inherits half of the parent's chromosomes. The sex of the unborn child depends on the sperm that fertilized the cell. After this, the embryo travels through the fallopian tube into the uterus. At the end of the second week, it attaches to the lining of the uterus. This insertion sometimes causes minor bleeding.
3 week
On the 18th day, the embryo’s heart begins to pulsate. The embryo separates from the membranes and actively develops. The nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems are emerging.
4 week
Often it is during this period that a woman finds out about her pregnancy. Signs of pregnancy appear and menstruation is absent.
5 week
The length of the embryo is 6-9 mm. The brain and spinal cord develop, and the central nervous system is formed. The heart, head, arms, legs, tail, and gill slit appear. You can consider a face with holes for future eyes, mouth, nostrils.
A pregnant woman should consume enough folic acid to prevent neural tube defects in her baby. By the end of this week, the heart begins to beat.
week 6
The placenta is formed, which is the lungs, liver, stomach, and kidneys for the fetus. The placenta is also called the baby's place.
week 7
The expectant mother's breasts are significantly enlarged. The length of the fetus reaches 12 mm, weight - 1 g. The fetus already has a vestibular apparatus, the rudiments of the abdomen, chest, and eyes. The brain and fingers are developing. The fruit begins to move.
8 week
The length of the embryo reaches 20 mm. The fetal body is formed. The face, nose, ears, and mouth are different. The skeleton continues to grow, the nervous system improves.
Skin sensitivity appears in the area of the mouth, face, and palms. The gill slits die off, and the rudiments of the genital organs appear.
Week 9
All fetal muscles develop. The fingers and toes already have marigolds. Sensitivity affects the baby's entire body. He touches his body, the umbilical cord, the walls of the amniotic sac. Thus, the tactile sensations of the fetus develop.
10 week
This is one of the most important stages in a baby's development. The nervous system and almost all organs develop. His eyelids are half-open and will fully form over the next few days.
It is very important for the mother not to drink alcohol or other toxic substances during this period. The placenta does not yet fully protect the baby, so significant harm to his health can be caused.
11 week
The amount of blood in a pregnant woman's body increases. The hormones produced during this period affect the body's thermoregulation. Therefore, a woman increasingly experiences changes in blood pressure, dizziness, weakness, and stuffiness.
The fetus has formed eyelids, arms, and legs. He is already making swallowing movements.
12 week
There are already red blood cells in the baby’s blood, and the production of leukocytes begins, which will be responsible for protecting the body. In the meantime, antibodies protect the baby from infection. They come from the mother through the blood and are passive immunity.
Week 13
The expectant mother already wears her protruding belly with pride. The fetus actively develops its skeleton and growth. This causes increased calcium intake. Therefore, a pregnant woman must take special medications to replenish this microelement.
The baby begins to hear thanks to special vibration receptors that are located on the skin. The fetal vocal cords begin to form. The baby's pancreas begins to produce insulin, and the liver begins to produce bile. Villi are formed in the intestines, which are of great importance for digestion.
Week 14
The fetus begins to develop training movements that are very important for the development of the lungs - inhalation and exhalation. The kidneys, bladder, and urethra begin to function. The urine excreted is eliminated by the placenta. The baby's body begins to become covered with lanugo. This is a fluff that performs a thermoregulatory and protective function for the fetal body.
In girls, the ovaries move to the pelvis. In boys, the prostate gland develops. Blood forms inside the baby's bones. Hair growth begins on the scalp.
Week 15
The baby's hematopoietic system is actively developing. Veins and arteries supply all organs and systems with blood. The fetus's heart beats twice as fast as the mother's, while passing about 23 liters of blood per day. The first foci of hematopoiesis appear in the walls of the gallbladder. You can find out the child's blood type and Rh factor.
Week 16
The baby exhibits greater physical activity. The child's eyes open. There is still no subcutaneous fat layer at all. The baby's skin is very thin, with blood vessels visible through it. The fetal skeleton consists of a flexible rod and a network of blood vessels.
Week 17
During this period, the fetus experiences rapid eye movement. In this regard, scientists claim that a child can dream. They are associated with his physical activity during the day.
Week 18
The length of the fetus reaches 14 cm. The baby blinks, opens its mouth, and makes grasping movements. He moves a lot in his mother's belly. All parts of the body are clearly visible, the face, the skin of the body turns pink.
Week 19
The mother feels the baby move. Later the movement turns into tremors. The strength of the shocks varies. It depends on the mother’s mood, activity, and time of day. On average, the baby makes 20-60 pushes in half an hour. The baby's brain is actively developing. He starts sucking his thumb.
Week 20
At this time, expectant mothers are seriously thinking about childbirth. It’s good to choose courses for expectant mothers.
21 weeks
The length of the fruit already reaches 20 centimeters. The fetus's kidneys are working, and meconium is produced in the intestines - pseudo-feces.
Week 22
The child hears his mother’s voice, her breathing, her heartbeat. All this is due to the fact that the auditory ossicles have ossified and become capable of conducting sounds.
The weight of the fetus increases and fat deposits accumulate.
Week 23
The length of the fetus reaches 30 cm, and the weight is 650 g. The lungs are quite developed. In case of premature birth during this period, the baby will be able to survive in the intensive care unit.
Week 24
You can hear the baby's heartbeat by placing your ear to the mother's belly. During this period, the placental blood circulation of the child is of primary importance. The dimensions of the child's pelvis and lower extremities are relatively smaller than the upper part. This is due to the fact that the upper part of the body is better supplied with lower arterial blood. At the same time, the lungs receive very little of the blood.
Week 25
Still soft cartilage of the nose and ears. The skin of the fetus is wrinkled, covered with grease, and vellus hair forms on it. The child is already falling asleep and waking up.
Week 26
The baby has a well-developed sucking reflex. He often sucks his thumb. This activity calms him down and strengthens his jaw and cheek muscles. Depending on the finger of which hand the child sucks, we can assume that he will be right-handed or left-handed.
The baby pushes, explores the space that surrounds him. At this time, the normal number of kicks for the baby is 10 times per hour.
The mother's uterus has quadrupled in size. It expands the lower ribs, resting on the hypochondrium.
Week 27
The length of the fetus reaches 350 mm, weight -900-1200 g. The child’s eyes open slightly and perceive light. The mouth and lips become even more sensitive.
The boys' testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. In girls, the labia minora are not yet covered by the labia majora.
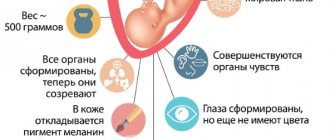
Week 28
The hair on the head becomes thicker. Although some children are born almost bald. All these are variants of the norm. Lanugo practically disappears. Although in some places there may still be fluff on the body, which will disappear in the first weeks after birth.
Week 29
The baby has eyelashes. His eyelids are already closing and opening. Toenails grow on my feet.
Week 30
The child reacts to sounds from the external environment and may cry. The central nervous system controls body temperature and breathing rhythm. The lungs can already breathe normal air.
31 weeks
While awake, the child opens his eyes. Closes them during sleep.
Week 32
The length of the fetus reaches 450 mm, its weight is about 2500 g. From this period, the baby is actively growing and gaining weight. His skin becomes thicker, pinkish, smooth.
Week 33
During this period, the brain mass, depth and number of convolutions increase significantly. The most important functions of the fetus are controlled by the spinal cord and parts of the central nervous system. After birth, the functions of the cerebral cortex will develop.
34 week
The child can lift and turn his head due to increased muscle tone. Actively reacts to light, can squint from direct rays of the sun.
Week 35
The baby's lungs are fully developed. The fetus quickly develops a grasping reflex.
Week 36
A pregnant woman may experience the first signs of future birth. “Prolapse” of the abdomen occurs when the height of the uterine fundus decreases. The mucus plug from the cervix may come off. Characteristic during this period is an increase in urination and defecation. Not only does the uterus put pressure on the intestines and bladder. Also, prostaglandins (hormones produced at that time) periodically cause the desire to have a bowel movement.
The child pushes and moves less. The cervix shortens and becomes softer. Sometimes the external os of the uterus can open 1-2 cm.
Week 37
The length of the child reaches 47 cm, weight - 2600 g.
Week 38
The fetus is already quite viable, ready to be born. There can be hairs up to three cm on the head. Its skin is pale pink and has a layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue. The child performs about 70 thyreflex movements.
Week 39
The baby reacts very sensitively to all movements and the psychological state of the mother. He responds with his movements to her anxiety, joy, fear.
40 week
The length of the child reaches 480-520 mm, weight - from 3200 to 3600 g. In girls, the labia minora are covered by the labia majora. The boys' testicles dropped into the scrotum. The cartilages of the nose and ears are elastic, the nails on the fingers. The baby is ready to be born.
In the first weeks after the birth of the baby, it is very important to stroke his body and gently hold him close to you. The child cannot yet feel himself and really misses being touched.
The baby's memory retains very well the sound and rhythm of the mother's heart. To calm the baby, sometimes it is enough to put it on the left side of the mother's body.
- and here is Lennart Nilsson’s book “A Child is Born!” The miracle of the birth of a new life."
Lennart Nilsson also filmed short videos about embryo development; I found them when I was studying information from his official website.
A selection of books about pregnancy and childbirth: - Mommy is Me, or the Diary of a Pregnant Woman about the most secret things. L. Lomanskaya
— A big book about pregnancy. McCarthy Jenny
If you liked the article, subscribe to updates, it will take less time than taking a pregnancy test =))
Features of the 1st trimester after IVF
The hardest thing is for women who have undergone IVF. Their chances of developing pathologies and miscarriage increase several times. The development of a newborn's life after the IVF procedure begins immediately after fertilization has taken place.
The woman is told how many fertilized eggs were implanted into her body. The egg transfer does not occur immediately, but gradually. Over a period of time, doctors ensure that the cells are formed correctly.
The decision to transfer a fertilized egg is made by two doctors at once: a reproductive specialist, who is responsible for the female body and its readiness for pregnancy, and an embryologist, who closely monitors the development of the egg.
2 weeks after the embryo transfer, the woman will know the result. It can be both positive and negative. The surest way to determine pregnancy after IVF is to donate blood for hCG. A high level will indicate that fertilization was successful.
How does an embryo develop?
21 days after the transplant, doctors do an ultrasound. Based on its results, it will be possible to judge the development of the baby in the mother’s body.
A woman in the 1st trimester after IVF should especially closely monitor her health and lifestyle. Unfortunately, no woman can completely influence the process of fertilization, but she can facilitate it.
Try to get as much rest as possible. But at the same time, there is no need to lie in bed. Spend more time outdoors and take walks. Do not forget that you will have to give up all bad habits: smoking, alcohol.
Include in your diet only healthy foods that are rich in vitamins. Eat as many seasonal vegetables and fruits as possible. They contain the largest amount of useful substances and microelements. Do not overuse pills, especially if they were not prescribed by a doctor.
Stages of embryo development in the 2nd trimester
The first trimester laid down all the vital and necessary organs. The task of the second trimester is to improve all body systems.
How does the embryo change day by day at 4 months?
The embryo gradually becomes human-like. The head and torso become more proportional. At the same time, all human organs are improved.
At the beginning of the second trimester, the woman undergoes the first screening. During an ultrasound examination, a specialist is able to determine the gestational age, understand how developed the embryo is and identify existing pathologies.
At week 14, the body’s musculoskeletal system begins to actively develop. From the 14th week, the reproductive system gradually forms. Girls develop ovaries, boys develop a prostate gland.
By the end of the 15th week, the baby’s height reaches 12 cm. All organs have already formed, the kidneys are working, which produce urine. The facial muscles begin to work, thanks to which the baby can make grimaces.
Pregnancy at 5 months
The baby has increased in size, and now the expectant mother can feel his movements. Primiparas feel tremors at approximately 18-19 weeks of pregnancy. Multiparous women may realize that the fetus is moving as early as 16 weeks.
From the 17th week, the baby’s own immune system is formed. Now he is protected from external influences not only by the placenta, but also by his own immunity. From the 18th week, the limbs actively grow, the head becomes more proportional. The structure of the brain will improve.
Since the sex has already formed, from the 19th week the thyroid and sex glands produce hormones. The skin is no longer so pale and transparent. It is becoming more dense and reliable. Every day more fuzz appears on the baby's head and entire body.
6th month: how does the human embryo change?
The 6th month marks the active work of the brain and the formation of the facial part. If you pay attention to the appearance of the embryo, it completely corresponds to a newborn child.
From 21 to 24 weeks, the baby's weight reaches approximately 530 grams. His height is 32 cm. Researchers believe that from the 23rd week of pregnancy the child begins to dream. He actively reacts to external stimuli. He may not like a loud voice, strong noise, or a strong smell.
The baby often shows his dissatisfaction in the form of pushing. The child tries to study everything that surrounds him. For example, he pulls the umbilical cord, tries to understand where he is and how everything works here. The baby already shows high curiosity during this period.
Which weeks of pregnancy are considered critical?
The first dangerous period occurs in the 2nd week of pregnancy, when implantation of the fertilized egg occurs. A woman may not yet be aware that she is pregnant. Miscarriage in the first weeks of pregnancy can be caused by excessive physical exertion, stress, abnormalities in embryo development, and abnormal structure of the uterus.
The period that occurs at the end of the first trimester is also dangerous for the embryo. At this time, the placenta is actively developing. Any unfavorable factors (overwork, stress) can provoke its incorrect formation. In the most dangerous cases, the pregnancy freezes and spontaneous abortion occurs.
The critical period of the second trimester is the time from the 18th to the 22nd week. At this time, the uterus is actively growing, and abnormalities in the development of the placenta may be observed. A woman should get more rest. You should not skip regular examinations with a gynecologist.
Feeling unwell at any stage of pregnancy is a reason to consult a doctor
From the 28th to the 33rd week, the risk of premature birth increases. This condition can be provoked by excessive physical exertion, nervous shock, and increased sexual activity. Any unpleasant symptoms (bleeding from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen, general deterioration in health) are a reason to seek help.