Pessary
- a device placed on the cervix to prevent miscarriage or premature birth. The main indication for its use is isthmic-cervical or isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI).
The pessary reduces the load on the cervix. The device prevents its opening and prolongs the process of bearing the baby.
A pessary is used to relieve pressure on the cervix. The ring is inserted onto the cervix, maintaining its physiological shape. The device imitates the normal shape of the uterine os during the gestation period.
The device places internal organs in the correct position. It prevents premature opening of the cervix. The pessary also helps keep the unborn child in the uterine cavity.
Pessaries are classified according to their shape:
- domed;
- annular;
- unloading
Dome or mushroom pessary
- the most common type of device. It looks like a perforated bowl with a large hole in the center. The medical device is made of silicone. The material has good elasticity and stretchability.
The main function of a dome-shaped pessary is to support the cervix in a physiological position. It moves the cervix towards the sacrum, preventing its further dilatation.
Ring pessary
- a round-shaped device with four notches on the inner surface. It is made of silicone with a denser structure.
A medical device allows you to compress the cervix, closing its lumen. The main purpose of the ring pessary is to restore and maintain the physiological diameter of the internal pharynx.
Relieving pessary
made of very dense silicone or plastic. The device has the shape of a trapezoid with rounded corners. Its narrow part is located on the side of the pubis, the wide part on the side of the sacrum.
The main function of this type of pessary is to reduce the pressure of the fetus and amniotic fluid on the cervix and relieve the load on the cervix. The device does not interfere with the act of defecation and urination.
Reasons for installation
During the normal course of gestation, the cervix is closed almost until the end of the gestation period. A few weeks before giving birth, the cervix dilates 1-2 centimeters. It holds the unborn baby, amniotic fluid and amniotic fluid in the uterus.
With ICI, the cervix dilates earlier than expected. Gynecologists attribute 9 etiological factors to the most common causes of complications:
- History of cervix ruptures.
- Surgical interventions on the neck.
- History of abortion.
- Carrying twins or triplets—multiple pregnancies increase pressure on the cervix.
- Congenital anatomical defect of internal organs.
- The source of the infectious process is in the genital tract.
- Constant physical activity during the gestation period.
- Increased amount of amniotic fluid.
- Increased secretion of male sex hormones.
The installation of a pessary is recommended for women with a cervical length of less than 3 centimeters. Also, medical manipulation is indicated for expectant mothers with a softened and smoothed uterine os.
An additional indication for the introduction of an obstetric device is low placentation. The pathology is accompanied by a high risk of spontaneous abortion. The pessary prevents miscarriage and premature birth.
The device is also indicated for expectant mothers with urological problems. The obstetric ring maintains the physiological position of the bladder and urethra. It is used for incontinence and neurogenic dysfunctions.
What is an obstetric pessary and when is it indicated?
• in the form of a round ring;
• short or soft uterus;
• threat of premature birth and miscarriage;
• prevention of irmic-circvical insufficiency;
• poor suture after surgical treatment.
Contraindications for installing a pessary
• location of the amniotic sac at the bottom of the vagina;
• inflammatory process of the genital organs;
• secretion of ichor and blood;
• the occurrence of an allergic reaction;
• copious vaginal discharge;
• the diameter of the vaginal opening is less than 50 mm.
Contraindications
The use of an obstetric pessary has a number of contraindications. To exclude them, the gynecologist conducts a thorough examination of the patient before installing the device.
The use of a medical device is strictly prohibited during a frozen pregnancy. The pessary prevents spontaneous abortion and the exit of a dead fetus from the uterine cavity. Its preservation in a woman’s body is a risk factor for a severe infectious process.
An obstetric ring is contraindicated if there is perforation of the membranes in the vagina. If the amniotic bladder has left the uterine cavity, then the application of a pessary will contribute to its traumatization and disruption of its integrity.
It is strictly prohibited to install a pessary if the expectant mother has reddish or brown vaginal discharge. Blood from the genital tract indicates that spontaneous abortion has begun. The woman needs urgent medical attention.
An inflammatory process in the vagina is a strict contraindication for medical manipulation. An obstetric pessary can contribute to the introduction of infection into the cervix and uterus.
Recommendations after administration
View gallery
After installing a pessary during pregnancy, a woman’s quality of life improves, as some restrictions on physical activity are removed. Despite this, she must adhere to certain rules:
- A categorical ban on sexual activity.
- Physical activity, especially bending and squats, is excluded.
- Every 2-3 weeks you need to be tested for infections.
- You cannot swim in pools or open water.
- As a rule, the doctor prescribes the introduction of vaginal suppositories for the entire period of use of the pessary in order to exclude sexually transmitted infections.
- Do not try to fix or remove the device yourself. If you experience any discomfort, you should consult a doctor immediately.
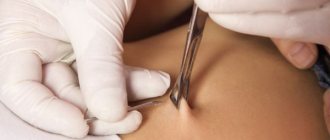
Installation of a pessary
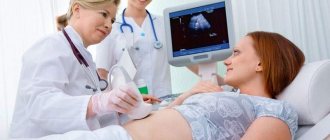
Before introducing a medical device, the doctor prescribes a series of examinations. Their list includes a gynecological examination in the speculum, an ultrasound examination of the cervix, and a smear for microflora. If pathogenic bacteria are detected, the expectant mother is prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs.
The installation of a pessary is carried out on an outpatient basis - in a public or private clinic. After the manipulation, the pregnant woman can go home. The procedure is performed by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Sometimes a pessary is installed at a later date - at 30-33 weeks. The duration of the medical procedure depends on the indications. Insertion of an obstetric ring after 36-37 weeks of pregnancy is not advisable. By this time, viable and healthy children are born.
The insertion of the ring is a painless procedure. Some expectant mothers experience mild discomfort during the procedure. Unpleasant sensations disappear 5-10 minutes after the manipulation.
Immediately before the procedure, the expectant mother empties her bladder. Then the woman settles into the gynecologist's chair. The specialist selects a pessary for a specific patient.
There are three main ring sizes. The smallest is indicated for young expectant mothers who have no history of pregnancy or childbirth. The second diameter of the pessary is intended for women with 1-2 children or older patients. The third ring size is recommended for expectant mothers who have had two or more births in the past.
Before inserting the pessary, treatment is carried out with an antibacterial drug. The procedure reduces the risk of infection. Sometimes the doctor lubricates the ring with glycerin - the substance facilitates the advancement of the obstetric device.
After treatment, the gynecologist inserts the device into the genital tract, reaching the cervix. A correctly installed pessary does not cause pain or discomfort in the expectant mother.
Installation of obstetric pessary Dr. Arabin:
How to place a pessary: does it hurt?
Only a gynecologist installs this device.
You shouldn't do this yourself. Is it painful to have a pessary inserted? Most women say yes, although in each case everything is individual. Some people experience slight discomfort, while others experience really great pain. Women whose cervix is very sensitive can take an antispasmodic tablet in about half an hour before installing the pessary to reduce discomfort. The installation procedure takes only a few minutes. There should be no discomfort if the ring has been selected with the appropriate diameter and installed correctly. If your stomach begins to hurt with the pessary installed, you should immediately inform your doctor. After installing the ring, the woman will have to undergo regular smear tests so that the doctor can monitor the state of the microflora. You will also need to use special vaginal suppositories with a bactericidal effect to prevent inflammatory processes that may occur.
Problems after installation
In 0.5-1% of cases, complications are observed after the introduction of a pessary. The most common of them is a violation of the position of the obstetric ring. It moves due to the onset of contractions or due to improper installation. Symptoms of device displacement include discomfort and pain in the vaginal and cervix areas.
A rare complication of wearing a pessary is infection of the cervix. It is accompanied by greenish or yellowish discharge from the genital tract, which has a rotten odor. Less commonly, the pathology causes pain in the lower abdomen and fever. Infection of the device is an indication for its immediate removal and antibiotic therapy.
Childbirth after PESSARY. How fast.
Days on site: 3093
When placing the pessary, the doctor warned that if it becomes dislodged, contact a gynecologist. Please tell me what or how it is possible to move it? If I have a delicate problem - constipation, this could be the reason. .
Yes, the pessary can move forward a little, due to constipation. but also a pessary can further aggravate this problem, try to drink more kefir every day, fresh, especially in the morning on an empty stomach! And if the pessary moves too much, then you will feel pain and discomfort in the urethral area. If such pain occurs, then consult your doctor!
Days on site: 3717
Days on site: 2933
It works out differently for everyone.
Days on site: 2924
Days on site: 3093
And my pessary will soon be removed at 39 weeks (December 19), so we’ll see how long it takes for labor to begin
Days on site: 2924
Days on site: 3093
Days on site: 2924
Days on site: 2934
Days on site: 2934
Days on site: 3093
The gynecologist ALWAYS does the rinsing (I personally did it with chlorhexidine, 1 bottle was enough for the entire pregnancy), this is also written in the instructions for the pessary. And thanks to these washings, I personally had very little discharge (although during pregnancy it increases, and with a pessary there should be a lot of it), even my doctor praised me. I’m 37 weeks, I’m going to take off the pessary, they said they’ll leave me in the hospital for 5 days, they’ll monitor the opening and do the treatment, they’ll restore the vaginal flora before giving birth. and maybe they will leave it there until the birth, because they say everyone reacts differently to removal, some give birth right away (the uterus is sensitive), some go to the last minute...
Hexicon suppositories are the same Chlorhexidine, when I use them at home, I also have no problems with discharge and it is not necessary to climb onto G’s chair every time and rinse. and set it up at home and went to bed)))
And in order not to give birth earlier, that’s why I will “remove” the pessary at 39 weeks and not 37-38. And the microflora of the vagina is already normal (if these suppositories are regularly placed or, moreover, washed by a Gynecologist), and there is no need to specially restore it, especially if it is observed in advance in the maternity hospital!
Discharges after installation
Normally, while wearing a pessary, the expectant mother experiences light mucous discharge. They have a transparent or whitish tint and are not accompanied by an unpleasant odor. If discharge with other characteristics appears, a pregnant woman is advised to consult a gynecologist.
Red or brown discharge indicates that spontaneous abortion has begun. Premature termination of pregnancy is often accompanied by cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
In the presence of an infectious process, leucorrhoea acquires a yellow, green or gray tint. They become abundant and have an unpleasant odor.
Clear and watery discharge may indicate leakage of amniotic fluid. When they appear, there is a risk of violating the integrity of the amniotic sac. Sometimes heavy liquid discharge is normal.
Lifestyle
The future mother's observance of the rules for caring for the obstetric ring will help preserve the pessary and bring the baby to term. A woman should not touch the device or try to change its position. Regular examinations by the attending obstetrician-gynecologist are required - at least once every 3 weeks.
If indicated, the doctor sanitizes the pessary using antiseptics. The procedure prevents infection of the medical device.
After the installation of an obstetric ring, restrictions appear in the life of the expectant mother. She is prohibited from having sexual activity and strenuous physical activity. A pregnant woman should avoid sports, going to the bathhouse and sauna.
Reviews
When many pregnant women hear a diagnosis of ICI from their doctor, they are scared. The fact of installing the ring is also frustrating. But almost 100% of women who installed a pessary claim that everything is not as scary as it seemed. In addition, they confirm that this method is very effective in maintaining pregnancy and ensuring normal intrauterine development for the baby.
But you should know that there are still cases of premature birth even with an obstetric ring installed.
Women say that after your pessary is removed, it can take anywhere from a day to three weeks before you go into labor.
Removing the pessary
If there are no complications, the pessary is removed at 38-39 weeks of pregnancy. The timing coincides with the date of physiological birth. Wearing the ring for a longer period of time is not advisable.
Sometimes the expectant mother is advised to remove the medical device earlier. Premature removal of the pessary is necessary if an infectious process develops. The proliferation of pathogenic microflora increases the risk of infection of the fetus.
Removal of the ring before 38 weeks is indicated at the onset of labor. Frequent and regular contractions and discharge of amniotic fluid are the main symptoms of pregnancy completion.
An additional indication for removal of a medical device is the need for urgent delivery. Induction of labor or cesarean section before 38 weeks is indicated against the background of eclampsia, acute oxygen starvation of the fetus, massive bleeding with low placentation.
Removal of the pessary is carried out on a gynecological chair. For most expectant mothers, the procedure is painless. Sometimes the manipulation is accompanied by slight discomfort.
Pessary or stitches
Cerclage is the placement of sutures on the cervix to prevent its premature dilatation. The procedure is more effective than a pessary.
However, cerclage is prescribed before the 20th week of gestation; its use later is inappropriate. Suturing is a full-fledged operation performed under anesthesia in a hospital setting.
The procedure is indicated in the presence of high risk factors for the development of ICI. Cerclage is the “gold standard” in the treatment of expectant mothers with a history of miscarriages due to ICI.
In the absence of serious indications for suturing the churchax, the use of a pessary is recommended for a pregnant woman. The obstetric ring is easy to install; general anesthesia is not required for manipulation.
Contraindications for device installation
But there are situations in which it is strictly prohibited to use a pessary during pregnancy.
These include:
- bloody or bloody discharge;
- inflammatory processes on the cervix or vagina (in this case, the device can be used after the inflammation has resolved);
- suspicion of frozen pregnancy;
- severe fetal malformations;
- diseases of a woman for which pregnancy is a contraindication;
- pronounced degree of ICI;
- violation of the integrity of the fetal bladder.
Pessary rating
The medical market offers many pessaries of various shapes, sizes and made from a variety of materials. To choose the right medical device, the expectant mother should consult her doctor.
An obstetric or gynecological pessary is a special ring that is installed on the cervix of the expectant mother during pregnancy to prevent late miscarriage or premature birth. It is used mainly in pregnant women with a period of more than 18-20 weeks, that is, from the middle of the second trimester.
This removable device, simple in appearance, plays a very important role. Without going into physiology, it relieves the load on the cervix that the child and amniotic fluid puts on it. The special shape of the vaginal ring redirects this load to the anterior wall of the uterus. The pessary also allows you to keep the cervix closed, which prevents the mucus plug from leaving it and the penetration of infectious pathogens from the vagina into the uterine cavity.
The pessary does not have any consequences for the child. It does not come into contact with the fetus and amniotic sac.
What types of pessaries are there?
Pessaries are made from hypoallergenic materials - silicone and modern types of plastic. In shape and type, the pessary can be similar to a round (“PortexLand”) or curved ring (“Hodge Pessary”), there is a cubic, mushroom- or cup-shaped pessary (“Dr. Arabin”), a flat pessary (“Juno”).
Which pessary to install (type and size) is determined by the doctor, taking into account the clinical situation (the purpose of the procedure), the number of births experienced, the number of developing fetuses, the gestational age at the time of installation and the anatomical features of the woman: parameters of the upper part of the vagina, the diameter of the cervix, etc. The smallest size is pessary No. 1.
Pessary or sutures during pregnancy: which is better, indications
In addition to the pessary, there is another method, well known to gynecologists, of keeping the cervix closed. This is her suturing or the so-called cerclage. Today this is the most reliable and proven way to prevent premature termination of pregnancy. However, it has a number of disadvantages:
- You can sew up the cervix only in the first half of pregnancy; in the first trimester, sutures will definitely be more effective than a pessary;
- the likelihood of prolapse (puncture) of the amniotic sac with instruments;
- the need for general anesthesia;
- psychological trauma, fear in the woman in labor, which again provokes the threat of interruption;
- the likelihood of stitches cutting through during pregnancy;
- cervical injury;
- mandatory hospitalization and hospital stay, etc.
The advantages of an unloading pessary are that it is placed on an outpatient basis to maintain pregnancy (including multiple pregnancy - with twins or triplets) at any stage. Typically, this is 20-30 weeks, and especially often 26-28 weeks - the critical period when many people go into premature labor. Unlike cerclage, this type of medical care is non-invasive. And it will never provoke labor or miscarriage on its own. Any gynecologist can place an obstetric ring on the cervix, even in a antenatal clinic. It will take no more than 1-2 minutes. No anesthesia or any preparation for the procedure is needed. The patient feels comfortable. And there are no restrictions until which week to install the pessary.
Why is an obstetric pessary installed during pregnancy?
Pregnancy does not always go smoothly. In this case, doctors prescribe certain medications to the woman, and sometimes also special devices, one of which is an obstetric pessary: during pregnancy, this is one of the ways to prevent the cervix from opening at the wrong time.
- What is Dr. Arabin's pessary or ring?
- Why is an Arabin ring installed during pregnancy?
- How to place a pessary: does it hurt?
- How much does a pessary cost?
- Is it possible to have sex?
- Discharge with a pessary: normal or not?
- When a pessary is removed during pregnancy, does it hurt?
- How long after removal does labor begin?
- Reviews from pregnant women
What is Dr. Arabin's pessary or ring?
This is a special device that is inserted into the vagina and brought to the cervix to support it. This is only required during pregnancy, when the risks of miscarriage or premature birth are high. It is made of silicone or soft plastic, which, after installation, follows the anatomy of the body and is practically not felt.
Why is an Arabin ring installed during pregnancy?
Dr. Arabin's obstetric pessary can be installed for:
- ICI (isthmic-cervical insufficiency);
- prevention of ICN;
- failed suture if ICN was treated by surgery.
That is, it is placed so that the cervix does not dilate and premature labor or miscarriage does not begin if the period is still short.
In 80−90% of cases, if a woman is diagnosed with ICI, the installation of a pessary allows the pregnancy to be maintained until the due date.
A pessary is also installed during multiple pregnancies, when a woman is expecting twins or triplets, because during this period the load on the cervix is also very high.
How to place a pessary: does it hurt?
Only a gynecologist installs this device. You shouldn't do this yourself. Is it painful to have a pessary inserted? Most women say yes, although in each case everything is individual. Some people experience slight discomfort, while others experience really great pain.
Women whose cervix is very sensitive can take an antispasmodic tablet in about half an hour before installing the pessary to reduce discomfort. The installation procedure takes only a few minutes.
There should be no discomfort if the ring has been selected with the appropriate diameter and installed correctly. If your stomach begins to hurt with the pessary installed, you should immediately inform your doctor.
After installing the ring, the woman will have to undergo regular smear tests so that the doctor can monitor the state of the microflora. You will also need to use special vaginal suppositories with a bactericidal effect to prevent inflammatory processes that may occur.
How much does a pessary cost?
The cost varies depending on the model and manufacturer. The price of obstetric pessaries fluctuates between 700 and 5,000 rubles.
Is it possible to have sex?
No. It is forbidden to have sex with a pessary in place, despite the fact that many couples neglect this prohibition. This is too risky, especially for the child. After all, the pessary was installed for a reason, and the pregnancy must be preserved.
Why are dexamethasone injections prescribed during pregnancy? Are they dangerous for the fetus?
When a mother needs to take Magnelis B6 during pregnancy, information is here.
About Kanefron tablets: https://mamafarma.ru/ginecology/tabletki-kanefron-pri-beremennosti.html.
Discharge with a pessary: normal or not?
If these are standard leucorrhoea, then there is nothing to worry about. After installing the ring, their number may increase slightly, which is a normal reaction of the body. If the discharge is brown, bloody, yellowish-green, or clear and liquid like water, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When a pessary is removed during pregnancy, does it hurt?
If everything is in order and the pregnancy is proceeding normally, this device is removed at 38 weeks. It's relatively painless. The sensations are the same as during installation.
Some will only experience discomfort, while others will experience pain. After removing the pessary, the genital tract is sanitized to prepare for childbirth.
Before 38 weeks, it can be removed urgently if labor has begun, amniotic fluid has leaked, or infection has occurred.
How long after removal does labor begin?
Here, too, everything is individual. For some, they may begin on the same day, while for others, after a few days, a week, 10 days, 2 weeks.
Reviews from pregnant women
Here's what reviews say about an obstetric pessary for uterine prolapse during pregnancy:
Angela, 24 years old
It was prescribed to me because of the risk of premature birth. I didn’t know what it was, so I thought, since it’s necessary, I’ll put it on. It was very painful to insert, but I endured it. It caused bleeding. They pulled me out.
I ended up in the hospital and the doctor insisted that I insert it again. As a result, he caused labor. The baby is fine, but I have a lot of tears and stitches. Instead of a week in the maternity hospital, I spent two.
I don't want anyone to experience this.
Yana, 31 years old
The pregnancy was unexpected and unplanned, but I really wanted this child. It didn't work out right away. Constant threats of miscarriage, I was in conservancy, took hormones, took care of myself like a crystal vase, but problems still appeared. At week 19, ICI was placed and the cervix was shortened. Put it in storage. The doctor said that they would install an obstetric pessary.
I had no idea what it even was. The girls in the ward called him a ring, and I started calling him that. When I saw him for the first time, I thought that he was huge and definitely wouldn’t fit into me. I was also afraid that he was tough and would be uncomfortable with him. But, as it turned out, no problems at all. Installation is difficult, unpleasant and a little painful.
Once installed, you don’t feel it because it is flexible plastic that adapts to the anatomy of the body. I wore it almost until the birth. The pessary needs to be looked after, namely, washed every 10-14 days with antiseptic solutions. You don’t need to do this yourself, but go to a gynecologist. And he does it without pulling it out!!! Another shock, but what to do? I endured it. She reported the child.
The ring and drug therapy helped.
Ekaterina, 26 years old
During my second pregnancy, I was given an obstetric pessary Juno, when there was a risk of premature birth, the cervix was partially dilated, and the fetus was positioned too low. They installed it quickly, it was a little painful, but tolerable. After 5 minutes I no longer felt it. It became much easier to walk, the heaviness disappeared. There was no particular discomfort.
The discharge and its volume increased, but after examination the doctor said that this was normal. It was impossible to have a sexual life, and it was impossible to lift weights. I followed all the rules. They took it off for me at 37 weeks. It was the end of December, and I really didn’t want to give birth on New Year’s holidays. My labor began exactly 10 days after this device was removed. Everything went fine.
The daughter was born healthy, with a normal weight.
Some information about pessaries in the video:
Source: https://mamafarma.ru/ginecology/pessarij-pri-beremennosti.html
Installation of a pessary on the cervix: timing and technique
The ring is installed at any stage of pregnancy, usually more than 12-14 weeks, if there are indications for “securing” the cervix. The maximum installation period is 34-35 weeks. There is no point in later, since full-term babies are already born at 37-38 weeks.
The ring is inserted on an outpatient or inpatient basis. The manipulation takes no more than 2-3 minutes. Many women are interested in whether it hurts to insert a ring. It all depends on the woman’s pain threshold. To some, yes. But for most, it’s just a little unpleasant, in principle, like any gynecological examination. Special gels—lubricants—help make insertion and sliding through the vagina more comfortable and faster.
How to place a pessary (in this case, the Doctor Arabin brand) is clearly shown in this video.
Immediately after installation, nagging pain in the abdomen appears. This is due to tension in the uterus as a result of medical actions. You can take No-shpa and use the Papaverine suppository rectally. In a hospital setting, if necessary, a drip with Ginepral or Magnesia will be placed.
The vaginal ring is removed at 37-38 weeks or earlier if labor has begun. It is believed that prolonged wearing of a pessary leads to slow dilation of the cervix during childbirth. There is no such dependence. And labor after removing the ring can begin either in the next 24 hours or in 2-3 weeks. Everything is individual.
Pessary during pregnancy reviews 26
I now have a pessary. Diagnosed at 22 weeks, the indication was shortening of the cervix to 23 mm. Everything else is good, everything is closed. They installed the smallest one for nulliparous women, it was incredibly painful, I screamed and climbed up on the chair.
When it was placed, it was sterile against infections, and did not even suffer from thrush; streptococcus and carinobacteria were recently discovered. I took antibiotics, I don’t know if it cured me or not. I haven’t had a repeat smear yet. My husband and I have sex carefully, but only after they told me that the cervix has lengthened and remained at a good level.
After a week, I take it off, and lately, under the weight of the fetus, the pessary has been causing me pain, I wake up every night from sharp pains, when I want to turn over from side to side. Every night for several weeks now. But again, it’s worth it, and I’m grateful to the doctors who noticed everything and installed this thing for me.
The question remains open as to why someone cannot give birth after this, they pace around, and eventually give birth artificially, while someone is immediately sent into labor when the pessary is removed. block.
Obstetric pessary unloading - your opinion
Before installing the pessary, the discharge was white - transparent, abundant, but without “porridge” or unpleasant odor. After installation, they remained the same, abundant, watery, with white.
There were curds only during the period when, before installing the pessary, a course of suppositories for thrush was inserted as a preventive measure, they said it was necessary, although the smear was good. But this is how the candle came out.
If there is no itching, burning, unpleasant smell of thick cottage cheese, etc., then you can ignore the abundance of discharge.
Recommended reading: A little blood at 11 weeks of pregnancy
I was discharged on the third day, since before that I had been hanging out in the second maternity hospital for almost three weeks, and before that in the gynecology department.
The little one was just starting to go hysterical about his mother-in-law. But I couldn’t even call, find out how they were doing, the little one heard that the mob was calling, started crying and calling for mom, and I heard this a couple of times and I generally felt bad.
Then I called my husband to find out how they were doing.
Obstetric pessary
I was diagnosed during 3 B. at 20 weeks. I took it out myself at 35 weeks. (moved). She gave birth at 36 weeks 3800. We treated her at home (with the help of her husband) with furatsilin and chlorhexidine. The insertion was unpleasant, but with the painkiller gel it was tolerable, I was breathing frequently, and it helped.
Taking it out is also unpleasant, but I didn’t try to put it back in (and, as the doctor said, I did the right thing). Anticipating the questions, I’ll answer, it was not possible to get to the hospital, the roads were snowy, they said they wouldn’t get through the ambulance, and walking 2 km was not realistic.
)))
All rights to materials posted on the site are protected by copyright and related rights legislation and cannot be reproduced or used in any way without the written permission of the copyright holder and placing an active link to the main page of the Eva.Ru portal (www.eva.ru) next to with the materials used.
Who received an obstetric unloading pessary during pregnancy?
Ekaterina, in your term, with such a short neck, I would lie down and not get up. I was 27 mm and at this time there was no dilatation, I generally didn’t lift more than 1 kg and didn’t do anything.
At 32 weeks, dilatation began with the pessary, and ginepral was injected. Still gave birth at 37 weeks. The water broke with the pessary.
I don’t want to scare you, the girl with a pessary gave birth at 27 weeks, unfortunately, the story ended sadly...
We recommend reading: Pampers 19 weeks pregnant
At what months should a pessary be removed during pregnancy?
All rights to materials posted on the site are protected by copyright and related rights legislation and cannot be reproduced or used in any way without the written permission of the copyright holder and placing an active link to the main page of the Eva.Ru portal (www.eva.ru) next to with the materials used.
Installation of a pessary during pregnancy PHOTO Obstetric pessary Juno (uterine ring)
— If a Juno pessary is installed, then if an imbalance of microflora occurs, you can prescribe any suppositories allowed during pregnancy. When installing imported pessaries, the list of possible drugs is significantly limited. The doctor said that the Juno pessary is more unpretentious in this regard.
Until what week is a pessary inserted?
There are not many contraindications to the installation of this gynecological device. The main ones are bloody vaginal discharge, colpitis or cervicitis. If a woman has a bad vaginal smear or there are signs of infection, she first needs to perform a so-called vaginal debridement. At least an antiseptic like Hexicon (chlorhexidine).
Where to buy and how much it costs
You can also order online in pharmacies, shops that sell various medical supplies, and private clinics. Or even ask your doctor. Sometimes they themselves help patients order pessaries, although they still have to pay for the device.
In Russia, two companies or types of pessaries are popular - “Junona” and “DR. Arabin" (Doctor Arabin) . Which one is better? The second one costs several times more and is made of silicone, produced in Germany. The first one is plastic. According to women's reviews, the one that is more expensive, that is, silicone, is better. It's not that painful to put it on. And German pessaries fall off less often.
Although, the success of wearing is influenced, rather, by other factors, such as the correctly selected size. The doctor must first examine the woman to determine what size of the uterine ring she needs. There are 3 sizes in total. 1 and 2 are suitable for nulliparous women. Young girls who are pregnant for the first time usually wear one. Threesomes are only for women who have given birth several times.
Lifestyle with a gynecological pessary - recommendations from gynecologists
1. Physical activity and sex life. Since the pessary is placed on women who are at risk of premature termination of pregnancy, they need rest. Both physical and sexual. It is prohibited to have sex, both with and without a condom, as this can lead to displacement of the pessary and hypertonicity of the uterus. Some mothers try to lie down almost all the time. Such strict restrictions are only needed if the amniotic sac prolapses into the cervix. If everything is not so bad, you are at home, a hospital is not indicated, you can simply not overexert yourself - do not walk a lot so as not to get tired.
2. Wearing a bandage. There is no scientific evidence that it prevents premature cervical dilatation. Nevertheless, most mothers feel calmer with it. Some even take a shower and go to the toilet with a bandage. The main thing is calm.
3. Care of the pessary and its sanitation. There is no need to process it yourself. And try to get it, of course, too. No special measures need to be taken. However, the doctor must take smears from the vagina once every 3 weeks, or even more often, in order to detect the inflammatory process in time and treat it. By the way, inflammation with a pessary is a very common side effect.
How is the pessary and vagina sanitized? Typically, antiseptics are used for this - antimicrobial drugs. The doctor may periodically rinse the vagina with chlorhexidine during an appointment.
For independent use, suppositories with the same active ingredient are prescribed, they are called “Hexicon”
or effective combination drugs, for example,
“Terzhinan”, “Neo-Penotran Forte”, “Pimafucort”, “Poliginax”
, which successfully cope with both fungi that cause thrush and bacteria - provocateurs of bacterial vaginosis, gardnerella and others.
Pimafucin, Clotrimazole, Livarol
can be prescribed - proven safe antifungal drugs.
Gynecological pessary: what is it - indications for use, types
It is worth noting that previously pessaries were made of wool, leather, even bronze. Nowadays, they are mainly made of plastic, soft hypoallergenic silicone, on which no bacteria multiply. It does not react with the human body, does not cause rejection, or any unpleasant sensations.
There are several options for pessaries and their uses. It all depends on the initial diagnosis, as well as the need for intervention. Most often, the pessary is used in obstetrics and gynecology.
Indications for use:
- Used in cases where isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed
- Shortening of the cervix,
- Increase in pharynx size in early and late pregnancy
- In order to relieve the cervix, reduce pressure on it, and also reduce the risk of premature birth
It resembles a plastic or silicone ring that is inserted into the vagina. This ring compresses the cervix and also encloses it, resting against the walls of the vagina. If installed correctly, there will be no unpleasant sensations or difficulties with moving, walking or even playing sports. Although in such a situation, expectant mothers are usually prohibited from heavy physical activity, as well as sports.
Varieties
The pessary is often made not only in the shape of a ring, but also in the shape of a bowl, as well as a prism, with smoothed corners of a trapezoid. Thus, thanks to the special shape, the cervix is enveloped, the pessary ring prevents its opening. And the corners rest against the vagina. Quite often, such pessaries are also used for pathologies of the pelvic organs.
For example, with urinary and fecal incontinence. To do this, they use a different kind of pessary, which basically does not rest on the cervix, but, on the contrary, puts pressure on the urethra in order to close it. Prevents premature urination and urinary incontinence.
Kinds:
- Domed obstetric pessary
- Ring obstetric pessary
- Unloading obstetric pessary
Types of pessaries