What is acute bronchitis
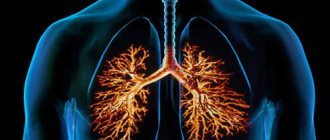
Acute bronchitis is a diffuse inflammation of the respiratory system and bronchi.
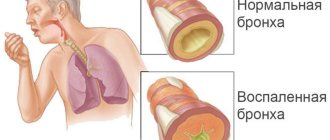
The bronchial tree is covered with a mucous membrane consisting of epithelium and is a protective inner layer. Due to colds, fungal, infectious bacteria, and nicotine abuse, the epithelium becomes infected with viral pathogens. This results in inflammation of the mucous membrane.
A large amount of sputum accumulates, and the respiratory channels swell, thereby complicating the air exchange of the lungs. In the initial stages it manifests itself as attacks of dry cough. It is characterized by a sharp symptom and rapid progression.
In medicine, there is a coding of different diseases according to the type of complexity, which is entered into the official document International Classification of Diseases. Acute bronchitis: ICD 10 code assigned j 20, this abbreviation is used for general reporting. Given the complexity of the development and occurrence of the disease, acute bronchitis ICD 10 may change or add a number.
What is bronchitis - briefly about the disease
If you ask a person who is very distant from medicine what bronchitis is, he will answer very predictably - a disease accompanied by a severe cough. But not everything is so simple - it is a much more complex disease, characterized by inflammatory processes that occur on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract . Inflammation spreads very quickly and spreads to one of the main human organs – the bronchi.
If you know exactly how to recognize bronchitis, symptoms and treatment in adults, you can immediately begin to influence the main signs of the disease. It is not recommended to start treatment before consulting with the doctor - only he can confirm this unpleasant and dangerous verdict.
Causes of acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a fairly common disease in both adults and children. The causes may be different:
- physiological: occurs against the background of respiratory injuries, congenital pathologies;
- environmental influences, polluted air, dampness, chemical fumes;
- abuse of smoking, alcohol and drugs;
- infectious: develop against the background of viruses and fungi. A weak immune system is susceptible to active damage;
- bacterial: attachment of infected bacteria to the body with the help of oxygen;
- allergic: due to disruption of the endocrine system;
- untreated diseases that transform into another form, causing inflammation. Frequent colds in the process of improper treatment affect the respiratory system;
- mixed causes, accordingly, carry a more difficult process.
Why does the disease occur?
Acute bronchitis does not appear for one reason. There are many factors that can give impetus to the development of the disease.
All causes of acute bronchitis can be divided into two main groups: infections and non-infectious agents.
Each of them should be considered in more detail.
Infections
It should be noted that in most cases, acute bronchitis, the cause of which was a microorganism, appears as a continuation of another respiratory ailment (inflammation of the nasopharynx, throat, trachea, etc.).
The disease most often occurs in the upper respiratory tract and then descends to the bronchi.
The following can be considered infectious pathogens:
- [Viruses] The main reason for the development of bronchitis in the autumn-winter period is viruses, which most often cause colds and, accordingly, acute bronchitis. Among the viral pathogens are influenza viruses, parainfluenza, RS virus (respiratory syncytial virus), adenovirus, etc.
- Bacteria Bacteria are extremely rarely the causative agents of primary acute bronchitis. Most often, the mechanism of damage to the bronchi by pathogenic bacteria is as follows. Initially, the bronchi are affected by pathogens of a viral nature, thereby creating a favorable platform for the proliferation of bacteria in the bronchial mucosa. Bacteria, entering already affected areas of the mucous membrane, begin their active activity. Thus, a viral infection is also accompanied by a bacterial one, which suggests the use of antibiotics in treatment. Among the bacteria that cause acute bronchitis, pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, streptococcus, and staphylococcus should be noted.
- Atypical microflora Cases of the development of acute bronchitis due to the fault of these pathogens are not so common, but they still occur. Such pathogens include chlamydia and mycoplasma.
Important to know: Acute bronchitis in pregnant women treatment
Any infection has its own ways of spreading: airborne (more typical for viruses), household contact (bacteria are more likely to spread through them) and hemophilic (when the infection enters the bloodstream through wounds or scratches).
Non-infectious agents
The mucous membrane of the bronchial tube can be damaged not only by microorganisms, but also by other factors:
- Physical factors If a person inhales air that is too hot or cold, or excessively dry or humid for a long enough time, this has a detrimental effect on the mucous membranes. It is where the processes described above begin.
- Chemical factors Inhalation of aggressive chemical components also causes the development of inflammatory phenomena in the bronchi: alkaline, acid fumes, oxides, nitrogen, silicon, etc.
- Allergens The main reason for the development of acute allergic bronchitis is that a person prone to allergic reactions inhales allergens. These include house dust, pet hair, pollen from flowering plants, strong odors, smoke, down and bird feathers, etc.
In addition to the main causes of acute bronchitis, there are a number of factors that favor the development of the disease.
Many of these factors simply reduce a person's immunity. Among the indirect reasons the following are known:
- previously suffered severe illnesses with corresponding complex therapy;
- frequent hypothermia of the body;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- drinking drinks that are too cold;
- acute infections in the nasopharynx;
- damage to nasal breathing;
- diseases of other organs and systems in the body that lead to stagnation;
- avitaminosis;
- bad habits: smoking, alcoholism;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- climatic conditions;
- poor production conditions.
All of the listed reasons for the development of the disease cause phenomena in the bronchi, which were described above.
Symptoms of acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis: symptoms are characterized by vivid manifestation and rapid recovery, provided that the diagnosis is made correctly and in a timely manner. Cough is the main symptom and acts as a protective reaction of the body.
Slightly moist, with transparent sputum, it is not dangerous. If the discharge is yellow-green, this indicates that the body is fighting viruses. The thicker the composition, the closer the recovery.
Features of the manifestation of acute bronchitis:
- At the initial stages of development, a sore throat appears, after a couple of hours attacks of dry cough, reminiscent of barking, attack for three days. The cough is especially painful at night. The spasms practically do not stop. Even in sleep, a tired patient suffers from a dry cough. The vocal cords are strained and the voice goes deep. Laryngitis subsequently develops;
- weakness, malaise provoke refusal of food and severe thirst;
- increased temperature (more than 38 degrees), dizziness;
- deep breathing, which may be accompanied by whistling and wheezing;
- in the absence of treatment at the secondary stage, the damage occurs deeper, and the process worsens, affecting other organs. If therapy begins on time, the dry cough should gradually change to a more viscous cough, and the temperature will be restored. The nights will become calmer, your strength will increase.
Symptoms
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Cough. At the beginning of the development of the disease, it is predominantly dry. This is due to the presence of particularly viscous sputum, which is difficult to separate. If treated correctly, after a few days the cough becomes productive. The mucus thins and leaves the lungs.
- There is intense sputum production. This is accompanied by coughing attacks, which can be quite painful. At the beginning of the development of the disease, sputum separation occurs especially intensively in the morning, but then this phenomenon becomes permanent.
- Shortness of breath. It becomes difficult for the patient to breathe, which is especially noticeable during physical activity, normal walking or running.
- Hemoptysis. Due to a strong cough, which provokes an increase in pressure in the chest, small vessels burst . Blood turns sputum pink.
- General symptoms of intoxication of the body caused by waste products of pathogenic microorganisms. Often there is a slight increase in body temperature, headaches, fatigue, body aches, and nausea.
- Increased sweating, which mainly occurs at night.
Types of acute bronchitis
In medicine, there are several subtypes of acute bronchitis:
- Simple acute bronchitis.
- Obstructive bronchitis.
- Acute bronchiolitis.
Simple acute bronchitis occurs against the background of a cold or seasonal hypothermia. With proper treatment, rare manifestations of cough are possible within a month.
Acute bronchitis is manifested by severe swelling of the bronchi, dry cough and subsequently copious sputum production.
Acute bronchiolitis mainly affects infants under seven months of age. It attacks the respiratory system, thereby complicating natural ventilation. Since swelling can cause suffocation, children are especially susceptible to the disease.
All subtypes, if treated incorrectly, develop into a chronic form of bronchitis.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of bronchitis in adults with folk remedies is a very pressing issue, especially if it is chronic. Recently, the use of natural products to get rid of many ailments has been very popular. For traditional medicine recipes, herbs, roots, fruits, oils, bee products and many other materials are used. Let's consider several recipes for the treatment of chronic bronchitis.
Linden blossom against cough
Linden blossom has long been known for its anti-inflammatory, expectorant and antiseptic properties. For bronchial diseases, both in children and adults, it is recommended to drink linden tea 3-4 times a day.
- To prepare it, pour a tablespoon of flowers into a bowl, pour a glass of boiling water, wrap in a towel for 15 minutes.
- After the drink has cooled slightly, strain and drink instead of tea.
Onions and milk
To prepare, you will need several small onions and a glass of milk.
- Finely chop the onion and pour into a container with milk.
- Bring to a boil over low heat and leave to simmer until the onion is completely softened. When the mixture has cooled, squeeze the milk through cheesecloth.
- Milk is used for treatment. You can add sugar or honey for taste. Take a few spoons three times a day.
Radish and honey
Grate black radish and squeeze out the juice. Mix it with a tablespoon of honey. The resulting product softens cough, removes phlegm and relieves inflammation.
carrot juice
Mix the juice of a small carrot with a glass of water and a tablespoon of sugar. Use the resulting medicine warm for severe coughing attacks.
Important! Many recipes contain honey. This product is extremely useful, however, it often causes allergic reactions, especially in children. Be careful.
Herbal treatment has a beneficial effect. Chamomile, thyme, anise, mint, and plantain are used to make tea. They can be brewed and drunk instead of tea, both for treatment and for prevention.
Diagnosis of acute bronchitis
Depending on the patient’s condition, a number of diagnostic procedures are performed. At the initial stage, the patient undergoes a general, biochemical blood and urine test. The pulmonologist examines the chest, listens to breathing, examines the nature of the cough and the presence of discharge. If necessary, sputum examinations are possible.
For more complex forms, thoracic radiography and spirogram are prescribed. Such activities are carried out to identify pneumonia and other possibly associated lung diseases. If the diagnosis is not specified, further complications are possible.
Treatment of acute bronchitis
After a correct diagnosis, the therapist or pulmonologist prescribes a course of treatment. Given the complexity of the patient's condition, hospitalization is possible.
While in the inpatient department, it is possible to provide the necessary sterility conditions. Monitor the condition through constant monitoring and examination of tests as necessary. Use physical therapy as an additional treatment method.
Mild forms are usually treated at home. The main condition is cleanliness and fresh cool air. When carrying out wet cleaning, do not use strong-smelling detergents.
The room should have a temperature of about 23 degrees and a constant flow of oxygen.
Medications should be combined with plenty of warm drinks.
Steam inhalations can be performed both at home and in a hospital. Using aromatic oil in the correct dosage, for example, tea tree, eucalyptus, this procedure can be carried out several times a day. Warm air will warm the bronchi and facilitate the passage of mucus.
Paraffin applications for warming the trachea are practiced in hospitals if the body temperature does not exceed 37 degrees. At home, you can replace it with warm salt.
Reference! Massage and breathing exercises will help restore the circulatory system. Light tapping alternates with deep breaths and exhalations for several minutes.
Drug treatment of acute bronchitis
To treat acute bronchitis, antipyretics, mucolytics, antihistamines, antibiotics, sulfonamides, and painkillers are used.
Antipyretic drugs are used only after the body temperature rises above 38 degrees. The body is fighting the infection, and there is no need to panic ahead of time. In this way, immunity to certain viruses and bacteria is developed.
Mucolytics enhance the functioning of the glands, and with the help of sputum, pathogenic secretions are coughed out.
Antihistamines play an important role in the treatment process, relieving swelling of the airways. Air permeability is stabilized, the arrival of oxygen forces the circulatory system to work properly, thereby increasing overall immunity. The inflamed walls of the bronchi do not touch, the possibility of suffocation disappears, and coughing attacks are reduced.
Drug treatment of chronic bronchitis
During remission, chronic bronchitis requires virtually no treatment, but during a relapse of the disease, a whole range of treatment procedures must be used. First on this list is drug treatment.
- No matter how much you would like to do without serious medications, with an exacerbation of chronic bronchitis you cannot do without intensive antibiotic therapy. Among the widest range of drugs in this pharmacological group, the following drugs have proven themselves best:
- penicillins (ospamox, augmentin, amoxiclav, amoxil),
- cephalosporin antibiotics (ceftriaxone, cefazolin, cefix, cifadox, suprax),
- fluoroquinone drugs (doxycycline, moxifloxacin).
Antibiotics have a quick healing effect, but in addition to pathogenic microflora, they also kill beneficial intestinal microflora, to restore which you need to take probiotic drugs (lactovit, bifiform, linex).- Considering that for chronic bronchitis the course of treatment can be quite long, we must not forget about supporting one of the most important organs of the human body - the liver. After all, this organ is a natural filter and passes all chemical elements through itself, while the liver cells weaken and die. To restore and support the liver, you need to take herbal hepatoprotectors (karsil, darsil, milk thistle extract, hepatophyte).
- If an exacerbation of chronic bronchitis is caused by influenza viruses or ARVI, then it is advisable to take antiviral drugs (groprinosin, amizon, anaferon, aflubin).
- For severe coughs, it is recommended to take expectorants such as carbocisteine, acetylcysteine, ambroxol, lazolvan, bromhexine, mucaltin, and thermopsis herb tablets.
- If there is shortness of breath, then it is advisable to take bronchodilators (aminophylline, teopek).
- Complex treatment of chronic bronchitis includes taking immunomodulatory drugs and multivitamin complexes.
Treatment of acute bronchitis in adults
For the treatment of acute bronchitis in adults, the therapist prescribes a course based on the form of development of the disease. If there are no complications, therapy takes place at home. For simple acute bronchitis, it is important to combine medications with traditional medicine:
- Inhalation and mucolytics in the form of tablets or ambroxol-based syrup will help soften a dry cough;
- You can relieve headaches and muscle pain and stabilize the temperature with Nurofen or Paracetamol. Cool compresses, wiping with damp gauze soaked in a 1:10 solution of alcohol and water. Constantly drinking plenty of fluids without aromatic irritants will calm coughing attacks and prevent dehydration;
- in more severe cases, the therapist prescribes antibiotics - Tsiprinol, Levoflox - together with drugs that protect the gastric flora;
- antihistamines are required, for example, Suprastin. They will relieve swelling of the respiratory system and prevent the development of allergic drugs during treatment. The functioning of oxygen metabolism will improve;
- breathing exercises will saturate the blood with the required amount of oxygen;
- During treatment, any type of exercise, smoking and drinking alcohol are excluded;
- Warm aromatic baths will warm up the muscles and relieve inflammation.
Treatment
Therapy for the acute form of the disease largely depends on its origin. You cannot immediately take antibiotics without understanding what caused the pathology. To alleviate the patient's condition, symptomatic treatment is used, the main drugs for which are cough tablets.
Antibiotics are prescribed based on the appropriate diagnosis and only if symptomatic treatment has failed within 2-3 days. From the first day, a course of antibiotics can only be prescribed to patients over 65 years of age, in order to avoid complications due to reduced immunity.
Antiviral drugs, on the contrary, are prescribed immediately after the onset of the first symptoms, if the etiology of the disease has a viral component. This is due to the fact that their use is most effective in the first stage of the disease.
What antibiotics to take for bronchitis in adults , and what other medications are used for treatment, are shown in the table.
| Kinds | Drugs |
| Antiviral | Rimantadine; orvirem; amantadine; anvimax; oseltamivir |
| Antibiotics | Erythromycin; clarithromycin; azithromycin; amoxiclav |
| Cough remedies | Omnitus; sinecode; oxaladine; codeine |
| Expectorants | Bromhexine; ambrobene; ambroxol; broncholithin |
| Antihistamines | Suprastin; loratadine; tavegil; diazolin |
| Beta-agonists | Berodual; salbutamol; ventolin. Used with a nebulizer. |
Infusions and decoctions based on coltsfoot, thyme and licorice are successfully used as expectorants. Some physical procedures are also very useful for treatment. As a rule, for acute bronchitis the following are prescribed:
- electrophoresis (exposure to local areas with electric current);
- UHF (exposure to high-frequency electromagnetic fields);
- salt baths;
- mud therapy.
Physiotherapy helps the body open its reserves and get rid of bronchitis, which also quickly helps to recover from illness.
Prevention
To avoid contracting acute bronchitis, it is necessary to follow preventive measures. Wash your hands regularly and avoid close contact with sick people, since viruses are easily transmitted through handshakes and through the air in the form of microparticles.
Particular caution is recommended for people suffering from asthma or other chronic respiratory diseases. It is very important for them to undergo an annual flu vaccination, monitor the state of their immune system, and adhere to the recommendations of their doctor.
Prevention
There are a number of preventive measures to combat acute bronchitis. An active lifestyle and exercise will help strengthen the immune system and fight viruses and bacteria. It is important to harden yourself and avoid temperature changes.
Stop any bad habits: smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction. Stick to proper nutrition. Perform aerial exercises to strengthen the muscles of the respiratory apparatus. Observe basic hygiene rules.
//youtu.be/Vbt2qvJI5Y8