You can prevent your child from getting sick
Heredity plays a huge role in the formation of a person.
We all borrowed certain appearance, character and health characteristics from our parents and grandparents from different generations. Genetics is a science that studies the mechanisms of diseases transmitted by inheritance. Currently, pregnant women are recommended to undergo examination by a geneticist in order to exclude pathologies or to detect them in a timely manner. How does this procedure happen and is it so important?
Genes and success
You can go down to the DNA level in research.
Human DNA is almost all the same—it's what makes us human—but in a population, we can record some of the differences in the elements that make it up across the genome and see how they correlate with differences in educational attainment. Another group of researchers led by Cornelius Rietveld conducted a study on 120,000 individuals - this is a very large sample. They took a broad measure: how many years these people devoted to education. It turned out that the predictive power of differences in DNA is very small: the correlations are very weak, and they can only be noticed in very large samples. This suggests that differences in educational achievement depend on many genes working together. This is very strange because the heritability of family traits is known to be about 40%, but the reported correlations between differences in DNA and educational achievement explained only 2% of the variance in educational achievement. Thus, if the family resemblance method is used, it turns out that genes account for 40% of the differences, but if genes are measured directly, then nothing similar is observed.
Interestingly, another study was conducted in New Zealand in which these DNA markers were applied to a different sample - this time to a group of adults who had already lived a long life. It was possible to find out what happened to them at different points in their lives. It turned out that the regions of DNA that predicted school success also predicted indicators unrelated to education, such as earnings. Interesting correlations have been discovered: if your DNA predicts that you will be successful in education, for example, you are likely to have a wealthy family.
And the third thing this study showed: although DNA predicts that a person will be successful in obtaining an education, this does not mean that he will have a happy life. Some of those who had good educational abilities were not happier or healthier than others. Thus, this complex of genes has common effects on success in mastering different disciplines. But, apparently, they do not affect happiness and health. Thus, mysteries still remain in this area.
The importance of genetic counseling during pregnancy
This procedure gained popularity in the last century because science has advanced far and it has become possible to diagnose diseases that are inherited or arise due to a number of other reasons in utero. Every parent is concerned about the health of their unborn baby, so the examination is important, especially for couples where the risk of pathologies is high. For example, if one of the partners suffers from epilepsy, hemophilia, asthma, diabetes and other serious illnesses.
When planning a pregnancy, many couples come for a consultation with a geneticist in advance to rule out problems, but it is not too late to do the procedure even after conception has taken place.
Consultation with a geneticist is necessary to ensure the baby’s health, identify predisposition to certain diseases, or identify existing mutations and pathologies.
This procedure is freely available and parents can make an appointment and undergo examination at any time. During the conversation, be sure to talk about the reasons, possible suspicions and take the appropriate tests.
Women at risk
As in any other case, there is a risk group that includes women in labor:
- Over the age of 35. Patients have a high risk of having a child with disabilities.
- If you have relatives who suffer from hereditary diseases.
- With a history of several miscarriages, stillbirths, and infertility.
- If the couple is blood relatives.
- Contact of a woman with aggressive toxic substances, radiation exposure or chemical exposure.
- The presence of children with chromosomal pathologies.
- Women with diseases of the endocrine system.
- Multiple pregnancy.
Additional reasons for conducting
Additional factors for prescribing the procedure are negative tests, perinatal screening indicators, or the pregnant woman’s own desire. Previous illnesses during pregnancy and taking medications that can adversely affect the health of the fetus.
What genetic tests should be taken before IVF?
If a couple is prescribed genetics for IVF, tests are taken for the following purposes:>
- carrying out HLA typing;
- study of karyotypes of husband and wife;
- testing for the presence of common genetic pathologies (phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis, galactosemia, amyotrophy).
In the field of reproductive medicine, several effective PGD methods have now been developed to help qualitatively study genetic tests before IVF.
- PCR. The essence of the polymerase chain reaction is to identify specific DNA duplicates. To isolate one fragment from a double strand of DNA for further research, geneticists carry out a denaturation procedure. Next, specialists mix special enzymes into the taken biomaterial, which gradually increase its volume by 2 times. Thanks to this, abnormal regions in the nucleotide can be easily detected. The PCR technique gives a good effect in identifying monogenic pathologies. It is recommended for studying biomaterials of spouses who are carriers of “bad” genes or have clinical signs of hereditary diseases.
- FISH. Helps diagnose changes in chromosomes that are structural or numerical in nature (translocations, aneuploidies). To identify pathological and healthy chromosomes using this method, specialists carry out a series of laboratory manipulations with cells. After taking a biopsy, the cells to be examined are mounted on a glass slide and subjected to heating and cooling. Due to temperature exposure, the cell membrane ruptures, and the cytoplasm emerges from it. A laboratory technician marks sections of DNA with a fluorescent dye, and then, using a special microscope, counts the number of abnormal chromosomes.
- Innovative NGS method. Diagnostics of the biomaterial is performed in a cryocycle using the NGS method. The scheme allows specialists to carefully study all pairs of chromosomes (of which there are 23). The method has the highest accuracy (99.9%). Simultaneously with the study of chromosome pairs, the study of their pathologies, mutations, and monogenic diseases is carried out. The diagnostic process is well automated, so additional inaccuracies are excluded. After NGS analysis, there is no need for blastomere biopsy.
What does a geneticist do during pregnancy?
The procedure is carried out using two methods:
- Non-invasive - the woman undergoes an ultrasound and takes a biochemical blood test for markers.
- Invasive - involves penetration into the uterine cavity, from where materials for examination are taken to identify the karyotype of the fetus. Chorionic villus biopsy, amniocentesis, placentocentesis, and cordocentesis are used. Cells are collected from the placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic fluid and fetal blood. These procedures are allowed only under strict doctor’s orders and in a hospital setting; after the manipulations are completed, the woman needs some time to get in order.
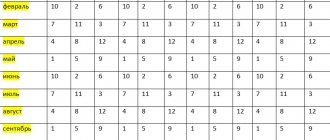
There are three levels of threat to a child:
- Probability 10% - this indicator means that there is no danger to the baby’s health.
- A value from 10% to 20% – the probability of having a healthy child and one with diseases is the same. This result requires further examination to identify the exact risk.
- Above 20% – there is no possibility of conceiving a baby without pathologies; an IVF procedure is recommended for bearing a healthy child.
Particular attention is paid to women with complex and multiple pregnancies.
For example, patients with diabetes must undergo testing for blood glucose (glucose tolerance test), protein and liver enzymes. There is no need to ignore the genetic research procedure even if there is no reason for anxiety or discomfort while carrying a child.
The main danger of chromosomal abnormalities is that in most cases they are completely silent and have no symptoms. A genetic disease can appear even after several generations, so it is important to get advice and tests to make sure that the baby does not have any problems.
Despite the high level of medicine, there is a percentage of error. There are cases when specialists identified mutations with which the child is not viable, but the woman had a healthy baby. However, such an outcome has a low probability.
Genealogical method for diagnosing hereditary diseases
This is one of the oldest existing diagnostic methods: for example, at the Moscow Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery, the corresponding service has been operating since 1970 [2]. And its basic principles were formulated back in the 19th century [3].
The essence of the genealogical method is to compile genetic maps that make it possible to find out whether a particular disease is hereditary, how exactly it is inherited and what is the likelihood of its manifestation in the patient. The method is also used to predict the birth of children with various diseases.
The main research tool in this case is a detailed interview with the patient and obtaining the most complete information about his relatives. If the patient is a child, then the geneticist collects the most complete information from the mother - about the course of pregnancy, childbirth, and the first years of life. If an adult consults a doctor, then collecting information is similar to collecting an anamnesis during a visit to a therapist, but more detailed. If possible, the doctor personally interviews the patient’s relatives.
This method involves a lot of analytical work based on the data obtained. Thus, the genealogical method is a kind of connecting link between theoretical genetics and practical medicine. If the study is carried out for the purpose of pregnancy planning, the doctor indicates the likelihood of a particular couple having children with certain genetic disorders. When examining a family, a circle of people who are at high risk of exhibiting hereditary diseases can also be identified. These people are advised to undergo more accurate laboratory diagnostics.
The cost of a consultation with a geneticist in Moscow starts from 2000 rubles [4].
Molecular genetic methods for studying hereditary diseases
These methods of detecting hereditary diseases allow you to actually look inside the DNA on which hereditary information is written. They are diverse: FISH (detection of genetic mutations using specially labeled fragments of DNA probes), PCR (the method is highly accurate and allows you to detect infection in the body, even if its presence is very limited), CGH (the method is used in cancer genetics), SKY ( a method that uses special dyes that react to specific sections of DNA) and others.
The scope of application of molecular genetic methods is wide. In particular, during perinatal diagnosis they make it possible to detect disorders in a child even before his birth. If a woman resorts to IVF, possible genetic defects can be identified even before the embryo is implanted into the uterus.
An analysis is also carried out for hereditary diseases in newborns.
Just a few years ago, expectant mothers were offered to undergo invasive genetic diagnostics to ensure the presence or absence of abnormalities in the fetus. Amniotic fluid was taken for analysis, and the manipulation carried a certain threat to the normal course of pregnancy. Today, there is a non-invasive diagnostic test (NIFTY), which allows the child’s DNA to be detected by testing the mother’s blood for hereditary diseases [5] . With a high degree of accuracy (more than 98% [6]), it helps to diagnose such dangerous pathologies as Down, Edwards, and Patau syndromes.
Molecular genetic methods are used not only for perinatal diagnosis, but also to identify other diseases: HIV, tuberculosis, encephalitis, hepatitis and others. The material for study is obtained from different tissues: it can be blood, saliva, sputum. Genetic studies not only allow accurate diagnosis, but also the selection of optimal treatment. In particular, they help determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to drugs and select the one that will give the most pronounced effect during treatment.
The cost of diagnostics depends on the scope of the study and can start from 1000 rubles (PCR) [7].
Biochemical methods
Biochemical methods can be used to identify many hereditary metabolic diseases (HMDs), such as phenylketonuria, purine metabolism diseases, and glycogen storage disease. With NBO, products of imperfect metabolism accumulate in the body, and their detection helps to establish a diagnosis.
As a rule, the presence of NBO can be assumed at a very early age: children experience developmental delays, various digestive disorders, skin pigmentation, allergies, etc. Blood or urine is taken for analysis.
Typically, biochemical diagnosis is carried out in two stages. First, a general analysis is carried out, for example, in all newborns for the presence of phenylketonuria. All pupils of special educational institutions can also undergo general examinations. Children with abnormal biochemical parameters are referred for a more detailed and complex examination, which is carried out in genetic laboratories.
The cost of a biochemical blood test for one parameter in Moscow is about 200 rubles [9].
Cytogenetic method
Cytogenetics, along with the genealogical method, is one of the oldest types of diagnosis of hereditary diseases. Back in the 19th century, scientists could observe cell chromosomes under a microscope [10]. Since that time, the tasks of cytogenetics have remained virtually unchanged: it studies the state of chromosomes and identifies pathologies in them. The method is included in the list of examinations for pregnant women, approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation [11]. Future mothers over the age of 35 who are carriers of familial diseases undergo cytogenetic examination. It is carried out if abnormalities that alarm the doctor are detected in the fetus.
For the study, blood is taken, the cells of which undergo special preparation. In the normal state, chromosomes seem to be twisted into a tight spiral, so it is impossible to assess the presence of damage in them. To study, cells are artificially put into a state of division, and when the chromosome strand unwinds, a drug is made from it.
Cytogenetic methods are used in the early diagnosis of pathologies in children, and also help to identify the causes of reproductive dysfunction, especially of unknown origin, in men and women.
The cost of a cytogenetic karyotype study in Moscow is about 6,700 rubles [12].
Read also
Prevention of hip dysplasia: how to prevent and prevent the development of the disease correctly?
Dermatoglyphics
Everyone is familiar with this method: fingerprinting, or the study of the skin pattern of the fingers, refers to dermatoglyphics. There are other methods - palmoscopy (study of the pattern on the palms) and plantoscopy (study of the skin pattern on the soles). The features of skin patterns were studied by the Czech scientist Jan Purkinje, who gave a fundamental classification of finger patterns [13]. His followers found that some changes in skin pattern compared to the norm indicate genetic diseases [14]. For example, by the location of ridges and furrows on the skin, one can assume pathologies such as Klinefelter syndrome, cry-the-cat syndrome, Turner syndrome, and even multifactorial diseases - diabetes, cancer and others.
Dermatoglyphic analysis is part of the examination of a patient in a genetic clinic.
Method for detecting heterozygous carriage
A number of hereditary diseases are determined by damage to only one gene (so-called monogenic diseases). These include some endocrine disorders, immune disorders, diseases of the central nervous system, etc. Since a child receives genetic information from two parents, a situation may arise where both the mother and father are healthy, but they give birth to a sick child, since both parents passed on mutated genes to him. To determine whether one of the parents (or both) is a carrier of hereditary diseases, and what is the likelihood of their manifestation in the child, a heterozygous carrier test is performed.
Some diseases, including Marfan syndrome or osteogenesis imperfecta, are passed on to children even if only one parent is a carrier. In this case, when planning a pregnancy, you must consult a geneticist: he will tell you the likelihood of having a child with a genetic pathology.
Diseases can be sex-linked, that is, the gene encoding them is contained only on the sex chromosome (hemophilia, muscular dystrophy). Based on these pathologies, the risk of their manifestation in children is also calculated. Heterozygous carriage is detected during various types of genetic diagnostics.
Genetic prediction
About 90% of all human diseases are multifactorial [15]. Genetic characteristics determine a person’s predisposition to pathology, and under the influence of certain environmental factors, the disease may or may not develop. Environmental factors are also diverse: this can be the ecology, the nutritional habits of both the person himself and his mother during pregnancy, the region of residence, etc.
It is possible to guess what the probability of the disease is during medical genetic counseling and based on the results of genetic tests. Today they are made in varying degrees of complexity and according to many parameters. For example, you can study the genetic health of a married couple, determine the likelihood of developing cancer from smoking, and determine how high the need to protect the skin from UV rays is.
Prenatal diagnosis of hereditary diseases
Due to the relevance of the problem, this area of genetic diagnostics deserves special attention. We are not talking about one research method, but about a combination. The examination is carried out during the period of intrauterine development of the child to identify congenital disorders. According to WHO estimates, they cause approximately 7% of neonatal deaths [16]. Early detection of these disorders, even before birth, allows you to quickly begin the necessary treatment, and in some cases even perform intrauterine surgery.
Indications for prenatal diagnosis are:
- genetic diseases occurring in family members;
- age of the woman (over 35–37 years);
- identified genetic carriage of a sex-linked pathology;
- heterozygosity of parents for a number of genetic pathologies;
- a history of unsuccessful pregnancies that were interrupted for unclear reasons.
Prenatal diagnostic methods are very diverse: fetal ultrasound, genetic analysis of amniotic fluid or umbilical cord blood, study of maternal blood serum, chorionic villus biopsy and others. The appropriateness of using each of these methods is determined by the doctor.
Thanks to advances in medicine, today we have the opportunity to undergo detailed diagnostics in the field of development of hereditary diseases. Future parents can learn about the likelihood of having a child with a particular pathology. Having this information helps you make the right decision, start treatment on time, adjust your lifestyle, and prevent the development of genetic diseases.
How long does it take to consult a geneticist during pregnancy?
The first examination is usually scheduled at the end of the first trimester - 10-12 weeks.
If the results are excellent and do not require additional tests, then the next consultation takes place after 20 weeks. Then a control study is done during the 30-32 weeks of pregnancy. In case of a difficult pregnancy and possible threats, a genetic appointment can be carried out at other times.
After the birth of a child, blood is taken from the toes of the newborn for the presence of pathologies.
Genetic testing is 85% likely to detect problems.
The current ecology and rhythm of people's lives do not have a very favorable effect on health. Therefore, in order to conceive and give birth to a healthy child without pathologies, it is strongly recommended by experts to visit a geneticist before planning.
How does an appointment with a geneticist work?
Expectant parents should go together to see a doctor, having previously prepared and taking with them medical records and test data. After all, the specialist, first of all, will have to obtain information about all serious and hereditary illnesses in the family. After this, the doctor will prescribe additional studies and draw conclusions and predictions based on their results.
What questions does a geneticist ask a pregnant woman?
First of all, the doctor will ask whether the future parents and their close relatives have any physical abnormalities. What serious illnesses did they suffer, what illnesses did their parents and grandparents suffer from? Are there any hereditary diseases or genetic abnormalities in the family? Perhaps one of the future parents already has a child with pathologies.
If changes in the development of the older child occurred due to circumstances during the intrauterine period (previous infection, trauma, and so on), then the new pregnancy can proceed without complications and the development of pathologies.