The female appendages refer to the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Their inflammation is one of the most common gynecological diseases. This disease is especially dangerous during pregnancy. The chronic process often worsens, although acute inflammation of the ovaries also occurs. This is why it is so important to undergo a medical examination before planning a pregnancy. Moreover, doctors strongly recommend doing this, since any inflammatory process during gestation can lead to undesirable consequences.
Does inflammation of the appendages occur in early pregnancy?
Many women in the first trimester of pregnancy complain of pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge. Upon examination, they are found to have an inflammatory process of the uterine appendages. There are cases when there were no prerequisites for the occurrence of the disease, since women monitored their health during this period. What can cause the disease?
The most common reason that provokes the inflammatory process is a decrease in the immunity of the expectant mother, as well as the onset of pregnancy already in the presence of the disease.
It is known that in the early stages of gestation, hormonal changes occur in the body. Since the ovaries are under a special load, pain may occur for this reason. In addition, the sensation of pain in the lower abdomen is also possible due to an enlarged uterus and sprained ligaments. If pain in the lower abdomen occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, this does not mean that the uterine appendages are inflamed. If such symptoms are detected, you need to consult a gynecologist. Chlamdia, candida, ureaplasma, and mycoplasma are also common causes of this disease.
Inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy: symptoms and signs
This disease is characterized by the following symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the lumbosacral spine. Basically, the pain is paroxysmal, but in some cases it is constant. Leucorrhoea of a milky or yellow-green hue is discharged from the vagina. The occurrence of painful attacks is facilitated by physical and mental stress, hypothermia of the body, and a decrease in its protective functions.
The acute form of the disease during pregnancy can occur with the following symptoms: high body temperature, chills, general weakness, pain in the lower abdomen and purulent discharge.
Is inflammation of the appendages dangerous during pregnancy: consequences
The inflammatory process of the uterine appendages in an interesting position can lead to an ectopic pregnancy. It occurs due to partial patency of the fallopian tube, as a result of which the egg cannot penetrate the uterus. The same cannot be said about sperm. Due to their size, it is not difficult for them to penetrate the egg and fertilize it. With this combination of circumstances, the fertilized egg is attached to the fallopian tube, where the fetus begins to actively develop. Naturally, this process leads to rupture of the fallopian tube.
It is very important for a woman to visit a gynecologist as early as possible after conception. If such a pathology occurs, it is possible to save the tube by removing the fertilized egg. This will make it possible, after appropriate treatment, to become pregnant again after some time.
If an inflammatory process occurs in the uterine appendages due to infection, infection of the fetus is also possible. There are cases when the child did not become infected during intrauterine development, but he can catch the infection during childbirth. In this case, gynecologists recommend giving birth by caesarean section.
When the inner layers of the uterus are damaged, the embryo is rejected by the uterus, in other words, a miscarriage. This is explained by the fact that the uterus perceives the embryo as a foreign body and gets rid of it.
Chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages during pregnancy can lead to the body producing antibodies to its own cells. This process promotes the formation of thrombosis. And this, in turn, leads to placental abruption or intrauterine growth retardation.
Gynecological diseases during pregnancy lead to disruption of the immune system, which performs the function of recognizing and blocking the development of foreign substances. In this case, the blood cells have a toxic effect on the formation of the placenta and the growth of the embryo.
To summarize the above, I would like to note that inflammation of the uterine appendages in an interesting position of a woman can lead to the following consequences:
- Fetal death.
- The absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg.
- Spontaneous miscarriages at different stages of gestation.
- Non-developing pregnancy (fetal fading).
- Infection of the unborn child.
- Premature birth.
Every expectant mother should be aware of the seriousness of this disease, understand the dangers of inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy, and remember that timely contact with a specialist eliminates the possibility of the above-mentioned consequences.
Inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy: treatment
If an inflammatory process is detected in a pregnant woman, hospitalization is inevitable, as constant medical supervision is required. Treatment is prescribed only by a specialist, having previously studied the results of all tests and other studies. Basically, drug therapy consists of the use of antiviral drugs. During pregnancy, some antibiotics can be used.
Inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy: antibiotics
Everyone knows about the harmful effects of antibiotics on the body. The fact is that their function is aimed at destroying harmful bacteria. But antibiotics do not distinguish between harmful and beneficial bacteria, and they destroy both.
Naturally, this has a negative impact on the intrauterine development of the fetus. Medicines pass through the placenta into the fetus and accumulate in its tissues. As for more or less safe drugs during pregnancy, these include: Erythromycin, Josamycin and Spiramycin. In case of severe forms of the disease, the doctor may prescribe Azithromycin. It is prohibited to use fluoroquinolone drugs during pregnancy.
How to treat inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy with folk remedies
There are many traditional methods of treatment. Many people got rid of the disease with the help of infusions of alcohol and steam baths using herbs. But for pregnant women, these methods are not suitable, as they can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus or lead to spontaneous miscarriage. Expectant mothers are recommended to use herbal infusions and decoctions.
There is a popular belief that the herb St. John's wort helps against 99 diseases. Inflammation of the uterine appendages is no exception. Brew St. John's wort as tea and consume three times daily before meals. This method can also be treated with the help of the following plants: sweet clover herb, blueberry leaves, thyme, coltsfoot, oak bark, chamomile flowers, marshmallow root, yarrow. You can mix herbs and take decoctions according to the above scheme. A good remedy for the disease is a decoction of the hair of blind corn cobs.
You need to be very careful when using herbs, as some plants can cause miscarriage. Before using them, be sure to familiarize yourself with their effect on the body. Decoctions of the above herbs can be douched. But before using this method, you need to consult a doctor. Douching with a decoction of chamomile or calendula eliminates the inflammatory process especially well.
It is also recommended to eat pumpkin in large quantities. You can eat the pulp of the vegetable, or you can drink freshly squeezed juice. This will help get rid of the disease and enrich the body with beneficial vitamins, which pumpkin is rich in.
It is also recommended to drink aloe juice three times a day, one dessert spoon before meals, or with honey.
The use of traditional methods for inflammation of the uterine appendages in pregnant women is the only way not to resort to medications. But this method is lengthy and initially requires medical consultation.
Who had inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy: reviews
Some women share their experiences of how they managed to bear and successfully give birth to a child with chronic inflammation of the appendages. It should be noted that bearing a fetus in this case requires constant monitoring by a gynecologist. Some expectant mothers used Viferon and Viburkol suppositories in the second half of pregnancy. They tied the lower back with a warm scarf or a wool belt. This significantly reduced pain.
Having studied the information on forums where this topic is discussed, many women write that inflammation of the appendages cannot occur in pregnant women. In the chronic form of the disease, pain may occur due to stretching of the adhesions that remain after inflammation. But in any case, you need to consult a doctor and have a full examination.
Especially for nashidetki.net - Ksenia Manevich
Salpingo-oophoritis (adnexitis), characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the ovaries and fallopian tubes, poses a great threat to the reproductive health of any woman. However, inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy is considered especially dangerous. During the period of bearing a child, the disease can negatively affect not only the body of the expectant mother, but also the fetus developing in her womb.
Causes
The main reason for the development of salpingoophoritis during pregnancy is the active proliferation of bacteria in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. These can be microorganisms belonging to the female body’s own flora (Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, Klebsiella, ureplasma) or pathogens of sexually transmitted infections (gonococci, chlamydia, mycoplasma).
The following factors contribute to the occurrence of adnexitis during pregnancy:
- natural decrease in immunity due to the body’s adaptation to pregnancy;
- hormonal changes;
- stress, physical overload;
- hypothermia;
- insufficient or improper intimate hygiene;
- the presence of chronic foci of infection in the body;
- unprotected sexual contacts with different sexual partners.
Salpingoophoritis rarely develops as an independent disease. Most often it is a complication:
- endometritis;
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- colpitis.
Infertility as a consequence of inflammation
Any inflammation of the reproductive system can potentially lead to infertility. Most often it is provoked by pathological processes in the tubes and ovaries. During the course of the disease, adhesions and scars form in the fallopian tubes. They prevent the normal movement of sperm to the egg, thereby eliminating the possibility of pregnancy. This condition is called tubal obstruction.
Another danger of this condition is the high probability of ectopic pregnancy. If fertilization does occur, the larger zygote simply will not be able to penetrate the uterus for implantation and will attach itself inside the tube, or much less often on the ovary or somewhere in the abdominal cavity. This risks rupture of the fallopian tubes and severe internal bleeding. Treatment is carried out exclusively by surgery.
Symptoms of the disease
A pathological process in the reproductive system of a pregnant woman can affect only the ovaries, causing oophoritis, but such isolated inflammation is extremely rare. Most often, all appendages are affected simultaneously.
Features of the symptoms of adnexitis largely depend on the form of the disease. Acute salpingoophoritis is characterized by a sharp onset, in which severe pain is observed in the lower abdomen, often radiating to the groin and back and accompanied by tension in the abdominal muscles. The sensation may be cutting or pulling. A pregnant woman's body temperature rises and:
- chills;
- headache;
- nausea;
- discomfort when urinating.
Vaginal discharge becomes profuse, greenish or yellow, acquires an unpleasant odor and leads to severe irritation of the mucous membrane of the genital organ.
In chronic salpingoophoritis, signs of inflammation are less pronounced. The pain is not so intense, there are no symptoms of intoxication. Discharge characteristic of adnexitis may appear only from time to time. Women suffering from this form of the disease often experience discomfort in the lower abdomen during sexual intercourse, which is caused by the formation of adhesions in the area of the appendages. For this reason, nagging pain can also intensify as the fetus grows, the uterus enlarges and the ligaments are sprained.
With exacerbation of chronic salpingoophoritis, a clinical picture characteristic of primary acute adnexitis is observed.
Reasons for formation
Before starting treatment, you should understand the causes of the pathological process. Pneumonia can develop without specific factors, resulting from a weakened body due to pregnancy. However, other reasons can also influence this - acute immune deficiency (even HIV), forms 1 and 2 of diabetes mellitus, diseases of the pulmonary and cardiac systems.
Other associated factors in the development of pneumonia in pregnant women are prolonged use of steroid-type hormones, damage to the sternal area, artificial ventilation and prolonged fainting. The indicated reasons provoke pneumonia, as well as other processes that weaken the body, slow down metabolism and other processes.
Before starting treatment, you should understand the symptoms associated with pneumonia in pregnant women. This will allow you to approach the recovery process more correctly.
Diagnostics
If you suspect adnexitis, a pregnant woman should consult a gynecologist to undergo an examination. Painful enlargement of the appendages is easily detected during a bimanual gynecological examination, which can be carried out with caution during pregnancy for diagnostic purposes. If the expectant mother has inflamed appendages, this can also be clearly seen on an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
To select an effective treatment regimen, an additional examination of smears taken from the vagina and urethra is performed.
These tests make it possible to identify the causative agent of adnexitis and establish the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibacterial drugs.
Consequences of inflammatory diseases during childbirth and the postpartum period
Inflammation in the organs of the reproductive system has a negative impact on the process of childbirth. They often provoke premature rupture of amniotic fluid, as well as weakness of labor and, as a consequence, protracted labor. This in turn is fraught with infection of the membranes of the fetus and uterus. In addition, too long labor always negatively affects the health of the baby.
Inflammation of the reproductive organs does not go away without a trace even after childbirth. It often causes increased bleeding from the vagina and postpartum endometritis. This is a dangerous complication that requires hospital treatment. It may well end in infertility, so it’s not worth taking risks and self-medicating.
Therapy of salphingoophoritis in pregnant women
Adnexitis that develops in a pregnant woman is treated in a hospital setting, since the expectant mother requires constant medical supervision due to the high risk of complications. The patient is provided with complete rest, a therapeutic diet is prescribed and complex therapy is carried out.
The basis of treatment for salpingoophoritis is the use of antibiotics. Preference is given to those types of drugs that are considered the safest for pregnancy and fetal development and can be used both in the early stages of gestation and in the last months of pregnancy. Pregnant women are allowed to take medications from the group of penicillins, macrolides and cephalosporins. Such drugs include:
- Amoxiclav;
- Flemoxin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Sumamed;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Vilprafen.
The duration of antibacterial therapy is determined individually, taking into account the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body. Most often, the course of treatment lasts 5–10 days.
To alleviate the symptoms of the disease, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine) and antipyretics (Paracetamol, Panadol), detoxification therapy is carried out using droppers and water-salt solutions.
To normalize the intestinal flora, the following are used: Linex, Acipol and other probiotic drugs. To restore the vaginal microflora after the end of antibacterial therapy, it is recommended to use suppositories with lactobacilli (Lactonorm, Lactobacterin, Acylact) for 10 days.
In case of an advanced form of salpingoophoritis and the absence of effect from conservative treatment, a pregnant woman undergoes laparoscopic surgery aimed at removing a purulent focus in the tubes or ovaries. When performed correctly, this procedure is safe for mother and baby.
Treatment of colpitis while carrying a baby
Treatment of colpitis in pregnant women in the early stages has certain difficulties. They are connected with the fact that most effective drugs are undesirable to use, since their effect on the developing embryo is unknown. Most medications are only allowed from the second trimester.
Treatment of non-infectious colpitis is aimed rather at preventing their occurrence. For example, when installing a pessary, it is recommended to periodically place suppositories in the vagina, even if nothing is bothering you. But prevention cannot always be carried out effectively.
Both local treatment with suppositories, vaginal tablets and other forms, and systemic treatment with oral medication are carried out.
Drug therapy
The main groups of funds used are as follows:
- Antiseptics based on chlorhexidine, iodine.
Most often these are suppositories; in some cases, douching can be done. For example, suppositories Ruvidon, Povidone-iodine, Betadine, and others are popular and effective. They are used for nonspecific inflammation, as well as in complex treatment. - Antibiotics orally or locally.
This group of drugs is used if the inflammation is chronic or does not go away with treatment with suppositories, as well as in cases where the true causative agent of the disease is initially identified. In early pregnancy, it is preferable not to use antibiotics, only when absolutely necessary. The safest macrolides (Azithromycin, Josamycin and others), penicillins (Ampicillin) and some others. - Antifungal agents are used to treat thrush or to prevent it.
In the early stages, it is safe to use Ginezol and others. - Antiviral agents are used if there are signs of this infection or a pathogen is identified during a PCR study. Treatment depends on the type of pathogen; Acyclovir and its analogues are most often used.
- Immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed only if truly necessary
- for chronic infections, as well as if inflammation is difficult to treat. Both vitamin complexes and interferons and other agents are used. - Preparations for restoring microflora.
They are used to consolidate treatment after completion of the main course. These are safe and quite effective drugs, such as Bifidumbacterin, Laktozhinal, Bioflor, Vaginorm and others. You can use suppositories in the vagina, or simply take them orally.
The most optimal combinations in each specific case can only be determined by a doctor after examination and examination.
In parallel with the main treatment, in most cases, preventive therapy is carried out.
If nothing bothers the girl, Papaverine (No-Shpa) or magnesium supplements are used. If there are any symptoms (including bleeding), therapy is broader and is often carried out in a hospital setting.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine can be used along with basic treatment. But it is better to coordinate all prescriptions with a doctor, and if there are symptoms of a threat, it is not at all advisable to engage in such self-medication.
The following treatment options can be used:
- douching,
- sitz baths,
- tampons with medicinal solutions.
To obtain solutions, simply brew chamomile, calendula, sage, and Chlorophyllipt. You can use either a mixture of plants or each separately. It is convenient to buy a ready-made alcohol solution, dilute it and use it for douching.
Why is adnexitis dangerous during pregnancy?
Adnexitis has an extremely negative effect on the condition of the reproductive organs and can cause infertility. Adhesions that form in the fallopian tubes after inflammation interfere with the full movement of the egg and its fertilization. In case of successful conception, the risk of an ectopic pregnancy increases, in which the embryo does not attach to the walls of the uterus, but remains in the ovary or tube and can cause rupture of the appendages.
If salpingoophoritis develops after a woman has managed to become pregnant, the consequences can be even more severe. Acute or chronic adnexitis causes:
- placental insufficiency;
- polyhydramnios;
- fetal hypoxia;
- miscarriage;
- premature birth.
The bacteria that cause the disease are able to penetrate the placenta and cause infection of the fetus, which leads to multiple malformations.
If left untreated for a long time, acute salpingoophoritis can provoke purulent melting of the ovaries and tubes, sepsis and peritonitis.
Complications of pregnancy
Pregnancy that occurs against the background of chronic adnexitis often ends in termination in the early stages. Miscarriage usually occurs between 6 and 10 weeks. A sluggish inflammatory process interferes with the normal attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus. Its nutrition is disrupted, and detachment of the fertilized egg occurs. The embryo dies and a miscarriage occurs. The onset of a miscarriage is accompanied by bleeding from the genital tract, the intensity of which will depend on the duration of pregnancy.
Chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages can cause a regressive pregnancy. In this case, the embryo dies, but the fertilized egg is not rejected from the uterine wall. For a long time, the woman does not notice any special changes. Bloody discharge occurs only 2-4 weeks after the death of the embryo and can be very scanty. Characterized by a sudden disappearance of toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy (breast engorgement, drowsiness, changes in vaginal secretion).
In the second half of pregnancy, chronic adnexitis can cause the following conditions:
- polyhydramnios;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- placenta previa;
- placental insufficiency;
- delayed fetal development;
- premature birth.
Placenta previa is a condition in which the fetal site blocks the exit from the uterine cavity. With complete presentation, independent childbirth is not possible. Partial presentation also poses a serious danger to the woman and her baby. This pathology is accompanied by frequent bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth. Complete placental abruption and fetal death are possible. Complete placenta previa is an indication for cesarean section.
Another problem that arises against the background of adnexitis is the low location of the placenta. Chronic endometritis and adnexitis often go together, accompanied by serious complications. Against the background of a sluggish inflammatory process, irreversible changes occur in the uterine cavity, interfering with the normal implantation of the fertilized egg. The baby is attached in an awkward place - too close to the cervix and the pelvic outlet. The placenta is located at a distance of less than 7 cm from the internal os, which leads to frequent bleeding and complications during childbirth.
A low location of the placenta provokes delayed fetal development. In this place, the endometrium is poorly supplied with blood, and throughout pregnancy the baby does not receive oxygen and nutrients in the required volume. The birth of a low-birth-weight fetus and the appearance of various health problems in the future are possible. The likelihood of premature birth increases significantly.
Chronic or acute adnexitis can lead to intrauterine infection of the fetus. In the early stages, this condition can cause the formation of serious anomalies, including those incompatible with life. In the second half of pregnancy, the infection leads to delayed fetal development and various diseases. Polyhydramnios occurs due to infection.
Preventive measures
To protect her body from inflammation of the appendages, a pregnant woman needs to constantly strengthen her immune system - eat right, spend enough time in the fresh air, give up bad habits and avoid stress and hypothermia.
It is important to promptly identify and treat any diseases of the genitourinary system, and to avoid contracting sexually transmitted infections, use condoms. Careful adherence to intimate hygiene will also reduce the risk of developing salpingoophoritis.
Treatment
The tactics for treating inflammatory processes during pregnancy are determined by the doctor. It depends on the localization of the inflammatory process and the characteristics of its course. In most such cases, doctors resort to antibiotic therapy. Taking antibacterial drugs does not always have a negative effect on the condition and development of the fetus. Many new generation medications can be used during pregnancy.
If the inflammatory process is in the organs of the reproductive system, the participation of both (all) partners may be necessary. It is quite possible that the carrier of the infection is a man and he also needs to be treated. Also in such situations, it is recommended to limit sexual relations or use condoms.
Adnexitis and pregnancy
The inflammatory process in the uterine appendages and in the organ itself creates serious obstacles on the way to conceiving a child. All women who had adnexitis during pregnancy also note the adverse effects of the disease on the body. An infection in the fallopian tubes and ovaries, which actively develops during gestation, can harm not only the health of the expectant mother, but also the baby.
Is it worth giving birth with adnexitis, and what difficulties will a pregnant woman who has been diagnosed with this have to face? We'll talk about this later.
Adnexitis and pregnancy: features of the course of the disease
If a woman diagnosed with “adnexitis” finds out about her pregnancy, the question immediately becomes relevant for her: “how can inflammation affect the health of the unborn baby?” Due to active inflammation, the structure of the uterine endometrium changes, so the likelihood of the fertilized egg attaching to it is too small. If pregnancy occurs with adnexitis, then the safety and development of the embryo is at risk. Adnexitis in pregnant women provokes the following problems:
- the unborn baby does not receive nutrition in the required quantities due to the fact that blood microcirculation in the endometrium is impaired (due to this, the risks of fading pregnancy or miscarriage greatly increase);
- inflammation from the appendages spreads to the fetus, and it eventually dies;
- uterine hypertonicity develops, due to which a miscarriage can occur at any stage of pregnancy.
Against the background of adnexitis, a woman develops obstruction of the fallopian tubes. As a result of this pathology, some women experience ectopic pregnancy.
If the conception of a child occurred against the background of chronic adnexitis or pregnancy is accompanied by acute manifestations of an inflammatory disease, the expectant mother should consult a gynecologist about preserving the fetus and appropriate therapy. In medicine, there are cases where pregnancy provoked an exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the appendages in women.
Diagnosis of adnexitis during pregnancy
To accurately diagnose adnexitis during pregnancy, gynecologists use several specialized techniques that are safe for the fetus.
- General and biochemical blood tests, which help to find out whether an inflammatory process is present in a woman’s body.
- Ultrasound diagnostics, which helps to identify echogenic manifestations of the pathological process.
- Smears taken from the surface of the uterus and mucous membranes of the vagina will help determine the degree of purity of the vaginal microflora. Also, using a cytological examination of smears, the type of infectious agent that caused the inflammation is determined.
Diagnostic measures for suspected adnexitis during pregnancy are similar to those carried out to clarify the diagnosis outside of conception.
Pregnancy and adnexitis - is conception possible with inflammation of the appendages?
The likelihood of pregnancy due to inflammation in the fallopian tubes and ovaries may vary. Here everything depends on the form and neglect of the pathology. For example, with unilateral salpingoophoritis, the chances of getting pregnant are higher than with inflammation of the appendages on both sides. This is due to the fact that one of the tubes remains healthy and passable, the uterine endometrium is not so severely affected and the hypertonicity of the uterus is not so high. Inflammation with unilateral adnexitis is exactly 2 times less than with bilateral adnexitis.
If the uterine appendages are inflamed on both sides at once, then the likelihood of conception is minimal. Blood circulation in the pelvic organs and the integrity of the mucous membranes are severely impaired, so fertilization virtually becomes impossible.
A separate question: is it possible to conceive a baby with chronic adnexitis? This form of the disease gives the patient the greatest chance of becoming pregnant. With chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages, disturbances in the mucous membranes are not so pronounced, so a woman can easily become pregnant and then carry a baby to term. But it should be borne in mind that during pregnancy, women’s immunity weakens, and against this background, chronic inflammation can turn into acute adnexitis. This pathology, in turn, is dangerous for the fetus and can lead to frozen pregnancy.
Can pregnancy occur after adnexitis?
So, adnexitis in pregnant women is not always beneficial for the health of the fetus and the woman herself. But is there a possibility of successful conception after curing the disease? Gynecologists claim that after salpingo-oophoritis is eliminated, reproductive functions in a woman’s body are completely preserved. However, there is one condition. Unilateral or bilateral inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries must be treated promptly and under the supervision of a qualified physician. Prolonged inflammation in the appendages leads to the formation of adhesions. They prevent eggs from entering the uterine cavity. This manifestation causes ectopic fertilization or infertility.
Complications in the form of adhesions after adnexitis occur in many women. But they can be easily corrected using laparoscopic surgery to cut adhesions.
Childbirth with adnexitis - how dangerous is it?
Childbirth in the presence of adnexitis poses a serious danger to the health of the baby. During birth, the baby may contract an infection. Another problem is that there is a possibility of complications of adnexitis during labor. For example, in pregnant women with a chronic inflammatory process in the appendages, rupture of amniotic fluid may occur prematurely. The consequence of this will be weakened labor, postpartum endometritis, fetal hypoxia due to prolonged periods without water. To ensure that the child does not suffer from the consequences of adnexitis, it is necessary to know the exact signs of the disease and deal with them in a timely manner.
More about symptoms
The symptoms that develop depend on the type of microorganism that provoked them. pneumococcal type is characterized by an acute onset and pronounced symptoms. Pneumonia of the atypical mycoplasma type is identified by pulmonologists by its smooth onset and weakened symptoms.
Pneumonia in pregnant women of viral origin is characterized by increased muscle and joint pain. The addition of the indicated symptoms indicates that the disease has reached its peak and poses a significant danger to the patient’s health.
Despite the fact that the line between the aggravated degree of acute respiratory infections and a minor degree of pneumonia is completely unclear, the pathology in pregnant women provokes much more critical consequences. That is why it involves conducting a thorough diagnosis, taking into account all the nuances of the presented condition.
Signs of adnexitis
Adnexitis in a pregnant woman can be caused by various reasons. Depending on them, the disease will manifest itself externally in the form of certain signs. Adnexitis of any form not only disrupts female reproductive function, but also leads to serious pathologies of pregnancy if it occurs. For example, in the 1st trimester, a woman with adnexitis risks losing her baby as a result of a miscarriage, or the pregnancy may be frozen. With adnexitis in the 6th month of pregnancy, the signs and symptoms of the disease are often mild or absent altogether. The adverse effects of inflammation can be avoided if you pay attention to the symptoms of the disease in time.
Consequences
Sometimes women, fearing the effects of drugs on the development of the fetus, postpone treatment of inflammation and or try to solve the problem using traditional methods. But in fact, untreated inflammation is much more dangerous than properly selected drug therapy. Depending on the duration of pregnancy and the location of the inflammatory process, it can provoke such consequences as:
- Anembryony or absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg;
- Fetal death and frozen pregnancy;
- Spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth;
- Fetal infection.
Self-medication also poses a great danger. Most traditional methods are much more dangerous than tried and tested medications.
Symptoms of adnexitis
If a woman develops adnexitis during pregnancy, its symptoms will depend on the form and severity of the pathology.
Manifestations of adnexitis during pregnancy are as follows.
- Leucorrhoea (pathological discharge) from the vagina.
- Pain localized in the lower abdomen.
- Bloating.
- Slight increase in temperature, chills.
- Painful sexual intercourse, persistent discomfort after intercourse with a partner.
Adnexitis of pregnant women in the acute phase of its development has the following symptoms.
- Heat.
- Problems with urination.
- Pain in the anus, discomfort in the lower back.
- Fever.
- General weakness.
- Nausea (usually this symptom is not accompanied by vomiting).
Untimely treatment of the acute stage of adnexitis leads to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
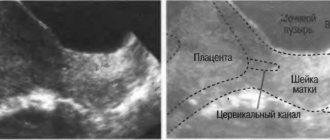
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is a viral disease of the cervix that develops against the background of certain sexually transmitted diseases, or is their consequence. In the vast majority of cases, cervicitis is transmitted sexually. This disease has very sparse symptoms, as a result of which it is often detected in a very advanced state. Its main symptoms are: slightly increased discharge; there may be pain in the lower abdomen; pain during urination and sexual intercourse. For a pregnant woman, or rather for an unborn baby, cervicitis poses a particular danger, since it may well cause disturbances in the formation of the internal organs of the fetus and can cause pseudodeformities.
Treatment of cervitis
Medicines for the treatment of cervicitis are prescribed exclusively by the gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy and depend on what microorganisms are the causative agents of the disease. As a rule, it becomes possible to get rid of such a disease with the help of antibiotics or antiviral drugs. In addition, the expectant mother is prescribed a course of vitamins.
Chronic adnexitis
Chronic adnexitis and pregnancy are 2 conditions of the female body, the combination of which is extremely undesirable. If a doctor diagnoses a woman with “chronic adnexitis,” she should first cure the pathology and only then start planning a pregnancy.
Is it possible to give birth with chronic adnexitis?
The danger of chronic adnexitis is that it occurs latently and is often asymptomatic. A gynecologist can detect pathology in a woman who is already pregnant. Due to weakened immunity and hormonal changes, the disease worsens, becoming more dangerous to the health and life of the baby. The question of whether it is possible to give birth with chronic adnexitis worries many expectant mothers. Doctors advise treating the disease first, and only then thinking about the child. But if it so happens that a woman learned about the diagnosis of “chronic adnexitis” after conceiving a baby, she should be under the supervision of a doctor throughout her pregnancy, be tested for genital tract infections and undergo a course of gentle anti-inflammatory therapy. Natural childbirth for chronic adnexitis is not recommended. A caesarean section is performed.
Why does adnexitis worsen during pregnancy?
Chronic adnexitis often worsens during pregnancy, causing pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Deterioration of the patient's condition may occur for the following reasons:
- hormonal surges, changes in hormonal levels;
- hypothermia;
- weakening of the immune system.
In any case, adnexitis in pregnant women is best diagnosed in the early stages (1st trimester), as it manifests itself with characteristic symptoms.
Acute adnexitis
Acute inflammation of the uterine appendages during pregnancy is quite rare. This condition prevents the conception of a child until the infectious process subsides. Pregnancy that occurs against the background of acute adnexitis often ends in miscarriage in the early stages.
Factors provoking the development of acute adnexitis:
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- taking drugs that reduce immunity.
Symptoms:
- severe pain in the lower abdomen and groin area;
- spread of pain to the sacrum, coccyx, perineum;
- increase in body temperature.
Inflammation of the uterine appendages is almost always bilateral. Isolated damage to the fallopian tube and ovary on one side is rare. With concomitant colpitis (inflammation of the vagina) or urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), pain during urination, itching and burning occur. The appearance of purulent discharge from the genital tract is characteristic.
Adnexitis in early pregnancy
Adnexitis in early pregnancy (1st trimester) has an adverse effect on its course and has a bad effect on the condition of the fetus. The main problem that women diagnosed with adnexitis may face is the high probability of early miscarriage. Violation of the functioning of the ovaries leads to such sad consequences.
Adnexitis in early pregnancy and its danger to the fetus
Adnexitis during early pregnancy can provoke the appearance of such an unpleasant phenomenon as ovarian pregnancy. The problem is that against the background of inflammation in the ovaries, the amount of connective tissue increases, due to which the lumen in the fallopian tubes greatly narrows.
In fact, pregnancy does not occur, but the woman feels the same as during conception. In addition, a pregnancy test with such a problem often shows a false positive result.
Another danger of adnexitis in pregnant women in the 1st trimester is the high probability of miscarriage due to pathological changes in the protective system of the reproductive organs and serious damage to the internal layers of the uterus. The female body perceives the embryo as a foreign agent that provokes inflammation. The uterine layers reject it and therefore miscarriage occurs in the early stages of pregnancy. Sometimes the fertilized egg manages to gain a foothold in the lower parts of the uterus. Due to low attachment of the fetus, placental presentation often develops. Against the background of such conditions, the expectant mother experiences bleeding during pregnancy.
Proper treatment of adnexitis at the stage of pregnancy planning or after conception will help to avoid the adverse consequences of the disease for the maternal and child's body.
The cause of ureaplasmosis during pregnancy
The intimate environment of the female body contains many bacteria and microorganisms, especially in the vaginal microflora. In their normal state, these substances do not pose any threat.
However, in the process of bearing a child, the immunity of the expectant mother is greatly weakened. In this regard, pathogenic infections appear that need to be treated. Ureaplasmosis in pregnant women is no exception, and the woman becomes not just a carrier of the infection, but belongs to the category of sick people.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Causes of ureplasmosis during pregnancy
The presence of this infection in the body, which can be either in a woman or ureplasmosis in a man, may not be suspected. The first causes of the disease can manifest themselves after intimacy. This is the main method of infection. As soon as the body’s immunity begins to decline or a person takes antibiotics, there is a risk of illness and harm to health.
It is worth noting other causes of infection:
- rapid decline in immunity;
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- sudden hormonal imbalance;
- frequent colds;
- abortion.
The main signs of ureaplasmosis during pregnancy include:
- the appearance of yellowish discharge;
- pain;
- discomfort;
- unpleasant odor;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Of course, if ureaplasmosis is detected during pregnancy, a comprehensive examination and proper treatment are necessary. Any infectious diseases that manifest themselves in an intensified form during pregnancy can be dangerous for the fetus.
How dangerous is the disease for the fetus?
Having discovered ureaplasmosis during pregnancy, it is worth knowing: the consequences for the fetus can be very dire. The first trimester is considered a particularly dangerous period, when there is a threat of miscarriage or serious problems during pregnancy.
The consequences of the disease occur during pregnancy and after it. With timely testing, you can detect the problem at an early stage of its manifestation and prescribe effective treatment.
A baby can become infected with ureaplasmosis during pregnancy. The consequences of the disease may be undesirable:
- hypoxia;
- increased tone;
- loosening of the cervix;
- various pathologies;
- early birth or miscarriage;
- disturbance in fetal development.
Ureaplasmosis in women does not have a positive effect on their body.
Important! Despite the fact that infection in the womb is minimized due to the placenta, which is the main protection of the fetus, the baby can become infected from the mother through the birth canal.
The entire genitourinary system of a pregnant woman, as well as the kidneys and their reproductive functions, can be subject to complications. If the infection spreads to the uterus, the woman may become infertile.
Previously, when ureaplasmosis was detected during pregnancy, the consequences for the child were considered so serious that this was considered a reason to terminate the pregnancy. If the fetus becomes infected, its development may stop. This disease is a favorable environment for the development of other infections.
It is necessary to systematically monitor the amount of ureaplasma during pregnancy in order to maintain the norm and prevent the development of the disease.
Modern medicine makes it possible to carry a healthy baby and give birth to him through natural childbirth, even if ureaplasma is detected.
The first trimester is considered the most dangerous. If infection occurs during this period, then the not yet fully formed placenta may not protect the child. This threatens infection in the blood of the fetus, which will be the main cause of the development of pathologies.
If you prescribe medication in time, you can help the mother’s body protect her baby. The same cannot be said about the female body itself. The cervix will suffer first. Its possible loosening and premature opening leads to the onset of fetal rejection.
In the early stages, a miscarriage may occur, and in the later stages, premature birth. Doctors can help with this problem by monitoring the behavior of the cervix so that it begins to open only at the appointed time.
How to treat an infection during pregnancy
It is possible to diagnose ureaplasmosis in women, determine the symptoms and prescribe timely treatment by carrying out bacteriological culture. However, such tests only indicate the presence of ureaplasma bacteria in the body of a pregnant woman. The gynecologist is required to give a referral for additional tests.
You can detect a danger to a woman’s body using the following studies:
- DNA diagnostics or polymer chain reaction method;
- immunofluorescence method.
Both methods make it possible to detect bacteria in a certain area where there is a source of their reproduction.
Of course, it is better to carry out all tests before planning a pregnancy. But if a woman has already discovered this disease and is wondering whether it is possible to get pregnant with ureaplasmosis, then this factor does not exclude the appearance of two lines on the test. However, it is in the first trimester that the threat of miscarriage or abnormal fetal development arises.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
If infection with ureaplasmosis occurred while carrying a child, then you need to understand that it will not be possible to completely cure ureaplasmosis, because this requires taking strong antibiotics. Such treatment during pregnancy is unacceptable.
Treatment of the disease will be based on gentle methods to keep the infection in a stable state, namely:
- douching;
- washing;
- baths with furatsilin (two tablets diluted in warm water);
- medicinal herbs in the form of infusion of chamomile, calendula, string or thyme;
- vitamins and immunostimulating drugs.
All these methods have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
The entire treatment complex proceeds according to the following algorithm:
- prescription of antimicrobial drugs;
- prescribing medications to restore the body’s immune system;
- preparations for restoring intestinal and vaginal microflora.
A diet is prescribed individually and suppositories are prescribed. Additional laboratory tests are prescribed every month to monitor the level of bacteria in the body and assess their actual harm to the woman’s body.
Important! Under no circumstances should you prescribe medications for yourself. Only a doctor can do this. A certain drug may be allowed in a specific trimester of pregnancy, otherwise it may cause harm to the fetus.
To be able to get pregnant after treating an infection, you need to take care of your health as early as possible. The disease can be easily overcome if the disease is detected early and the correct medications are prescribed.
To prevent infection with ureaplasmosis, you need to follow some rules:
- do not have promiscuous sex life;
- if the partner is not permanent, then be sure to use a condom;
- When having oral sex, be sure to rinse your mouth with furatsilin solution.
In this way, a woman will protect her body from unwanted sexually transmitted diseases, will be able to become pregnant and bear a healthy baby.
Treatment of adnexitis
If an expectant mother is diagnosed with adnexitis during pregnancy, the disease is treated according to a special regimen. The main cause of inflammation is insufficiently strong immunity. The presence of infectious agents in the body of a pregnant patient increases the risk of infection of the fetus. But it is also impossible to fight pathogenic microorganisms with antibiotics and chemical medications (this will have a bad effect on the condition of the fetus).
Inflammation in the fallopian tubes and ovaries with adnexitis gradually spreads to other organs of the female reproductive system. The gynecologist selects a complex of medications in such a way as not to harm the fetus. Preference is given to folk remedies for combating inflammation of the appendages:
- herbal mixtures from centaury, flowers and leaves of coltsfoot, medicinal clover;
- tampons soaked in honey and propolis;
- fresh potato juice.
Therapy for adnexitis in case of intrauterine infection of the fetus is inappropriate. Pregnancy in such a situation is terminated spontaneously or with medication.
If the infection has not penetrated to the fetus and uterus until the end of pregnancy, the risk of infection of the baby when passing through the birth canal still remains. Therefore, the expectant mother is recommended to have a caesarean section.
Treatment of adnexitis during pregnancy also depends on the type of infectious agent. For example, if the disease is provoked by opportunistic microorganisms (Gardnerella, Candida), therapy is prescribed taking into account the complexity of the disease and the timing of pregnancy. Adnexitis in pregnant women, which occurs against the background of infection with sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhea, syphilis, treponemas, trichomoniasis, etc.) leaves no chance for the birth of a healthy baby. Pregnancy is terminated artificially.
Sometimes it is useful to find out how other women treated adnexitis during pregnancy. Typically, patients with this problem share their personal experiences on forums.
Treatment options
Treatment of pregnant women with inflammation of the pulmonary system deserves special attention. The recommended measure is recovery not at home, but in a hospital. It should be noted that until the 22nd week of pregnancy, the expectant mother should be in a regular hospital, and after 22 weeks - in the obstetric department. This will keep her condition under constant control, which will avoid complications and other negative consequences.
In the treatment of pneumonia in pregnant women, antibiotic components and detoxification drugs are used. In accordance with special recommendations, expectorants and desensitizers may be needed, as well as diuretics, vitamin complexes and immunological stimulants. It should be noted that:
Treatment of inflammation of the pulmonary system in pregnant women takes no more than one month. If after the indicated period the symptoms persist or decrease, but only slightly, then the presented course should be considered protracted. In this case, the use of stronger medications and constant monitoring by a pulmonologist and gynecologist are required. This will avoid complications and consequences of pneumonia.
Forum
On forums on the Internet you can find many topics regarding adnexitis and pregnancy. Many patients and doctors call adnexitis and pregnancy in reviews as incompatible concepts. The inflammatory process in the uterine appendages is caused by infectious microorganisms that can cause irreparable harm to the unborn baby. By visiting medical forums, you can find out the opinion of doctors regarding how dangerous adnexitis is for a pregnant woman and her baby. Experts on such resources give recommendations on whether it is worth saving the fetus during adnexitis or whether it is better to terminate the pregnancy.
Adnexitis during pregnancy: forum, doctors’ opinion
Qualified gynecologists who conduct correspondence consultations on forums leave reviews of various types about adnexitis during pregnancy. Most doctors say that the development of acute inflammation in pregnant women is impossible. On the contrary, pregnancy can become, to some extent, a healing factor for women who constantly suffer from inflammation of the appendages.
Another group of doctors on forums defends a different position on adnexitis in pregnant women. In their opinion, conceiving a child becomes a provoking factor if a woman already had adnexitis before pregnancy. The pathology could easily enter the chronic stage and proceed hidden. After conception, against the background of weakened immunity and hormonal changes in the body, the disease makes itself felt with renewed vigor. And in this situation, the decision regarding treatment or termination of pregnancy is made individually.
Adnexitis or pregnancy (forum)
The question of whether it is worth planning conception during adnexitis or whether it is better to postpone pregnancy until complete recovery is relevant on the forums. Medical experts advise to first cure inflammation of the appendages, and only then engage in childbearing planning.
Chronic adnexitis and pregnancy (forum)
The combination of chronic adnexitis and pregnancy is also a fairly discussed topic on forums. After reading the opinions of specialists and ordinary women, we can conclude that with chronic inflammation of the appendages, the likelihood of conception is maximum. However, the course of pregnancy against the background of pathology is often difficult. Patients who were pregnant with chronic adnexitis talk on forums about how the chronic process, under the influence of hormonal surges, worsened and was accompanied by symptoms of acute inflammation.
Long-term chronic adnexitis is best cured before the child is conceived. The treatment process will take a lot of time, and after its completion the woman must undergo a second gynecological examination, during which the doctor will find out whether the patency of the fallopian tubes has decreased after the illness, and whether the functions of the ovaries have been impaired.
Adnexitis during pregnancy: reviews of treatment success from patients
Women describe the consequences of the combination of adnexitis and pregnancy differently in reviews on forums and thematic portals. Many forum members note that a chronic inflammatory process (even bilateral) did not prevent them from conceiving a baby. True, in some cases you have to wait a long time for conception to occur (4-6 months).
The effectiveness of treatment for inflammation of the appendages, according to reviews on forums, depends on the general condition of the woman and the duration of pregnancy. Treatment of the disease in pregnant women is complicated, because they cannot take antibiotics so as not to harm the fetus. In the reviews, most women note that chronic adnexitis does not interfere with pregnancy, but in order to avoid a severe course and artificial birth, the disease is better treated before conception.
On the forums there are also useful experiences of young mothers regarding non-drug therapy for adnexitis. For example, there is an opinion that the disease recedes if you give the abdominal muscles regular exercise. The best option is oriental dance classes. Another way to overcome adnexitis during pregnancy is a trip to the sea. Visitors to the forums note that sea air has a beneficial effect on their health. After “treatment” by the sea, inflammation of the appendages disappears without a trace.
Another safe way to cure adnexitis in pregnant women is mud therapy. Usually it is carried out in special sanatoriums. Reviews of this technique on online forums indicate its high effectiveness. Mud helps to dissolve adhesions formed due to inflammation.
Some patients share their experience of treating adnexitis during pregnancy with herbs (knotweed, hogweed, red brush). Herbal components have a gentle effect on the weakened female body, but to achieve a therapeutic effect they need to be taken for a long time (for several months). You can continue phytotherapy of adnexitis with plants after the birth of the child.
Management of pregnancy with adnexitis
In case of acute adnexitis, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. The choice of drug will depend on the stage of pregnancy. Priority is given to products that are safe for women and babies. The course of therapy is 5-10 days and is carried out under constant monitoring of the fetal condition. The question of the possibility of continuing pregnancy is decided individually.
There is no treatment for chronic adnexitis during pregnancy. In case of exacerbation, antibacterial agents are used. The rest of the time, no specific therapy is prescribed.
If complications develop against the background of chronic or acute adnexitis, they are treated. The following drugs are prescribed:
- antispasmodics and agents that reduce uterine tone (if there is a threat of miscarriage);
- antibacterial drugs (for polyhydramnios and fetal infection);
- agents that improve blood flow in the uterus and placenta (for placental insufficiency);
- vitamins;
- agents that restore vaginal biocenosis (with concomitant infection of the genital tract).
Childbirth with adnexitis occurs through the natural birth canal when the condition of the woman and fetus is satisfactory. If complications develop, a planned or emergency caesarean section is performed.
Treatment of cervicitis
Treatment of cervicitis depends on the reasons that caused it and on the duration of the inflammatory process. Taking antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal drugs may be indicated. In addition, immunostimulants and vitamin complexes can be prescribed. Vaginal dysbiosis requires restoration of normal microflora. If the basis of cervicitis is a hormonal imbalance, the doctor may recommend replacement therapy. Chronic cervicitis is much less treatable. In some cases, surgical treatment (laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, etc.) may be used.
How does cervicitis affect pregnancy?
Normally, the mucous membrane of the cervix acts as a boundary barrier between the uterus and the vaginal microflora. Cervical mucus helps create a protective plug that prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity.
The mucus produced by the uterine cervix has a pronounced bactericidal effect and also contains a large amount of immunoglobulins that prevent the development of infection and support local immunity. The development of the disease leads to a sharp decrease in the protective function of cervical mucus and creates favorable conditions for the development of infection.
For reference. Chronic cervicitis during pregnancy is often accompanied by the development of cervical ectopia (which increases the risk of miscarriage). Also, in patients with acute or untreated chronic cervicitis, pregnancy can trigger the progression of the disease.
In such patients, destructive processes in the mucous membrane rapidly progress, erosions develop, and the risk of developing cervical cancer (in the future) increases.
Local treatment of the disease
Involves the use of agents that directly affect the cervix. The list of such drugs includes:
- candles;
- antiseptic solutions;
- tampons with ointments.
The situation is complicated by the fact that during the period of bearing a child, most drugs are prohibited.
What medications can be prescribed to a woman:
- Chlorophyllipt in solution as a natural antiseptic.
- Tampons with Vishnevsky ointment at night - to speed up regeneration processes.
- Calendula suppositories for vaginal administration.
It is not forbidden to douche with a solution of chamomile and oak bark, take sitz baths and increase immunity with the help of vitamin supplements and proper nutrition.
What is not recommended to do:
- use antibacterial agents for local treatment.
- insert ointments into the vagina for other purposes;
- carry out medical procedures without prior consultation with a gynecologist.
Do not forget that medical procedures can cause serious harm to the body, cause allergies and other undesirable consequences. Therefore, a pregnant woman must coordinate their implementation with a gynecologist in order to avoid undesirable consequences.
How to avoid ovarian inflammation during pregnancy?
The likelihood of developing inflammation while expecting a baby is much higher, since immunity decreases at this time. Therefore, expectant mothers are required to be careful and attentive to their health. To prevent inflammation of the ovaries you need to:
- Avoid contracting sexually transmitted diseases;
- Keep your feet warm and dress appropriately for the weather to avoid freezing;
- Observe the rules of intimate hygiene, occasionally use antibacterial detergents;
- Immediately pay attention to any infectious processes in the body and tell your doctor about them.
It is also important to lead an active lifestyle. It is known that one of the reasons for frequent inflammation of the genital area in expectant mothers is blood stagnation in the pelvic organs. Frequent walks at a pleasant pace and simple exercises will help prevent it. A healthy lifestyle and sufficient activity are an indispensable condition for a normal pregnancy.
Atrophic cervicitis
In addition to infection by various types of microorganisms and injury to the cervix, atrophic cervicitis can be caused by prolapse of the vagina and cervix, a decrease in estrogen levels during menopause, and the use of certain contraceptives, which, for example, include chemical spermicides. As a rule, atrophic cervicitis develops as a result of a long (chronic) course of the pathological process. The mucous membrane of the cervix becomes thinner and ulcers form on it.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The main reasons for the development of cervicitis during pregnancy are:
- chlamydial infection;
- gonococcal flora;
- human papillomavirus (HPV);
- genital herpes virus;
- mycoplasma;
- Trichomonas;
- coli;
- Klebsiella;
- fungi of the genus Candida.
Inflammations of a mixed nature, caused by several pathogens, are also often recorded.
If left untreated, pathogens overcome the protective layer of cervical mucus and penetrate the uterine cavity, leading to the development of severe complications.
Products for general use
Complex therapy is most effective; it allows you to cope with the disease faster and avoid complications. Therefore, in addition to topical agents, women are also prescribed other drugs:
- Antibiotics in the form of tablets or injections.
- Antiviral or antifungal agents.
Much depends on the causative agent of inflammation. If pathogenic bacteria are to blame, then broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. Most often, Ceftriaxone is preferred; it is considered conditionally safe (not capable of harming the mother or child).
If the analysis shows that viruses are the cause, then Viferon is prescribed in the form of rectal suppositories. The average duration of therapy is 10 days. If necessary, other medications may be recommended: immunostimulants and immunomodulators.
Antifungal agents help normalize the microflora. These could be suppositories or medications. The choice remains with the gynecologist.
Exocervicitis of the cervix during pregnancy - how to detect pathology?
To diagnose the disease in a pregnant woman, various laboratory and instrumental methods are used.
At the first consultation, the doctor examines the patient’s medical history and carefully listens to complaints. After this, an examination is carried out on a gynecological chair using mirrors. This diagnostic method is effective, since you can immediately see and assess the condition of the cervix. In addition to damage to the mucous membrane, the doctor may detect specific purulent discharge.
If the disease occurs in a chronic form, then such manifestations will not be so pronounced. To clarify and confirm the diagnosis, the doctor takes a smear for analysis. This is done to identify bacteria and white blood cell counts.
In addition, a woman needs to undergo other diagnostic procedures, these are:
- Ultrasound OMT;
- Taking a urine test;
- PCR to detect infections;
- Cytological smear analysis;
- Biopsy in the first half of the menstrual cycle.
If a large number of leukocytes are detected in the smear, this will confirm the development of the inflammatory process. This result is usually detected if a pregnant woman has an acute form of the disease. If this indicator is increased slightly, then we can assume the presence of a chronic form of exocervicitis.
After clarifying the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an individual treatment regimen using carefully selected medications.
Many women who are just planning to conceive are interested in the question: is it possible to get pregnant immediately after treatment for exocervicitis? In fact, there are no contraindications provided that the treatment is completely cured.
Is it possible to get pregnant with cervicitis?
Chronic cervicitis, as well as acute forms of the disease, accompanied by severe disease or ectopia of the mucosa, can lead to infertility . However, with adequate and timely treatment, the risk of developing infertility is minimal.
For reference. In case of acute or aggravated cervicitis, the likelihood of becoming pregnant is low, however, during the period of treatment it is recommended to use condoms or completely abstain from sexual intercourse (at least until acute symptoms disappear).
This is due to the fact that sexual intercourse increases the risk of introducing infection into the uterine cavity and has a traumatic effect on the inflamed mucous membrane of the cervix. Also, with infectious cervicitis, there is a high risk of infection of the sexual partner.
After treatment of acute cervicitis, the patient can become pregnant without risk to her health and the unborn baby.
With chronic cervicitis, pregnancy can also occur, however, you must first consult with a gynecologist and, if necessary, select a planned anti-relapse therapy (safe for the fetus).