What kind of research?
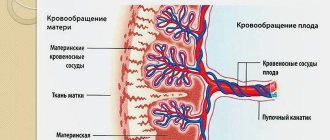
To identify possible serious deviations in the development of the child, survey methods, ultrasound at 11 weeks of pregnancy, and blood serum testing for AFP, hCG and raar-a are used. All these methods provide only approximate results. If they reveal a high risk of congenital pathology
, then the pregnant woman is referred for a more in-depth study.
A more serious study (amniocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy, placentocentesis, cordocentesis) gives more accurate results, but involves taking material from the uterine cavity, which can result in the death of 1-2% of children.
Analysis of the fetus for genetics during pregnancy
Fetal genetic testing during pregnancy can be done in a variety of ways. Today there are both non-invasive and invasive techniques. For example, tests can be taken for the so-called biochemical screening, based on determining the level of specific substances in the mother’s blood, which can vary depending on the increased risk of a particular pathology in the fetus. But this is a screening method that does not give an exact answer to the question whether there is whether pathology. It is performed on all pregnant women at certain stages in order to identify a high-risk group for the presence of pathologies in the fetus. Such women are recommended to undergo a more accurate analysis in the future - this is an invasive method of studying the fetus for genetics.
Before you do tests
Experts believe that before prescribing this study, parents should be informed about the consequences of this diagnosis.
and decide for yourself whether to do it. The generalized experience of pregnancy and childbirth under the leadership of Murray Enkin (the results of 15 years of work of 40,000 obstetricians in Europe were analyzed) made it possible to convince obstetricians to be careful when prescribing screening for genetic malformations of the fetus.
are already stressed due to fear before genetic testing
If their child has a birth defect, it will be a huge relief for them to learn that no developmental defects have been identified (although this result does not provide a 100% guarantee of the birth of a healthy child).
Remember that if you interfere with the uterus while taking material for genetic research, the death of a healthy child is possible.
It is worth remembering that diagnostic errors are possible. To reduce them, before a biochemical blood test, you need to avoid eating fatty and protein foods on the day before the test and in the morning before the test (you can have an apple, banana, etc.). You should take a biochemical blood test in the morning.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis and features of its implementation
Performing preimplantation genetic diagnostics becomes possible only as part of a complex of IVF/ICSI procedures (artificial insemination of male seminal fluid). This need arises because when performing a standard IVF protocol, a large number of male germ cells are added to one female egg. It turns out that excess sperm do not take part in the fertilization process. However, they are preserved and can end up in the biomaterial that is taken for genetic premiplantation analysis.
PGD involves both spouses undergoing testing to identify genetic defects. If this analysis shows the presence of mutations of unknown origin or does not reveal the nature of genetic abnormalities, then preliminary diagnosis before IVF becomes impossible.
Carrying out PGD makes it possible to perform biopsies at different stages of embryonic development.
- Collection of polar bodies from an egg or zygote. The biomaterial allows you to study only the chromosome set of the mother of the unborn baby. The method is highly effective if genetic abnormalities in the family are inherited only by women. Using the analysis, the health status of the egg is determined, and the egg itself is not susceptible to damage. If no genetic abnormalities are found in the egg, it is fertilized and then, together with the embryo, is implanted into the woman’s uterus.
- Taking cells at the stage of their fragmentation (blastomeres, embryo, which includes 6-10 cells). The indicated period corresponds to the 3rd day of embryo development. The biopsy procedure here involves the analysis of 1-2 blastomeres. It is performed remotely, and the embryos continue to develop. The transfer of the highest quality embryos into the uterine mucosa occurs 5 days after fertilization.
- Collection of cells from an embryo at the blastocyst stage. Repeated analysis, which is carried out in cases where the results of the study at the crushing stage turned out to be doubtful.
The optimal scheme for preimplantation genetic diagnosis is selected for patients by a geneticist. It often happens that the study of polar bodies is carried out in conjunction with the analysis of blastomeres. This allows you to obtain more accurate diagnostic results.
How reliable are the results?
Numerous scientific data and the experience of individual parents indicate that the results are unreliable and approximate.
genetic studies during pregnancy. When making a decision, study and analyze all the information available to you.
Professor A.Yu. Asanov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Medical Genetics, Moscow Medical Academy. Sechenova in her article “Prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus” talks about possible errors or errors in genetic research
during pregnancy.
According to doctors in England and Wales, prenatal genetic screening annually prevents the birth of about 660 children with Down syndrome, but at the same time leads to the loss of 400 children whose chromosomes were examined after an abortion and the diagnosis was not confirmed
.
Parents say
On forums for parents of children with Down syndrome, you can often find stories about errors in prenatal diagnosis.
. For example, these:
My son is 5.5 years old and has Down syndrome. During pregnancy, I did all the tests that the geneticist prescribed for me, everything was normal. No analysis guarantees
that the child will not have genetic or other characteristics.
There are many reviews about what future parents experienced when they were told the results of a genetic study in early pregnancy. They say that they rejected the abortion
for moral or religious reasons. And as a result, an absolutely healthy child was born.
The importance of genetic counseling during pregnancy
This procedure gained popularity in the last century because science has advanced far and it has become possible to diagnose diseases that are inherited or arise due to a number of other reasons in utero. Every parent is concerned about the health of their unborn baby, so the examination is important, especially for couples where the risk of pathologies is high. For example, if one of the partners suffers from epilepsy, hemophilia, asthma, diabetes and other serious illnesses.
When planning a pregnancy, many couples come for a consultation with a geneticist in advance to rule out problems, but it is not too late to do the procedure even after conception has taken place.
Consultation with a geneticist is necessary to ensure the baby’s health, identify predisposition to certain diseases, or identify existing mutations and pathologies.
This procedure is freely available and parents can make an appointment and undergo examination at any time. During the conversation, be sure to talk about the reasons, possible suspicions and take the appropriate tests.
Women at risk
As in any other case, there is a risk group that includes women in labor:
- Over the age of 35. Patients have a high risk of having a child with disabilities.
- If you have relatives who suffer from hereditary diseases.
- With a history of several miscarriages, stillbirths, and infertility.
- If the couple is blood relatives.
- Contact of a woman with aggressive toxic substances, radiation exposure or chemical exposure.
- The presence of children with chromosomal pathologies.
- Women with diseases of the endocrine system.
- Multiple pregnancy.
Additional reasons for conducting
Additional factors for prescribing the procedure are negative tests, perinatal screening indicators, or the pregnant woman’s own desire. Previous illnesses during pregnancy and taking medications that can adversely affect the health of the fetus.
If developmental abnormalities are detected, what next?
Detection of a fetal malformation is not yet a reason to terminate the pregnancy. This diagnosis sometimes allows parents to prepare for the birth of a special child.
. However, for some parents this only causes long-term suffering.
There are certain statistics indicating that pregnancy, accompanied by the development of chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus, most often ends in the early stages (miscarriage)
. For those who have refused an abortion, this natural rejection of a non-viable fetus is expected and natural.
You need to understand that the only possible recommendation from doctors is
after detection of a child's defect in the early stages of 11 weeks of pregnancy, it is an abortion.
If an abortion is refused (recognized as the murder of a person in the womb) after childbirth, if a suspected developmental defect is confirmed, parents are asked to abandon the child
and transfer it to the Orphanage.
To make a decision, parents should get to know families who have decided to raise a special child at home. Find out about their joys and sorrows to make a decision for yourself
caring for a seriously ill child or transferring him to state social institutions.
Spouses, of course, should feel freedom in any of their choices. But it is worth remembering that only they themselves are responsible for their choice.
.
Genetic analysis in a newborn
In the maternity ward, on the fourth day, blood is taken from the heel of newborns for examination. For premature babies, this procedure is postponed until the seventh day of life. Genetic testing accurately identifies up to 300 diseases in newborns, the symptoms of which only appear with age. Based on the carriage of defective genes, the following is determined:
- phenylketonuria, leading to developmental delays;
- cystic fibrosis, which disrupts the secretion of internal organs;
- hypothyroidism (thyroid hormone deficiency)
- galactosemia (carbohydrate metabolism disorder);
- other diseases leading to early mortality.
What can you do before conception?
Meanwhile, genetic research of both spouses is possible even before conception. The risk of birth defects is reduced
when taking folic acid 3 months before conception and 3 months after conception, giving up bad habits and improving the health of both spouses.
The importance of diet and vitamin therapy for reducing the risk of birth defects, according to research by M. Enkin, is greatly exaggerated. Practicing obstetricians and gynecologists advise modern parents to conceive a child in August-September
and avoid conceiving in the spring.
The older the future parents are and the more chronic diseases they have, the more carefully they should prepare for the conception and birth of a healthy child.
Health and joy to you!
HLA typing
HLA typing is indicated for miscarriage, unsuccessful IVF attempts or infertility, when immunological incompatibility of the parents is suspected. As with karyotyping, future parents need to donate blood from a vein. Leukocytes will be isolated from the collected material. The analysis is carried out using the PCR method - polymerase chain reaction. This is one of the most accurate diagnostic methods used today. By assessing the results obtained, the geneticist will determine the degree of immunological compatibility of the parents. If a couple has a high percentage of matches, the doctor speaks of complete immunological incompatibility. If the incompatibility is partial, then the result cannot be considered the main cause of miscarriages or infertility.
The ideal option for a problem-free pregnancy is a complete mismatch of partners.
Indications for analysis
A genetic test is mandatory if a pregnant woman is included in the risk group:
- the expectant mother is over 35 years of age;
- the expectant mother has already given birth to children with congenital anomalies or deviations;
- in a previous pregnancy the woman suffered dangerous infections;
- the presence of a long period of alcohol or drug addiction before the onset of fertilization;
- the presence of cases of spontaneous miscarriage or stillbirth.
Common genetic defects
Inherited disorders are caused by changes in a person's chromosomes. The cause of disorders (deviations) is gene mutations. At the moment, doctors can predict the following birth defects with high accuracy:
- Cystic fibrosis . Cystic fibrosis is a life-threatening condition that causes lung damage and digestive problems.
- Sickle cell anemia . A blood disorder that weakens the immune system.
- Down syndrome . This condition causes developmental problems: learning disabilities and mental retardation, abnormalities in facial and body features. The reason is extra chromosome 21.
- Tay-Sachs disease . It manifests itself as damage to the nervous system, which often leads to death in early childhood.
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) . A chromosomal disorder that causes problems with the brain and heart.
- Edwards disease . Characterized by severe mental disability and serious physical abnormalities: small head, heart defects and deafness.
Although advances in genetic testing have improved doctors' ability to diagnose and treat certain diseases, limitations still exist. The tests identify the specific problematic gene, but cannot always predict how much it will affect the child's health.