Stomach ulcers, the treatment of which during pregnancy is quite feasible, are diagnosed quite easily. The main thing is to consult a doctor in time when you see the first symptoms of the disease. Very often, due to our busyness, we neglect proper nutrition, subsisting on sandwiches and fast food every day. Such careless attitude towards your body is fraught with consequences, one of which is a stomach ulcer. The disease can affect absolutely everyone and at any age; its manifestation is especially dangerous in pregnant women. Treatment of stomach ulcers during pregnancy must be carried out in order to eliminate the negative impact of the consequences of the disease on the health of the mother and baby.
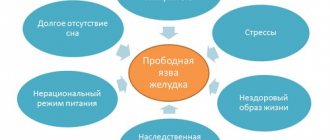
A peptic ulcer can develop in a pregnant woman due to the following factors:
- anxiety, depression, stress;
- heredity;
- poor nutrition (eating large quantities of fried and fatty foods);
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- uncontrolled use of medications such as aspirin and glucocorticoids.
Causes of ulcer development
It has been noticed that peptic ulcer almost always occurs against the background of gastritis. This is not surprising, because each of these diseases has the same cause of origin. The direct culprit in the development of ulcers is Helicobacter pylori. These bacteria live in the digestive tract of almost every person, but only in some of them does infection lead to peptic ulcers. What is the reason for this feature of the disease?
There are several factors that provoke the appearance of ulcers:
- heredity;
- stress and increased anxiety;
- nutritional features;
- taking medications (glucocorticosteroids, NSAIDs and others);
- bad habits (smoking and addiction to alcohol).
Any of these factors are thought to increase a person's risk of developing peptic ulcers. This disrupts the balance of the stomach environment and increases the production of aggressive hydrochloric acid. An ulcer occurs - a defect in the inner lining of the stomach. On the mucous membrane of the duodenum, an ulcer is formed by the same mechanisms as in the stomach.
Pregnancy usually has a beneficial effect on peptic ulcer disease. Changes in hormonal levels lead to changes in the secretory activity of the digestive tract. The production of hydrochloric acid decreases, the level of protective mucus increases and the blood supply is activated. All this leads to the fact that exacerbations of the disease during gestation occur quite rarely. In addition, even formed ulcers heal faster due to increased blood flow and tissue regeneration.
Why are ulcers dangerous for the expectant mother and fetus?
An uncomplicated ulcer does not have a negative effect on fetal development. Even in case of surgical intervention, the chance of maintaining the pregnancy is very high.
The danger to the unborn child is:
- exacerbation of the disease in the later stages, accompanied by vomiting and bleeding. Treatment not started on time can lead to fetal death;
- development of iron deficiency anemia in a woman. Disruption of oxidative processes can cause hypoxia.
important Ulcers are often inherited.
The hormonal background of a pregnant woman has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease, promotes long-term remission, and sometimes complete healing of the ulcer.
Life-threatening complications pose a danger to women:
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- perforation (perforation) of the ulcer.
Symptoms
Attacks of peptic ulcers in expectant mothers occur mainly in autumn and spring . Sudden changes in weather and daylight hours do not have a very favorable effect on the body. The situation is complicated by stress, anxiety and fatigue - inevitable companions of the off-season. It is at this time that most pregnant women notice the appearance of typical symptoms of peptic ulcer disease.
The first sign of an ulcer is pain in the epigastric region. Pain that occurs within an hour after eating is called early pain. Such painful sensations are characteristic of an ulcer in the stomach. If the duodenum is affected, discomfort appears 2 hours after eating. “Hungry” pain occurs in any form of pathology.
A typical symptom of the disease is nausea . In the early stages, this sign can be mistaken for toxicosis. At the same time, vomiting occurs, bringing noticeable relief and reduction of pain. Many women complain of severe belching and heartburn. Constipation may develop due to disruption of all parts of the intestine.
Exacerbations of the disease most often occur in the first trimester of pregnancy, as well as several weeks before childbirth. Often, an ulcer manifests itself already in the postpartum period due to a sharp change in hormonal levels. In the second and early third trimester, the ulcer usually does not cause concern. The disease may remain asymptomatic throughout pregnancy.
What to do for ulcers in pregnant women?
Correcting your diet will ease the symptoms of the disease.
Only after a complete diagnosis can the disease be treated. For non-drug treatment of milder exacerbations, bed rest, drinking mineral water and frequent small doses of healthy food are prescribed. During serious exacerbations of gastric ulcers in pregnant women or the body does not respond to a non-drug method, the ulcer is treated with medications, which will not harm the condition of the fetus, but will accelerate the suppression of ulcerative pathology. Often, traditional medicine methods are included in therapy, which are also used to prevent the disease.
Treatment with drugs
It is important to alleviate the condition of the pregnant woman without aggravating the position of the fetus. For flatulence, enzyme agents are used. The following are used in therapy:
- Antacids. Resisting ulcerative progression due to decreased acidity, for example, Gaviscon.
- Antispasmodic. Eliminate spasm and pain: “No-shpa”, “Duspatalin”.
- Astringent medicines. They act on the body as bactericidal laxatives and antispasmodics: “Vicair”.
Nutrition when affected by illness
Preference is given to boiled or steamed dishes.
During the progression of an ulcer in a pregnant woman’s body, it is important to exclude all spicy, pickled, sour, fatty, salty and fried foods, but at the same time, the body of the expectant mother and child should be moderately saturated with vitamins and microelements. In the absence of consumption of important nutrients, the condition of the expectant mother may deteriorate and the fetus may develop underdevelopment or pathological processes may develop in it. A pregnant woman's diet should include:
- light soups;
- lean meat and fish;
- steam cutlets;
- porridge;
- dried bread;
- boiled vegetables and fruits;
- eggs;
- dairy products;
- compotes;
- weak teas;
- as well as non-carbonated mineral water.
ethnoscience
The oil has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Sea buckthorn oil is considered a fairly effective remedy, taken a teaspoon 30 minutes before meals for a month.
- Consuming honey gives excellent results. On an empty stomach, drink a glass of warm water, sweetened with a teaspoon of honey.
- Tea brewed with pumpkin seeds crushed together with the skin is also known to have a healing effect.
Often, doctors may recommend using traditional methods as part of the treatment so that the peptic ulcer goes away sooner. They are used for drug therapy, bed rest, and are also simply included in the regimen for taking preventive measures during pregnancy. Thus, it is possible to avoid exacerbation during pregnancy and the postpartum period, when the risk of progression of the disease is high. Before using folk recommendations during pregnancy, it is important to consult a doctor in order to prevent unwanted consequences for yourself and your unborn child.
Complications of pregnancy
Peptic ulcer disease has virtually no effect on the ability to bear and give birth to a child . Only in the early stages can an ulcer make itself known by the appearance of severe vomiting. Against the background of the disease, toxicosis is quite severe. Constant nausea and vomiting provoke the development of anemia and hypovitaminosis, which further worsens the condition of the expectant mother. With peptic ulcers, as with other diseases of the stomach and intestines, toxicosis can last up to 14-16 weeks or even more.
In many pregnant women, peptic ulcer disease is accompanied by the development of iron deficiency anemia. Lack of oxygen leads to disruption of nutrition of all organs, including the placenta. With prolonged anemia, placental insufficiency and hypoxia in the fetus inevitably develop. Iron supplements are used to prevent and treat this condition.
Causes and signs of exacerbation of the disease
In the case when a woman with a history of peptic ulcer disease decides to give birth to a child, she needs to be prepared for the fact that its acute form may develop. The exacerbation of the disease is seasonal, that is, the signs of the disease most clearly appear in spring and autumn. This is affected by sudden climate change. It always has a negative effect on the body, and in pregnant women any external natural influences are most pronounced.
The situation is also aggravated by emotional depression, as well as chronic fatigue. In women in this position, manifestations of disease of the duodenum or stomach are characterized by the following main symptoms:
- acute painful sensations appear in the abdomen, which intensify after eating. If the intestine is affected, they will appear at night and be aching in nature, and if the ulcer is localized in the stomach, they will radiate to the interscapular area;
- nausea often progresses to vomiting. This sign of the disease in the early stages is usually confused with the onset of toxicosis, but special attention should be paid to it if, after expelling vomit, pain decreases and general well-being is significantly improved;
- the presence of heartburn and frequent belchings, which have a sour taste given by gastric juice;
- bowel function becomes dysfunctional, leading to constant constipation.
If an exacerbation of the ulcer provokes internal bleeding, the following symptoms appear: sharp, pronounced pain, fainting, vomit and feces streaked with blood, pallor of the skin, general weakness, constant dizziness and decreased blood pressure.
If signs of exacerbation appear, you must immediately call an ambulance, and do not take any medications until it arrives. Also, you should not eat or drink anything until examined by a doctor.
Complications of peptic ulcer
An ulcer of any localization can provoke the development of the following conditions:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding . Bleeding is considered one of the most dangerous complications of an ulcer. However, neither the duration nor the severity of the disease affects the likelihood of bleeding. This symptom may be one of the first signs of the disease (so-called “silent” or asymptomatic ulcers). With heavy bleeding, vomit of an unusual dark color with streaks of blood occurs. Characterized by general weakness, pallor, dizziness. Subsequently, a persistent decrease in blood pressure occurs. The stool turns black due to blood. If bleeding develops, a pregnant woman should be immediately taken to the hospital.
- Perforation of the ulcer . Perforation of an ulcer is damage to the wall of an organ with a violation of its integrity. With this complication, severe “dagger” pain occurs in the abdomen (in the epigastric region). Blood pressure drops sharply, pulse quickens, and cold sweat appears. After a few hours, a temporary improvement in well-being occurs: the pain subsides, the abdominal muscles relax. Despite the apparent well-being, a pregnant woman should definitely call a doctor. Perforation of an ulcer inevitably leads to peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) and sepsis, so help should be provided as soon as possible.
DO YOU STILL THINK THAT IT IS HARD TO CURE YOUR STOMACH?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side.
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction. All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? We recommend reading the story of Galina Savina, how she cured her stomach. Read the article >>
Content:
Among the numerous etiological factors in the development of ulcers, doctors put neuro-emotional stress, decreased immunity and metabolic disorders in first place. That is, the processes that accompany a pregnant woman throughout the entire period of gestation.
At the same time, the body of expectant mothers begins to actively produce histamine. The nutrient normalizes the level of acid balance and protects the digestive system from the development of pathologies. Many women with a history of ulcers note an improvement in their health.
Diagnostics
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) in pregnant women is performed only when complications of an ulcer develop. In other situations, doctors make a diagnosis based on typical symptoms and examination data. An endoscopic examination can provoke an increase in uterine tone, so if possible, doctors try to avoid this manipulation.
X-ray contrast examination of the digestive tract during gestation is also not performed. If necessary, the doctor can perform an ultrasound of the stomach and evaluate its size, as well as its functioning features. It is not possible to detect ulcerative defects with ultrasound.
General information
Gastric ulcer is a rare extragenital pathology detected in 0.025% of pregnant women. These statistical indicators may be somewhat underestimated due to the difficulties of diagnosing the disease during gestation. Currently, the prevalence of gastric ulcer in the female population as a whole is 8-11%, with a trend towards an increase in incidence. Most likely, this is due to increasing stress loads, high social activity, and family instability. Thanks to the use of modern methods of eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium associated with gastric ulcers, the number of complicated forms of the disease has significantly decreased.
Treatment methods
As with any diseases of the digestive tract, special attention is paid to diet in the treatment of peptic ulcers. Without a significant change in diet, no therapy will bring the desired effect. How should pregnant women eat to prevent the progression of ulcers?
Dietary recommendations for peptic ulcers:
- Meals should be frequent: 5-6 times a day with a break of 3-4 hours.
- It is recommended to reduce the usual portion of food by 1.5-2 times (taking into account the increase in the frequency of meals).
- All dishes are boiled, steamed or baked in the oven.
- Fried foods are excluded.
- Salt is limited to 5 g per day.
- It is not recommended to eat foods that are too cold or hot.
Products allowed for peptic ulcers:
- stale bread, unhealthy cookies;
- vegetable and dairy soups;
- lean meat;
- chicken;
- River fish;
- cereals and pasta;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- non-acidic juices (berry, fruit, vegetable).
Products prohibited for peptic ulcers:
- fresh bread and pastries;
- fat meat;
- sea fish;
- soups with meat and fish broths;
- hot and spicy dishes;
- salty dishes, marinades;
- smoked products;
- canned food;
- sour fruits and berries (as well as juices from them);
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
Prevention
If a woman suffered from an ulcer before conceiving a child, she is recommended to register with a doctor in advance, mentioning the presence of the disease. Also, regardless of the presence of a history of illness, it is recommended to follow a diet, switch to small meals, avoid stress, and normalize work and rest.
An ulcer during pregnancy poses a serious threat to both the mother and the fetus. Self-medication during this period is strictly prohibited; medical assistance is required.
Author: Arina Volkova, doctor, especially for Zhkt.ru
Drug treatment
Medicines for ulcers in pregnant women are prescribed with great caution. To destroy the causative agent of the disease (Helicobacter pylori), antibiotics are required, but this treatment regimen is not used during pregnancy. Antibiotics needed to treat peptic ulcers are considered dangerous to the fetus and cannot be used in expectant mothers.
To normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, antacid drugs (Almagel, Maalox, Rennie) are used. These drugs bind hydrochloric acid in the stomach, thereby eliminating pain and other symptoms of the disease. Antacids should be taken half an hour after meals. With long-term use, antacids cause constipation, so such products should be used for no more than 14 days.
Various enzyme preparations . They restore stomach function, improve digestion and eliminate discomfort after eating. In cases of severe intestinal dysfunction, sorbents are added to treatment to facilitate the removal of toxins from the body.
Peptic ulcer disease is a condition that does not interfere too much with the normal course of pregnancy. If you follow the diet and follow all the recommendations of the therapist, pregnancy and childbirth usually go well, despite the pathology of the digestive tract. If any complications occur (sudden sharp pain in the abdomen, vomiting blood, loss of consciousness), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of ulcers during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is unacceptable to self-medicate. The doctor carries out therapy for peptic ulcer disease based on the results of laboratory tests and examination, including ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and gastroscopy. The pregnant woman will be offered hospital treatment. First of all, bed rest is necessary.
- diet No. 1 or 1b according to Pevzner. Very hot and very cold foods are excluded from the menu, dishes that irritate the mucous membrane and stimulate secretory function are prohibited;
- medicinal mineral water (for example, “Essentuki” No. 14);
- fractional meals in small portions up to 6 times a day;
- herbal medicine: various stomach preparations (calamus rhizomes, chamomile, dill seeds, peppermint leaves).
Medications
During an exacerbation, the doctor prescribes drug therapy, taking into account the effect of drugs on the tone of the uterus and the fetus. Usually prescribed:
- non-absorbable antacids (Almagel, Maalox) an hour after meals;
- injection of Metacin or Cerucal (for vomiting) during an exacerbation;
- Ferroplex for the prevention of anemia;
- B vitamins to normalize digestion and reduce flatulence.
For severe pain, no-spa or papaverine will help.
Traditional medicine
Official medicine recognizes the effectiveness of folk remedies in the treatment of ulcers in pregnant women. The expectant mother should definitely consult a doctor.
important Some herbs can cause spontaneous abortion!
Ease the course of the disease:
- infusions of herbs with an astringent effect. Place an equal amount of St. John's wort, chamomile, and yarrow flowers in a thermos and pour boiling water over it. Leave for 3 hours. Take 50 ml 3 times a day. Instead of tea, it is better to drink a decoction of chamomile; it has no contraindications and is safe for the fetus;
- sea buckthorn oil: 1 tablespoon on an empty stomach;
- propolis (in the absence of allergies!). Eat 5 g of the product 3 times a day after meals. Not recommended for exacerbation;
- oats ground to a powder (not flakes!). Pour a glass of oats into 2 liters of hot water and cook for 40 minutes over low heat. Strain the broth, drink 100 ml warm before each main meal.