It's no secret that many changes occur in a woman's body during pregnancy. Often, pain occurs in those places and organs that have not previously bothered the expectant mother.
One of the most important organs of the body is the liver. During the period of gestation, it is she who is responsible for cleansing the body of the mother and baby, which means that the load on her doubles. Therefore, women may note that their liver hurts during pregnancy. Let's consider what needs to be done in such a situation, what treatment to carry out, what tests to take.
Peculiarities
Liver problems can make pregnancy worse, causing unwanted complications. Sometimes it happens that the function of this organ is slightly impaired, and after the birth of the child its functioning is restored.
If you have a history of chronic liver disease, you will have to be under the strict supervision of a specialist throughout your pregnancy.
Features of the female body during pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, hormones are produced that prevent uterine contractions. After all, if the uterus contracts, there is a possibility of miscarriage. A woman begins preparing to feed her baby already during the second trimester; for this, the hormone prolactin is produced. Its concentration in the blood increases tens of times. When a woman is in an “interesting” position, a temporary organ is formed - the placenta. She develops and matures independently. Functions of the placenta:
- Protective. The organ protects the fetus from pathogenic bacteria and toxins.
- Nutritious. The fetus is provided with air and nutrients by the placenta.
Physiological causes of pain
As already mentioned, a woman’s body undergoes many changes, certain types of metabolism (fat, protein, carbohydrate) are disrupted, which leads to an increase in the load on the liver. As a result, all this causes pain.
During late pregnancy, the baby usually moves around a lot in the belly. It can purely accidentally touch the liver, thereby causing aching pain in the right side. Some women may complain of nausea, heartburn, and lack of appetite.
As the child grows, the uterus also enlarges, which can create pressure on the liver. Some expectant mothers experience biliary dyskinesia. As a result, the output of bile and the functioning of the bile ducts in general are disrupted. But this does not have a negative effect on the fetus. After the birth of the child, the functioning of the gallbladder is restored.
Poor nutrition and disruption of the digestive system can also be one of the causes of pain. During the period of bearing a baby, women are not always picky in terms of food, which they consume in large quantities, which has a detrimental effect on the liver.
During normal pregnancy, the blood supply to the liver and its size remain virtually unchanged. But all these criteria are controlled by the leading physician.
Liver during pregnancy: gland diseases, liver failure and poor tests
The time of bearing a child is both a wonderful and difficult period for a woman.
Due to the increased load, systems and internal organs cannot cope with their tasks, which is manifested by compensatory reactions - the body works to the limit. During pregnancy, the liver is subjected to enormous stress as it performs double work. Sometimes the organ cannot cope with its functionality, which leads to the development of symptoms - pain in the right side, unpleasant taste in the mouth, loss of appetite, nausea, and bouts of vomiting.
In the human body, the liver performs more than 500 functions and filters more than 2000 liters of blood every day. Therefore, the gland needs support. So, let's figure out why pain occurs, what diseases occur in pregnant women?
Pathogenesis of pain syndrome
The etiology of pain during pregnancy is pathologies that developed already during pregnancy. The most common ailments include the acute form of fatty infiltration, gestosis, which provokes the development of preeclampsia and eclampsia.
5-10% develop HELLP syndrome, which is accompanied by a complex of negative symptoms. Pain can be caused by disorders of the biliary tract, acute rupture of the gland, and hepatosis.
During pregnancy, especially in the third trimester or while carrying twins, the cause of pain is the pressure of the fetus on the liver. Due to strong compression of the liver areas, the flow of bile is disrupted. Because of this, dilation of the intrahepatic ducts is detected, and dyspeptic symptoms appear.
When the cause of pain is pressure from the fetus on the liver, treatment is not prescribed. To make you feel better, it is recommended to spend more time lying on your left side. After the birth of the child, the symptom goes away on its own.
Why does the gland enlarge?
An enlarged liver during pregnancy without transformation of structural tissues and an increase in liver enzymes is not a sign of a pathological process. The reason may be a high load on the digestive or circulatory system. This problem appears in the third trimester, but does not occur in the early stages.
The development mechanism is due to swelling of the organ parenchyma. Because of it, metabolic processes in the body are disrupted and hypoxia of the gland is detected. In this case, the liver needs to be supported - corrective treatment is carried out before labor.
If the liver is enlarged, a transformation of the structural structure is revealed, liver enzymes are elevated, and the patient complains of dyspeptic syndrome, then a viral infection, a severe form of gestosis, or steatosis is suspected.
Diseases during pregnancy and etiology
Medical practice knows a lot of liver diseases during pregnancy. They pose a certain danger to the woman and child, so timely and appropriate treatment is required.
Hemangioma
The occurrence of liver problems during pregnancy may be a consequence of the formation of hemangioma. This is a neoplasm of a benign nature, vascular in nature. Most often, this is a congenital condition; emergency medical intervention is not necessary. Symptoms depend on the size of the tumor.
If the size of the hemangioma is 60-70 mm, it was diagnosed by ultrasound, then treatment for the pregnant woman is not prescribed. In most cases there are no symptoms. With a larger size, nausea, vomiting, and pain during pregnancy in the right side appear, which is observed constantly.
For a long time, the hemangioma can “sleep”. But due to changes in hormonal levels, it is capable of growing rapidly. The danger is that a rupture may occur during labor. Therefore, at the end of the third trimester, a control ultrasound examination of the gland is performed.
Based on the results of the instrumental examination, a decision is made on the method of delivery - natural birth or cesarean section. The tumor itself is removed after childbirth. A classic operation is performed, or laser exposure or cryodestruction is used.
Increased liver enzymes
Sometimes the liver fails to cope during pregnancy due to a high enzyme load combined with fetal pressure. This fact is confirmed by an increase in the concentration of liver enzymes - AST, ALT, LDH and other substances.
The increase in concentration is based on the toxic effect on the parenchyma of the gland, which leads to a destructive process in the organ itself. Depending on the stage of pregnancy, some deviations from the norm are allowed. Therefore, dynamic monitoring of increasing values is always carried out.
Fatty infiltration
Fatty liver is a rare but dangerous phenomenon during pregnancy. The pathology is accompanied by the accumulation of lipids on the organ itself. The main reason is a hereditary factor.
The clinic begins to manifest itself in the third trimester and is represented by the following symptoms in a pregnant woman:
- Nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Pain in the epigastric region, in the side.
- General deterioration in health.
- Yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the eyes.
- Headache.
If therapy is not started in a timely manner, coma and liver failure during pregnancy develop. There is a high probability of maternal death and fetal death.
Hepatosis
Hepatoses are a group of pathologies that are characterized by a disorder of metabolic processes in liver cells. Most often, the cholestatic form of hepatosis is diagnosed. Development occurs at 25-26 weeks and occurs in 1% of women.
Clinical manifestations are similar to fatty infiltration. The main signs include weakness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, itching of the skin, jaundice, and change in the color of feces.
With such a diagnosis, it is imperative to support the liver. In 80% of cases, premature delivery is required to prevent negative consequences. After childbirth, hepatosis can provoke severe bleeding, since the synthesis of blood coagulation factors in the gland is disrupted.
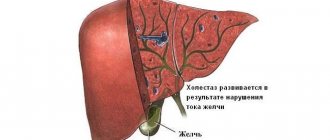
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Liver diseases during pregnancy include intrahepatic cholestasis, a pathology characterized by impaired production and outflow of bile. For this reason, bile acids accumulate in the blood.
Symptoms appear in the 2-3 trimester:
- The palms of the hands and soles of the lower extremities begin to itch, and sometimes the whole body itches severely. In some cases, the itching is severe and constant, which leads to sleep disturbances and emotional instability.
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes because the amount of bilirubin in the blood increases.
Intrahepatic cholestasis leads to premature birth in 60% of cases. And premature babies are at increased risk of health problems (including serious irreversible damage).
Diagnosis of liver pathologies
If you have characteristic symptoms, you should visit a doctor. Laboratory and instrumental methods are used for diagnosis. A blood test allows you to determine the number of leukocytes and platelets. Using a coagulogram, the activity of coagulation factors is determined.
Biochemistry is carried out - the total amount of protein and its fractions, the concentration of bilirubin, liver enzymes, urea, and electrolytes are determined. An ultrasound is required to assess the size, structure, and identify the presence of possible neoplasms.
Ultrasound during pregnancy is performed only when indicated, for example, when a woman complains of symptoms that appear due to liver disease.
Normally, the ultrasound transcript looks like this:
- The dimensions of the right lobe are 12-13 cm, the left – 7-8 centimeters.
- The structure of the parenchyma is homogeneous.
- Normal echogenicity.
- The vascular pattern is within normal limits.
- There is no expansion of the portal vein, its diameter is 10-13 cm.
- No neoplasms were detected.
- The intrahepatic ducts are not dilated.
- The common bile duct has no expansion.
Any abnormalities on ultrasound should be considered in conjunction with the woman’s laboratory tests.
Treatment methods and preventive measures
Medicines aimed at improving liver function are prescribed by a doctor. The specific treatment regimen is determined by the disease and severity. In case of fatty infiltration, cesarean section is recommended if time permits. In the early stages, the woman is hospitalized, undergoes a thorough examination, and uses symptomatic medications.
Intrahepatic cholestasis requires the use of hepatoprotectors. According to reviews, Ursofalk gives the best effect. The drug restores liver function, quickly relieves itching, and prevents complications. Additionally, vitamins are prescribed.
Diffuse changes and hemangioma do not require medical correction if there are no negative symptoms. The main treatment is carried out after the birth of the child.
Regardless of the diagnosis, a woman is recommended to eat properly and avoid junk food. They add a lot of healthy vegetables and fruits, natural juices, cereals to the menu, and reduce the amount of animal products.
Folk remedies are effective, for example, milk thistle decoction and herbal remedies for the liver. It ensures cleansing and restoration of the organ. But use is allowed only after consultation with a medical specialist.
Source: //blotos.ru/pechen-pri-beremennosti
Pathological causes
The problem may be a sign of chronic illness. During pregnancy, sometimes there is an exacerbation of cholelithiasis (stones in the gallbladder and its ducts), which causes colic. Changes in hormonal levels can also cause the formation of stones. The pain is very sharp.
Another reason is intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Most often, this pathology is observed in the third trimester. Due to the increase in the level of sex hormones, the formation of bile increases, and its secretion is inhibited.
This disease is accompanied during pregnancy by nausea, bitterness in the mouth, itchy skin, and pain in the right hypochondrium. Many women experience vomiting. Itching begins from the limbs, feet, and then spreads to the entire torso. The urine also darkens and the stool becomes lighter. After giving birth, everything returns to normal.
Another symptom of liver problems is yellowing of the skin and sclera. This sign may indicate hepatitis. During pregnancy, testing for the presence of viruses of this disease is mandatory. While the baby is in the belly, infection will not occur, but it is possible during childbirth, although the probability is low.
Uncontrollable vomiting may be a signal of increased bilirubin due to liver dysfunction. Heart failure may also be the cause, as blood is poorly pumped and accumulates in the liver and lungs. Some old injuries can also cause pain in the liver area.
The influence of liver diseases on pregnancy
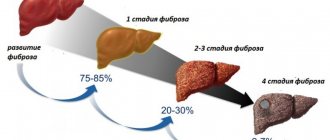
It was believed that both the deterioration of liver function and its improvement were due to immunological changes characteristic of pregnancy, when it comes to autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Chronic viral hepatitis without cirrhosis during pregnancy is rarely a cause for serious concern. Treatment interventions are aimed primarily at preventing infection in the newborn. Perinatal vaccination is very effective. It reduces the risk of developing HBV infection. Neonatal infection of a child with hepatitis C from an infected mother is approximately 5%. Unfortunately, there is currently no vaccine against this form of hepatitis. There is also no convincing data indicating one or another preferred method of delivery from the point of view of the risk of transmission of infection. Some nucleoside analogues (for example, lamivudine) can be safely prescribed to pregnant women for the treatment of hepatitis B, but the use of ribavirin for hepatitis C due to the teratogenicity of the drug is absolutely contraindicated.
Cirrhosis of the liver very often leads to amenorrhea, and pregnancy is impossible. If pregnancy occurs, in the second and third trimesters the risk of bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus, which appears against the background of portal hypertension, increases especially sharply. Prevention with β-blockers should not be stopped during pregnancy. Pregnancy after liver transplantation can be successful, but the risk of complications is increased.
Hepatitis
These diseases are of infectious and non-infectious nature. With hepatitis, the nutrition of the organ is disrupted and its cells are destroyed.
There are seven types of hepatitis, designated by Latin letters. The most dangerous in terms of virulence are A and E, since these viruses can be infected not only from a patient or a virus carrier, but also through the fecal-oral route. This means that germs can enter the body of a pregnant woman with unwashed food, dirty hands, and untreated water.
Other types of hepatitis occur only through contact with a patient, during blood transfusion, or during any manipulation with a poorly processed instrument (for example, during a visit to the dentist).
Hepatitis C is considered a very dangerous disease, as without treatment it can lead to cirrhosis of the liver. If infection occurs during pregnancy, it can cause intrauterine fetal death or the death of the baby a few days after birth.
All types of hepatitis have a detrimental effect on the development of the fetus, leading to impaired circulation and blood clotting, which leads to serious consequences. If such a disease is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, the child is vaccinated immediately after birth. In 95% of cases, the disease does not develop in infants.
Acute fatty liver degeneration
pregnant women Most often occurs during the first pregnancy and pregnancy with twins. The disease usually occurs between the 31st and 38th weeks of pregnancy and is characterized by jaundice, vomiting and abdominal pain. In severe cases, lactic acidosis, coagulopathy, encephalopathy and renal failure, and hypoglycemia occur. These manifestations are characteristic of impaired β-oxidation of fatty acids in the mitochondria, which leads to the formation of small droplets of fat in the liver cells (microvesicular fatty liver). Some women are heterozygous for long-chain 3-hydroxy-CoA dehydrogenase (LCCAD) deficiency.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with toxicosis of pregnant women. In contrast to toxicosis of pregnant women, there is no hemolysis in fatty liver degeneration of pregnant women, and a high concentration of uric acid is found in the blood serum. A combination of acute fatty liver degeneration of pregnant women, HELP syndrome and toxicosis may occur. Early diagnosis and delivery have led to a reduction in maternal mortality to 1-15%.
Diagnostics
According to statistics, 2-3% of pregnant women suffer from hepatocholecystitis, hepatitis or cholelithiasis. Only with correct diagnosis and therapy will pregnancy result in a normal physiological birth. Therefore, if unpleasant symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
The doctor sends the patient for a general clinical blood test to check the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin, and white blood cell count. These indicators help detect inflammatory diseases in the body.
Next, a biochemical blood test is performed:
- ALT and AST are indicators of liver health. Normally they are 31 U/l. If there are unpleasant sensations in the liver area, bad tests during pregnancy are ALT and AST levels above 31 U/l. This result indicates disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
- Total bilirubin. Norm 5 - 21 µmol/l. If the numbers in the analysis are higher than normal, this may indicate liver damage or jaundice.
- Bilirubin is direct. The norm is 0 - 7.9 µmol/l. The value may increase with jaundice in pregnancy, bile stagnation, and liver damage.
Markers of viral hepatitis B and C are also determined. Usually, a test for hepatitis B is done at the beginning of pregnancy, but if a woman visited a nail salon, a dentist, or underwent injection treatment, then the test must be repeated.
Also, for pain in the liver area, it is prescribed to undergo an ultrasound of the liver during pregnancy. This study helps to detect inflammatory processes in the organ, determine its size, and check the condition of the gallbladder and ducts.
To diagnose gallbladder dyskinesia, check its size before and after a special breakfast, which usually consists of 2 raw egg yolks. Using this method, you can confirm or refute the presence of gallstones and the absence of inflammatory diseases. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy is quite difficult to establish. Usually this conclusion is reached after excluding other possible complications.
If a woman is bothered by itching (the very first symptom of cholestasis), she is referred to a dermatologist. The doctor prescribes the necessary tests, including a liver test and determination of bile acids. The results of these tests may be negative. They may be re-appointed to clarify the picture. If this time no abnormalities are found, a diagnosis of cholestasis of pregnancy is made. When performing a liver test, an increase in the level of direct bilirubin, triglycerides and globulins can be a marker of cholestasis.
Preeclampsia (eclampsia) in pregnant women. HELLP syndrome. Liver rupture
In severe cases of gestosis in pregnant women (preeclampsia, eclampsia), liver damage is observed, the cause of which is microangiopathy as part of generalized vascular disorders. Spasm of arterioles and damage to the endothelium of liver vessels with deposits of fibrin and platelets in them leads to ischemia, necrosis of hepatocytes and hemorrhages into the liver parenchyma.
The appearance of signs of liver damage in eclampsia (preeclampsia) is typical at the end of the second - third trimester of pregnancy against the background of a detailed clinical picture of gestosis, characterized by a triad of signs - arterial hypertension, proteinuria and edema. Often only laboratory changes are observed. In severe cases of progression of liver gestosis, moderate jaundice develops with a 5-6-fold increase in the level of bilirubin (conjugated and unconjugated), combined with the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, intravascular hemolysis (microangiopathic hemolytic anemia), thrombocytopenia - the so-called HELLP syndrome (by the first letters main clinical manifestations – Haemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelet count). HELLP syndrome complicates 0.1-0.6% of all pregnancies - in 70% of these patients it develops between 27 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, in about a third of patients the development of the syndrome is observed in the first 2 days after birth.
Clinically, the condition manifests itself in addition to the symptoms of preeclampsia and eclampsia by abdominal pain syndrome (in 65-90% of patients), nausea and vomiting (in 50% of patients), complications of DIC syndrome and may resemble acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP). The condition can be combined with APPD, which has been proven morphologically: in addition to fibrin thrombi in the sinusoids, centrilobular necrosis and hemorrhage characteristic of HELLP syndrome, small-droplet obesity of hepatocytes is often detected. A rare and very severe complication of liver damage due to eclampsia is the formation of subcapsular hematomas with liver rupture and the development of intra-abdominal bleeding (read about how to provide first aid for different types of bleeding here).
Treatment of biliary dyskinesia
The goal of therapy is to normalize the flow of bile to avoid its stagnation. One of the most important points is proper nutrition.
Food should be taken in small portions, 5-6 times a day. Foods that promote the flow of bile should be included in the diet.
These include meat or fish broths, eggs, sour cream, cream, butter and vegetable oil. Cottage cheese, rosehip decoction, cod, bran, cabbage, and carrots are useful. In general, you need food rich in plant fiber and magnesium.
The second step is the use of choleretic drugs. Most often, preparations or teas are prescribed. The choleretic collection includes immortelle flowers, yarrow herb and coriander fruits. If it is tea, then it may contain tansy, corn silk, and rose hips.
In the second half of pregnancy, when edema develops, it is convenient to use “Flamin”, which is a dry concentrate of immortelle flowers. Take 1-2 liver tablets during pregnancy 3 times a day, half an hour before meals. Also a good drug is “Holosas”, which is taken one teaspoon 3 times a day.
Preventive measures
Treating a disease is much more difficult than adhering to the rules that help maintain the health of a pregnant woman. For normal liver functioning, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle before pregnancy. At the stage of planning a child, it is worth undergoing a liver examination and, if necessary, starting treatment in advance. The first point in prevention is a diet for the liver during pregnancy. Dietary nutrition is based on compliance with the following rules:
- Eating fruits and vegetables as the basis of the diet.
- It is worth choosing rye bread without yeast.
- Refusal of confectionery products in favor of dried fruits.
- Consume healthy fats found in fish, avocados and nuts.
- It is better to cook it yourself, thereby controlling the usefulness of all ingredients.
- It is useful to drink mineral water without gas. It is worth remembering that the water requirement is about 2 liters daily.
Physical exercise can help prevent liver disease. During pregnancy, you should choose walks in the fresh air or special yoga designed for pregnant women. It is recommended to walk at a free pace, and sports activities in a group will not only improve your health, but will help you relax emotionally. It is important to get enough sleep, at least 8 hours, or even more.
Treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy
If you have this disease, you must strictly monitor what food the pregnant woman eats. Fatty foods, smoked foods and pickles should be excluded from the diet. It is also recommended to drink more fluids. In addition, Vitamin K is prescribed to prevent postpartum hemorrhage.
One of the symptoms of this disease is itching. You won't be able to completely get rid of it, but you can reduce it. To do this, use Calamine lotion or baby creams with calendula. Clothing should be light, made of cotton. This will help avoid itching.
Drug therapy and treatment with liver pills should be supported by diet. The diet should contain a lot of protein foods and vitamins. After giving birth, women who have suffered from this disease are registered at the antenatal clinic.
Can pregnant women eat liver, harm and beneficial properties of the product, recipes for pregnant women
The question of whether pregnant women can eat liver arose relatively recently and there is serious debate around this topic. The health of mother and child undoubtedly depends on a woman’s nutrition. And eating some foods can harm a pregnant woman. So is it worth giving up offal while carrying a baby or, on the contrary, should you include them in your diet?
Beneficial properties of liver for pregnant women
While carrying a baby, a woman, or rather her body, is subjected to high stress. As a result, the need for certain substances, including hemoglobin, increases.
Hemoglobin is responsible for the transport of oxygen; if its level decreases, then the tissues begin to lack this substance. A low hemoglobin level in a pregnant woman is dangerous because:
- Leads to weakness and decreased performance.
- May cause dizziness and loss of consciousness.
When a woman has low levels of hemoglobin in her blood, the baby's brain does not receive enough oxygen. Hypoxia is potentially dangerous, as it can lead to the development of various pathologies in the baby.
During pregnancy, a woman often donates blood for analysis, which helps the doctor monitor the hemoglobin level in her blood.
Liver, like other animal products, helps increase the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Its absence in the diet is difficult to compensate for.
What kind of liver can pregnant women eat:
- First of all, we are talking about beef liver, which is considered a dietary product;
- You can also eat chicken liver.
But it is better to avoid fish by-products; as a rule, they are sold in canned form, which means they are rich in salt, seasonings and other harmful substances.
Why you should include this product in your diet:
- Contains many useful substances, vitamins and microelements.
- It is not high in calories.
- Rarely leads to the development of indigestion.
Liver, as a dietary product, is often included in the diet of pregnant women due to its low calorie content, but in addition to its beneficial properties, the product also has harmful ones.
Why you shouldn't eat during pregnancy
Women who are waiting for a new addition to their family should carefully monitor their diet. It is better to avoid certain foods because they may:
- cause serious harm to the mother's body;
- cause problems in the functioning of the digestive system;
- “saturate” the body with toxic substances.
In the first trimester, women often encounter a phenomenon called toxicosis. It is almost impossible to get rid of it; treatment brings temporary relief.
Gynecologists believe that one of the causes of toxicosis is excessive consumption of an element such as beta-carotene.
In medicine, beta-carotene is known under another name - vitamin A. Its excessive consumption leads to increased symptoms of toxicosis. Liver contains large amounts of beta-carotene. For this reason, it should not be used in the first trimester.
Other product hazards:
- Contains other substances that can increase the severity of toxicosis.
- There may be parasites in the liver that can harm the mother and baby.
The liver is a detoxification organ; its main task is to remove harmful substances from the body. Due to increased blood flow, parasites may be present in this organ.
We are talking about toxoplasma, which will harm the child. Infection with these parasites can result in fetal death.
By-products, not just liver, are dangerous, especially when undercooked. For this reason, if you decide to cook them, then subject them to thorough heat treatment. This will help avoid problems.
In what cases should you not use:
- there is individual intolerance, hypersensitivity to food;
- the woman is worried about toxicosis, its classic manifestations;
- the hemoglobin level is normal and there are no problems with excess weight;
- pregnancy has not yet entered the 2nd trimester;
- there are problems with blood cholesterol levels.
Still, you should not include by-products in your diet if we are talking about a problematic pregnancy, which occurs with complications and pronounced toxicosis.
In addition to beta-carotene, the liver contains a high concentration of animal fats, which contribute to increased cholesterol levels. If a woman has such problems, then it is better to give up offal, at least during pregnancy.
What else should pregnant women not eat:
- Eggs, raw or half-raw, carry a risk of becoming infected with salmonella.
- Cheeses may contain palm oil, which can hardly be considered a healthy substance.
- Unpasteurized milk carries a high risk of becoming infected with bacteria that will cause an infection.
- Predatory fish tend to accumulate harmful substances; their meat contains mercury, which is not excreted from the human body.
These products can be replaced, which will help compensate for the deficiency of nutrients and microelements.
How to replace offal
You can replace the liver with meat; it also contains healthy animal fats and helps increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
What meat should a pregnant woman choose:
- preference should be given to veal, it is considered a dietary product and, at the same time, helps compensate for the deficiency of beneficial microelements;
- you can give preference to chicken, turkey, rabbit - these products will also be useful for a woman during pregnancy.
You should not compensate for the lack of animal protein with sausages, semi-finished products, canned food - it is unlikely that eating such products will be beneficial.
Pregnant women should not eat pork and duck - the concentration of fat is high, which can cause weight gain.
When a woman cannot eat meat and has an aversion to it, she is prescribed medications that increase the level of iron in the blood. Such treatment is prescribed by a doctor and carried out if indicated.
Recommended video:
Read: Sunflower oil on an empty stomach: indications for use
Cooking rules
If a pregnant woman decides to cook and eat liver, she can be advised to study the rules for preparing offal.
What to do:
- Buy and defrost the product, and then rinse it under running water.
- Place the liver in a saucepan and cover it with lightly salted water.
- When the water in the container turns red, drain it; this can be done after 25 minutes.
- Then the offal is left in salted water for 3 hours, then the water is drained.
The water will have to be changed several times; the liver will be soaked for at least 3 hours. It's better to keep it in the refrigerator. Soaking in pasteurized milk will help make the product soft and delicate in taste.
Soaking will help remove toxic substances from the offal that may be contained in the organ. Another procedure will relieve bitterness.
Before cooking or soaking, remove the “film” from the offal, peel it and rinse it thoroughly, it is better to do this several times.
Pregnant women are recommended:
- stew, boil or bake food;
- you can make a cake from the liver;
- and also make a roast or grill without using oil.
You should not fry the offal, marinate it or use a large amount of spices - this is unlikely to benefit the body, especially considering the woman’s position.
How and with what to combine offal, recipes for pregnant women
Let's talk about how to prepare a delicious dish without harming your health, taking into account the “interesting situation”.
Three simple recipes, table:
| Stewed with potatoes. | To prepare the dish, you should rinse and clean the offal and soak it. Then cut into cubes and place on the bottom of a roasting pan or deep frying pan. Chop the onion and saute it in butter for a few minutes. Then add to the liver. Place a roasting pan or frying pan on the fire. Wash and peel the potato tubers, cut them into strips or cubes. When the liver boils, add the vegetable. Simmer over medium heat for at least 35 minutes, first filling everything with 2 glasses of clean water or broth. Stir occasionally, after the specified time, open the lid, add spices and salt. Simmer for another 10 minutes, add chopped herbs. Cover with a lid and turn off the heat. |
| Cake with liver and sour cream. |
We take sour cream with a low fat content. Place minced liver on the bottom of a greased frying pan, coat it with sour cream or a sauce based on it. Then add the onions. The top layer is made of minced meat, we level everything and put it in the oven, preheated to 200 degrees. Bake the cake for at least 45 minutes, then take it out of the oven and try it. |
| Rice with offal. | You can use buckwheat instead of rice or give preference to other cereals. Before cooking, soak the liver in milk, then clean and rinse under running water. Grate carrots, cut tomatoes and onions. Sauté the onion in butter along with carrots and tomatoes. Then we add it to the liver and fill everything with water, or better yet, broth. Add the cereal to other products, set the multicooker timer for 45 minutes, select the program: “stewing”, or “pilaf”. This recipe is not suitable for women whose pregnancy is at an early stage of development. After all, carrots and offal are prohibited in the first trimester. |
Read: Feijoa - benefits and harms of the product, rules of use
Liver should be considered a universal product; you can use it to make casseroles, cakes and even pancakes. The main thing is to follow all the rules, do not forget about precautions and choose recipes wisely.
Foods to eat
The list of foods for the liver is varied. You definitely need to eat more vegetables, porridge, and drink vegetable juices. For example, carrot prevents the development of fatty liver.
Foods rich in cholesterol should be excluded. It is better to include vegetable fats (nuts or sunflower seeds) in your diet. From animals, butter or ghee is suitable.
Contraindications
Many people make the mistake of thinking that this offal is useful in any form; this is not entirely true. After all, the quality of the product, its storage and method of preparation are responsible for its beneficial properties and their safety.
Spoiled chicken or beef liver will never bring you any benefit; on the contrary, it will lead to poisoning and indigestion. The longer an offal is stored, the more toxins accumulate in it.
Women carrying a child under their hearts should eat only fresh liver, boiled, cooked in a slow cooker or steamed.
It is worth noting that if you have high blood cholesterol, kidney problems or an allergy to offal, do not overuse this delicacy. It is best to consult with your doctor to avoid serious consequences and not harm yourself and your baby.
1) All meat products are classified as perishable. Therefore, it is very important to look at the expiration date when purchasing. The fresher it is, the better! It is also necessary to take into account the rules of heat treatment and storage rules.
2) The liver of any animal is an organ that circulates blood, absorbs consumed food, etc. This means that if the chicken was fed food laced with antibiotics and other harmful additives, it could cause more harm than good.
3) Vegetarianism is a selfish decision of the expectant mother, who decided to put her principles above the health of the child. It’s good that now obstetricians-gynecologists are trying to compensate for the lack of everything useful with the help of vitamin complexes and similar foods that they prescribe to their wards.
Liver is a useful product that, in small quantities, has a positive effect on the body of the expectant mother. However, not everyone can consume the offal. It is not recommended to include liver in the diet during the gestational period if you have the following health problems:
- individual intolerance to liver components;
- high cholesterol in the blood;
- vascular pathologies;
- severe kidney disease;
- obesity.
Whether you can use liver during pregnancy or not, the doctor decides based on the woman’s health condition and the characteristics of the gestational period. In most cases, contraindications are temporary.