At different ages, children may experience rare urination, and parents begin to sound the alarm: what’s wrong with the baby? Most often, panic turns out to be completely in vain: a small organism can simply adapt to a new age regime, because it grows, its food becomes more solid - accordingly, the number of urinations per day becomes less.
But sometimes there are cases when the cause of this phenomenon is a serious pathology of the urinary system, which requires long-term treatment. Therefore, first of all, you need to find out what factor caused the decrease in urine output per day.
Causes of rare urination in children
The reasons for this phenomenon can be very different. Often, infrequent urination in an infant occurs due to the high fat content of the mother's milk. In such cases, the nurse must follow a certain diet in order to dilute the natural food for the baby. The second most common reason for this phenomenon is a decrease in urine output per day in accordance with age standards that every mother should know:
The third common cause of rare urination is improper drinking regimen. It often happens that a small body does not give signals that it needs liquid: the child does not ask to drink at all. In this case, it is necessary to regularly remind him that he needs to do this and even force him. If there is neither the fat content of breast milk, nor the age limits indicated in the table, nor the drinking regime, rare urination may be dictated by more serious reasons:
- pathology of the kidneys, which partially lose the ability to produce the required amount of urine;
- diseases of the ureters, their partial blockage;
- damage to the bladder (often occurs when abstaining from emptying it for too long);
- uncontrolled, improper use of diuretics;
- hysteria, hypochondria, nervous fever;
- excessive distension of the bladder;
- back or brain injuries;
- stones, sand in the kidneys or bladder;
- urethral pinching;
- new formation of blood vessels;
- urinary tract infections.
Rare urination in a child caused by these diseases and pathologies will require long-term drug treatment, including surgical intervention. Therefore, it is so important to carefully monitor the condition of a small organism and recognize trouble in time.
Natural and pathological causes
The first reason has already been mentioned above - age. The younger the child is, the smaller his bladder is, and accordingly he will empty himself more often. Another reason may be excessive psychophysiological stress, especially at the age of 4–5 years.
Some medications may have diuretic side effects. If your child is taking antiallergic medications, this must be taken into account.
The reaction to cold causes a decrease in the amount of circulating blood because the blood vessels narrow. The mucous membranes and skin are less well supplied with blood, so that more of it ensures the functioning of the internal organs. Because of this, all excess fluid must be removed, which is what the body does.
A large amount of liquid drunk, as well as food that contains it - soup, cucumbers, watermelons, etc. - also affect the amount of urine. Some pediatricians believe that disposable diapers cause additional urination, but this is a controversial issue.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with What kind of Sildenafil C3 tablets are these: instructions and reviews, price
In this regard, adrenaline is intensively produced, and the bladder begins to secrete more fluid. Most often this is noted at 3–5 years of age.
It happens that frequent urination does not depend on natural causes, but is a matter of pathology. This phenomenon indicates signs of the following diseases:
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- sand in the kidneys;
- diabetes mellitus;
- neoplasms.
What do you need to know to differentiate physiological pollakiuria from frequent urination caused by the disease?
How often a child goes to the toilet depends on the temperature and humidity of the air, clothing, and how active the child is. Hypothermia may cause a temporary increase in urination. Cold air and high humidity impair blood supply to the kidneys.
What he eats and drinks also affects the frequency of his urges. For example, cucumbers, watermelon, melon, berry fruit drinks, compotes, caffeine-containing drinks and foods, carbonated water, and any heavy drink can provoke frequent urination in a child.
The use of diuretics, or medications with diuretic side effects, also affects the frequency of urination, so you should carefully read the instructions for the drugs used.
Household chemicals used when bathing a child: bubble bath, soap, shampoo or gel, can irritate the urinary canal.
False urges to go to the toilet can be associated with stress, which children aged 4-6 years often experience, caused by the start of kindergarten or traumatic situations in the family. Pollakiuria caused by stress can last a long time (up to 5 months) and usually resolves without treatment.
Symptoms of problematic urination
A serious illness can be suspected if the following symptoms are present, which usually accompany infrequent urination in such cases:
- the urine stream is thin and has low pressure;
- urine is released in drops;
- this process becomes possible only with some specific, specific position of the body;
- burning, soreness;
- The urge to empty the bladder is felt, but is accompanied by pain and a feeling of strong pressure.
If such problems arise, it is recommended to immediately contact a pediatrician, who will be able to redirect parents to a more specialized specialist or independently identify and treat the underlying disease.
Urination due to inflammation
Urinary tract infection is the main cause of inflammation and all people are susceptible to this disease, but children are at particular risk. In infants who are constantly in diapers, diaper rash and poor hygiene can become a breeding ground for infection.
. And girls, due to physiology, suffer from inflammation much more often than boys.
The main symptoms of this disease are pain when urinating and in the lower abdomen, fever and general weakness. If these problems exist, the child urgently needs to be shown to a doctor.
Treatment
The main therapy is to eliminate the factors that provoked the disease. An individual approach is applied to each little patient. The main methods of treating bladder pathologies that result in rare urination are:
- 1. Sitz bath
At the very beginning of treatment, the water temperature of such a bath is 26 °C, but gradually it is increased to 30 °C. For inflammatory processes, sitz baths are prescribed once a day for 15 minutes.
- 2. Compresses
Compresses may be prescribed to the location of the bladder. Sometimes more extensive compresses may be prescribed for the entire body. If there is an inflammatory process in the body, soothing compresses are applied to the baby’s lower abdomen.
- 3. Therapeutic diet
This condition in children may also depend on their diet, so with this pathology it is recommended to follow a certain diet. Firstly, food should not irritate the walls of the stomach. Secondly, you need to let your child drink as much liquid as possible.
- 4. Douching
Douching is prescribed to a child only by a doctor only if rare emptying of the bladder is accompanied by pain and discomfort. If the disorder is severe, this procedure is performed using a catheter in a hospital.
If all of the above treatment methods turn out to be ineffective, and the baby’s condition does not change or improve, the only way out can only be surgical intervention (in case of serious pathology of the genitourinary system). But to confirm the diagnosis, numerous laboratory tests, tests, ultrasound and other diagnostic methods are first carried out. However, most often, rare urination in a child does not have such serious reasons and very soon goes away with the normalization of the drinking regime and proper nutrition.
Not very abundant or infrequent urination in a child can be observed at any age. Considering the fact that the norms for this indicator change as the baby grows older, parents should familiarize themselves with the basic figures in advance. If it seems to the mother that her little one has begun to urinate little or rarely, you should not take rash independent actions, you should immediately consult a doctor and take all the necessary tests to make a diagnosis.
Only with the permission of a specialist can you use folk diuretics and even adjust the baby’s diet. According to statistics, all worries in most cases turn out to be in vain, or the condition requires only minor intervention.
Uro Vaxom for cystitis
Chronic bladder inflammation lasts for decades. Antimicrobial drugs temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition and the disease returns again. Immunomodulatory agents are an alternative to antibiotics. This article talks about the drug Uro Vaxom, which stimulates the production of interferon, which destroys pathogens.
Compound
The medicine is a hard gelatin capsule. The active component is 6 mg of E. coli culture, inactivated, dried in a vacuum.
Release form
Cardboard pack with three blisters of 10 capsules each. A prescription is required to purchase. The medicine is stored at room temperature.
Irina, 30 years old: “The only remedy that helped defeat chronic cystitis, be sure to read the article!”
Indications
Used in combination with antiseptics, antibiotics or independently. Recommended for adults and children over four. There is no information about the effect on the fetus and newborn. Therefore, the medicine is not prescribed.
Application
The medicine for cystitis Uro Vaxom is taken in the morning before meals, 1 capsule, the dose for children and adults is the same. If the child does not want to swallow the pellet, the contents can be mixed with milk or fruit juice.
When treating exacerbations, the duration of use is ten days. If prevention of manifestations is indicated, the drug is taken for 90 days after consultation with a doctor.
Side effects
Undesirable effects occur in people who are hypersensitive to the substances of the drug. They manifest themselves as digestive disorders or skin rashes.
Therefore, the answer to the question: “Can Uro Vaxom cause cystitis” is negative.
Contraindications
The safety of the drug for the fetus and infants has not been proven, since no studies have been conducted. Therefore, Uro Vaxom is not prescribed to pregnant women or breastfeeding women. You must be careful when carrying out routine vaccinations for your child.
It is not recommended to use an immunomodulator 2 weeks before and 30 days after vaccination. A reasonable solution in this case would be to delay vaccination. The immunomodulator is contraindicated in alcoholics.
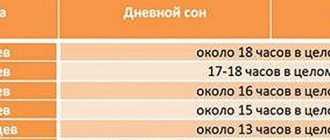
Age norms for daily and one-time volume of urine excreted, number of urinations
Before you go to the doctor, you need to take into account an important circumstance. Mothers often feel that the child has begun to write less than he did several weeks or months ago. In fact, this may simply be a consequence of age-related changes. Parents should stock up on a memo that indicates how many times a day at what age the baby should relieve himself, and what the normal single and daily volumes of urine are.
- From birth to six months of life. A newborn baby is able to pee up to 20-25 times a day, releasing 20-35 ml of fluid at a time. On average, they excrete up to 400-500 ml of urine per day.
- From six months to a year. The number of urinations is reduced to 15-17 per day. The one-time volume increases by approximately 5-10 ml, the daily volume - by 100 ml.
- Up to three years. The number of “approaches” is already 10-12 times. During one urination, the child excretes about 60-90 ml of the product, per day - 700-800 ml.
- Up to seven years old. The number of urinations is no more than 7-9. But, if up to five years of age, 70-90 ml of liquid is removed from the child’s body at a time, then in the next two years the one-time volume is already 100-150 ml. It turns out that up to five years the daily volume of urine is 900-1100 ml, after that – 1100-1300 ml.
- Up to nine years old. With the same number of urinations, the one-time volume increases by 50 ml, the daily volume - by 200 ml.
- Up to 13 years old. Children go to the toilet little by little up to 6-7 times a day. The single volume of fluid released is close to 250 ml, the daily volume is 1800-1900 ml.
It should be taken into account that the instructions contain average indicators. Data in each specific case may shift slightly in one direction or another depending on the characteristics of the child’s development, activity and nutrition.
The baby is urinating very poorly! Don't miss the symptoms!
At home, it is quite possible to suspect the presence of the disease.
- The stream of urine became thin and the pressure weak.
- Urine is not released in a stream, but in separate droplets.
- A child can pee in only one position (squatting, standing or leaning back, but obviously not in the way intended by physiology).
- The child complains that “the pussy burns, cuts or hurts.”
In any case, parents should not let their guard down. Have you noticed that your child is writing less often? Watch him. This can be either normal or a sign of a urological disease. Any doubt should bring parents to the doctor's office, first of all, taking general urine and blood tests.
Remember that any disease can always be successfully treated only at an early stage .
A short course of medication, a trip to a sanatorium, and a light diet will save your child from troubles forever. But in any case, the best medicine at all times is attention and love for the baby.
The main physiological reasons for infrequent urination and methods of assistance
In cases where a child begins to write little, it is first necessary to consider the possibility of exposure to physiological factors:
- The child is not eating properly. In the case of a baby, this may be the result of non-compliance with the postpartum diet by the nursing mother. Often, a baby begins to pee less than usual when switching from natural feeding to mixed or artificial feeding.
- The drinking regime is not observed. The specificity of a child’s body is such that it does not always give signals in the form of thirst, indicating a lack of fluid. An adult should monitor how much water the child receives per day and, if necessary, replenish these supplies.
- Fluid leaves the body in a different way. During the summer heat, with increased activity of the child, with vomiting or diarrhea, there is simply no liquid left for the formation of urine.
If the likelihood of these causes being influenced is very low, you need to visit a doctor who will conduct the necessary studies and determine why the baby urinates little or rarely.
What examinations will help to understand the situation?
Any diagnostic search is built from simple to complex. Diagnosis of urinary tract pathology begins with a general urine test. This routine research method helps guide further research in the right direction. Any diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract are manifested by changes in the general analysis of urine; accordingly, the absence of changes as such allows us to exclude such diseases.
For a more detailed examination, the following are usually prescribed:
- urine analysis using the Nechiporenko method (study of the content of erythrocytes and leukocytes in 1 ml of urine);
- urine analysis using the Zimnitsky method allows you to study in detail the amount of urine excreted during the day and its laboratory parameters);
- ultrasound and tomography to study the anatomical structure of the excretory system;
- X-ray examination with a contrast agent allows you to evaluate the rate and nature of urine output.
Possible pathological factors provoking the condition
All pathological causes can be divided into two large groups: in some cases, urine is not formed, in others it accumulates in the bladder, but does not come out. This is a consequence of the following factors:
- Kidney disease, which causes tissues to lose their ability to produce urine.
- Partial or complete blockage of the ureters (stones, sand in the kidneys or bladder).
- Problems with the bladder due to prolonged refusal to empty it (for example, excessive distension).
- Incorrect or prolonged use of diuretics.
- Psychological discomfort, hysteria, nervous breakdown.
Advice: Changes in the frequency and quality of urination are often observed in children who find themselves in a new environment (kindergarten, school). In some cases, due to the child’s shyness, in others, due to improper behavior of the staff, the baby stops writing as needed. He begins to tolerate it, which quickly becomes a habit. Sometimes a simple conversation is enough to discover this reason.
- Neoplasms in the ureters and blood vessels.
- Consequences of spinal or brain injuries.
- Infectious processes in the genitourinary system.
The listed conditions are not diagnosed by eye. Even an experienced doctor must first conduct a series of studies. Parents should pay attention to the presence of symptoms characteristic of problems in this area.
Signs of illness in diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus
These are two different pathologies, but they have one common symptom - increased urine output. Diabetes occurs due to disturbances in the endocrine system. The body suffers from a lack of insulin, causing blood sugar levels to rise. The disease is accompanied by disorders of fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism and disruptions in water-salt balance. Parents need to be more attentive to the growth of the baby’s appetite if at the same time body weight decreases and the skin becomes dry.
Due to frequent urine output, children are susceptible to dehydration, which must be eliminated with the help of special medications. Otherwise, after some time, the baby’s skin will be covered with blisters with pus. The distinctive symptom is painful itching of the skin.
This disease is less common than diabetes, but it requires hormonal adjustments.
Symptoms of pathology and tests that need to be taken if problems are suspected
In cases where a child pees a little, but no additional signs of pathology are observed, physiological reasons are most often to blame for the condition. You should think about problems if the following symptoms occur against the background of retention or insufficient amount of urine:
- Urine is released in drops or a very thin intermittent stream.
- A child may not write all day, and the process becomes possible only when his body is given a certain position.
- A newborn cries while passing urine, and an older baby complains of burning or soreness.
- There is an increase in body temperature, even a slight one.
- The baby's behavior changes. He becomes moody, lethargic, drowsy.
- The color or smell of urine changes significantly.
- After sleep, no matter how long it lasts, the baby develops swelling on the face.
The process of diagnosing the condition begins with a general urine test. For the purpose of a more detailed examination, urine tests are often prescribed using the Nechiporenko or Zemnitsky method, ultrasound of the excretory organs, and x-rays of the urinary ducts using a contrast agent. Only after it becomes obvious why the child’s body retains or does not produce urine, therapeutic manipulations and medications are introduced.
What tests need to be done to find the cause?
When a child pees frequently , the root cause of this phenomenon can be identified through laboratory diagnostics.
The pediatrician will definitely prescribe a general urine test - it is collected in a clean container. It is necessary to rinse the pot thoroughly to avoid distortion of the analysis. You cannot collect urine in the evening; you only need morning urine. After this, you need to take the container for analysis - storing it in the refrigerator is prohibited, this will distort the result. Based on this general analysis, it will be clear whether the baby is healthy and whether he has pyelonephritis, gloperulonephritis, cystitis, or urethritis.
To more accurately diagnose the disease, urine testing for protein and glucose may be necessary. To do this, daily urine is collected; such an analysis is necessary for diagnosing glomerulonephritis and other kidney diseases. If there is a lot of glucose in the urine, then this is evidence of diabetes. With a large amount of salts, the baby may develop cystitis, as an addition to another disease.
Home Treatment Options
In cases where the diagnosis allows us to exclude pathological processes, doctors recommend ensuring that the baby does not have a large amount of salty foods in his diet. Both newborns and adolescents should receive enough fluids per day. Its volume must be increased as the child’s activity or ambient temperature increases.
If the cause of the phenomenon turns out to be a pathological process, the approach to each child should be selected individually. Most often, in case of problems with the passage of urine in a normal volume or with the required frequency, the following manipulations are used:
- Sitz baths. Initially, cool water is used, then the temperature gradually rises.
- Compresses. Most often these are soothing compresses on the bladder area, but treatment of larger areas is also allowed.
- Medical nutrition. Food prepared for a child should not irritate the walls of the stomach.
- Douching. Used as an auxiliary method for painful emptying of the bladder.
Medications are prescribed only by a doctor. You should not hope that the baby will begin to write as it should if you give him a diuretic. Such actions can significantly complicate the situation.
Read the article on how to treat erythema toxicum in newborns
Violation of the frequency of urination can be either a variant of the norm or a sign of various urological diseases. Laboratory tests and specialist consultation are required to clarify all the details of the situation. In accordance with the results of a comprehensive examination, the necessary examination may be prescribed.
Reasons for the situation
The main key to solving the problem of infrequent urination is to find out the cause. Often, correction of the drinking regime and diet, and more careful care of the child almost instantly eliminate the problem.
On the other hand, knowledge of the causes of the disease helps to correctly influence them or radically eliminate them, that is, to prevent the development of the disease or its transition to a chronic form.
The causes of infrequent urination are different for babies and older children. A small (infant) child pees little as a result of the following points:
- transition from full breastfeeding to mixed or artificial breastfeeding;
- insufficient volume of fluid consumed, especially in the hot season;
- transition from drinking from a bottle to a baby cup;
- refusal to use modern diapers (so-called “pampers”).
Rare urination in an older child, who already clearly understands and exercises control over his own excretory functions, is caused by the following situations:
- various types of psychological discomfort (reluctance to show intimate parts of the body to other people, for example, at school; lack of proper sanitary and hygienic conditions in public toilets, a false sense of something shameful in natural practices in the appropriate environment in a children's group);
- insufficient fluid intake or inconsistency with physical activity;
- urological diseases themselves.
Thus, in this situation, there are 2 main possible reasons for rare urination in children:
- producing insufficient urine;
- production of a sufficient amount of urine, but it is retained in the bladder or other parts of the urinary tract.
It is important to understand that it is possible to thoroughly and definitively understand the causes of rare urination only with the help of a specialist. Any independent attempts at treatment can lead to a worsening of the condition and provoke irreversible disorders of the urinary system.
Clinical picture
The famous Soviet pediatrician A.V. Papayan compiled a table corresponding to the age of the child and the volume of urine excreted.
Based on the data in this table, parents of a child of any age can quite accurately determine whether the child really has impaired urination or whether this is the age norm. In this case, it is necessary to evaluate physical activity, foods included in the diet, temperature conditions, that is, all points that influence the process of urine formation.
Monitoring the number of urination acts and urine volume should be carried out over several days. It is advisable to record the amount of fluid you drink and the volume of urine you pass.
Parents should pay attention to obvious symptoms of diseases of the urinary system, namely:
- increase in body temperature (even slight);
- change in the child’s behavior (moody, lethargy, drowsiness, unusual tendency to quiet games);
- change in urine color;
- pain during urination (a small child begins to cry when sitting on the potty, and then quickly calms down);
- strong smell of urine;
- swelling of the face, especially if it occurs in the morning or is noted immediately after sleep (so-called “renal edema”).
Any of the above signs is a reason to consult a doctor and further conduct a detailed laboratory and instrumental examination.
If no changes in the child’s behavior are noted, and rare urination appears from time to time, then most likely this is an individual characteristic of a particular child.
What examinations will help to understand the situation?
Any diagnostic search is built from simple to complex. Diagnosis of urinary tract pathology begins with a general urine test. This routine research method helps guide further research in the right direction. Any diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract are manifested by changes in the general analysis of urine; accordingly, the absence of changes as such allows us to exclude such diseases.
For a more detailed examination, the following are usually prescribed:
- urine analysis using the Nechiporenko method (study of the content of erythrocytes and leukocytes in 1 ml of urine);
- urine analysis using the Zimnitsky method allows you to study in detail the amount of urine excreted during the day and its laboratory parameters);
- ultrasound and tomography to study the anatomical structure of the excretory system;
- X-ray examination with a contrast agent allows you to evaluate the rate and nature of urine output.
General principles of therapy
Treatment for urinary disorders is determined by its cause. If pathology of the urinary tract is excluded, then the following must be done:
- give the child enough fluids;
- do not overuse salty foods in your diet;
- increase the amount of fluid when the ambient temperature rises (during the hot season) or during active physical activity.
It is important to teach the child not to be embarrassed by the situation that arises and not to teach him to restrain natural urges for a long time. Prolonged overfilling of the bladder leads to backflow of urine into the ureters and higher-lying sections. In case of chronic obstruction of urine outflow, ureteral reflux and even renal failure can form.
A pediatric urologist treats diseases of the urinary tract. It is with its help that you can quickly cope with the disease and prevent its transformation into a chronic form.
Dr. Komarovsky at the forum emphasizes the need to consult a specialist at the slightest suspicion of kidney disease. Only timely treatment will help avoid complications and chronicity of the process. The laboratory and instrumental examination will not cause any harm to a healthy child.
Urinary problems in children
Children never have stable physical indicators, and the younger the child, the more they can vary. At a certain age, a child may urinate quite rarely. In such situations, most parents wonder: what’s wrong with the baby’s health?
Detailed reasons will be discussed below, but for now it is enough to understand that this may not be a disease, but a variant of the age norm. And, of course, rare urination in a child can be pathological.
If the cause is a disease, a correct and thorough diagnosis will be required, as well as a full course of treatment so that the childhood illness remains in childhood.
In addition to the frequency of urination, it is necessary to note changes in other qualities - urine indicators, its volume per day and in a single portion, the rhythm of urination.
Intermittent urination in a child is a reason to contact a specialist. Do not hesitate, since any acute pathology of the urinary tract leads to increased intoxication of the body and can be complicated by acute inflammatory processes in other organs and systems. In addition, untreated pathology of the kidneys and urinary tract often develops into a chronic condition and worries a person throughout his life.
Diseases that cause frequent urination
There are a number of diseases that cause a child to frequently run to the toilet. Here are the main ones:
- Urinary tract infection, which has already been written about above.
- Diabetes mellitus, in which the child not only often runs to the potty, but also drinks a lot. This is the so-called latent period
.
At the same time, the child begins to eat poorly, loses weight and weakens before our eyes
. In this case, timely seeking help from an endocrinologist will help. - A hyperactive bladder is, rather, not a disease, but a psychological state of the baby, which should be addressed by a neuropsychiatrist.
- Enuresis is not only frequent, but also erratic urination, especially at night.
- Kidney pathologies can also cause frequent trips to the potty.
In any case, if a child begins to pee frequently for no reason, you should consult a doctor. Even if no pathologies or inflammatory processes are identified, and the cause turns out to be the most banal, this is in any case better than an advanced disease.
27 March 2014, 13:42
girls, the situation is like this... my daughter has been sick for 4 days... only today there is no fever... all these days she drank a lot and peed... but today she drinks a lot and doesn’t pee! completely... I woke up in the morning, took off the diaper, it was full, and that’s it... 7 hours and I didn’t pee or poop... what needs to be done??
Subscribe to the baby.ru channel in
27 March 2014 13:43
Nothing! it replenishes your fluid supply! pee later! At night he also sleeps and doesn’t pee, so everything is ok I think
27 March 2014 13:44
Button
She still pees at night, so we put on a diaper at night
27 March 2014 13:45
I'm speaking figuratively! no big deal, keep watching until the evening, he will pee again! and drink more!
27 March 2014 13:43
DID THE DOCTOR CALL?
27 March 2014 13:45
I lovecontests
that they called her sick, she will come again tomorrow... but specifically for today’s situation, no... the doctor is no longer seeing her, she has an appointment, only an ambulance... but they don’t go without a fever..
27 March 2014 13:43
Let's drink more water! It happens, there's nothing wrong with it
27 March 2014 13:46
Nadinka
and so he drinks all day, eats like a mouse... he’s sick, poor thing..((one was cured, the other is sick(
27 March 2014 13:55
Get well soon, daughter! Don't worry, the body's water supply will be replenished and it will start writing
27 March 2014 13:57
Nadinka
Thanks, I'll keep watching..
27 March 2014 13:44
wait, after a high temperature, most of the liquid is absorbed as it replenishes lost moisture. In general it's ok
27 March 2014 13:44
in the bathtub, put water in the keys and let her go to the toilet in the potty in the bathtub
Other articles on this topic
Current posts
Pimple in a child
12 November 2020, 15:04
Girls, there was some kind of red pimple on the side of my daughter’s nose and she picked it off until it bled, I burned it with brilliant green... I’m thinking...
Antibiotic for fever
12 November 2020, 15:04
Girls, hello. Today I called a private doctor
.
He listened and said that his breathing was heavy, but there was no wheezing
. But he still prescribed antibi...
Does your child rarely go to the toilet? This phenomenon occurs in children of all ages. Often the phenomenon can be eliminated after minor adjustments to lifestyle and nutrition. But it happens that rare urination becomes a sign of a serious illness.
. In what cases can a phenomenon be considered normal, and when does it indicate a pathology of the urinary system? What can parents do?
What kind of urination in children is considered rare?
When looking for the reasons for rare urination in a child, you should start with an understanding of the process itself and its norms.
Urination is the process of filtering and removing urine from the body through voluntary muscle contraction and emptying the bladder. There are two important processes in urination - filtration and absorption (suction). The quality of urination depends on the activity and coherence of these processes.
The frequency of urination varies among different age groups. Human kidneys are one of the few organs that can develop outside the womb. The renal cortex and medulla can develop over several years, and the above-mentioned processes of absorption and filtration occur with their own characteristics in each age period.
To understand the facets of pathology, you need to understand what is considered normal. According to data adopted by the WHO (World Health Organization), the norms for urination in children are as follows.
| 1 - 5 days of life | 4 — 6 |
| Up to 6 months | 20 — 25 |
| 6 -12 months | 15 — 16 |
| 1 -3 years | 10 — 12 |
| 35 years | 7 — 10 |
| 5 -7 years | 7 — 10 |
| 7 - 9 years | 7 — 9 |
| 9 – 11 years | 5 -7 |
| 11 – 13 years | 5 — 7 |
Accordingly, a decrease in the frequency of urination compared to the lower limit of the age norm can be considered rare urination.
Why might urinary frequency change?
When considering this issue, it is necessary to highlight two main criteria - the child’s age and physiology. If everything is relatively clear with the first, then the second may raise questions.
The physiological nature of the problem of rare urination is caused by reasons not related to the child’s illnesses. Pathological is the opposite of physiological, indicating the presence of a disease.
Further, the causes of rare urination in children will be considered from the point of view of both criteria.
Physiological reasons.
- During the neonatal period and infancy, when the child is fed with single-component feeding (milk or formula), the reason for rare urination may be the increased fat content of the mother's milk. High-fat milk can also cause infrequent bowel movements in babies. The only effective way to avoid such problems is to regularly change the nursing breast. Primary milk, that is, milk from the “new” breast, is the least fatty. Additional soldering is also acceptable.
- In the period from 6 months and beyond, the cause may be either a physiological change in the rhythm of urination in a child or a violation of the diet. In the latter case, you need to adjust the calorie intake and the amount of fluid consumed.
Pathological reasons.
- Kidney diseases, both congenital and acquired. Parents, as a rule, learn about congenital pathologies in the first months. And acquired diseases include infectious diseases. In addition to rare urination, pain, burning, itching, and pain in the lower abdomen may be observed. These diseases are treated according to the cause that causes them.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract or mechanical blockage of the ureters (presence of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract). They are characterized by intermittent rather than rare urination in the child. Additional symptoms are the same as for inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- Long forced abstinence from urination. After it, a reflex spasm of the bladder and urinary canal occurs, which causes urinary retention in children. Often this condition goes away on its own, but if it lasts a long time and causes severe pain, catheterization of the bladder is resorted to. In this case, painful urges and tension in the walls of the bladder, felt as a spasm, may occur.
- Neurological and mental disorders. Thus, hysterical seizures can cause both urinary incontinence and acute retention. Elimination of the seizure or neurological syndrome resumes spontaneous urination. In this case, symptoms characteristic of neurological pathologies will be observed - tics, paralysis and paresis. With mental disorders, disturbances of consciousness and behavior immediately catch the eye.
- High body temperature, leading to dehydration, and as a result, rare urination. Insufficient fluid replacement when it is lost will not allow the body to get rid of toxins.
- Problems with urination in children can also arise due to injuries to the spinal cord and brain (concussion, fracture). In such cases, the child is given a bladder catheter for the entire period of recovery and treatment of the injury.
What tests are prescribed for children with rare urination?
For urinary disorders in children, a pediatrician, nephrologist or urologist should order examinations to determine the causes and make a diagnosis.
The following tests are prescribed:
- a general urinalysis determines the amount of fluid, its acidity, the presence of sediment, salts, glucose, leukocytes and erythrocytes, which allows us to judge the probable nature of the pathology;
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko allows you to identify the source and localization of the infectious process in 1 ml of urine;
- A general blood test helps determine the state of the immune system in general terms, as well as the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- Bacteriological culture of urine if a bacterial infection is suspected allows one to identify the pathogen in order to prescribe the necessary treatment.
In addition, research is being conducted:
- measuring the number of urination acts per day. This is the first thing parents or the child himself pays attention to;
- measuring the volume of a single portion of urine, which allows you to determine the deviation from the age norm;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and ultrasound of the kidneys, which helps to see structural changes in the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract;
- voiding cystourethrography - this innovative method allows you to visualize congenital malformations of the bladder, kidneys, and ureters;
- scintigraphy to detect tumors in the kidneys and urinary tract.
Age norms
In order not to start sounding the alarm in vain, but also not to miss the onset of the disease, parents should know how many times their child has to go to the toilet to defecate.
Pediatric urologists usually associate the daily number of bowel movements with the following figures:
- from the first days of life – 5;
- up to six months – 20;
- about a year – 15;
- 1–3 years – 10;
- 3–6 years – no more than 8;
- after 6 years – 5.
This difference in the number of micturitions is due to the growth characteristics of children and the formation of the organs of the urinary system. All life support systems complete their final formation by adolescence. So, the kidneys develop for several years after birth. At the same time, the growth of the baby, the level of physical activity, natural changes in the body, etc., influence the formation of paired organs, which respond to all this by increasing the number of mictions.
Sometimes - hypothermia. If your baby has been sledding all day, and then at home you give him tea with honey, then frequent urination is a natural phenomenon.
What can parents do?
If urinary retention is not painful, you can try to provoke it with warm sitz baths and the sounds of flowing water.
If urination does not occur, you should call an ambulance to have the bladder catheterized.
If a child has urinary disorders, the first thing you need to pay attention to is nutrition and water consumption. Not every liquid is equal to water, so it is worth teaching your child to drink regular clean water regularly. Fatty and spicy foods, as well as fast carbohydrates and coffee, which tend to retain fluid in the body, should be excluded from the diet.
Urinary problems in children are not a cause for panic, but a cause for concern. Therefore, timely contact with a specialist is the main and first thing parents should do when such problems arise.
Author: Sukhorukova Anastasia Andreevna, pediatrician
ARVI and influenza
After harmful microorganisms enter the upper and lower respiratory tract, a primary infection occurs. And after it is carried by the bloodstream throughout the body, a secondary one may appear, which can affect the organs of the urinary system. Harmful microorganisms produce waste products that can lead to intoxication of the child’s body, and then urination becomes more frequent.
In addition, respiratory infection in children is sometimes accompanied by the presence of neurogenic urinary dysfunction. With it, there is no pain during urination, no inflammation in the urinary tract and kidneys. But if the disease is not treated, urinary incontinence may develop.
Prevention
If you have a hereditary predisposition to diabetes, you should regularly undergo blood tests to determine your glucose level. If necessary, this will allow timely correction of the indicators, preventing the development of vulvitis and subsequent damage to the genital tissues. Parents need to ensure that children are not on contaminated surfaces without underwear.
Physical inactivity is harmful to health and creates favorable conditions for the deposition of rocky conglomerates. Therefore, even if a child is disabled, it is necessary to promote his mobility - turn him over, help him take a half-sitting position. Controlling the quality of food and water consumed minimizes the risk of developing stones.