A headache in the back of the head is a very unpleasant phenomenon, causing a lot of inconvenience and often limiting performance. The causes of pain in the occipital part of the head can be very different, from diseases of the cervical spine to neuralgic pathologies.
If you don’t know why the back of your head hurts, then this article is for you. It collects the main causes and describes methods of treating headaches in the back of the head. In any case, you must remember: if you have a headache in the back of your head, you should not self-medicate, you need to seek medical help. Of course, we are not talking about isolated cases of pain in the occipital region. As a rule, they are caused by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, stress, extreme hunger, and also due to excessive consumption of foods with caffeine or chemical additives.
- Initial consultation – 3,200
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
Causes of pain in the back of the head
A severe headache in the back of the head never occurs without a reason. It can be a signal of diseases:
Depending on the cause of the headache in the back of the head, it can be of a different nature and be accompanied by certain clinical manifestations, which must be clearly described to the doctor.
Pain in the back of the head due to osteochondrosis
If the neck and back of the head hurt, the reasons may be the presence of a disease such as osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The disease manifests itself in the destruction of the discs of the cervical vertebrae, and pain appears constantly and is felt not only in the neck and back of the head, but also in the temples. They become more intense with head movements and may be accompanied by:
- tinnitus;
- nausea;
- coordination disorders;
- veil before the eyes and double vision.
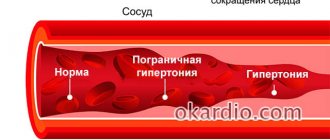
Pain in the back of the head with hypertension
Hypertensive attacks are characterized by the appearance of bursting pain, which is accompanied by pulsation. They may appear when waking up after a night's sleep. In addition, it is observed:
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased pain when trying to tilt your head;
- reduction of pain after sudden vomiting.
Pain in the back of the head with increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is characterized by:
- pressing, bursting pain in the occipital region or throughout the head;
- increased pain in bright light and loud sounds;
- heaviness in the head and pain in the eyeballs;
- vomiting, which does not reduce pain syndromes.
Pain in the back of the head due to cervical myositis
Inflammatory processes in the neck muscles caused by hypothermia or injury are characterized by pain symptoms that spread from the neck to the occipital, shoulder and interscapular areas. It appears when you move your head and is asymmetrical.
Pain in the back of the head due to occipital neuralgia
Neuralgia of the occipital nerve, resulting from hypothermia or accompanying osteochondrosis, is characterized by very strong shooting pains. They occur periodically, like attacks with any attempt to change the position of the head.
During rest, a slight pressing pain is felt in the occipital region.
Pain in the back of the head due to vascular diseases
Spasms of the cranial arteries cause throbbing pain, which becomes stronger when trying to move the head and subsides somewhat at rest. The pain begins in the back of the head and eventually spreads to the frontal area. It is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the head and begins in the morning after waking up.
Pain in the back of the head and dizziness are the most common complaints with which patients turn to doctors.
The causes of unpleasant sensations may be due to various pathological processes localized in the head and neck area, the presence of psychogenic or somatic diseases.
Severe organic lesions (tumors, injuries, congenital anomalies) are diagnosed only in 5-8% of patients. In other cases, doctors diagnose “migraine”, “tension headache”, “disease of the cervicothoracic spine” or “hypertension”.
What to do if you feel sick and have pressure in the frontal or occipital part of your head?
Cephalgia (or headache) can occur with various disorders in the functionality of organs.
More often it is provoked by changes in blood pressure, but sometimes it occurs regardless of this indicator. If the pressure is normal, but the head still hurts, then in weather-dependent people this condition is associated with changes in atmospheric pressure.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:5ODFn1tbTzc
In this case, the body does not have time to adapt to new conditions, which increases intracranial pressure and blood viscosity. Poor oxygen supply to the brain causes headaches.
In addition, when there are no changes in pressure, but the head hurts, the causes may be organ damage (for example, skull trauma, brain abscess or meningitis).
If the back of your head hurts, this immediately raises the question of what kind of pressure is wrong. But with normal tonometer readings, discomfort also occurs, and it is usually associated with the following reasons:
- skull injuries;
- infectious pathologies;
- neuralgia;
- brain abscess;
- pituitary adenoma;
- meningitis.
Often, when the question arises as to why there is a headache, nausea, or vomiting, but the blood pressure is normal, the cause should be sought in injuries to some organ (for example, the skull).
At the site of injury, blood circulation is disrupted, hematomas occur, and sometimes intracranial pressure rises.
With an infectious lesion, headaches occur due to intoxication. The pressure is normal or low.
Knowing at what pressure the back of the head hurts, sometimes you have to deal with the fact that discomfort is observed with normal tonometer readings. The problem may be neuralgia.
Pain occurs due to impaired conduction of impulses, when pinching or inflammation constantly provokes the sending of alarm signals.
With a brain abscess, the tissue degrades and pus appears in the cavities. The condition is accompanied by migraine, fever, tremor, intoxication, and blurred vision.
Pituitary adenoma is manifested by cephalalgia, vomiting, deterioration of vision, speech, and functioning of the genital area.
Meningitis is characterized by inflammation of the membranes of the cerebral cortex. It can occur due to fungal, viral, bacterial infection, hypothermia, or a decrease in the body’s protective functions.
Other factors
You can determine what pressure a patient has if the back of his head hurts using a tonometer.
If the indicators are normal, then, in addition to the physiological factors that cause discomfort against the background of stable normal blood pressure, it is worth paying attention to optional reasons:
- increased muscle tension;
- mental stress, frequent stress;
- alcohol abuse;
- errors in nutrition;
- excessive consumption of caffeine-containing drinks;
- dehydration;
- smoking;
- changing weather conditions.
When the back of the head hurts under normal pressure, the cause can be both mental and physical stress, as well as more serious health problems.
If the back of the head hurts, a therapist will help you understand what pressure is causing occipital discomfort in the patient.
If you have a headache in the back of your head, your local therapist will measure your blood pressure at your appointment, listen to the patient’s complaints, and prescribe tests.
Based on the diagnostic results, he will give a recommendation on which specialist should be contacted next. So, when observed:
- nausea with frequent cephalgia, this may be a consequence of head injuries (in this case, examination by a traumatologist is recommended; brain damage is possible, which leads to these symptoms and requires urgent help);
- the pain is pulsating, but there was no damage, then you need to visit a vertebrologist;
- pain that occurs with every movement of the neck, then you need to see a neurologist;
- problems with blood vessels - consultation with a cardiologist is required;
- suspicion of tumor development; treatment is continued by the oncologist.
They form a bed for the occipital lobe of the brain, which is responsible for processing information coming from the eyes (it is in the brain that the image is formed). The brain itself does not hurt, but with inflammation or tumor in this area, the membranes of the brain will react to the increase in intracranial volume. With such pathologies, visual symptoms are also observed.
- Deep in the brain lies the pons
This is a formation of white matter interspersed with gray. It is not fused with the occipital lobe, but is the second conditional continuation of the spinal cord into the cranial cavity (the first continuation, which directly passes into the spinal structures, is the medulla oblongata). From the pons depart the cranial nerves that carry commands to the face (trigeminal, facial and abducens), as well as the nerve that carries information from the vestibular apparatus and the inner ear. With pathology in this area, there will be a headache in the back and hearing impairment along with balance.
- Cerebellum
The cerebellum, an organ responsible for balance, muscle tone and coordination of movements, extends from the pons not downwards, but sideways, under the hemispheres of the brain. It consists of two hemispheres and a small area in the middle - the cerebellar vermis. If there is inflammation or swelling in this area, the head will hurt in the back, and there will be a lack of coordination and muscle tone.
- The pons enters the medulla oblongata
Here are the starting points of the four cranial nerves, which carry commands to the muscles of the pharynx, mouth and neck, coordinating the work of the heart, bronchi, lungs and intestines. On the surface of the medulla oblongata there is also the main path along which cerebrospinal fluid - a liquid that supports metabolic and nutritional processes between all parts of the brain and blood - passes from the cranial cavity to the spinal canal of the spine.
- The medulla oblongata passes into the spinal cord, and the spinal nerves depart from the latter
This brain exits the cranial cavity through the foramen rotundum. All the cranial nerves formed in the area of the pons and above exit next to it. There are also vessels here: arteries that bring blood to the occipital lobe of the brain and its trunk (this includes the pons, cerebellum, midbrain), veins and lymphatic vessels.
It is located inside a special canal in the spine, its membranes are located around it (the same ones surround the brain), and cerebrospinal fluid circulates between them. Compression of the spinal cord or the nerves that come from it by bony structures can cause pain in the back of the head and neck area. Basically, the symptom accompanies pinching or inflammation of the occipital nerve, which, formed from the fibers of several pairs of spinal nerves, provides sensitivity to the skin from the back of the head to the area behind the ears.
- The neck contains a large number of muscles
They can become inflamed and pinched by the bone structures of the spine. This is also accompanied by headache.
The spine is held in the required position using the ligamentous apparatus. It is especially developed in the cervical region, where the first two vertebrae are connected to each other and to the occipital bone by an extremely unstable joint.
- The head and neck are covered with soft tissues: skin and subcutaneous tissue. Inflammation can also develop here, and this will cause pain.
With intracranial pressure and head injuries, severe nausea occurs. The head begins to ache in the occipital area and the attack does not go away after taking painkillers.
Pain increases with:
- coughing and sneezing;
- walking;
- sudden movements;
Intracranial pressure is accompanied not only by nausea, but also by the following symptoms:
- sweating;
- cold extremities;
- severe headache in the morning;
- inflamed capillaries and bruises under the eyelids;
- double vision;
- strong heartbeat;
- a sharp decrease in overall performance and attention.
Main reasons:
- congenital vascular defects;
- injuries;
- intoxication;
- meningitis;
- hematomas;
- encephalitis;
- concussion.
In some cases, hunger lowers blood pressure.
Symptoms:
- irritability;
- difficulty concentrating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lethargy and increased drowsiness.
Diagnosis of the causes of changes in intracranial pressure is carried out in medical centers.
Violations are detected thanks to:
- visiting an ophthalmologist - if the pressure is elevated, the retinal vessels will be dilated or retinal edema will be diagnosed;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound of the brain;
- MRI;
- electroencephalography.
To stabilize the condition it is recommended:
- regularly take medications and drinks with a diuretic effect;
- increase the dose of vitamin C, citrus fruits;
- do not visit baths and saunas;
- swimming;
- avoid mental and physical overload;
- give up excessive consumption of fatty and salty foods;
- refrain from using air transport;
- include foods rich in potassium in your diet.
During an attack, fasting is recommended, then increased intake of fluids and citrus fruits. After an attack, it is recommended to relax, ventilate the room and remove clothing that restricts movement and the flow of oxygen.
Symptoms of a concussion:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- loss or confusion of creation;
- temporary blindness;
- loss of appetite.
If signs of a concussion appear, it is recommended to go to the hospital.
Before the ambulance arrives, it is recommended:
- apply cold and ice to the forehead and back of the head;
- place the patient on his back or side;
- treat wounds if they exist with hydrogen peroxide.
Head injuries are accompanied by symptoms:
- flow of blood or light fluid from the ears and nose;
- the skin darkens or turns blue around the eyes;
- swelling of the neck;
- loss of consciousness;
- sharp pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Help for head injuries is as follows:
- the patient is placed on his back;
- wounds are treated with hydrogen peroxide;
- if necessary, artificial respiration is performed;
- ice in a bag is placed in place of the damage;
- if fragments of bone or metal protrude from the wound, they cannot be removed - you must wait for the help of a specialist;
- the patient is provided with complete rest.
Diseases
- Basilar form of migraine. During an attack, the vessels of the brain suffer the most - spasm of cerebral vessels occurs, followed by progression of cerebral ischemia, which provokes disorders of the vestibular apparatus. The back of the head suddenly begins to hurt severely; the attack may be accompanied by dizziness and short-term loss of consciousness.
- Cervical form of migraine. Diagnosed in patients with a history of spondylosis and osteochondrosis. The attack is caused by tension in the muscular cervical apparatus and a sharp turn of the body. Cervical migraine is determined by a set of characteristic symptoms: pressure in the occipital segment, vestibular, visual, and auditory disturbances.
- Tension headache. There are chronic and episodic forms. Mental disorders, including depression, play a priority role in the pathogenesis. Localization is bilateral - the back of the head and neck hurt, dizziness, fatigue, irritability, loss of appetite, and anxiety are observed.
- Vascular. Causes: fluctuations in vascular tone due to surges in blood pressure. In most hypertensive patients, there is no correlation between increased blood pressure and pain. Heaviness in the occipital part of the head and dizziness are usually characterized by a hypertensive crisis, but in 30% of patients these symptoms indicate the presence of chronic hypertension or hypotension.
Diseases of the cervical spine:
- Spondylosis: with spondylosis, cracks and tears develop in the cartilage discs, and as the pathology progresses, intervertebral hernias develop. The pain is dull, prolonged - the back of the head begins to press, the shoulders ache, the mobility of the cervical segment of the spinal column is limited;
- Osteochondrosis: the disease is accompanied by moderate headaches, aggravated by movement and sudden turns of the body;
- Myositis, causes of the disease: hypothermia, prolonged muscle tension, scoliosis or injury. This leads to tightening of the muscles - attempts to relax them provoke heaviness in the back of the head and slight dizziness;
- Occipital neuralgia: sharp pain attacks radiating to the jaw, ears, neck. The intensity of sensations increases as the body turns.
Cervical osteochondrosis
At the articulation of the vertebrae with each other there is soft tissue (pulp), which acts as a shock absorber, helping to evenly distribute the load across the entire cervical region, holding the head in the desired position. In the presence of degenerative processes, the pulp becomes less elastic, degenerating into bone tissue. As a result, the distance between the vertebrae is reduced and friction increases.
Those people who are in a horizontal position for a long time while working at a computer or machine are at risk.
In the case when nerve endings are pinched between the vertebrae, radicular syndrome develops, which is characterized by:
- a feeling of goosebumps along the spine;
- numbness of the limbs;
- pain in the back of the head;
- nausea and dizziness.
Lack of oxygen in the brain leads to weakness and nausea.
In the presence of osteochondrosis, it is important to separate dizziness according to the symptoms shown, which are a distinctive feature:
- Systemic dizziness - it is impossible to concentrate on one object, they all float and do not have clear contours, which indicates a lack of oxygen and perception disturbances.
- Unsystematic dizziness - manifested by general weakness, but without the “buoyancy” of objects. May be accompanied by numbness of the face (facial nerve paresis), ears, eyelids, and tingling.
The pain is dull, aching, deafening. A person feels as if in a vacuum. It can manifest itself as attacks of headache, which goes away on its own after rest and neck massage.
Upper cervical vertebrae, back of the head, shoulder blades, limbs.
The clinical manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis have much in common with other pathologies, therefore, hardware methods are used for diagnosis, including:
- X-ray – displays the anatomical state of the vertebrae relative to the spinal column. Shows the presence of degenerative processes, as well as the likelihood of infringement of nerve endings.
- MRI and CT – shows the general picture of the disease, which allows you to establish the root cause and select the most optimal treatment.
- Duplex scanning is performed to assess the condition of blood vessels.
The main goal of therapy is to relieve pain, as well as reduce the harmful mechanical effects on the nerve endings and vascular system, which are directly connected to the brain. The following drugs can alleviate the unpleasant manifestations of osteochondrosis:
- NSAIDs: Naproxen, Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Nimid - used both orally and topically in the form of ointments and creams for external use.
- Glucocorticosteroids: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone - help relieve acute pain by acting on painful foci, blocking them by reducing the body's sensitivity to pain.
- Antidepressants and muscle relaxants that help you relax and have a good rest.
Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary treatment, which includes:
- Exercise therapy - helps to increase blood flow to the neck and head, used only under the supervision of a specialist.
- Massage – helps eliminate muscle spasms.
- Swimming in the pool has a beneficial effect on the entire spine.
- Wearing a correction collar is necessary when there is a high level of compression (squeezing) of the nerve roots by the vertebrae of the neck.
Cause of pain
- Depression and stress. Long-term emotional stress impairs performance, causes drowsiness, anxiety, obsessive thoughts, worsens appetite and general condition. Pressure in the back of the head is episodic, the pain is moderate or mild, occurring at any time of the day.
- Traumatic brain injury. Post-traumatic pain begins 10-12 days after the injury. Acute ones are caused by hemorrhage, intracranial hematomas, brain contusion, vascular or inflammatory abnormalities, and damage to surface tissues. Chronic ones most often have a progressive course. The pain is localized in the occipital area, dull and pressing, and extremely rarely pulsating. They gain intensity in a standing position, in the morning, when moving, against a background of dizziness, intolerance to sound and light, and nausea.
- Brain tumors. Heaviness in the back of the head due to brain tumors (benign or malignant) can be blurred or pronounced. The pain is one-sided, slowly progressive, tending to occur after coughing, bending, or sleep. Over time, it increases and other disorders are added - vision, balance, coordination of movement, speech.
- Arnold-Chiari malformation. The cerebellum, due to the disproportionately small part of the skull, is forced, together with the spinal cord, to move downwards - to the upper segment of the spine, which leads to pain in the neck and back of the head, and dizziness. Due to impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, it becomes difficult to turn the head, straighten or tilt the neck. Against this background, numbness of the hands, noise in the ears, difficulty urinating, and compression behind the sternum are observed.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before starting therapy, it is necessary to carry out diagnostic measures and establish the causes of pain in the back of the head and dizziness. Diagnostics includes studying the patient's history, complaints, neurological and general examination, obtaining detailed information about previous treatment and its effectiveness.
Primary headache
Treatment consists of two stages - pain relief and treatment of chronic forms. For isolated episodes, anxiolytics and simple analgesics are indicated; for chronic processes, muscle relaxants (baclofen) and antidepressants (amitriptyline) are indicated.
Non-drug therapy is also quite effective - manual therapy, physiotherapy, massage, phototherapy, acupuncture.
To quickly eliminate a migraine attack, sedalgin, paracetamol, pentalgin, dihydroergotamine preparations, imigran, naramig, zomig are used.
Secondary (symptomatic) headaches
Diagnostic criteria: the presence of clinical symptoms of the underlying disease, data from instrumental and laboratory studies that confirm the presence of this disease.
If a serious pathology is suspected, all third-party examinations are mandatory and additional studies are prescribed (radiography, electroencephalography, Doppler ultrasound, computed tomography) and consultations with specialized specialists.
Treatment of headaches due to hypertension
With high blood pressure, headaches are caused by vascular spasms. In them, under the influence of negative factors of the disease, pathological changes occur, atherosclerosis develops, cholesterol deposits and salts of heavy metals accumulate. The drug Papaverine helps improve well-being and relieve painful spasms. It is allowed to be replaced with Dibazol, which will also smoothly reduce vascular tone and lower blood pressure.
The classic antispasmodic No-shpa is widely popular, but it does not eliminate the cause of the pain, but only relieves it temporarily. Tempalgin relieves the condition for a long time, but you cannot constantly swallow pills to drown out the pain symptom. It is necessary to visit the clinic and undergo an examination in order to treat not the headache, but its cause - arterial hypertension or other pathologies.
Hypertensive patients are prescribed some antidepressants and tranquilizers along with antihypertensive drugs:
- Valium;
- Phenazipam;
- Xanax;
- Imipramine;
- Amitriptyline;
- Clomipramine;
- Minseran.
Such medications have a positive effect on the nervous system, irritation of which often leads to hypertensive crises, pre-infarction conditions and strokes. It is quite possible to replace them at the initial stage of the disease with herbal preparations with a sedative effect, which contain motherwort, valerian, peony, lemon balm, and peppermint.
Severe painful vascular spasms are relieved with analgesics - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Analgin, Nurofen. They do not eliminate the cause of high blood pressure, but they temporarily alleviate the condition.
Danger Signals
- intense “thundering” pain is typical of a cerebral hemorrhage;
- the first occurrence of strong compression in the occipital area may indicate an intracranial tumor or temporal arteritis;
- unpleasant sensations that increase over 2-3 weeks can be triggered by a large brain tumor;
- the presence of obvious disruptions in the sphere of consciousness (mental abnormalities, confusion, stupor);
- the unexpected occurrence of unusual pain during physical activity that increases intracranial pressure may indicate the presence of a tumor process.
Prevention
Heaviness in the back of the head is often the result of stress, mental or physical strain.
For prevention purposes, you should adhere to a diet with limited consumption of foods containing tyramine (citrus fruits, chocolate, red wine, cheese), reduce daily stress, perform regular massage of the collar area, take water procedures, and spend more time in the fresh air.
If episodes of severe headaches become regular and are not relieved by analgesics and other medications, you should consult a doctor to rule out oncology and potentially life-threatening diseases.
Painful sensations that are localized in the head area are considered the most insidious. It is impossible to determine on your own what kind of pain it is: a headache or due to problems in the cervical vertebrae.
Today there are many diseases, including very dangerous ones, that begin to manifest themselves with pain in the back of the head or dizziness.
Diseases of the neck and vertebrae can lead to feelings of heaviness in the head and dizziness, general weakness and sometimes nausea.
The main causes of dizziness and a feeling of tightness in the back of the head can be:
Malysheva: statistics show that more than 70% of people are, to one degree or another, infected with parasites, which can cause a person to have HEADACHES, Dizziness, Fainting, as well as more dangerous diseases, including cancer. To find out if there are PARASITES in the body, just take it.
- mental or physical stress;
- constant stress, depression. Mostly women over 25 years of age are susceptible to this condition. But men can also suffer;
- various diseases of the cervical spine;
- may occur as a result of vegetative-vascular dystonia, as well as when the pressure of the intracranial box is disturbed;
- Similar problems can arise when blood pressure is compromised. With low or significantly increased blood pressure, pain occurs in the back of the head and dizziness occurs. Most often this concerns elderly patients;
- Sometimes the causes of dizziness, weakness and pain in the back of the head can be head injuries or bruises in the neck;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. In addition to compression in the back of the head, tinnitus and blurred vision may occur.
If you experience frequent dizziness, a feeling as if your head is numb and there is pressure in the back of your head, then you need to consult a specialist, as these may be symptoms of serious diseases.
Hypertonic disease
Severe headache, nausea appears with a sharp increase in blood pressure. Headache in this condition is accompanied by severe vomiting, dizziness, and redness of the face.
Painful sensations with hypertension are caused by:
- stress;
- consumption of alcohol, coffee and strong tea, abuse of fast food, spicy and fatty meat dishes;
- weather change;
- severe fatigue;
- mental overload;
- smoking.
During an attack, in addition to headache and nausea, the following may be observed:
- excitation;
- inability to turn the head to the side;
- impaired coordination of movements and balance;
- blurred vision;
- the face turns red and the limbs become icy;
- swelling of the limbs;
- strong heartbeat;
- panic attack with fear of death.
The following measures will help relieve an attack and alleviate symptoms:
- a cold compress is applied to the head, in the temple area;
- squeezed boiled beet juice or beet kvass is taken in a glass in the absence of nausea;
- cold berry juice made from cranberries, lingonberries and strawberries reduces blood pressure;
- cyclomethiazide – take 1 tablet per day for 5 days;
- cariol – take 1 tablet per day for 3 days;
- After an attack, it is recommended to follow a diet limiting spicy, meat and fatty foods, avoiding energy drinks and alcoholic drinks, strong coffee and tea.
What should be done in case of such phenomena?
If you feel pain or pressure in the back of your head, try to ventilate the room well. Open all windows if possible. Lie down on the sofa and try to completely relax, massage your neck and back of your head.
Try to calm down. If the pain was caused by stress or overexertion, then you can drink valerian, motherwort or other sedatives.
If pain or pressure in the back of the head, as well as dizziness occur quite often, you should consult a doctor. It is not recommended to prescribe medication on your own. First you need to determine the cause of such pain.
Sometimes these can be quite serious diseases that require careful diagnosis. Depending on the disease, the doctor may prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory, sedative and painkillers. Additionally, a course of massage or acupuncture may be prescribed.
If the cause of pain in the back of the head or dizziness is blood pressure, then you first need to measure it.
If you have low blood pressure, you can drink caffeinated drinks or medications. Tinctures of lemongrass, ginseng and eleutherococcus will help raise blood pressure.
If the pressure is significantly low, it is necessary to take a horizontal position; the use of any medications is not recommended. Low blood pressure contributes to dizziness and loss of consciousness.
The patient needs complete rest. If you have low blood pressure, you can drink a cup of black tea with lemon or still water. Next, consult a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.
Additionally, it is necessary to undergo an MRI of the cervical spine and head to find out the condition of the brain vessels.
First aid: what and how to do?
The algorithm of actions directly depends on the symptoms. For women with long hair, we suggest loosening your hair first. Also, take a horizontal position and close your eyes. Aromatherapy oils can help relieve the feeling of a vice on the back of your head. An ideal remedy to combat discomfort is lemon or pine essential oil. Smells quickly relieve spasms, calm the nervous system and relax. If you experience frequent headaches at work, we recommend placing cotton wool or sticks soaked in lemon and pine aromatic oils on your desk.
If a person is vomiting, then wash him with cold water, let him suck a slice of lemon, drink mineral water. If you experience persistent vomiting and dizziness, call an ambulance.
If pain in the back of the head goes away without the above symptoms and is a fairly rare occurrence for you, then hold off on taking the pill for now. Self-massage helps a lot. Manual therapy is contraindicated only for hypertension. In other cases it is effective.
What to do? First, warm up your hands thoroughly. Then begin circular movements behind the ears clockwise and counterclockwise 3 times.
Tilt your head or even lay it on the table. Using your fingertips, gently massage the base of your neck, where it meets your head. You can press lightly, insert clockwise and in the opposite direction. Rubbing the back of the head helps a lot. As a rule, after such self-massage, even without a pill, it becomes easier.
Many people find it helpful to shower at room temperature with water jets directed at the back of the head. Massaging streams relax the skin, remove spasms and improve blood circulation. It would also be a good idea to drink a glass of water with lemon. The acid will dilute too thick blood, making it easier for it to move through the vessels, and moisture will replenish the water balance.